文章目录
- LeetCode 236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
- 题目讲解
- 思路
- LeetCode 701.二叉搜索树中的插入操作
- 题目讲解
- 思路
- LeetCode 450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点
- 题目讲解
- 思路
- 示图
- 总结
- 既然还是要生活,那么就学会主宰生活
LeetCode 236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
题目讲解
思路
-
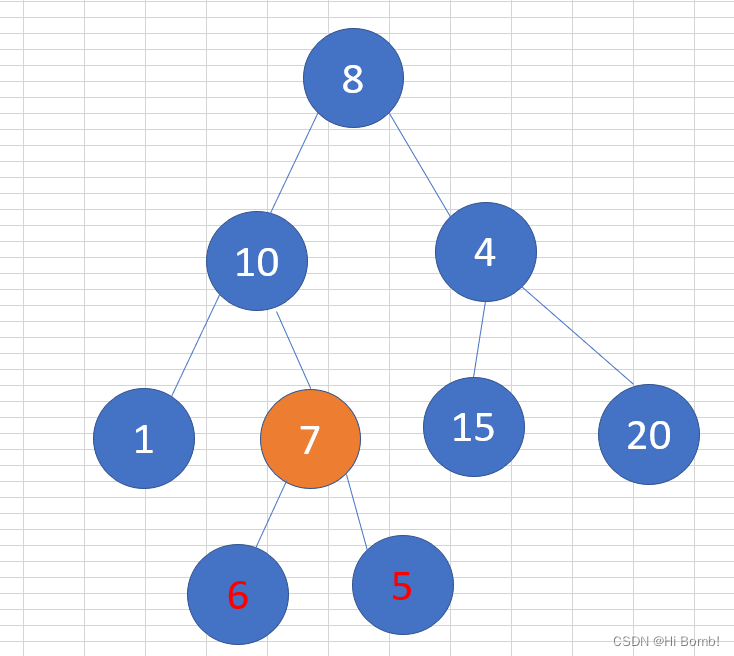
求最小公共祖先,需要从底向上遍历,那么二叉树,只能通过后序遍历(即:回溯)实现从底向上的遍历方式。
-
在回溯的过程中,必然要遍历整棵二叉树,即使已经找到结果了,依然要把其他节点遍历完,因为要使用递归函数的返回值(也就是代码中的left和right)做逻辑判断。
-
要理解如果返回值left为空,right不为空为什么要返回right,为什么可以用返回right传给上一层结果
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if( root==null || root ==p|| root== q)
{
return root;
}
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if( right== null&& left== null)
return null;
else if( left ==null && right !=null)
return right;
else if(right ==null &&left!=null)
return left;
else
return root;
}
}
LeetCode 701.二叉搜索树中的插入操作
题目讲解
思路
只要遍历二叉搜索树,找到空节点 插入元素就可以了,那么这道题其实就简单了。

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if( root ==null)
{
return new TreeNode(val);
}
if( val>root.val)
root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right,val);
if( val<root.val)
root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left,val);
return root;
}
}
LeetCode 450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点
题目讲解
思路
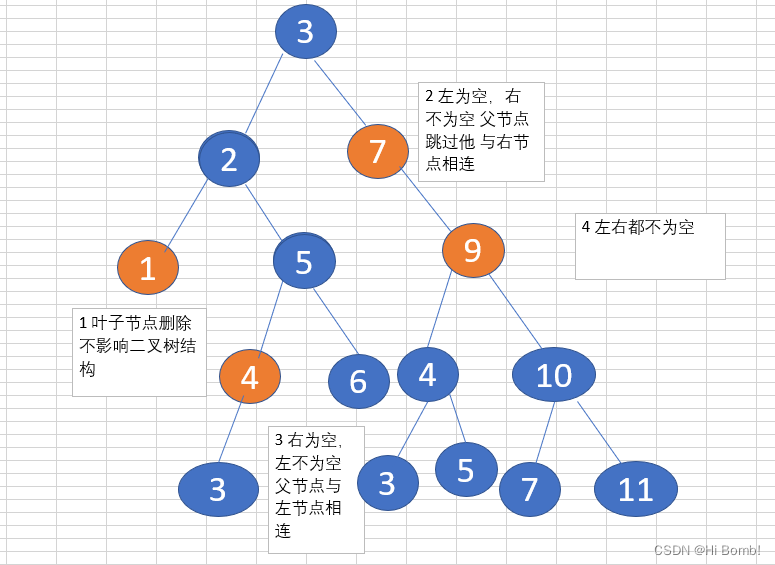
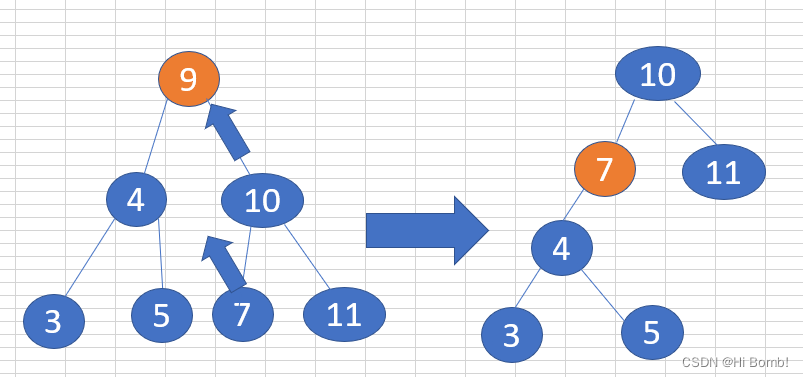
分成了五种情况进行讨论
- 找不到要删除的点
- 删除的点为叶子节点
- 左节点 为空 右节点 不为空
if( root.left ==null) return root.right; - 右节点为空, 左节点不为空
if( root.right ==null ) return root.left; - 找到要删除的点 两边都是不为空
//先创建一个临时节点
TreeNode tmp = root.right
while( root.left !=null)
{
tmp. left = root.left
}
root.val = tmp.val;
root.right = delete( root.right,tmp.val);
}
return root;
上面是部分代码的梗概
示图
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
root =delete(root,key);
return root;
}
public TreeNode delete(TreeNode root, int key)
{
if( root ==null)
return null;
// 左搜索
if( root.val> key)
root.left = delete(root.left,key);
//右搜索
else if( root.val <key)
{
root.right = delete(root.right,key);
}
else //平层的逻辑
{
if( root.left ==null) return root.right;
if(root.right ==null ) return root.left;
TreeNode temp = root.right;
while(temp.left!=null)
{
temp=temp.left;
}
root.val = temp.val;
root.right = delete(root.right,temp.val);
}
return root;
}
}





![穿越万年的轮回[期望dp]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/71bfc0057bb44e109448762d98baba94.png)