文章目录
- RPN 整体代码
- RPN 具体实现过程
- 数据标注
- 读取标注数据
- 固定图片大小调整目标框
- 使用预训练模型获取 feature_shape
- 定义 RPN 网络
- 生成RPN 的 CLS 和 REG 数据集
- 获取所有的锚点
- 计算锚点与目标框的IOU
- 定义 RPN loss 和 训练过程
- 参考资料
这里实现的是二阶段目标检测,其主要由一个RPN框架和ROI框架构成,后者只是一个图片分类任务,前者较为麻烦,这里只实现前者RPN过程
RPN 整体代码
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def generate_anchors(sizes = [128, 256, 512], ratios = [[1, 1], [1, 2], [2, 1]]):
num_anchors = len(sizes) * len(ratios)
anchors = np.zeros((num_anchors, 4))
anchors[:, 2:] = np.tile(sizes, (2, len(ratios))).T
for i in range(len(ratios)):
anchors[3 * i: 3 * i + 3, 2] = anchors[3 * i: 3 * i + 3, 2] * ratios[i][0]
anchors[3 * i: 3 * i + 3, 3] = anchors[3 * i: 3 * i + 3, 3] * ratios[i][1]
anchors[:, 0::2] -= np.tile(anchors[:, 2] * 0.5, (2, 1)).T
anchors[:, 1::2] -= np.tile(anchors[:, 3] * 0.5, (2, 1)).T
return anchors
def shift(shape, anchors, stride=16):
shift_x = (np.arange(0, shape[1], dtype=np.float32) + 0.5) * stride
shift_y = (np.arange(0, shape[0], dtype=np.float32) + 0.5) * stride
shift_x, shift_y = np.meshgrid(shift_x, shift_y)
shift_x = np.reshape(shift_x, [-1])
shift_y = np.reshape(shift_y, [-1])
shifts = np.stack([shift_x, shift_y, shift_x, shift_y], axis=0)
shifts = np.transpose(shifts)
number_of_anchors = np.shape(anchors)[0]
k = np.shape(shifts)[0]
shifted_anchors = np.reshape(anchors, [1, number_of_anchors, 4]) + np.array(np.reshape(shifts, [k, 1, 4]), dtype=np.float32)
shifted_anchors = np.reshape(shifted_anchors, [k * number_of_anchors, 4])
return shifted_anchors
def get_anchors(input_shape, feature_shape, sizes = [128, 256, 512], ratios = [[1, 1], [1, 2], [2, 1]], stride=16):
anchors = generate_anchors(sizes = sizes, ratios = ratios)
anchors = shift(feature_shape, anchors, stride = stride)
anchors[:, ::2] = np.clip(anchors[:, ::2], 0, input_shape[1])
anchors[:, 1::2] = np.clip(anchors[:, 1::2], 0, input_shape[0])
return anchors
%%time
anchors = get_anchors([600,600], [37,37])
anchors
## 数据准备
def get_xml_box(file_path, return_object_name=False):
"""返回的形式类似于:..[filename, object_name, xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax]"""
tree = ET.parse(file_path)
root = tree.getroot()
filename = root.find('filename').text
object_name_list = []
box_list = []
for item in root.iter('object'):
object_name = item.find('name').text
box = item.find('bndbox')
xmin = box.find('xmin').text
ymin = box.find('ymin').text
xmax = box.find('xmax').text
ymax = box.find('ymax').text
object_name_list.append(object_name)
box_list.append([xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax])
return [filename, object_name_list, box_list]
xml_files = ['../data/VOC2007/Annotations/' + xml_file for xml_file in os.listdir('../data/VOC2007/Annotations/') if xml_file.endswith('xml')]
data = [get_xml_box(xml_file) for xml_file in xml_files]
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.columns = ['filename', 'object_name_list', 'box_list']
df['filename'] = '../data/VOC2007/JPEGImages/' + df['filename']
df.head()
class_name = set([item for items in df.object_name_list.values.tolist() for item in items])
class_nums = len(class_name) + 1
class_name2index = dict(zip(class_name, range(1, class_nums)))
class_index2name = dict(zip(range(1, class_nums), class_name))
df['object_name_list'] = df['object_name_list'].map(lambda x: [class_name2index[item] for item in x])
df.head()
## 固定图片大小
def get_final_image_and_box(filename, box, input_shape=[600, 600]):
image = Image.open(filename)
box = np.array(box).astype(np.float32)
iw, ih = image.size
h, w = input_shape
scale = min(w/iw, h/ih)
nw = int(iw*scale)
nh = int(ih*scale)
dx = (w-nw)//2
dy = (h-nh)//2
# 获取final_image
image = image.resize((nw,nh), Image.BICUBIC)
new_image = Image.new('RGB', (w,h), (128,128,128))
new_image.paste(image, (dx, dy))
image_data = np.array(new_image, np.float32)
# 获取final_box
box[:, [0,2]] = box[:, [0,2]]*nw/iw + dx
box[:, [1,3]] = box[:, [1,3]]*nh/ih + dy
box[:, 0:2][box[:, 0:2]<0] = 0
box[:, 2][box[:, 2]>w] = w
box[:, 3][box[:, 3]>h] = h
box_w = box[:, 2] - box[:, 0]
box_h = box[:, 3] - box[:, 1]
box = box[np.logical_and(box_w>1, box_h>1)]
return image_data, box
filename = '../data/VOC2007/JPEGImages/000001.jpg'
target_box = [[9, 16, 374, 430], [378, 86, 625, 447]]
input_shape = [600, 600]
image_data, target_box = get_final_image_and_box(filename, target_box, input_shape)
image_data.shape, target_box
def compute_iou(boxes0: np.ndarray, boxes1: np.ndarray):
"""
计算多个边界框和多个边界框的交并比
boxes0: `~np.ndarray` of shape `(A, 4)`
boxes1: `~np.ndarray` of shape `(B, 4)`
Returns iou: `~np.ndarray` of shape `(A, B)`
"""
boxes0 = np.array(boxes0)
boxes1 = np.array(boxes1)
A = boxes0.shape[0]
B = boxes1.shape[0]
xy_max = np.minimum(boxes0[:, np.newaxis, 2:].repeat(B, axis=1),
np.broadcast_to(boxes1[:, 2:], (A, B, 2)))
xy_min = np.maximum(boxes0[:, np.newaxis, :2].repeat(B, axis=1),
np.broadcast_to(boxes1[:, :2], (A, B, 2)))
# 计算交集面积
inter = np.clip(xy_max-xy_min, a_min=0, a_max=np.inf)
inter = inter[:, :, 0]*inter[:, :, 1]
# 计算每个矩阵的面积
area_0 = ((boxes0[:, 2]-boxes0[:, 0])*(
boxes0[:, 3] - boxes0[:, 1]))[:, np.newaxis].repeat(B, axis=1)
area_1 = ((boxes1[:, 2] - boxes1[:, 0])*(
boxes1[:, 3] - boxes1[:, 1]))[np.newaxis, :].repeat(A, axis=0)
return inter/(area_0+area_1-inter)
def get_cls_and_reg_data(anchors, target_box, threshold_min=0.3, threshold_max=0.7, sample_size=256):
positive_iou = compute_iou(anchors, target_box)>threshold_max
negative_iou = compute_iou(anchors, target_box)<threshold_min
positive_cls = np.any(positive_iou, axis=1).astype(np.float32)
negative_cls = np.all(negative_iou, axis=1).astype(np.float32)
positive_index = np.random.choice(np.where(positive_cls==1)[0], size=sample_size)
negative_index = np.random.choice(np.where(negative_cls==1)[0], size=sample_size)
rpn_cls = np.concatenate([positive_index, negative_index], axis=0)
rpn_reg = [np.where(positive_iou[:,ix]==True)[0].tolist() for ix in range(len(target_box))]
return rpn_cls, rpn_reg
class RPN(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self, num_anchors):
super(RPN, self).__init__()
self.get_feature_model = tf.keras.applications.vgg16.VGG16(include_top=False, input_shape=[600, 600, 3])
self.get_feature_model = tf.keras.models.Model(inputs=self.get_feature_model.input, outputs=self.get_feature_model.layers[-2].output)
self.get_feature_model.trainable = False
self.conv_base = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(512, (3, 3), padding='same', activation='relu', name='rpn_conv1')
self.conv_class = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(num_anchors, (1, 1), activation='sigmoid', name='rpn_out_class')
self.conv_regr = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(num_anchors * 4, (1, 1), activation='linear', name='rpn_out_regress')
self.flatten = tf.keras.layers.Flatten()
def call(self, x):
x = self.get_feature_model(x)
x = self.conv_base(x)
x_cls = self.flatten(self.conv_class(x))
x_reg = tf.reshape(self.conv_regr(x), [tf.shape(x)[0], -1, 4])
x_reg = tf.transpose(x_reg, perm=[0, 2, 1])
return x_cls, x_reg
rpn = RPN(9)
x = np.stack([image_data,image_data])
y = [[[9, 16, 374, 430], [378, 86, 625, 447]], [[9, 16, 374, 430], [378, 86, 625, 447]]]
def compute_rpn_loss(x, y, return_cls=None, return_reg=None):
x_cls, x_reg = rpn(x)
y_true = tf.concat([tf.ones(256), tf.zeros(256)], axis=0)
anchors = get_anchors([600,600], [37,37])
cls_loss = 0
reg_loss = 0
for i in tf.range(tf.shape(x)[0]):
try:
rpn_cls, rpn_reg = get_cls_and_reg_data(anchors, y[i])
y_pred = tf.gather(x_cls[i], rpn_cls, axis=-1)
cls_loss += tf.keras.losses.binary_crossentropy(y_pred=y_pred, y_true=y_true)
for ix, indexes in enumerate(rpn_reg):
if indexes:
da = tf.transpose(tf.gather(x_reg[i], indexes, axis=-1))
g = [y[i][ix]]
a = tf.gather(anchors, indexes)
g = tf.cast(g, tf.float32)
a = tf.cast(a, tf.float32)
t_w = tf.math.log((g[:, 2] - g[:, 0]) / (a[:, 2] - a[:, 0]))
t_h = tf.math.log((g[:, 3] - g[:, 1]) / (a[:, 3] - a[:, 1]))
t_x = ((g[:, 0] + g[:, 2]) / 2 - (a[:, 0] + a[:, 2]) / 2) / (a[:, 2] - a[:, 0])
t_y = ((g[:, 1] + g[:, 3]) / 2 - (a[:, 1] + a[:, 3]) / 2) / (a[:, 3] - a[:, 1])
t = tf.stack([t_x, t_y, t_w, t_h], axis=1)
reg_loss += tf.reduce_mean(tf.abs(da - t))
except:
pass
if return_cls:
return cls_loss
if return_reg:
return reg_loss
return cls_loss, reg_loss
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=1e-4)
def train_one_step(x, y):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
reg_loss = compute_rpn_loss(x, y, return_reg=True)
rpn.conv_class.trainable = False
rpn.conv_regr.trainable = True
grads = tape.gradient(reg_loss, rpn.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(grads_and_vars=zip(grads, rpn.trainable_variables))
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
cls_loss = compute_rpn_loss(x, y, return_cls=True)
rpn.conv_class.trainable = True
rpn.conv_regr.trainable = False
grads = tape.gradient(cls_loss, rpn.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(grads_and_vars=zip(grads, rpn.trainable_variables))
return cls_loss, reg_loss
def train_one_epoch(times, size=10, steps=10):
cls_loss_total = []
reg_loss_total = []
for step in range(steps):
data = df.sample(size)
x_list = []
y_list = []
for filename, box in data[['filename', 'box_list']].values:
box = list(np.array(box).astype(np.int32))
img, box = get_final_image_and_box(filename, box)
x_list.append(img)
y_list.append(list(box))
x_list = np.stack(x_list)
y_list = [[list(item) for item in items] for items in y_list]
cls_loss, reg_loss = train_one_step(x_list, y_list)
cls_loss_total.append(cls_loss)
reg_loss_total.append(reg_loss)
cls_loss = tf.reduce_mean(cls_loss_total).numpy()
reg_loss = tf.reduce_mean(reg_loss_total).numpy()
tf.print(f'第{times}epochs, 得到cls_loss:{cls_loss}, reg_loss:{reg_loss}')
for i in range(1, 30):
train_one_epoch(times=i)
def nms(boxes, scores, iou_threshold):
"""boxes 是一个 [-1, 4], scores 是一个 [-1] """
def compute_iou(boxes, box):
# 计算交集
boxes, box = tf.cast(boxes, dtype=tf.float32), tf.cast(box, dtype=tf.float32)
xy_max = tf.minimum(boxes[:, 2:], box[2:])
xy_min = tf.maximum(boxes[:, :2], box[:2])
inter = tf.clip_by_value(xy_max - xy_min, clip_value_min=0., clip_value_max=tf.int32.max)
inter = inter[:, 0]*inter[:, 1]
# 计算面积
area_boxes = (boxes[:, 2]-boxes[:, 0])*(boxes[:, 3]-boxes[:, 1])
area_box = (box[2]-box[0])*(box[3]-box[1])
return inter/(area_box+area_boxes-inter)
boxes, scores = tf.cast(boxes, tf.float32), tf.cast(scores, tf.float32)
nms_indices = tf.TensorArray(tf.int32, size=0, dynamic_size=True)
def cond(boxes, scores, nms_indices):
return tf.reduce_any(tf.not_equal(scores, 0))
def body(boxes, scores, nms_indices):
idx = tf.argsort(scores, direction='DESCENDING')
scores = tf.gather(scores, idx)
boxes = tf.gather(boxes, idx)
current_box = tf.gather(boxes, idx[0])
nms_indices = nms_indices.write(nms_indices.size(), idx[0])
ious = compute_iou(boxes, current_box)
mask = tf.math.less(ious, iou_threshold)
scores = tf.cast(mask, tf.float32) * scores
return boxes, scores, nms_indices
_, _, nms_indices = tf.while_loop(cond, body, [boxes, scores, nms_indices])
final_indices = nms_indices.stack()
final_boxes = tf.gather(boxes, final_indices)
return final_boxes
rpn(np.expand_dims(image_data, axis=0))[0]
nms(tf.reshape(anchors, [-1,4]), tf.reshape(rpn(np.expand_dims(image_data, axis=0))[0], -1), 0.9)
def bbox_to_rect(bbox, color):
return plt.Rectangle(
xy=(bbox[0], bbox[1]), width=bbox[2]-bbox[0], height=bbox[3]-bbox[1],
fill=False, edgecolor=color, linewidth=0.5)
# 一步到位
def plot_anchors(anchors):
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
# 获取范围,方便限制坐标轴
a, b = np.min(anchors, axis=0), np.max(anchors, axis=0)
plt.imshow(image_data.astype(np.int32))
plt.scatter([a[0], b[2]], [a[1], b[3]], c='white')
ax = plt.gca()
for anchor in anchors:
ax.add_patch(bbox_to_rect(anchor, 'red'))
plt.axis('off')
zz = nms(tf.reshape(anchors, [-1,4]), tf.reshape(rpn(np.expand_dims(image_data, axis=0))[0], -1), 0.9)
plot_anchors(zz)
RPN 具体实现过程
数据标注

通常来说,像目标检测识别这种数据标注使用的工具是 LabelImg, 但是随着开源社区的发展和通用模型的成熟,较为推荐使用Label Studio,该工具几乎可以标注任何任务的数据,同时 LabelImg 集成于其中,不同点在于,LabelImg 像一个桌面应用程序,而 Label Studio 是一个端口网页,同时 Label Studio 类似于社区的形式,需要登入。
Label Studio 的安装方式如下:注意:最好在一个新的虚拟环境安装,避免于原来的库发生冲突;
# Requires Python >=3.8
pip install label-studio
# Start the server at http://localhost:8080
label-studio
安装之后打开 http://localhost:8080 ,默认是这个,如果占用了基本上是+1就可以使用;
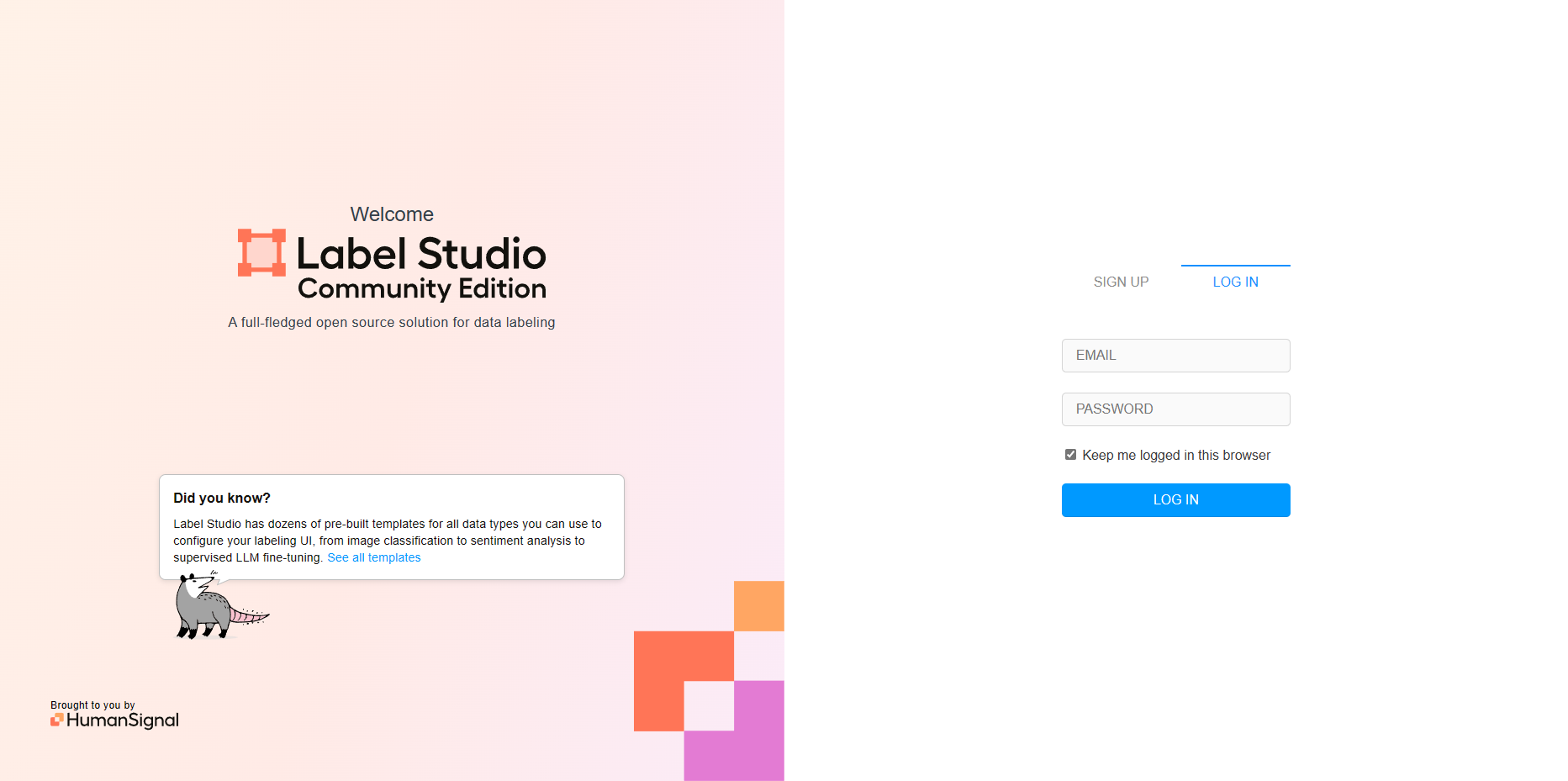
发现以上页面,点击 SIGN UP 进行注册,注册登入完毕后,得到以下界面,点击 Create Project
![![[Pasted image 20240529125046.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/ae64751fe5084182a1173f241ef65f54.png)
把该填完的填写完毕,在 Data Import 中导入数据,在 Labeling Setup 中选取任务类型,最后点击 Save ,可以开始执行数据标注任务了。
![![[Pasted image 20240529125310.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/3a989131563c4eb5ad0de3e9cc405d67.png)
标注页面如下
![![[Pasted image 20240529125525.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/384b4d1b5b7445a1a643c2c3454437f5.png)
标注好数据后,对数据进行导出
![![[Pasted image 20240529125922.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/799edeb33ba24d0f931261b43ccfc270.png)
所谓数据标注,也就是创造数据的过程,这里导出有不同的形式对应不同模型库的处理方法,在这里我们选择文章中一样的格式,Pascal VOC XML ,之后我们还需要把创造的数据进行转化制作数据集;
读取标注数据
Pascal VOC XML 数据集由两个文件夹构成,分别是 Annotations 和 images,前者存储标注数据,文件格式为 xml,后者对应 JPEGImages ,存储照片数据;
![![[Pasted image 20240529130200.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/a0039cd2bab34dda9d5c0dc60168bdb2.png)
由于标注数据过于麻烦,这里直接采用 VOC2007 数据集进行训练,首先读取 Annotations 中的 xml 数据,xml 数据格式如下
<annotation>
<folder>VOC2007</folder>
<!--文件名-->
<filename>000005.jpg</filename>.
<!--数据来源-->
<source>
<!--数据来源-->
<database>The VOC2007 Database</database>
<annotation>PASCAL VOC2007</annotation>
<!--来源是flickr,一个雅虎的图像分享网站,下面是id,对于我们没有用-->
<image>flickr</image>
<flickrid>325991873</flickrid>
</source>
<!--图片的所有者,也没有用-->
<owner>
<flickrid>archintent louisville</flickrid>
<name>?</name>
</owner>
<!--图像尺寸,宽、高、长-->
<size>
<width>500</width>
<height>375</height>
<depth>3</depth>
</size>
<!--是否用于分割,0表示用于,1表示不用于-->
<segmented>0</segmented>
<!--下面是图像中标注的物体,每一个object包含一个标准的物体-->
<object>
<!--物体名称,拍摄角度-->
<name>chair</name>
<pose>Rear</pose>
<!--是否被裁减,0表示完整,1表示不完整-->
<truncated>0</truncated>
<!--是否容易识别,0表示容易,1表示困难-->
<difficult>0</difficult>
<!--bounding box的四个坐标-->
<bndbox>
<xmin>263</xmin>
<ymin>211</ymin>
<xmax>324</xmax>
<ymax>339</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
</annotation>
所有导入的包如下
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
我们只需要获取图片中所有对象的名称以及坐标,代码如下
def get_xml_box(file_path, return_object_name=False):
"""返回的形式类似于:..[filename, object_name, xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax]"""
tree = ET.parse(file_path)
root = tree.getroot()
filename = root.find('filename').text
object_name_list = []
box_list = []
for item in root.iter('object'):
object_name = item.find('name').text
box = item.find('bndbox')
xmin = box.find('xmin').text
ymin = box.find('ymin').text
xmax = box.find('xmax').text
ymax = box.find('ymax').text
object_name_list.append(object_name)
box_list.append([xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax])
return [filename, object_name_list, box_list]
遍历 Annotations 文件夹,提取出 Annotations 信息
# 遍历 Annotations 文件夹
xml_files = ['../data/VOC2007/Annotations/' + xml_file for xml_file in os.listdir('../data/VOC2007/Annotations/') if xml_file.endswith('xml')]
data = [get_xml_box(xml_file) for xml_file in xml_files]
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.columns = ['filename', 'object_name_list', 'box_list']
# 给filename 添加文件路径 得到file_path
df['filename'] = '../data/VOC2007/JPEGImages/' + df['filename']
df.head()
获得表格如下
![![[Pasted image 20240531082732.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/9001ec7034cc4f218da276b0ed82ae82.png)
接下来获取 object_name_list 中包含的所有类别并构建 name2index 和 index2name 两个字典,利用 name2index 字典对 object_name_list 进行转换
class_name = set([item for items in df.object_name_list.values.tolist() for item in items])
class_nums = len(class_name) + 1
class_name2index = dict(zip(class_name, range(1, class_nums)))
class_index2name = dict(zip(range(1, class_nums), class_name))
df['object_name_list'] = df['object_name_list'].map(lambda x: [class_name2index[item] for item in x])
df.head()
获取最终的表格如下
![![[Pasted image 20240531082932.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/fd6987b60c8c44f6bb9ad35d28964661.png)
固定图片大小调整目标框
由于神经网络模型需要输入的图像大小一致,我们需要将大小不同的图片转化成大小相同的图片进行输入,由于图片发生了变化,目标框也会发生变化。这里以dataframe中第一个数据为例子,我们把图片大小固定为 600 × 600 600 \times 600 600×600;
def get_final_image_and_box(filename, box, input_shape=[600, 600]):
image = Image.open(filename)
box = np.array(box).astype(np.float32)
iw, ih = image.size
h, w = input_shape
scale = min(w/iw, h/ih)
nw = int(iw*scale)
nh = int(ih*scale)
dx = (w-nw)//2
dy = (h-nh)//2
# 获取final_image
image = image.resize((nw,nh), Image.BICUBIC)
new_image = Image.new('RGB', (w,h), (128,128,128))
new_image.paste(image, (dx, dy))
image_data = np.array(new_image, np.float32)
# 获取final_box
box[:, [0,2]] = box[:, [0,2]]*nw/iw + dx
box[:, [1,3]] = box[:, [1,3]]*nh/ih + dy
box[:, 0:2][box[:, 0:2]<0] = 0
box[:, 2][box[:, 2]>w] = w
box[:, 3][box[:, 3]>h] = h
box_w = box[:, 2] - box[:, 0]
box_h = box[:, 3] - box[:, 1]
box = box[np.logical_and(box_w>1, box_h>1)]
return image_data, box
filename = '../data/VOC2007/JPEGImages/000001.jpg'
target_box = [[9, 16, 374, 430], [378, 86, 625, 447]]
input_shape = [600, 600]
image_data, target_box = get_final_image_and_box(filename, target_box, input_shape)
image_data.shape, target_box
使用预训练模型获取 feature_shape
这里使用 VGG16 模型来获取 feature_shape
get_feature_model = tf.keras.applications.vgg16.VGG16(include_top=False, input_shape=[600, 600, 3])
get_feature_model = tf.keras.models.Model(inputs=get_feature_model.input, outputs=get_feature_model.layers[-2].output)
测试一下特征模型输出
get_feature_model(np.expand_dims(image_data, axis=0)).shape
# TensorShape([1, 37, 37, 512])
可以得到 feature_shape 为
37
×
37
37 \times 37
37×37
定义 RPN 网络
RPN 网络是在预训练模型的基础上进行的,其有两个输出,一个是 classification、一个是regression,前者维度为 num_anchors, 后者维度为 4 * num_anchors,其中 num_anchors 等于 9,其中 9 表示下文中 generate_anchors 生成的 基础锚框个数 len(sizes) * len(ratios)
class RPN(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self, num_anchors):
super(RPN, self).__init__()
self.get_feature_model = tf.keras.applications.vgg16.VGG16(include_top=False, input_shape=[600, 600, 3])
self.get_feature_model = tf.keras.models.Model(inputs=self.get_feature_model.input, outputs=self.get_feature_model.layers[-2].output)
self.get_feature_model.trainable = False
self.conv_base = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(512, (3, 3), padding='same', activation='relu', name='rpn_conv1')
self.conv_class = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(num_anchors, (1, 1), activation='sigmoid', name='rpn_out_class')
self.conv_regr = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(num_anchors * 4, (1, 1), activation='linear', name='rpn_out_regress')
self.flatten = tf.keras.layers.Flatten()
def call(self, x):
x = self.get_feature_model(x)
x = self.conv_base(x)
x_cls = self.flatten(self.conv_class(x))
x_reg = tf.reshape(self.conv_regr(x), [tf.shape(x)[0], -1, 4])
x_reg = tf.transpose(x_reg, perm=[0, 2, 1])
return x_cls, x_reg
rpn = RPN(9)
生成RPN 的 CLS 和 REG 数据集
获取所有的锚点
def generate_anchors(sizes = [128, 256, 512], ratios = [[1, 1], [1, 2], [2, 1]]):
num_anchors = len(sizes) * len(ratios)
anchors = np.zeros((num_anchors, 4))
anchors[:, 2:] = np.tile(sizes, (2, len(ratios))).T
for i in range(len(ratios)):
anchors[3 * i: 3 * i + 3, 2] = anchors[3 * i: 3 * i + 3, 2] * ratios[i][0]
anchors[3 * i: 3 * i + 3, 3] = anchors[3 * i: 3 * i + 3, 3] * ratios[i][1]
anchors[:, 0::2] -= np.tile(anchors[:, 2] * 0.5, (2, 1)).T
anchors[:, 1::2] -= np.tile(anchors[:, 3] * 0.5, (2, 1)).T
return anchors
def shift(shape, anchors, stride=16):
shift_x = (np.arange(0, shape[1], dtype=np.float32) + 0.5) * stride
shift_y = (np.arange(0, shape[0], dtype=np.float32) + 0.5) * stride
shift_x, shift_y = np.meshgrid(shift_x, shift_y)
shift_x = np.reshape(shift_x, [-1])
shift_y = np.reshape(shift_y, [-1])
shifts = np.stack([shift_x, shift_y, shift_x, shift_y], axis=0)
shifts = np.transpose(shifts)
number_of_anchors = np.shape(anchors)[0]
k = np.shape(shifts)[0]
shifted_anchors = np.reshape(anchors, [1, number_of_anchors, 4]) + np.array(np.reshape(shifts, [k, 1, 4]), dtype=np.float32)
shifted_anchors = np.reshape(shifted_anchors, [k * number_of_anchors, 4])
return shifted_anchors
def get_anchors(input_shape, feature_shape, sizes = [128, 256, 512], ratios = [[1, 1], [1, 2], [2, 1]], stride=16):
anchors = generate_anchors(sizes = sizes, ratios = ratios)
anchors = shift(feature_shape, anchors, stride = stride)
anchors[:, ::2] = np.clip(anchors[:, ::2], 0, input_shape[1])
anchors[:, 1::2] = np.clip(anchors[:, 1::2], 0, input_shape[0])
return anchors
input_shape = [600, 600]
feature_shape = [37,37]
# 获取瞄框
anchors = get_anchors(input_shape, feature_shape)
# CPU times: total: 0 ns
# Wall time: 607 µs
计算锚点与目标框的IOU
def compute_iou(boxes0: np.ndarray, boxes1: np.ndarray):
"""
计算多个边界框和多个边界框的交并比
boxes0: `~np.ndarray` of shape `(A, 4)`
boxes1: `~np.ndarray` of shape `(B, 4)`
Returns iou: `~np.ndarray` of shape `(A, B)`
"""
boxes0 = np.array(boxes0)
boxes1 = np.array(boxes1)
A = boxes0.shape[0]
B = boxes1.shape[0]
xy_max = np.minimum(boxes0[:, np.newaxis, 2:].repeat(B, axis=1),
np.broadcast_to(boxes1[:, 2:], (A, B, 2)))
xy_min = np.maximum(boxes0[:, np.newaxis, :2].repeat(B, axis=1),
np.broadcast_to(boxes1[:, :2], (A, B, 2)))
# 计算交集面积
inter = np.clip(xy_max-xy_min, a_min=0, a_max=np.inf)
inter = inter[:, :, 0]*inter[:, :, 1]
# 计算每个矩阵的面积
area_0 = ((boxes0[:, 2]-boxes0[:, 0])*(
boxes0[:, 3] - boxes0[:, 1]))[:, np.newaxis].repeat(B, axis=1)
area_1 = ((boxes1[:, 2] - boxes1[:, 0])*(
boxes1[:, 3] - boxes1[:, 1]))[np.newaxis, :].repeat(A, axis=0)
return inter/(area_0+area_1-inter)
生成 CLS 和 REG 任务的数据
def get_cls_and_reg_data(anchors, target_box, threshold_min=0.3, threshold_max=0.7, sample_size=256):
positive_iou = compute_iou(anchors, target_box)>threshold_max
negative_iou = compute_iou(anchors, target_box)<threshold_min
positive_cls = np.any(positive_iou, axis=1).astype(np.float32)
negative_cls = np.all(negative_iou, axis=1).astype(np.float32)
positive_index = np.random.choice(np.where(positive_cls==1)[0], size=sample_size)
negative_index = np.random.choice(np.where(negative_cls==1)[0], size=sample_size)
rpn_cls = np.concatenate([positive_index, negative_index], axis=0)
rpn_reg = [np.where(positive_iou[:,ix]==True)[0].tolist() for ix in range(len(target_box))]
return rpn_cls, rpn_reg
# CPU times: total: 0 ns
# Wall time: 4.26 ms
定义 RPN loss 和 训练过程
def compute_rpn_loss(x, y, return_cls=None, return_reg=None):
x_cls, x_reg = rpn(x)
y_true = tf.concat([tf.ones(256), tf.zeros(256)], axis=0)
anchors = get_anchors([600,600], [37,37])
cls_loss = 0
reg_loss = 0
for i in tf.range(tf.shape(x)[0]):
try:
rpn_cls, rpn_reg = get_cls_and_reg_data(anchors, y[i])
y_pred = tf.gather(x_cls[i], rpn_cls, axis=-1)
cls_loss += tf.keras.losses.binary_crossentropy(y_pred=y_pred, y_true=y_true)
for ix, indexes in enumerate(rpn_reg):
if indexes:
da = tf.transpose(tf.gather(x_reg[i], indexes, axis=-1))
g = [y[i][ix]]
a = tf.gather(anchors, indexes)
g = tf.cast(g, tf.float32)
a = tf.cast(a, tf.float32)
t_w = tf.math.log((g[:, 2] - g[:, 0]) / (a[:, 2] - a[:, 0]))
t_h = tf.math.log((g[:, 3] - g[:, 1]) / (a[:, 3] - a[:, 1]))
t_x = ((g[:, 0] + g[:, 2]) / 2 - (a[:, 0] + a[:, 2]) / 2) / (a[:, 2] - a[:, 0])
t_y = ((g[:, 1] + g[:, 3]) / 2 - (a[:, 1] + a[:, 3]) / 2) / (a[:, 3] - a[:, 1])
t = tf.stack([t_x, t_y, t_w, t_h], axis=1)
reg_loss += tf.reduce_mean(tf.abs(da - t))
except:
pass
if return_cls:
return cls_loss
if return_reg:
return reg_loss
return cls_loss, reg_loss
定义训练 train_one_step 和 train_one_epoch
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=1e-4)
def train_one_step(x, y):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
reg_loss = compute_rpn_loss(x, y, return_reg=True)
rpn.conv_class.trainable = False
rpn.conv_regr.trainable = True
grads = tape.gradient(reg_loss, rpn.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(grads_and_vars=zip(grads, rpn.trainable_variables))
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
cls_loss = compute_rpn_loss(x, y, return_cls=True)
rpn.conv_class.trainable = True
rpn.conv_regr.trainable = False
grads = tape.gradient(cls_loss, rpn.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(grads_and_vars=zip(grads, rpn.trainable_variables))
return cls_loss, reg_loss
def train_one_epoch(times, size=10, steps=10):
cls_loss_total = []
reg_loss_total = []
for step in range(steps):
data = df.sample(size)
x_list = []
y_list = []
for filename, box in data[['filename', 'box_list']].values:
box = list(np.array(box).astype(np.int32))
img, box = get_final_image_and_box(filename, box)
x_list.append(img)
y_list.append(list(box))
x_list = np.stack(x_list)
y_list = [[list(item) for item in items] for items in y_list]
cls_loss, reg_loss = train_one_step(x_list, y_list)
cls_loss_total.append(cls_loss)
reg_loss_total.append(reg_loss)
cls_loss = tf.reduce_mean(cls_loss_total).numpy()
reg_loss = tf.reduce_mean(reg_loss_total).numpy()
tf.print(f'第{times}epochs, 得到cls_loss:{cls_loss}, reg_loss:{reg_loss}')
在训练了30个epoch后效果如下
for i in range(1, 30):
train_one_epoch(times=i)
训练过程损失变化
第1epochs, 得到cls_loss:7.311850547790527, reg_loss:37.811378479003906
第2epochs, 得到cls_loss:8.812080383300781, reg_loss:39.66188430786133
第3epochs, 得到cls_loss:7.56036376953125, reg_loss:38.44755172729492
第4epochs, 得到cls_loss:6.361146450042725, reg_loss:38.41288375854492
第5epochs, 得到cls_loss:4.806685924530029, reg_loss:34.26782989501953
第6epochs, 得到cls_loss:5.582345008850098, reg_loss:32.031654357910156
第7epochs, 得到cls_loss:4.612250328063965, reg_loss:26.891027450561523
第8epochs, 得到cls_loss:5.257579326629639, reg_loss:26.739116668701172
第9epochs, 得到cls_loss:4.4021315574646, reg_loss:26.248144149780273
第10epochs, 得到cls_loss:4.2677903175354, reg_loss:25.118724822998047
第11epochs, 得到cls_loss:4.390046119689941, reg_loss:20.355392456054688
第12epochs, 得到cls_loss:4.0723371505737305, reg_loss:18.319538116455078
第13epochs, 得到cls_loss:3.915370225906372, reg_loss:16.594970703125
第14epochs, 得到cls_loss:3.9558539390563965, reg_loss:18.293819427490234
第15epochs, 得到cls_loss:3.6445891857147217, reg_loss:14.1051607131958
第16epochs, 得到cls_loss:3.8050498962402344, reg_loss:15.811358451843262
第17epochs, 得到cls_loss:4.375217437744141, reg_loss:15.368804931640625
第18epochs, 得到cls_loss:3.943711757659912, reg_loss:10.533037185668945
第19epochs, 得到cls_loss:3.752122402191162, reg_loss:12.843942642211914
第20epochs, 得到cls_loss:3.458630323410034, reg_loss:10.283559799194336
第21epochs, 得到cls_loss:3.7187225818634033, reg_loss:11.331975936889648
第22epochs, 得到cls_loss:3.6269428730010986, reg_loss:12.088125228881836
第23epochs, 得到cls_loss:3.8386969566345215, reg_loss:10.8582124710083
第24epochs, 得到cls_loss:3.748070478439331, reg_loss:9.630635261535645
第25epochs, 得到cls_loss:4.043728828430176, reg_loss:8.781991958618164
第26epochs, 得到cls_loss:3.3101487159729004, reg_loss:7.175162315368652
第27epochs, 得到cls_loss:3.6511452198028564, reg_loss:6.6876630783081055
第28epochs, 得到cls_loss:4.238692283630371, reg_loss:7.911011695861816
第29epochs, 得到cls_loss:3.6738617420196533, reg_loss:6.6059465408325195
使用 NMS 在猫狗图片效果如下
def nms(boxes, scores, iou_threshold):
"""boxes 是一个 [-1, 4], scores 是一个 [-1] """
def compute_iou(boxes, box):
# 计算交集
boxes, box = tf.cast(boxes, dtype=tf.float32), tf.cast(box, dtype=tf.float32)
xy_max = tf.minimum(boxes[:, 2:], box[2:])
xy_min = tf.maximum(boxes[:, :2], box[:2])
inter = tf.clip_by_value(xy_max - xy_min, clip_value_min=0., clip_value_max=tf.int32.max)
inter = inter[:, 0]*inter[:, 1]
# 计算面积
area_boxes = (boxes[:, 2]-boxes[:, 0])*(boxes[:, 3]-boxes[:, 1])
area_box = (box[2]-box[0])*(box[3]-box[1])
return inter/(area_box+area_boxes-inter)
boxes, scores = tf.cast(boxes, tf.float32), tf.cast(scores, tf.float32)
nms_indices = tf.TensorArray(tf.int32, size=0, dynamic_size=True)
def cond(boxes, scores, nms_indices):
return tf.reduce_any(tf.not_equal(scores, 0))
def body(boxes, scores, nms_indices):
idx = tf.argsort(scores, direction='DESCENDING')
scores = tf.gather(scores, idx)
boxes = tf.gather(boxes, idx)
current_box = tf.gather(boxes, idx[0])
nms_indices = nms_indices.write(nms_indices.size(), idx[0])
ious = compute_iou(boxes, current_box)
mask = tf.math.less(ious, iou_threshold)
scores = tf.cast(mask, tf.float32) * scores
return boxes, scores, nms_indices
_, _, nms_indices = tf.while_loop(cond, body, [boxes, scores, nms_indices])
final_indices = nms_indices.stack()
final_boxes = tf.gather(boxes, final_indices)
return final_boxes
效果如下
![![[Pasted image 20240531222535.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/d5c2b546134e41feb19973602d2247a7.png)
这里并没有加入边框回归的效果,可以看到这里效果还不错,这是RPN过程,后面的ROI过程和RPN过程一致,单纯一个图片分类问题,这里就不进行实现了
参考资料
- 【数据准备001】标注工具Labelimg安装与使用(附txt与xml文件相互转化代码)-CSDN博客
- 标注工具——Label Studio安装与简单使用-CSDN博客
- 如何使用 numpy 和 pytorch 快速计算 IOU - 之一Yo - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
- Python深度学习基于Tensorflow(10)目标检测_tensorflow 检测 定位-CSDN博客