前言
针对 Compose UI 工具包,开发者不仅需要掌握如何使用新的 UI 组件达到 design 需求,更需要了解和实现与 UI 的交互逻辑。
比如 touch 事件、Accessibility 事件等等。
- Compose 中对 touch 事件的处理和原理,笔者已经在《通过调用栈快速探究 Compose 中 touch 事件的处理原理》里进行了阐述
- Compose 中对 Accessibility 事件的支持和基本原理,笔者已经在 《一文读懂 Compose 支持 Accessibility 无障碍的原理》 里进行了介绍
那么将两个话题相结合,不禁要好奇:利用 Accessibility 针对 Compose 界面模拟 touch 交互,是否真的有效,个中原理又如何?
本文将通过无障碍 DEMO 对 Google Compose 项目 Accompanist 中的 Horizontal Pager sample 模拟注入 Scroll 滚动事件,看下实际效果,并对原理链路进行剖析。
向 Compose 模拟滚动事件
无障碍 DEMO,本来想直接复用曾经红极一时的 AccessibilityTool 开源项目。奈何代码太老编译不过,遂直接写了个 DEMO 来捕捉 AccessibilityEvent 然后分析 AccessibilityNodeInfo。
当发现是节点属于 Accompanist 的包名(com.google.accompanist.sample),且可滚动 scrollable 的话,通过无障碍模拟注入 ACTION_SCROLL_FORWARD 的 action。
public class MyAccessibilityService extends AccessibilityService {
...
@Override
public void onAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent event) {
Log.i(TAG, "onAccessibilityEvent() event: " + event);
AccessibilityNodeInfo root;
ArrayList<AccessibilityNodeInfo> roots = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<AccessibilityNodeInfo> nodeList = new ArrayList<>();
try {
switch (event.getEventType()) {
case AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_WINDOW_STATE_CHANGED:
Log.i(TAG, "TYPE_WINDOW_STATE_CHANGED()");
roots.add(service.getRootInActiveWindow());
findAllNode(roots, nodeList);
printComposeNode(nodeList);
roots.clear();
nodeList.clear();
break;
...
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void printComposeNode(ArrayList<AccessibilityNodeInfo> root) {
for (AccessibilityNodeInfo node : root) {
if (node.getPackageName().equals("com.google.accompanist.sample")
&& node.getClassName().equals("android.view.View")) {
node.performAction(AccessibilityNodeInfo.ACTION_SCROLL_FORWARD);
}
}
}
...
}
《一文读懂 Compose 支持 Accessibility 无障碍的原理》 里我们介绍过,Compose 通过无障碍代理 AccessibilityDelegate 依据 UI 组件的类型、情况,进行 AccessibilityNodeInfo 实例的构造。
为了兼容传统 View 的内容,会针对实例里的 className 属性进行一定程度的了改写,但范围有限。
像 LazyColumn 这种的组件,并没有和传统的可滚动的 ListView、ScrollView、RecylerView 的名称进行转换,用的仍然是默认的 View 名称。
所以咱们的无障碍 DEMO 不能像以前那样在判断 isScrollable 之外再额外判断 ListView 等传统可滚动 View 的名称了。
话不多说,我们将无障碍 DEMO 在系统的无障碍设置中启用,选择 “allow” 即可。
然后运行下 Accompanist 的 Horizontal Pager 界面,打印下收集到的 AccessibilityNodeInfo 信息。
android.view.accessibility.AccessibilityNodeInfo@1cfed; ...
packageName: com.google.accompanist.sample; className: android.view.View; ...
enabled: true; ... scrollable: true; ...
actions: [AccessibilityAction: ... AccessibilityAction: ACTION_SCROLL_FORWARD - null]...
可以看到:
- className 果然是 android.view.View
- scrollable 是 true
- 支持的 AccessibilityAction 有 ACTION_SCROLL_FORWARD 等
模拟滚动的效果如下,可以看到一打开 Horizontal Pager 的界面,就自动往右进行了翻页。
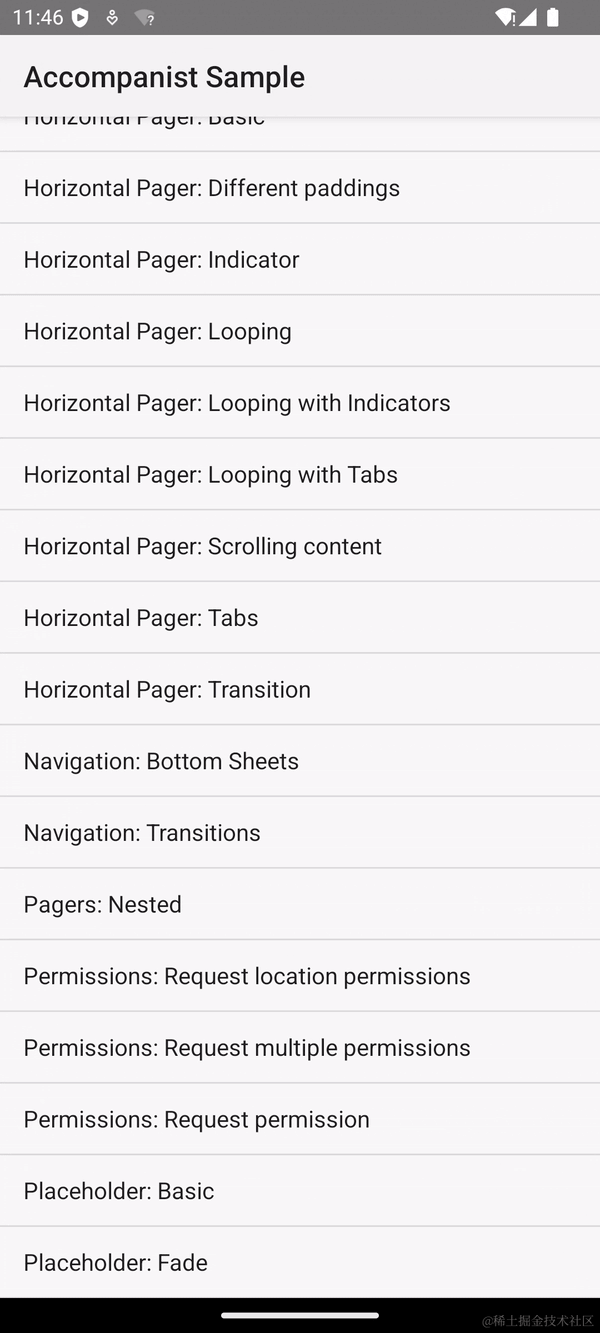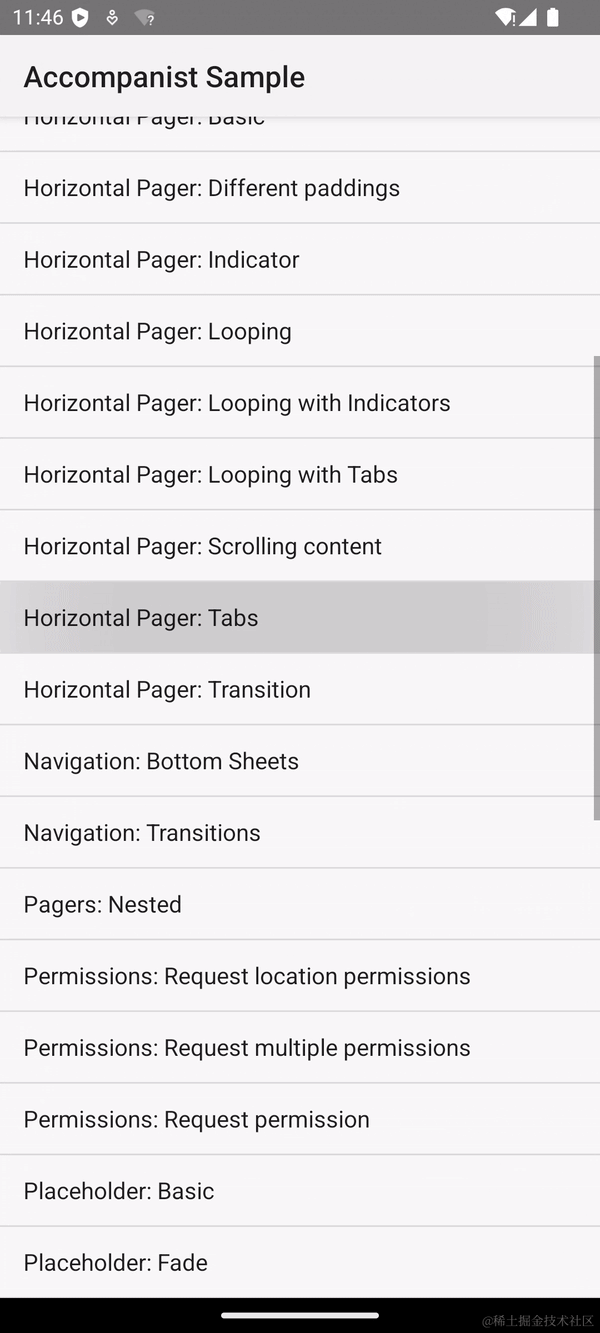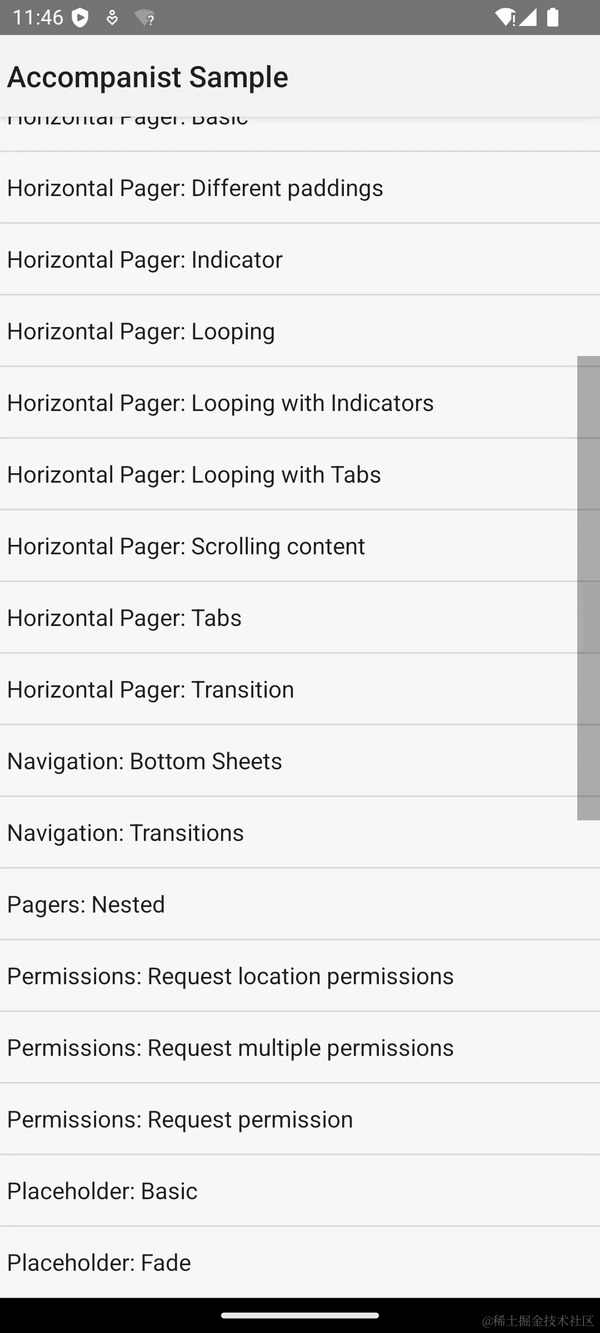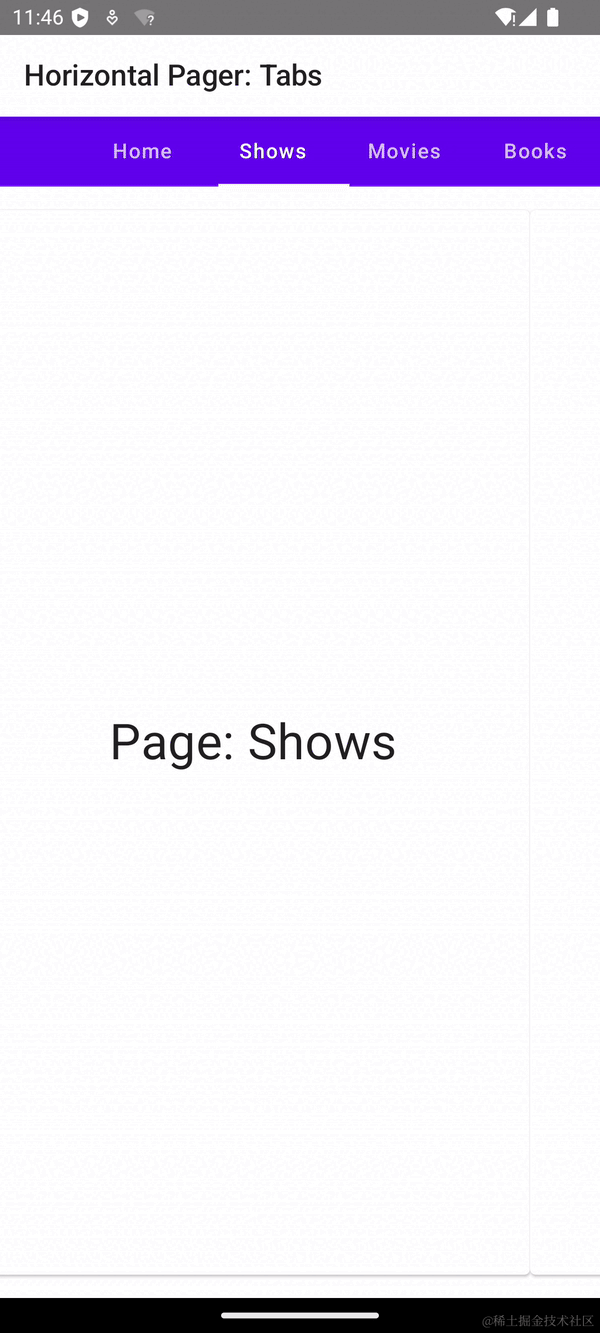
Compose 支持模拟滚动的原理
滚动界面 Horizontal Pager
想了解 Compose 支持通过无障碍模拟滚动的原理,首先需要了解一下 Horizontal Pager 界面的布局和物理手势上触发滚动的一些背景知识。
该布局主要采用 TopAppBar 展示 Title 栏,内容区域由 Column 组件堆叠。其中:
ScrollableTabRow负责可以横向滚动的 Tab 栏的内容展示HorizontalPager负责各 Tab 对应内容的展示,会依据 page index 展示对应的 Text 文本,还需要监听 scroll 手势进行横向滚动
ScrollableTabRow 还需要监听 Tab 的点击事件进行 PagerState 的滚动,采用 animateScrollToPage() 进行。
class HorizontalPagerTabsSample : ComponentActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
...
setContent {
AccompanistSampleTheme {
Surface {
Sample()
}
}
}
}
}
@Composable
private fun Sample() {
Scaffold(
topBar = {
TopAppBar(
title = { Text(stringResource(R.string.horiz_pager_title_tabs)) },
backgroundColor = MaterialTheme.colors.surface,
)
},
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()
) { padding ->
val pages = remember {
listOf("Home", "Shows", "Movies", "Books", "Really long movies", "Short audiobooks")
}
Column(Modifier.fillMaxSize().padding(padding)) {
...
ScrollableTabRow(
selectedTabIndex = pagerState.currentPage,
...
) {
pages.forEachIndexed { index, title ->
Tab(
...
onClick = {
coroutineScope.launch {
pagerState.animateScrollToPage(index)
}
}
)
}
}
HorizontalPager(
...
) { page ->
Card {
Box(Modifier.fillMaxSize()) {
Text(
text = "Page: ${pages[page]}",
...
)
}
}
}
}
}
}
animateScrollToPage() 的实现如下,主要是依据 page 计算滚动的 index 和 scrollOffset。然后调用通用的 LazyListState 的 animateScrollToItem() 执行 smooth 的滚动操作。
public suspend fun animateScrollToPage(
@IntRange(from = 0) page: Int,
@FloatRange(from = -1.0, to = 1.0) pageOffset: Float = 0f,
) {
requireCurrentPage(page, "page")
requireCurrentPageOffset(pageOffset, "pageOffset")
try {
...
if (pageOffset.absoluteValue <= 0.005f) {
lazyListState.animateScrollToItem(index = page)
} else {
lazyListState.scroll { }
...
if (target != null) {
lazyListState.animateScrollToItem(
index = page,
scrollOffset = ((target.size + itemSpacing) * pageOffset).roundToInt()
)
} else if (layoutInfo.visibleItemsInfo.isNotEmpty()) {
...
}
}
} finally {
onScrollFinished()
}
}
animateScrollToItem() 由 LazyLayoutAnimateScrollScope 完成。
首先需要通过 LazyListState 的 scroll() 挂起函数请求准备执行 scroll 处理,获得调度之后通过 lambda 回调最重要的步骤:ScrollScope 的 scrollBy()。
internal suspend fun LazyLayoutAnimateScrollScope.animateScrollToItem(
...
) {
scroll {
try {
...
while (loop && itemCount > 0) {
...
anim.animateTo(
target,
sequentialAnimation = (anim.velocity != 0f)
) {
if (!isItemVisible(index)) {
// Springs can overshoot their target, clamp to the desired range
val coercedValue = if (target > 0) {
value.coerceAtMost(target)
} else {
value.coerceAtLeast(target)
}
val delta = coercedValue - prevValue
val consumed = scrollBy(delta)
...
}
if (isOvershot()) {
snapToItem(index = index, scrollOffset = scrollOffset)
loop = false
cancelAnimation()
return@animateTo
} ...
}
loops++
}
} catch (itemFound: ItemFoundInScroll) {
...
}
}
}
在内容区域手动滚动触发 scroll 的入口和点击 Tab 不同,来自 scroll gesture,但后续都是调用 ScrollScope 的 scrollBy() 完成。
详细链路不再赘述,感兴趣的同学可以 debug 跟一下。
private class ScrollDraggableState(
var scrollLogic: ScrollingLogic
) : DraggableState, DragScope {
var latestScrollScope: ScrollScope = NoOpScrollScope
...
override suspend fun drag(dragPriority: MutatePriority, block: suspend DragScope.() -> Unit) {
scrollLogic.scrollableState.scroll(dragPriority) {
latestScrollScope = this
block()
}
}
...
}
收集滚动的无障碍语义
Compose 界面所需的 Accessibility 信息,都是通过 Semantics 语义机制来收集的,包括:AccessibilityEvent、AccessibilityNodeInfo 和 AccessibilityAction 信息。
Horizontal Pager 界面里负责主体内容展示的 HorizontalPager 组件,本质上是扩展 LazyRow 而来的,而 LazyRow 和 LazyColumn 一样最终经由 LazyList 抵达 LazyLayout 组件。
internal fun LazyList(
...
) {
...
LazyLayout(
modifier = modifier
.then(state.remeasurementModifier)
.then(state.awaitLayoutModifier)
// 收集语义
.lazyLayoutSemantics(
itemProviderLambda = itemProviderLambda,
state = semanticState,
orientation = orientation,
userScrollEnabled = userScrollEnabled,
reverseScrolling = reverseLayout
)
.clipScrollableContainer(orientation)
.lazyListBeyondBoundsModifier(
state,
beyondBoundsItemCount,
reverseLayout,
orientation
)
.overscroll(overscrollEffect)
...
...
)
}
而 LazyLayout 初始化的时候会调用 lazyLayoutSemantics() 收集语义。
internal fun Modifier.lazyLayoutSemantics(
...
): Modifier {
val coroutineScope = rememberCoroutineScope()
return this.then(
remember(
itemProviderLambda,
state,
orientation,
userScrollEnabled
) {
val isVertical = orientation == Orientation.Vertical
...
val scrollByAction: ((x: Float, y: Float) -> Boolean)? = if (userScrollEnabled) {
{ x, y ->
...
coroutineScope.launch {
state.animateScrollBy(delta)
}
true
}
} else {
null
}
...
Modifier.semantics {
...
if (scrollByAction != null) {
scrollBy(action = scrollByAction)
}
...
}
}
)
}
fun SemanticsPropertyReceiver.scrollBy(
label: String? = null,
action: ((x: Float, y: Float) -> Boolean)?
) {
this[SemanticsActions.ScrollBy] = AccessibilityAction(label, action)
}
lazyLayoutSemantics() 会定义一个 scrollByAction 名称的 AccessibilityAction 实例,然后以 ScrollBy 为 key 存放到语义 map 中等待 Accessibility 机制查找和回调。
无障碍回调滚动 action
当其他 App 通过 AccessibilityNodeInfo 执行了 Action 之后,通过 AIDL 最终会进入目标 App 的 performActionHelper()。
我们以 ACTION_SCROLL_FORWARD 为例,关注下处理逻辑。
internal class AndroidComposeViewAccessibilityDelegateCompat ... {
...
private fun performActionHelper(
...
): Boolean {
val node = currentSemanticsNodes[virtualViewId]?.semanticsNode ?: return false
...
when (action) {
...
AccessibilityNodeInfoCompat.ACTION_SCROLL_FORWARD,
AccessibilityNodeInfoCompat.ACTION_SCROLL_BACKWARD,
android.R.id.accessibilityActionScrollDown,
android.R.id.accessibilityActionScrollUp,
android.R.id.accessibilityActionScrollRight,
android.R.id.accessibilityActionScrollLeft -> {
// Introduce a few shorthands:
val scrollForward = action == AccessibilityNodeInfoCompat.ACTION_SCROLL_FORWARD
val scrollBackward = action == AccessibilityNodeInfoCompat.ACTION_SCROLL_BACKWARD
...
val scrollHorizontal = scrollLeft || scrollRight || scrollForward || scrollBackward
val scrollVertical = scrollUp || scrollDown || scrollForward || scrollBackward
...
val scrollAction =
node.unmergedConfig.getOrNull(SemanticsActions.ScrollBy) ?: return false
val xScrollState =
node.unmergedConfig.getOrNull(SemanticsProperties.HorizontalScrollAxisRange)
if (xScrollState != null && scrollHorizontal) {
var amountToScroll = viewport.width
if (scrollLeft || scrollBackward) {
amountToScroll = -amountToScroll
}
if (xScrollState.reverseScrolling) {
amountToScroll = -amountToScroll
}
if (node.isRtl && (scrollLeft || scrollRight)) {
amountToScroll = -amountToScroll
}
if (xScrollState.canScroll(amountToScroll)) {
return scrollAction.action?.invoke(amountToScroll, 0f) ?: false
}
}
val yScrollState =
node.unmergedConfig.getOrNull(SemanticsProperties.VerticalScrollAxisRange)
if (yScrollState != null && scrollVertical) {
...
if (yScrollState.canScroll(amountToScroll)) {
return scrollAction.action?.invoke(0f, amountToScroll) ?: false
}
}
return false
}
...
}
}
- 当 Action 类型为 ACTION_SCROLL_FORWARD 的时候,赋值 scrollForward 变量
- 从 node 里获取是否支持 x 轴滚动:xScrollState
- 两者皆 OK 的话,从语义 map 里以 ScrollBy 为 key 查到的 AccessibilityAction 实例并回调
该 Action 即回到了语义收集时注入的 lambda:
coroutineScope.launch {
state.animateScrollBy(delta)
}
State 的实现为 LazyLayoutSemanticState。
internal fun LazyLayoutSemanticState(
state: LazyListState,
isVertical: Boolean
): LazyLayoutSemanticState = object : LazyLayoutSemanticState {
...
override suspend fun animateScrollBy(delta: Float) {
state.animateScrollBy(delta)
}
...
}
其 animateScrollBy() 实际通过 LazyListState 的 animateScrollBy() 进行,其最终调用 ScrollScope 的 scrollBy()。
虽然入口稍稍不同,但最后的逻辑便和物理上手动点击 Tab 或者横向 scroll 一样,完成滚动操作,殊途同归。
suspend fun ScrollableState.animateScrollBy(
value: Float,
animationSpec: AnimationSpec<Float> = spring()
): Float {
var previousValue = 0f
scroll {
animate(0f, value, animationSpec = animationSpec) { currentValue, _ ->
previousValue += scrollBy(currentValue - previousValue)
}
}
return previousValue
}
结语
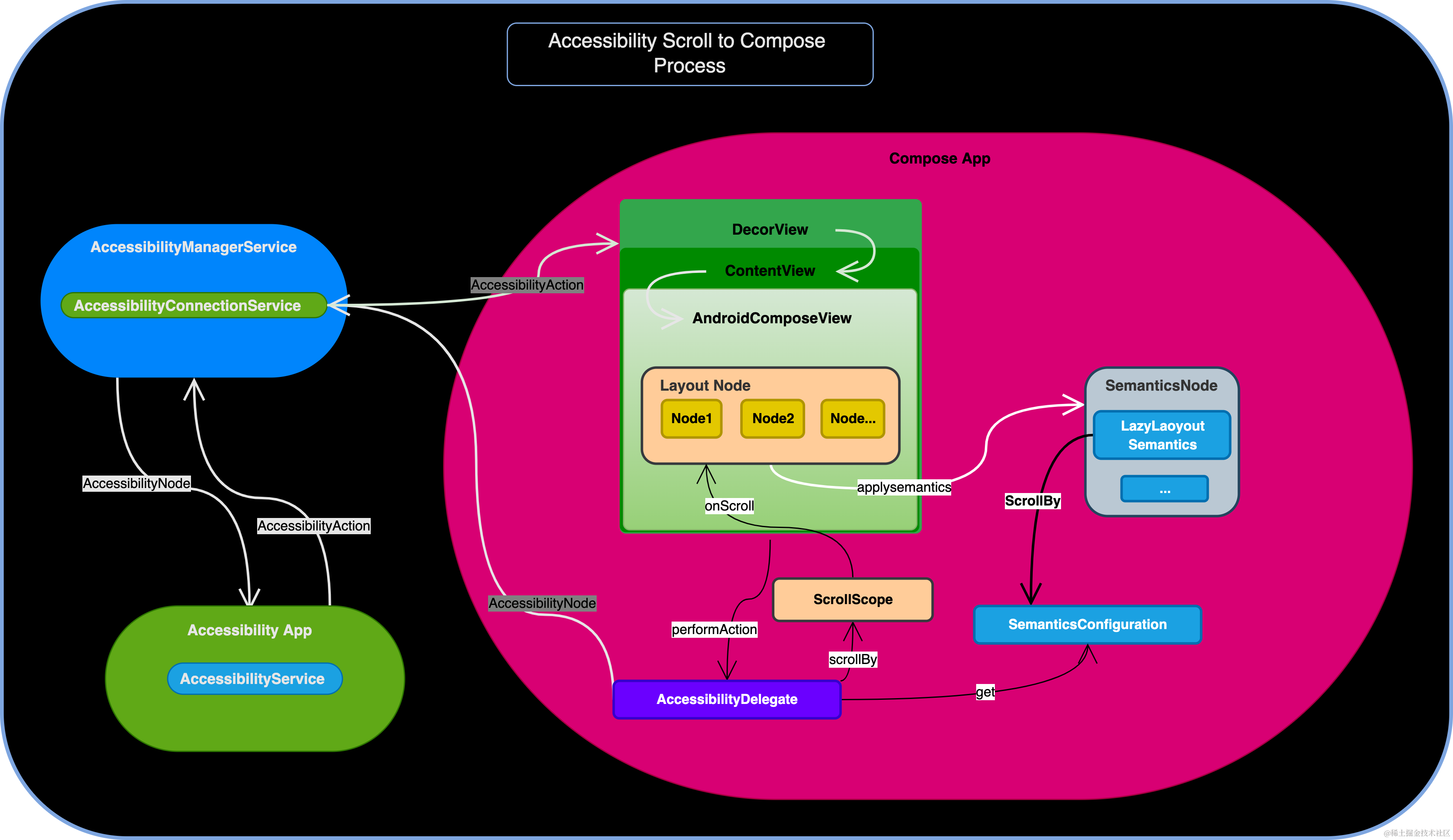
《一文读懂 Compose 支持 Accessibility 无障碍的原理》 里已经介绍过 Compose 和 Accessibility 交互的大体原理,这里只将重点的 scroll 差异体现出来。
- Compose 启动的时候根据可滚动组件收集对应语义,以 ScrollBy key 存到整体的
SemanticsConfiguration中 - 接着在 Accessibility 激活需要准备 Accessibility 信息的时候,将数据提取到
AccessibilityNode里发送出去 - 当
AccessibilityService发送了 scroll Action 的时候,经由AccessibilityDelegate从 SemanticsConfiguration 里查找到对应的AccessibilityAction并执行 - scrool 的执行由
ScrollScope的scrollBy()完成,这和物理上执行滚动操作是一样的逻辑。
看了上述的 Compose 原理剖析之后,读者或许能感受到:除了开发者需要留意 UI 以外的交互细节,Compose 实现者更需要考虑如何将 UI 的各方各面和原生的 Android View 进行兼容。
不仅仅包括本文提到的 touch、accessibility,还包括大家不常关注到的相关开发细节。比如:
- 如何 AndroidView 兼容?
- 如何嵌套的 AndroidView?
- 如何支持的 UIAutomator 自动化?
- 如何支持的 Layout Inspector dump?
- 如何支持的 Android 视图的性能检查?
- 如何支持的 AndroidTest 机制?
- 等等
待 Compose 愈加成熟,对于这些相关的开发能力的支持也会更加完善,后期笔者仍会针对其他部分进行持续的分析和介绍。
推荐阅读
- 《通过调用栈快速探究 Compose 中 touch 事件的处理原理》
- 《一文读懂 Compose 支持 Accessibility 无障碍的原理》