文章目录
- 1、启动类
- 2、mapper 接口
- 3、控制类
- 4、补充:返回数据时的封装
- 5、补充
- a、mybatisplus
1、启动类
在启动类上加入@MapperScan扫描自己所写的mapper接口
package com.example.bilili_springboot_study;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.example.bilili_springboot_study.mapper")
public class BililiSpringBootStudyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(BililiSpringBootStudyApplication.class, args);
}
}
2、mapper 接口
注意加上@Mapper注解
package com.example.bilili_springboot_study.mapper;
import com.example.bilili_springboot_study.entity.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("SELECT * FROM user")
public List<User> selectAll();
}
如果接口中的sql语句比较麻烦,也可在resources目录下,新建mapper/UserMapper.xml文件,通过该文件控制sql语句例如:
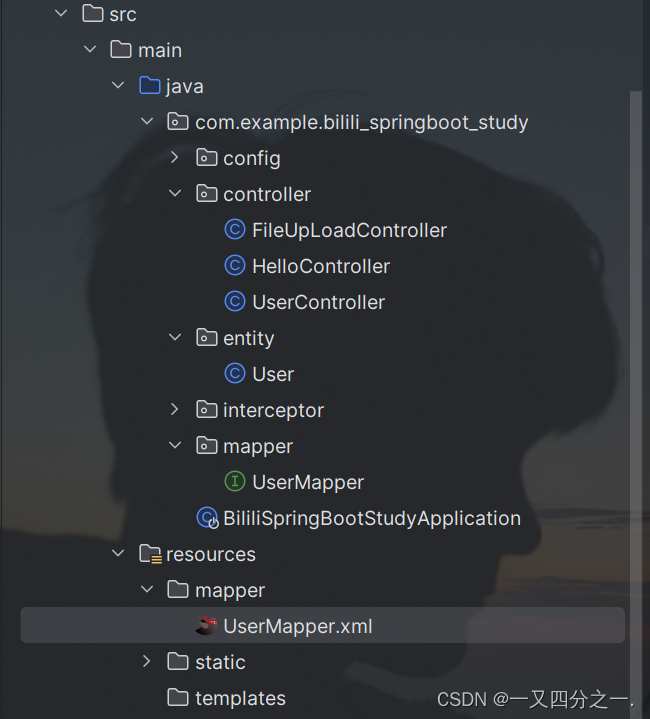
<mapper namespace="com.whd.system.mapper.SysUserMapper"> 对应所绑定的接口的位置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.whd.system.mapper.SysUserMapper">
<select id="getUserById" resultType="com.example.bilili_springboot_study.entity.User">
select *
from user
where id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
在该文件中,select语句要加上返回值的类型,使用resultType=" " 进行设置,他指定了返回的结果类型为什么,id为接口中的方法名
insert update 一般都是int ,因为返回的是影响的结果数
在接口的方法中,如果要进行传参,在sql中使用 #{ } 来进行引用,注意变量和形参一样
完整事例:
UserMapper.xml中
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.bilili_springboot_study.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="getUserById" resultType="com.example.bilili_springboot_study.entity.User">
select * from user where id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
mapper 接口中
UserMapper.java
package com.example.bilili_springboot_study.mapper;
import com.example.bilili_springboot_study.entity.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("SELECT * FROM user")
public List<User> selectAll();
User getUserById(int id);
}
控制器中
UserController.java
package com.example.bilili_springboot_study.controller;
import com.example.bilili_springboot_study.entity.User;
import com.example.bilili_springboot_study.mapper.UserMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@GetMapping("/select/userAll")
public List<User> getAllUser() {
return userMapper.selectAll();
}
@GetMapping("/find/user/{id}")
public User findUserById(@PathVariable int id) {
return userMapper.getUserById(id);
}
}
3、控制类
注意要引入所写的接口
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
在使用接口查询数据库中的信息后,直接return即可返回json格式的数据,也可以将查询到的数据在此进行处理然后再return给前端
package com.example.bilili_springboot_study.controller;
import com.example.bilili_springboot_study.entity.User;
import com.example.bilili_springboot_study.mapper.UserMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@GetMapping("/select/userAll")
public List<User> getAllUser() {
return userMapper.selectAll();
}
<-- --------- 以上方法通过接口实现 -->
@GetMapping("/user/{id}")
public String getUserById(@PathVariable int id) {
System.out.println(id);
return " 根据用户id获取用户信息";
}
@PostMapping("/user")
public String saveUser() {
return "添加用户信息";
}
@PutMapping("/user")
public String updateUser() {
return "更新用户信息";
}
@DeleteMapping("/user/{id}")
public String deleteUser(@PathVariable int id) {
System.out.println(id);
return "根据用户id删除用户";
}
}
4、补充:返回数据时的封装
创建有着泛型的类,和一个枚举类型(设置状态码),以后在返回数据的时候,不仅仅是直接返回接口返回的数据,而是通过AxiosResult<T>实现,
package com.whd.system.common;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
@Getter
@Setter
public class AxiosResult<T> {
private int code;
private String msg;
private T data;
private AxiosResult(CodeEnum codeEnum, T data) {
this.code = codeEnum.getCode();
this.msg = codeEnum.getMsg();
this.data = data;
}
private AxiosResult(CodeEnum codeEnum) {
this.code = codeEnum.getCode();
this.msg = codeEnum.getMsg();
}
//方法重载
//成功
public static <T> AxiosResult<T> success(T data){
return new AxiosResult<T>(CodeEnum.SUCCESS,data);
}
public static <T> AxiosResult<T> success(CodeEnum codeEnum,T data){
return new AxiosResult<T>(codeEnum,data);
}
//失败
public static <T> AxiosResult<T> error(){
return new AxiosResult<T>(CodeEnum.ERROR);
}
public static <T> AxiosResult<T> error(CodeEnum codeEnum){
return new AxiosResult<T>(codeEnum);
}
}
package com.whd.system.common;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Getter;
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor
public enum CodeEnum {
SUCCESS(200, "success"),
ERROR(500, "error"),
UNKNOWN_ERROR(100, "未知错误"),
USER_LOGIN_ERROR(501, "用户名或者密码有误"),
USER_INVALID_ERROR(502, "用户已被禁用");
private final int code;
private final String msg;
}
例如以下例子:
package com.whd.system.controller;
import com.whd.system.common.AxiosResult;
import com.whd.system.common.CodeEnum;
import com.whd.system.domain.SysUser;
import com.whd.system.domain.vo.SysRoleVo;
import com.whd.system.domain.vo.SysUserVo;
import com.whd.system.mapper.SysUserMapper;
import lombok.Getter;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
//@CrossOrigin // 允许类跨域请求
public class SysUserController {
private static final String PAO_PATH = "http://127.0.0.1:8080";
@Autowired
private SysUserMapper SysUserMapper;
@PostMapping("/login")
public AxiosResult<Integer> login(@RequestBody Map<String, String> params) {
String username = params.get("username");
String password = params.get("password");
SysUser user = SysUserMapper.selectByUser(username, password);
if (user == null) {
return AxiosResult.error(CodeEnum.USER_LOGIN_ERROR);
}
return AxiosResult.success(user.getId());
}
//查找用户信息
@GetMapping("/find/{id}")
public AxiosResult<Map<String, Object>> findUserAndRoleInfo(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
Map<String, Object> map = SysUserMapper.findUserAndeRole(id);
return AxiosResult.success(map);
}
// 查找角色信息
@GetMapping("/find/getRoleList")
public AxiosResult<List<SysRoleVo>> findRoleInfo() {
List<SysRoleVo> list = SysUserMapper.findRoleInfo();
return AxiosResult.success(list);
}
// 修改管理/用户信息 状态 0/1
@GetMapping("/update/status/{id}/{status}")
public AxiosResult<Integer> updateStatus(@PathVariable("id") Integer id, @PathVariable("status") Integer status) {
int i = SysUserMapper.updateStatus(id, status);
return AxiosResult.success(i);
}
// 修改管理员信息
@PostMapping("/update/adminInfo")
public AxiosResult<Integer> updateAdminInfo(@RequestBody Map<String, Object> params) {
String id = (String) params.get("id");
String username = (String) params.get("username");
String phone = (String) params.get("phone");
String sex = (String) params.get("sex");
String password = (String) params.get("pass");
int roleId = (int) params.get("role");
Map<String, Object> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("id", id);
map.put("username", username);
map.put("phone", phone);
map.put("sex", sex);
map.put("password", password);
map.put("roleId", roleId);
int i = SysUserMapper.updateAdminInfo(map);
return AxiosResult.success(1);
}
}
注意本例子中的这个方法:他传进.xml中的是一个map类型的数据,那么在使用的时候,还要指定他的类型
// 修改管理员信息
@PostMapping("/update/adminInfo")
public AxiosResult<Integer> updateAdminInfo(@RequestBody Map<String, Object> params) {
String id = (String) params.get("id");
String username = (String) params.get("username");
String phone = (String) params.get("phone");
String sex = (String) params.get("sex");
String password = (String) params.get("pass");
int roleId = (int) params.get("role");
Map<String, Object> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("id", id);
map.put("username", username);
map.put("phone", phone);
map.put("sex", sex);
map.put("password", password);
map.put("roleId", roleId);
int i = SysUserMapper.updateAdminInfo(map);
return AxiosResult.success(1);
}
<update id="updateAdminInfo" parameterType="map">
UPDATE sys_user
SET
username = #{username, jdbcType=VARCHAR},
phone = #{phone, jdbcType=VARCHAR},
gender = #{sex, jdbcType=VARCHAR},
password = #{password, jdbcType=VARCHAR},
role_uid = #{roleId, jdbcType=INTEGER}
WHERE id = #{id, jdbcType=VARCHAR}
</update>
5、补充
a、mybatisplus
在mapper 接口中,通过继承BaseMapper<T>类,可以实现所有的增删改查,复杂的可能还是要手敲的
1、由于我们写的实体类的名字可能和表的名字有很大差异,所以在继承后,所用的实体类添加@TableName("表名")注解,用户确定该实体类所对应的表的名字
2、实体类的名字不一定要和表中字段的名字一致,但是,不一致的要添加@Result(column = "db_column_name", property = "propertyName")用于映射,不然怎么实现智能化对应了,但是还是建议直接用一样的就行了
对于 mybatisplus 还有很多用法,自行查找吧 >_<