函数式组件和类式组件的优缺点儿
函数组件(Function Component)和类组件(Class Component)是React中的两种定义组件的方式。函数组件是以一个函数的方式定义组件,而类组件则是以ES6的类继承React.Component来定义组件。
函数组件的优点:
1.更简单的代码,无需使用this关键字。
2.更容易理解和调试,因为它们是纯函数。
3.更好的性能,因为它们不支持shouldComponentUpdate生命周期钩子。
默认的性能优化,如React Fiber的diff算法会更好地处理函数组件。
函数组件的缺点:
1.缺乏状态(state),需要使用hooks API(如useState)。
2.缺乏生命周期方法,需要使用hooks API(如useEffect)或者将函数组件转换为类组件。
3.不支持refs。
类组件的优点:
1.支持更多的React特性,如状态(state),生命周期方法,refs等。
2.可以在任何生命周期中使用this.setState来更新状态,而不需要考虑是否在合成事件中。
3.类组件可以复用状态逻辑和生命周期逻辑,通过高阶组件等方式。
类组件的缺点:
1.需要使用this关键字,可能会导致this指向问题。
2.类组件在每次渲染时都会创建一个新的实例,可能会影响性能。
3.代码可能会更复杂,因为需要处理this和生命周期方法。
在新的React项目中,推荐使用函数组件,特别是对于简单的组件,因为它们更易于理解和维护。但是,当需要使用state、refs或生命周期方法时,就应该使用类组件或hooks
代码示例
主入口文件index.js 代码配置项如下:
import ReactDOM from "react-dom/client";
import React from "react";
import App from "./App";
import { Provider } from "react-redux";
//数据持久化,刷新页面数据不丢
import { PersistGate } from "redux-persist/integration/react";
//store 存储及数据持久化
import { store, persistor } from "./store/index";
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root"));
root.render(
<React.StrictMode>
{/* 全局提供核心 store */}
<Provider store={store}>
{/* 提供持久化入口 */}
<PersistGate loading={null} persistor={persistor}>
<App></App>
</PersistGate>
</Provider>
</React.StrictMode>
);
Store 核心文件代码配置如下:
import { configureStore, combineReducers } from "@reduxjs/toolkit";
import personReducer from "./reducers/personReducer";
import { persistStore, persistReducer } from "redux-persist";
// import storage from 'redux-persist/lib/storage'; // 使用local storage来持久化存储
import storageSession from "redux-persist/lib/storage/session"; // 使用session storage 临时会话模式
// 定义root reducer
const rootReducer = {
person: personReducer,
};
// 配置持久化选项,localStorage模式
const persistConfig = {
key: "root",
// storage:storage,//local storage 存储模式
storage: storageSession, //session storage 会话模式存储模式存储
};
//让所有的reducer,持久化
const persistedReducer = persistReducer(
persistConfig,
combineReducers({ person: personReducer })
);
export const store = configureStore({
reducer: persistedReducer,
middleware: (getDefaultMiddleware) =>
getDefaultMiddleware({
serializableCheck: false,
}),
});
//导出持久化配置
export const persistor = persistStore(store);
store 目录下 reducer 目录下personReducer.js配置如下:
import { createSlice } from "@reduxjs/toolkit";
const personSlice = createSlice({
name: "person",
initialState: {
personList: [],
},
reducers: {
addPerson: (state, action) => {
state.personList = [action.payload, ...state.personList];
},
},
});
//分别导出所有的工作
export const { addPerson } = personSlice.actions;
//默认导出reducer动作
export default personSlice.reducer;
####### Person.js 页面组件代码如下:
import { useRef, useState } from "react";
import { useSelector, useDispatch } from "react-redux";
import { nanoid } from "nanoid";
import { addPerson } from "../../store/reducers/personReducer";
export default function Person() {
//通过ref 方式获取用户名称
const userNameRef = useRef();
//通过受控组件模式获取年龄
const [age, setAge] = useState(0);
//通过useSelect获取state
const personList = useSelector((state) => state.person.personList);
//通过调用useDispatch 分发action
const dispatch = useDispatch();
//添加用户
function addUser() {
const obj = { userName: userNameRef.current.value, age: age, id: nanoid() };
//分派,分发
dispatch(addPerson(obj));
}
//通过受控组件的模式获取年龄的值
function getAgeValue(e) {
setAge(e.target.value);
}
return (
<div>
<div>
<label htmlFor="userName">用户名:</label>
<input type="text" id="userName" name="userName" ref={userNameRef} />
</div>
<div>
<label htmlFor="age">年龄:</label>
<input type="text" id="age" name="age" onChange={getAgeValue} />
</div>
<div>
<button onClick={addUser}>添加用户</button>
<button>异步获取用户信息</button>
</div>
<hr />
<div>用户信息显示:</div>
<ul>
{personList.map((item) => {
return (
<li key={item.id}>
{item.userName}-{item.age}-{item.id}
</li>
);
})}
</ul>
</div>
);
}
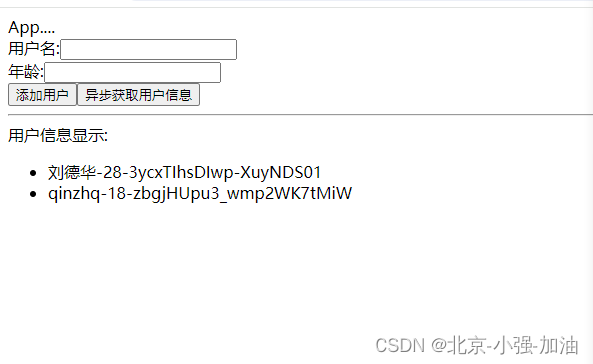
页面效果如下: