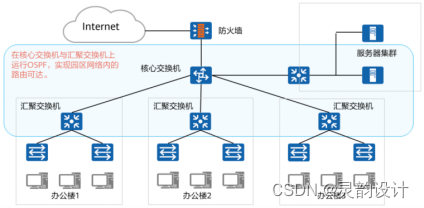
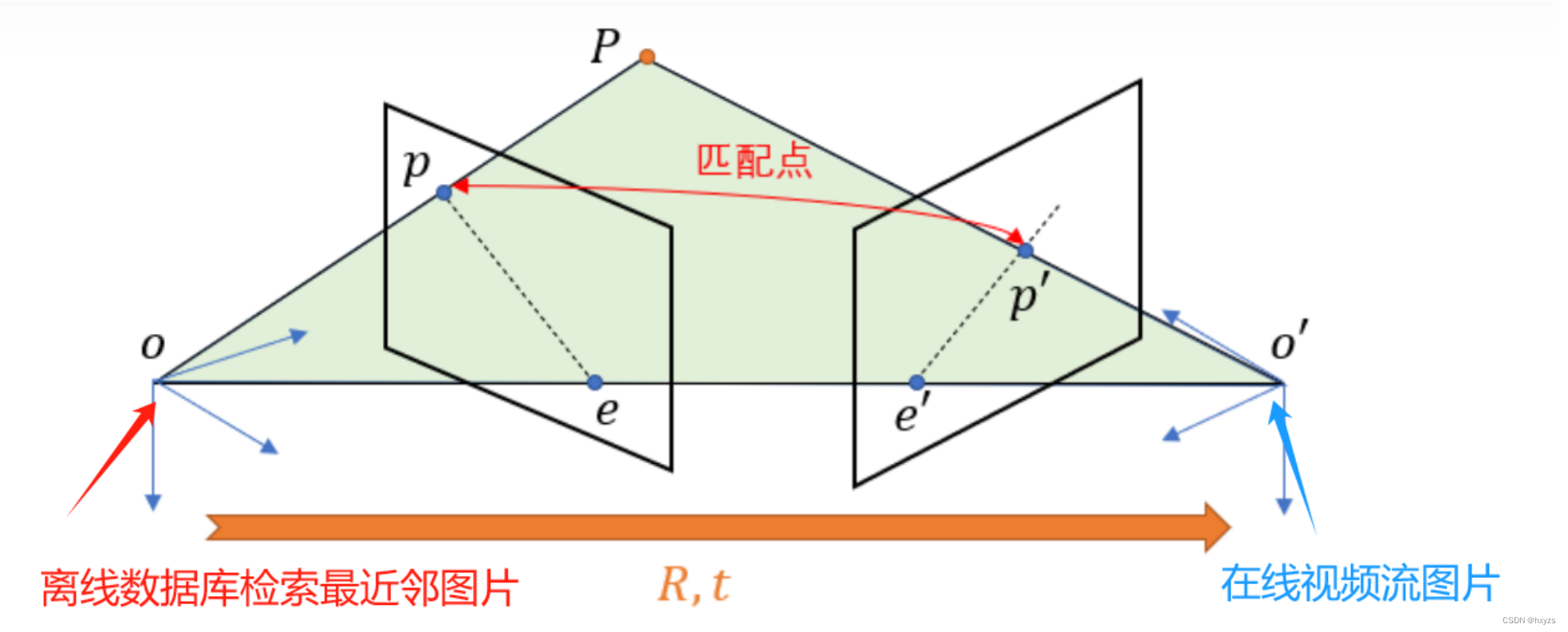
相对位姿估计
示意图
理论推导
离线数据库:
P的位置 P = [ X , Y , Z ] T P=[X,Y,Z]^{T} P=[X,Y,Z]T
相机内参 k 1 k_{1} k1
安卓手机:
相机内参 k 2 k_{2} k2
两个像素点位置 : p 1 和 p 2 p_1和p_2 p1和p2
公式一:
s 1 p 1 = K 1 P s_1p_1=K_1P s1p1=K1P s 2 p 2 = K 2 ( R P + t ) s_2p_2=K_2(RP+t) s2p2=K2(RP+t)
**公式二:**归一化平面上的坐标
x 1 = K 1 − 1 p 1 x_1=K_1^{-1}p_1 x1=K1−1p1 x 2 = K 2 − 1 p 2 x_2=K_2^{-1}p2 x2=K2−1p2
公式三:
x 2 = R x 1 + t x_2=Rx_1+t x2=Rx1+t
公式四:
t ^ x 2 = t ^ R x 1 \hat{t}x_2=\hat{t}Rx_1 t^x2=t^Rx1
公式五
x 2 T t ^ x 2 = x 2 T t ^ R x 1 x_2^{T}\hat{t}x_2=x_2^{T}\hat{t}Rx_1 x2Tt^x2=x2Tt^Rx1
x 2 T t ^ R x 1 = 0 x_2^{T}\hat{t}Rx_1=0 x2Tt^Rx1=0
公式六:
( K 2 − 1 p 2 ) T t ^ R K 1 − 1 p 1 (K_2^{-1}p_2)^{T}\hat{t}RK_1^{-1}p_1 (K2−1p2)Tt^RK1−1p1
结论:
本质矩阵: E = t ^ R E=\hat{t}R E=t^R ---------------------已知相机参数的情况下
基础矩阵: F = K 2 − T E K 1 − 1 F=K_2^{-T}EK_1^{-1} F=K2−TEK1−1 -----------未知相机参数的情况下
伪代码
input:image_src,k_src,image_dst,k_dst
output:R,t
1 feature_detect(image_src,image_dst)---->keypoints and deccriptors
2 feature_match(image_src,image_dst)---->matched_features
3 find_essentialmatrix(matched_keypoints,k_src,k_dst)----->essential_matrix
4 decompose_E(essentialmatrix)----->R,t
5 judge "left or right"
实现代码
import cv2
import numpy as np
def find_keypoints_and_descriptors(image):
# 使用SIFT算法检测关键点和计算描述符
sift = cv2.SIFT_create()
keypoints, descriptors = sift.detectAndCompute(image, None)
return keypoints, descriptors
def match_keypoints(descriptors1, descriptors2):
# 使用FLANN匹配器进行关键点匹配
FLANN_INDEX_KDTREE = 0
index_params = dict(algorithm=FLANN_INDEX_KDTREE, trees=5)
search_params = dict(checks=50)
flann = cv2.FlannBasedMatcher(index_params, search_params)
matches = flann.knnMatch(descriptors1, descriptors2, k=2)
# 保留良好的匹配
good_matches = []
for m, n in matches:
if m.distance < 0.7 * n.distance:
good_matches.append(m)
return good_matches
def estimate_relative_pose(keypoints1, keypoints2, good_matches, camera_matrix_src,camera_matrix_dst):
# 提取匹配点对应的关键点
src_pts = np.float32([keypoints1[m.queryIdx].pt for m in good_matches]).reshape(-1, 1, 2)
dst_pts = np.float32([keypoints2[m.trainIdx].pt for m in good_matches]).reshape(-1, 1, 2)
# 使用基础矩阵估计相机的相对位姿
essential_matrix, _ = cv2.findEssentialMat(src_pts, dst_pts, camera_matrix_src, camera_matrix_dst)
# 从基础矩阵中恢复旋转和平移矩阵
_, R, t, _ = cv2.recoverPose(essential_matrix, src_pts, dst_pts, camera_matrix_src, camera_matrix_dst)
return R, t
def determine_camera_direction(t):
if t[0] > 0:
print("相机偏向右侧")
elif t[0] < 0:
print("相机偏向左侧")
else:
print("相机方向正前方")
# # 示例平移向量
# t = np.array([[1.5], [0.2], [0.3]]) # 假设平移向量 t = [1.5, 0.2, 0.3]
# determine_camera_direction(t)
def main():
# 加载两张图片
image1 = cv2.imread('image1.jpg', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
image2 = cv2.imread('image2.jpg', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
# 假设你已知相机内参
fx_src = 1000.0 # 举例:相机的焦距
fy_src = 1000.0
cx_src = 320.0 # 图像中心点的x坐标
cy_src = 240.0 # 图像中心点的y坐标
camera_matrix_src = np.array([[fx_src, 0, cx_src],
[0, fy_src, cy_src],
[0, 0, 1]])
fx_dst = 1000.0 # 举例:相机的焦距
fy_dst = 1000.0
cx_dst = 320.0 # 图像中心点的x坐标
cy_dst = 240.0 # 图像中心点的y坐标
camera_matrix_dst = np.array([[fx_dst, 0, cx_dst],
[0, fy_dst, cy_dst],
[0, 0, 1]])
# 检测关键点和计算描述符
keypoints1, descriptors1 = find_keypoints_and_descriptors(image1)
keypoints2, descriptors2 = find_keypoints_and_descriptors(image2)
# 匹配关键点
good_matches = match_keypoints(descriptors1, descriptors2)
# 估计相机的相对位姿
R, t = estimate_relative_pose(keypoints1, keypoints2, good_matches, camera_matrix_src,camera_matrix_dst)
# 计算旋转矩阵的欧拉角
angles = cv2.Rodrigues(R)[0]
yaw = np.arctan2(angles[1, 0], angles[0, 0]) * 180.0 / np.pi
# 判断相机的方向
if yaw > 0:
print("相机偏向右侧,您应该向左转")
elif yaw < 0:
print("相机偏向左侧,您应该向右转")
else:
print("相机方向正前方")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()