Toc
欢迎光临我的Blog,喜欢就点歌关注吧♥
前面介绍了顺序表、单链表、双向循环链表,基本上已经结束了链表的讲解,今天谈一下栈、队列。可以简单的说是前面学习的一特殊化实现,但是总体是相似的。
前言
栈是一种特殊的线性表,它只允许在一端进行插入和删除操作。这一端被称为栈顶,另一端被称为栈底。栈的特点是后进先出(LIFO),即最后进入的元素最先被移除。
队列是另一种特殊的线性表,它允许在一端进行插入操作,在另一端进行删除操作。插入操作的一端称为队尾,删除操作的一端称为队头。队列的特点是先进先出(FIFO),即最先进入的元素最先被移除。
栈和队列有各自的特点,严格讲用顺序表还是链表的实现都可以。但我们根据结构特点选择一个更加适合的结构进行是实现。
一、栈和队列的理解
对于栈的理解:
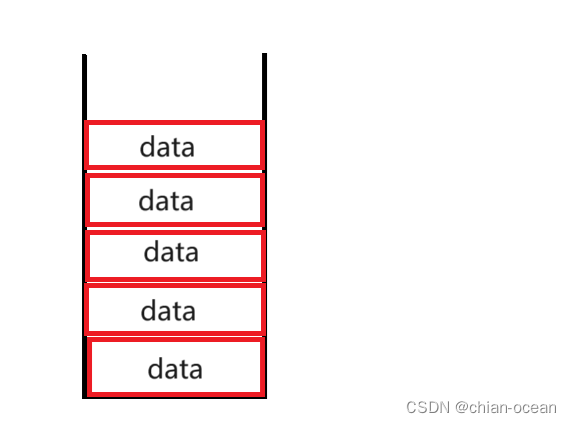
栈如同这个图一样,要是想拿出数据,必须从上面一个一个往下面拿。这也正是 LIFO 的体现。
对于队列的理解:
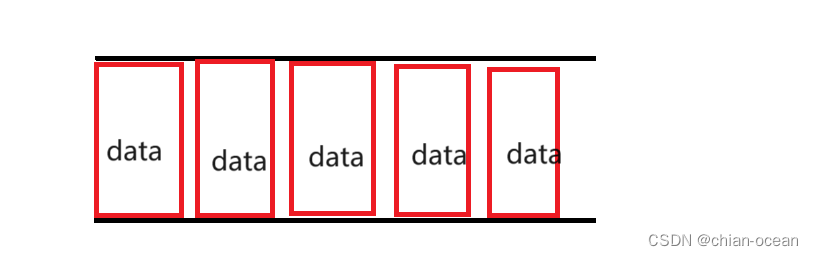
队列如同这个图一样,要是想拿出数据,必须前面一个一个往向后面拿。这也正是 FIFO 的体现。
二、栈的实现(顺组表)
2.1 栈的功能
//初始化
void STInit(ST* ps);
//压栈
void STpush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
//删除
void STPop(ST* ps);
//大小
int STSize(ST* ps);
//判空
bool STEmpty(ST* ps);
//出栈
STDataType STTop(ST* ps);
//检查容量
void CheckCapacity(ST* ps);
//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* ps);
2.2 栈结构体的定义及其初始化
结构体的定义
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
初始化(开辟空间)
void STInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = (ST*)malloc(sizeof(ST)*4);
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
ps->capacity = 4;
ps->top = 0;
}
2.3 压栈(存储数据)
//压栈
void STpush(ST* ps,STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
2,4 删除数据
在这里面删除数据是配合,栈顶出栈。每次拿出一个数据,就要减少一个数据。
void STPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}
2.5 计算栈内元个数
//大小
int STSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
2.6 判断栈内是否为空
这里运用 bool 类型直接返回,比较方便。
bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
2.7 出栈
//出栈
STDataType STTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->a[ps->top-1];
}
2.8 增加容量
//检查容量
void CheckCapacity(ST*ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
ST* tmp = (ST*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(ST) * (ps->capacity) * 2);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
ps->capacity *= 2;
ps->a = tmp;
}
}
2.9 销毁栈
//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->top = 0;
}
三、队列的实现(单链表)
3.1 队列的功能
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* ps);
//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* ps);
//入队
void QueuePush(Queue* ps, QDataType x);
//删除
void QueuePop(Queue* ps);
//大小
int QueueSize(Queue* ps);
//判空队
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* ps);
//出队头
QDataType QueueTop(Queue* ps);
//出队尾
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* ps);
3.2 队列的结构体定义以及初始化
结构体定义
定义两个结构体,第一个为存放数据,第二个结构体为两个指针,分别指向头和尾
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QNode
{
struct QNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode*head;
QNode*tail;
int szie;
}Queue;
初始化
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->head = ps->tail = NULL;
ps->szie = 0;
}
3.3 队列销毁
//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
QNode* cur = ps->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
ps->head = ps->tail = NULL;
ps->szie = 0;
}
3.4 入队(插入数据)
//入队
void QueuePush(Queue* ps,QDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
QNode* newcode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newcode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return ;
}
newcode->next = NULL;
newcode->data = x;
if (ps->head == NULL)
{
ps->head = ps->tail = newcode;
}
else
{
ps->tail->next = newcode;
ps->tail = newcode;
}
ps->szie++;
}
3.5 删除数据(头删)
//删除
void QueuePop(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->head != NULL);
assert(!QueueEmpty(ps));
if (ps->head->next == NULL)
{
free(ps->head);
ps->head = ps->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = ps->head->next;
free(ps->head);
ps->head = next;
}
ps->szie--;
}
3.6 计算队列元素个数
//大小
int QueueSize(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->szie;
}
3.7 判断是否队列为空
//判空队
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->szie == 0;
}
3.8 出队(头)
//出队头
QDataType QueueTop(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!QueueEmpty(ps));
return ps->head->data;
}
3.9 出队(尾)
//出队尾
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->tail->data;
}
四、栈和队列的源码
栈
Stack.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
//初始化
void STInit(ST* ps);
//压栈
void STpush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
//删除
void STPop(ST* ps);
//大小
int STSize(ST* ps);
//判空
bool STEmpty(ST* ps);
//出栈
STDataType STTop(ST* ps);
//检查容量
void CheckCapacity(ST* ps);
//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* ps);
Stack.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "stack.h"
//初始化
void STInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = (ST*)malloc(sizeof(ST)*4);
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
ps->capacity = 4;
ps->top = 0;
}
//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->top = 0;
}
//检查容量
void CheckCapacity(ST*ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
ST* tmp = (ST*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(ST) * (ps->capacity) * 2);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
ps->capacity *= 2;
ps->a = tmp;
}
}
//压栈
void STpush(ST* ps,STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
//删除
void STPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}
//判空
bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
//出栈
STDataType STTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->a[ps->top-1];
}
//大小
int STSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "stack.h"
void teststack()
{
ST st;
STInit(&st);
STpush(&st, 1);
STpush(&st, 2);
STpush(&st, 3);
STpush(&st, 4);
STpush(&st, 5);
printf("%d", STSize(&st));
printf("\n");
while (!STEmpty(&st))
{
printf("%d ", STTop(&st));
STPop(&st);
}
printf("\n");
printf("%d", STSize(&st));
STDestroy(&st);
}
int main()
{
teststack();
return 0;
}
队列
Queue.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QNode
{
struct QNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode*head;
QNode*tail;
int szie;
}Queue;
//单链表的实现,FIFO
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* ps);
//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* ps);
//入队
void QueuePush(Queue* ps, QDataType x);
//删除
void QueuePop(Queue* ps);
//大小
int QueueSize(Queue* ps);
//判空队
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* ps);
//出队头
QDataType QueueTop(Queue* ps);
//出队尾
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* ps);
Queue.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "queue.h"
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->head = ps->tail = NULL;
ps->szie = 0;
}
//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
QNode* cur = ps->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
ps->head = ps->tail = NULL;
ps->szie = 0;
}
//入队
void QueuePush(Queue* ps,QDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
QNode* newcode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newcode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return ;
}
newcode->next = NULL;
newcode->data = x;
if (ps->head == NULL)
{
ps->head = ps->tail = newcode;
}
else
{
ps->tail->next = newcode;
ps->tail = newcode;
}
ps->szie++;
}
//删除
void QueuePop(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->head != NULL);
assert(!QueueEmpty(ps));
if (ps->head->next == NULL)
{
free(ps->head);
ps->head = ps->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = ps->head->next;
free(ps->head);
ps->head = next;
}
ps->szie--;
}
//大小
int QueueSize(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->szie;
}
//判空队
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->szie == 0;
}
//出队头
QDataType QueueTop(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!QueueEmpty(ps));
return ps->head->data;
}
//出队尾
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->tail->data;
}
test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "queue.h"
void testQueue()
{
Queue s;
QueueInit(&s);
QueuePush(&s, 1);
QueuePush(&s, 2);
QueuePush(&s, 3);
QueuePush(&s, 4);
//printf("%d ", QueueTop(&s));
//QueuePop(&s);
//printf("%d ", QueueTop(&s));
//QueuePop(&s);
//printf("%d ", QueueTop(&s));
//QueuePop(&s);
//printf("%d ", QueueTop(&s));
//QueuePop(&s);
//printf("\n");
while (!(QueueEmpty(&s)))
{
printf("%d ", QueueTop(&s));
QueuePop(&s);
}
QueueDestroy(&s);
}
int main()
{
testQueue();
return 0;
}










![[AI OpenAI] 提取GPT-4中的概念](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/55f7a4fe4abe2b66b0f1698f8b131147.gif)