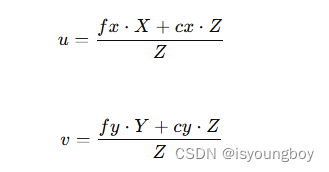1、DETR架构
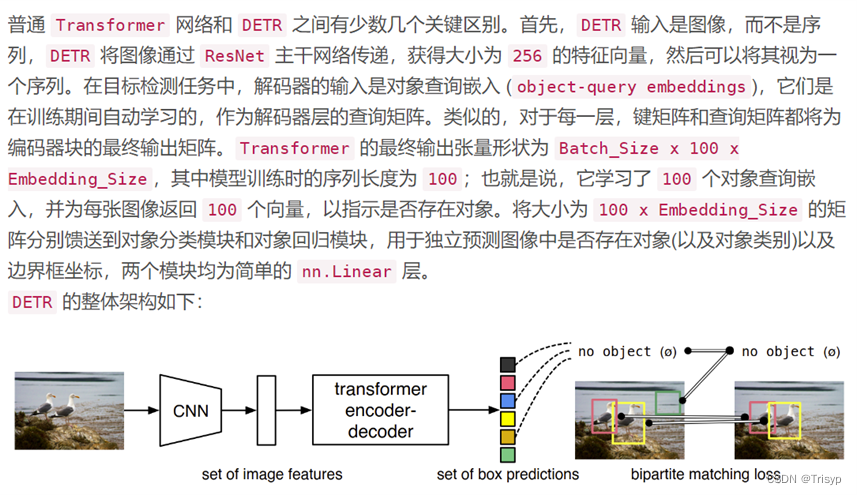
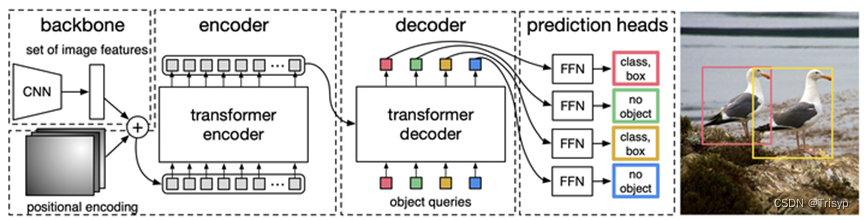
DETR(Detection Transformer)是一种新型的目标检测模型,由Facebook AI Research (FAIR) 在2020年提出。DETR的核心思想是将目标检测任务视为一个直接的集合预测问题,而不是传统的两步或多步预测问题。这种方法的创新之处在于它直接预测目标的类别和边界框,而不是先生成大量的候选区域,然后再对这些区域进行分类和边界框回归。
DERT的特点主要有二:
一是Transformer结构在CV网络中的应用;
二是提出了一种新的或者说不同的损失函数(Loss Function)。
2、模型下载
模型代码下载地址:
GitHub - facebookresearch/detr: End-to-End Object Detection with Transformers
预训练模型(即权重文件)下载地址:
GitHub - facebookresearch/detr: End-to-End Object Detection with Transformers
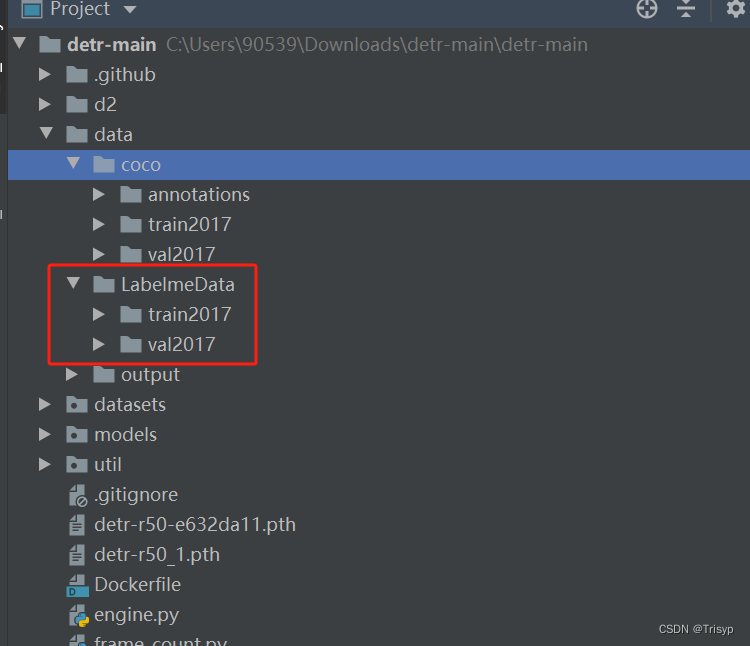
下载后放到项目下待使用:

3、labelme标注文件转为coco模式
首先,labelme标注的文件存放在指定位置,包含json和jpg文件
然后,利用代码将labelme的标注文件转化为coco。包含annotations(两个json文件)、train2017(训练集图片)、val2017(验证集图片)
备注:必须严格按照笔者图中的文件命名方式进行命名,训练集清一色命名为instances_train2017.json,验证集清一色命名为instances_val2017.json,这是模型本身的命名要求,用户需要严格遵守。

实现代码如下:
import json
from labelme import utils
import numpy as np
import glob
import PIL.Image
class MyEncoder(json.JSONEncoder):
def default(self, obj):
if isinstance(obj, np.integer):
return int(obj)
elif isinstance(obj, np.floating):
return float(obj)
elif isinstance(obj, np.ndarray):
return obj.tolist()
else:
return super(MyEncoder, self).default(obj)
class labelme2coco(object):
def __init__(self, labelme_json=[], save_json_path='./tran.json'):
self.labelme_json = labelme_json
self.save_json_path = save_json_path
self.images = []
self.categories = []
self.annotations = []
# self.data_coco = {}
self.label = []
self.annID = 1
self.height = 0
self.width = 0
self.save_json()
def data_transfer(self):
for num, json_file in enumerate(self.labelme_json):
with open(json_file, 'r') as fp:
data = json.load(fp) # 加载json文件
self.images.append(self.image(data, num))
for shapes in data['shapes']:
label = shapes['label']
if label not in self.label:
self.categories.append(self.categorie(label))
self.label.append(label)
points = shapes['points'] # 这里的point是用rectangle标注得到的,只有两个点,需要转成四个点
points.append([points[0][0], points[1][1]])
points.append([points[1][0], points[0][1]])
self.annotations.append(self.annotation(points, label, num))
self.annID += 1
def image(self, data, num):
image = {}
img = utils.img_b64_to_arr(data['imageData']) # 解析原图片数据
height, width = img.shape[:2]
image['height'] = height
image['width'] = width
image['id'] = num + 1
image['file_name'] = data['imagePath'].split('/')[-1]
self.height = height
self.width = width
return image
def categorie(self, label):
categorie = {}
categorie['supercategory'] = 'Cancer'
categorie['id'] = len(self.label) + 1 # 0 默认为背景
categorie['name'] = label
return categorie
def annotation(self, points, label, num):
annotation = {}
annotation['segmentation'] = [list(np.asarray(points).flatten())]
annotation['iscrowd'] = 0
annotation['image_id'] = num + 1
annotation['bbox'] = list(map(float, self.getbbox(points)))
annotation['area'] = annotation['bbox'][2] * annotation['bbox'][3]
annotation['category_id'] = self.getcatid(label) # 注意,源代码默认为1
annotation['id'] = self.annID
return annotation
def getcatid(self, label):
for categorie in self.categories:
if label == categorie['name']:
return categorie['id']
return 1
def getbbox(self, points):
polygons = points
mask = self.polygons_to_mask([self.height, self.width], polygons)
return self.mask2box(mask)
def mask2box(self, mask):
"""从mask反算出其边框
mask:[h,w] 0、1组成的图片
1对应对象,只需计算1对应的行列号(左上角行列号,右下角行列号,就可以算出其边框)
"""
# np.where(mask==1)
index = np.argwhere(mask == 1)
rows = index[:, 0]
clos = index[:, 1]
# 解析左上角行列号
left_top_r = np.min(rows) # y
left_top_c = np.min(clos) # x
# 解析右下角行列号
right_bottom_r = np.max(rows)
right_bottom_c = np.max(clos)
return [left_top_c, left_top_r, right_bottom_c - left_top_c,
right_bottom_r - left_top_r] # [x1,y1,w,h] 对应COCO的bbox格式
def polygons_to_mask(self, img_shape, polygons):
mask = np.zeros(img_shape, dtype=np.uint8)
mask = PIL.Image.fromarray(mask)
xy = list(map(tuple, polygons))
PIL.ImageDraw.Draw(mask).polygon(xy=xy, outline=1, fill=1)
mask = np.array(mask, dtype=bool)
return mask
def data2coco(self):
data_coco = {}
data_coco['images'] = self.images
data_coco['categories'] = self.categories
data_coco['annotations'] = self.annotations
return data_coco
def save_json(self):
self.data_transfer()
self.data_coco = self.data2coco()
# 保存json文件
json.dump(self.data_coco, open(self.save_json_path, 'w'), indent=4, cls=MyEncoder) # indent=4 更加美观显示
if __name__ == '__main__':
labelme_json = glob.glob('data/LabelmeData_frame_count/val2017/*.json') # labelme标注好的.json文件存放目录
labelme2coco(labelme_json, 'data/coco_frame_count/annotations/instances_val2017.json') # 输出结果的存放目录4、修改训练模型参数
先在pycharm中新建python脚本文件detr_r50_tf.py,代码如下:
import torch
pretrained_weights = torch.load('detr-r50-e632da11.pth')
num_class = 1 # 类别数
pretrained_weights["model"]["class_embed.weight"].resize_(num_class + 1, 256)
pretrained_weights["model"]["class_embed.bias"].resize_(num_class + 1)
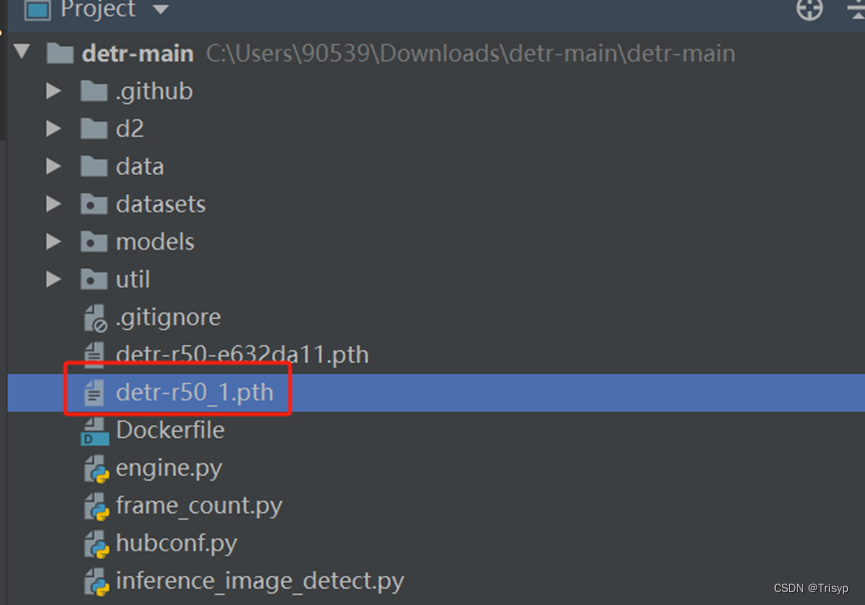
torch.save(pretrained_weights, "detr-r50_%d.pth" % num_class)将其中类别数改成自己数据集的类别数即可,执行完成后会在目录下生成适合自己数据集类别的预训练模型:
然后在models文件夹下打开detr.py,修改其中的类别数(一定要全部保持一致):

最后打开main.py,修改其中的coco_path(数据存放路径)、output_dir(结果输出路径)、device(没有cuda就改为cpu)、resume(自己生成的预训练模型)。

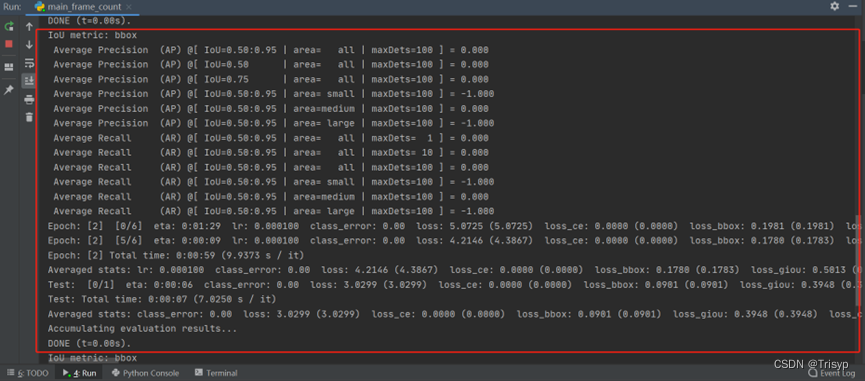
5、执行main.py来开始训练模型
如果不想跑太多了轮可以修改epochs数:

训练好的模型会保存在结果输出路径中:
跑起来的效果是这样的: