原创 风度玉门 拍码场
前言
Apache Dubbo 是一款高性能的 Java RPC 框架,主要用于构建分布式服务。Dubbo 的架构设计包括多个层次,其中传输层和交换层是非常重要的两个组成部分。
其中传输层(Transport)只负责对二进制数据的收发,交换层(Exchange)负责对Dubbo协议的编解码,然后调用Transport层的接口收发数据,其大致流程如下所示:

在介绍Dubbo的Channel和ChannelHandler之前,我们先看一下Netty的框架设计。
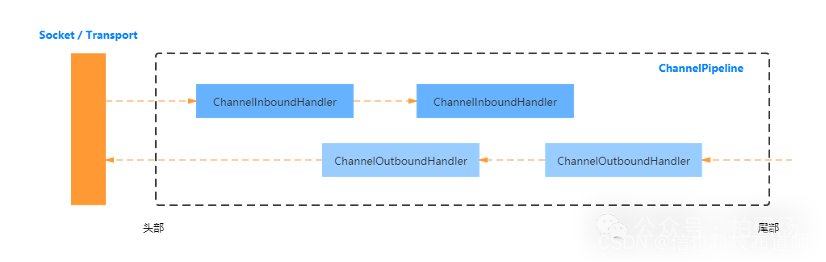
Netty中的Channel是对网络Socket的封装,通过Channel可以和网络对端进行数据的收发。在数据收发的过程中,会经过入站和出站的ChannelHandler处理。通常来说在连接建立/数据发送/数据接收等阶段,在ChannelHandler会产生对应的事件回调。这样ChannelHandler可以根据事件的类型,执行具体的处理逻辑。
Dubbo的网络层也是参考了Netty的设计,重新定义了Channel和ChannelHandler,下面我们依次看一下其类之间的关系及骨架代码实现。
1. Channel

在 Dubbo 中,最终的 Channel 由底层的通信框架实现。常见的 Channel 实现包括 NettyChannel、MinaChannel 等,它们分别基于 Netty 和 Apache MINA 框架来实现底层的网络传输。从继承关系可以看出,Channel 继承了Endpoint接口,Endpoint 是对一个网络节点的抽象,有着数据收发,获取Dubbo的URL的能力。而Channel在Endpoint的基础上,又增加了属性存取的方法。
public interface Endpoint {
/** * get url. */ URL getUrl();
/** * get channel handler. */ ChannelHandler getChannelHandler();
/** * get local address. */ InetSocketAddress getLocalAddress();
/** * send message. */ void send(Object message) throws RemotingException;
/** * send message. * @param sent 是否已发送完成 */ void send(Object message, boolean sent) throws RemotingException;
/** * close the channel. */ void close();
/** * Graceful close the channel. */ void close(int timeout);
/** * is closed. */ boolean isClosed();
}
public interface Channel extends Endpoint {
/** * get remote address. */ InetSocketAddress getRemoteAddress();
/** * is connected. */ boolean isConnected();
/** * has attribute. */ boolean hasAttribute(String key);
/** * get attribute. */ Object getAttribute(String key);
/** * set attribute. */ void setAttribute(String key, Object value);
/** * remove attribute. */ void removeAttribute(String key);
}
对于AbstractChannel,其实现了Channel接口之外,又继承了AbstractPeer,AbstractChannel类本身并没有逻辑性的代码。下面我们看下AbstractPeer的实现:
private final ChannelHandler handler;private volatile URL url;private volatile boolean closed;
public AbstractPeer(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) { if (url == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null"); } if (handler == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("handler == null"); } this.url = url; this.handler = handler;}
AbstractPeer 封装了网络传输层的细节,提供了与远程节点的连接、关闭连接和数据传输等功能。是后面将要谈到的Server/Client的抽象父类,从上面的属性可以看出其有着ChannelHandler和URL。下面我们看下NettyChannel的实现:
private static final ConcurrentMap<org.jboss.netty.channel.Channel, NettyChannel> channelMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<org.jboss.netty.channel.Channel, NettyChannel>();private final org.jboss.netty.channel.Channel channel;private final Map<String, Object> attributes = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>();
private NettyChannel(org.jboss.netty.channel.Channel channel, URL url, ChannelHandler handler) { super(url, handler); if (channel == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("netty channel == null;"); } this.channel = channel;}
首先NettyChannel有个static的变量,里面保存着Netty的Channel到自身对象的映射Map,然后就是组合了Netty的Channel和当前Dubbo的Channel属性的attributes。也就是说,Dubbo的Channel通过组合通信框架(如Netty)的Channel,来实现自身通信的功能。
2. ChannelHandler
对于ChannelHandler,从名字上就可以看出,是对Channel上产生的一系列事件,所产生的事件回调触发。这个我们可以类比Netty的ChannelHandler,下面看下Dubbo的ChannelHandler定义:
public interface ChannelHandler {
/** * on channel connected. */ void connected(Channel channel) throws RemotingException;
/** * on channel disconnected. */ void disconnected(Channel channel) throws RemotingException;
/** * on message sent. */ void sent(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException;
/** * on message received. */ void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException;
/** * on exception caught. */ void caught(Channel channel, Throwable exception) throws RemotingException;
}
从接口声明可以看出,当有连接建立或断开,数据接收或发送等网络事件触发时,会回调ChannelHandler的对应的方法,让调用方执行相应的业务逻辑。
对于ChannelHandler而言下面主要分2个方面讲述:基于ChannelHandler所形成的Server和Client 和 ChannelHandler触发的执行模式。
2.1 Server和Client

从上图可以看出,AbstractPeer具有Endpoint(网络节点)和ChannelHandler(网络事件回调)的能力。在AbstractPeer的基础上,AbstractEndpoint又增加了编码器和重置超时时间的能力。其核心代码如下所示:
private Codec codec;private int timeout;private int connectTimeout;
public AbstractEndpoint(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) { super(url, handler); this.codec = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Codec.class).getExtension(url.getParameter(Constants.CODEC_KEY, "telnet")); this.timeout = url.getPositiveIntParameter(Constants.TIMEOUT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT); this.connectTimeout = url.getPositiveIntParameter(Constants.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_KEY, timeout);}
对于Server端,我们看下AbstractServer所实现的一个接口Server。
public interface Server extends Endpoint, Resetable {
/** * is bound. */ boolean isBound();
/** * get channels. */ Collection<Channel> getChannels();
/** * get channel. */ Channel getChannel(InetSocketAddress remoteAddress);
}
除了网络节点和网络事件处理的能力之外,在Server接口上又增加了,获取连接到服务端的所有Channel,和根据IP获取对应的Channel等。对于Server这条线,我们下面看下AbstractServer的实现:
ExecutorService executor;private InetSocketAddress localAddress;private InetSocketAddress bindAddress;// 最大连接数private int accepts;private int idleTimeout = 600; //600 seconds
public AbstractServer(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) throws RemotingException { super(url, handler); localAddress = getUrl().toInetSocketAddress();
String bindIp = getUrl().getParameter(Constants.BIND_IP_KEY, getUrl().getHost()); int bindPort = getUrl().getParameter(Constants.BIND_PORT_KEY, getUrl().getPort()); if (url.getParameter(Constants.ANYHOST_KEY, false) || NetUtils.isInvalidLocalHost(bindIp)) { bindIp = NetUtils.ANYHOST; } bindAddress = new InetSocketAddress(bindIp, bindPort); this.accepts = url.getParameter(Constants.ACCEPTS_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_ACCEPTS); this.idleTimeout = url.getParameter(Constants.IDLE_TIMEOUT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_IDLE_TIMEOUT); try { // 开启服务, 监听端口 doOpen(); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Start " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " bind " + getBindAddress() + ", export " + getLocalAddress()); } } catch (Throwable t) { throw new RemotingException(url.toInetSocketAddress(), null, "Failed to bind " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " on " + getLocalAddress() + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t); } //fixme replace this with better method DataStore dataStore = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(DataStore.class).getDefaultExtension(); executor = (ExecutorService) dataStore.get(Constants.EXECUTOR_SERVICE_COMPONENT_KEY, Integer.toString(url.getPort()));}
从AbstractServer的核心代码可以看出,抽象类提供了创建的模板方法,其中包含了回调子类的doOpen(),去完成一个真正的端口监听。从属性上看,上面有服务端限制连接的最大数accepts和绑定的IP等信息。再往下走,就到了具体的实现类了。我们看一下Netty4的实现(dubbo 2.6.0):
private Map<String, Channel> channels; // <ip:port, channel>private ServerBootstrap bootstrap;private io.netty.channel.Channel channel;private EventLoopGroup bossGroup;private EventLoopGroup workerGroup;
public NettyServer(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) throws RemotingException { // 对ChannelHandler做包装,形成异步化 super(url, ChannelHandlers.wrap(handler, ExecutorUtil.setThreadName(url, SERVER_THREAD_POOL_NAME)));}
@Overrideprotected void doOpen() throws Throwable { NettyHelper.setNettyLoggerFactory();
bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1, new DefaultThreadFactory("NettyServerBoss", true)); workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(getUrl().getPositiveParameter(Constants.IO_THREADS_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_IO_THREADS), new DefaultThreadFactory("NettyServerWorker", true));
final NettyServerHandler nettyServerHandler = new NettyServerHandler(getUrl(), this); channels = nettyServerHandler.getChannels();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, Boolean.TRUE) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, Boolean.TRUE) .childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception { NettyCodecAdapter adapter = new NettyCodecAdapter(getCodec(), getUrl(), NettyServer.this); ch.pipeline()//.addLast("logging",new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))//for debug // 设置编解码 .addLast("decoder", adapter.getDecoder()) .addLast("encoder", adapter.getEncoder()) // 设置处理请求响应的Handler .addLast("handler", nettyServerHandler); } }); // 绑定IP ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.bind(getBindAddress()); channelFuture.syncUninterruptibly(); channel = channelFuture.channel();}
从上面Netty4的实现可以看出,在构造器中,直接调用了AbstractServer的构造器。不过对ChannelHandler做了包装处理,形成了异步处理的效果。然后AbstractServer会调用子类的doOpen()方法,进入具体的IP绑定和服务启动。这里对于Netty4本身的一些API就不做过多的解释了,这里我们来看下在pipeline中设置的编解码及处理请求响应的Handler。
对于编解码的Handler,这里面使用了NettyCodecAdapter去封装了编码和解码器,这两个编解码器分别是作为内部类实现的,这里我们先看下NettyCodecAdapter的核心属性:
private final ChannelHandler encoder = new InternalEncoder();private final ChannelHandler decoder = new InternalDecoder();private final Codec2 codec;private final URL url;private final com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.ChannelHandler handler;
public NettyCodecAdapter(Codec2 codec, URL url, com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.ChannelHandler handler) { this.codec = codec; this.url = url; this.handler = handler;}
可以看出,除了编码和解码器,还有具体的编解码实现Codec2,这里面通常是DubboCodec。其他的属性都是辅助编码实现的,下面我们分别看下InternalEncode和InternalDecode的实现
private class InternalEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder { @Override protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception { com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.buffer.ChannelBuffer buffer = new NettyBackedChannelBuffer(out); Channel ch = ctx.channel(); NettyChannel channel = NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(ch, url, handler); try { codec.encode(channel, buffer, msg); } finally { NettyChannel.removeChannelIfDisconnected(ch); } }}
编码器还是相对比较简单的,对于Netty4的实现,直接继承了MessageToByteEncoder。在重写encode的方法里,直接使用了Codec2(通常为DubboCodec,新版本使用的DubboCountCodec也是对DubboCodec的简单封装)的编码。对于InternalDecoder而言,实现如下:
private class InternalDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder { @Override protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf input, List<Object> out) throws Exception { ChannelBuffer message = new NettyBackedChannelBuffer(input); NettyChannel channel = NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(ctx.channel(), url, handler); Object msg; int saveReaderIndex;
try { // decode object. do { saveReaderIndex = message.readerIndex(); try { msg = codec.decode(channel, message); } catch (IOException e) { throw e; } if (msg == Codec2.DecodeResult.NEED_MORE_INPUT) { message.readerIndex(saveReaderIndex); break; } else { //is it possible to go here ? if (saveReaderIndex == message.readerIndex()) { throw new IOException("Decode without read data."); } if (msg != null) { out.add(msg); } } } while (message.readable()); } finally { NettyChannel.removeChannelIfDisconnected(ctx.channel()); } }}
可以看出,当解码时如果此时接收到的字节数不完整,此时会解码器会返回 NEED_MORE_INPUT,此时会继续接受数据,直到接收到完整的报文,最终完成解码过程。
2.2 ChannelHandler
ChannelHandler可以立即为在消息收发之后的一个回调事件。在通讯框架层(如Netty),ChannelHandler主要可以分为2类:编解码器和业务处理器。对于Dubbo而言,ChannelHandler指的就是业务处理器。而对于编解码器,前面已经说过了,这里不再赘述。
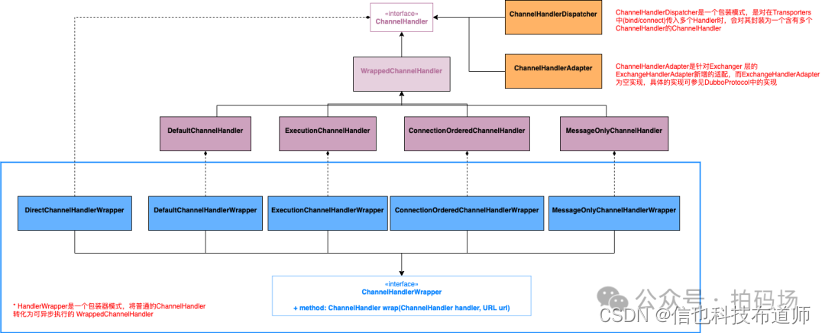
下面我们解析一下ChannelHandler的类图结构,上面的结构是ChannelHandler执行模式的类图。也就是说,它支持了ChannelHandler里面的方法,不同的异步执行模式。
首先对于ChannelHandler有个WrappedChannelHandler实现,里面的逻辑就是直接调用原ChannelHandler的对应connected、sent等方法。对于异步执行,Dubbo又分离出了4个类型出来:Default(所有方法异步)、Execution(除了sent方法是同步,其他的都是异步)、ConnectionOrdered(connect和disconnect使用单线程的线程池,received和caught都是异步,sent同步)、MessageOnly(只有received是异步,其余都是同步)。WrapperChannelHandler使用了装饰模式,将原先同步执行的ChannelHandler,装饰成了不同异步模式执行的ChannelHandler。
而对于下面蓝色的框里面的类,看起来和上面紫色的类名非常类似。这里面主要是方便 Dubbo SPI 的调用,其代码中也没有具体的业务逻辑,只是直接new了对应的紫色类的对象,最终通过ChannelHandlers工具类,暴露了转异步的能力。最终的结果就是在原先的ChannelHandler套了一层。
除此之外,右上方还有2个橙色的类实现。其中ChannelHandlerDispatcher 就是一个批量操作,当传入多个ChannelHandler时,循环调用Handler数组中的对应方法。ChannelHandlerAdapter则是给Exchange层的ExchangeHandlerAdapter新增的适配,但其实现也为空,最终的使用方是 DubboProtocol的requestHander 内部属性实现。
3. Exchange层
Exchange层是对Transport层的封装,让传输的二进制数据转换为Dubbo可以识别的Request / Response,这个我们从开篇的交互示意图就可以看出来。下面我们看下Exchange的类结构。

Exchange层的每个组件,都对应这Transport层的组件,分别为 Handler、Channel、Server、Client。我们首先看下ExchangeHandler,其继承了TelnetHandler和ChannelHandler,新增了reply方法如下所示:
3.1 ExchangeHandler
public interface ExchangeHandler extends ChannelHandler, TelnetHandler { /** * reply. */ Object reply(ExchangeChannel channel, Object request) throws RemotingException;}
其子类有个抽象的 ExchangeHandlerAdapter,这个Adapter中的 reply方法是个空实现,最终在DubboProtocol中实现了reply方法,实现Dubbo协议相关的相应方法,这个方法是在Server端接收到消息后(received方法中)调用的,对于DubboProtocol的代码这里不详细展开。
最后我们看到了HeaderExchangeHandler,它并不是继承了ExchangeHandler,而是以组合的方式获取DubboProtocol中的实现。但是其继承了ChannelHandler接口,这主要是为了封装上层的ChannelHandler给底层的通讯框架使用(如Netty)。下面罗列了HeaderExchangeHandler的主要代码:
private final ExchangeHandler handler;
public HeaderExchangeHandler(ExchangeHandler handler) { if (handler == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("handler == null"); } this.handler = handler;}
Response handleRequest(ExchangeChannel channel, Request req) throws RemotingException { Response res = new Response(req.getId(), req.getVersion()); if (req.isHeartbeat()) { res.setHeartbeat(true); return res; }
if (req.isBroken()) { Object data = req.getData();
String msg; if (data == null) { msg = null; } else if (data instanceof Throwable) { msg = StringUtils.toString((Throwable) data); } else { msg = data.toString(); } res.setErrorMessage("Fail to decode request due to: " + msg); res.setStatus(Response.BAD_REQUEST);
return res; }
// find handler by message class. Object msg = req.getData(); if (handler == null) {// no handler. res.setStatus(Response.SERVICE_NOT_FOUND); res.setErrorMessage("InvokeHandler not found, Unsupported protocol object: " + msg); } else { try { // handle data. Object result = handler.reply(channel, msg); res.setStatus(Response.OK); res.setResult(result); } catch (Throwable e) { res.setStatus(Response.SERVICE_ERROR); res.setErrorMessage(StringUtils.toString(e)); } } return res;}
可以看出 handleRequest()方法中拿到了ExchangeCodec解码出来的请求对象 Request,然后封装响应报文,最终会调用DubboProtocol中的reply() 方法获取到服务端的invoker 桩对象,然后执行对应的业务逻辑,拿到结果result 后,封装返回Response。
对于HeaderExchangeHandler作为Transport层的入参,最终注入到 Transport层的Handler的实现如下:
public class HeaderExchanger implements Exchanger { public static final String NAME = "header";
@Override public ExchangeClient connect(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException { return new HeaderExchangeClient(Transporters.connect(url, new HeaderExchangeHandler(handler))); }
@Override public ExchangeServer bind(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException { return new HeaderExchangeServer(Transporters.bind(url, new HeaderExchangeHandler(handler))); }
}
3.2 ExchangeChannel
下面我们看一下ExchangeChannel,从类图上可以看出,它继承了Channel接口。然后新增了和Dubbo协议相关的方法。如下方的request(Object request) 中的request对象就是业务层的请求,在HeaderExchangeChannel中封装成了Dubbo协议的Request对象。它的返回值是ResponseFuture,这是通过Future模式,让RPC请求同步转异步,对于ResponseFuture这里不展开阐述。
public interface ExchangeChannel extends Channel {
/** * send request. * * @param request * @return * @throws RemotingException */ ResponseFuture request(Object request) throws RemotingException;
/** * send request. * * @param request * @param timeout * @return * @throws RemotingException */ ResponseFuture request(Object request, int timeout) throws RemotingException;
/** * get message handler. * * @return message handler */ ExchangeHandler getExchangeHandler();
/** * graceful close. * * @param timeout */ @Override void close(int timeout);
}
对于HeaderExchangeChannel的实现,还是相对比较简单的,这里我们简单的看下它的sent方法,也就是直接对业务的请求message,封装成了Dubbo协议的Request对象:
@Overridepublic void send(Object message, boolean sent) throws RemotingException { if (closed) { throw new RemotingException(this.getLocalAddress(), null, "Failed to send message " + message + ", cause: The channel " + this + " is closed!"); } if (message instanceof Request || message instanceof Response || message instanceof String) { channel.send(message, sent); } else { Request request = new Request(); request.setVersion("2.0.0"); request.setTwoWay(false); request.setData(message); channel.send(request, sent); }}
3.3 ExchangeClient
对于ExchangeClient而言,其中没有定义接口方法,仅仅是继承了Client和ExchangeChannel。也可以简单的理解为拥有了消息的发送能力即可。下面我们看下HeaderExchangeClient的主要实现,构造器中的Client是Transport层的Client(如NettyClient)。其含有2个属性,Transport层的Client和ExchangeChannel。我们知道HeaderExchangeChannel是用来收发Dubbo的Request/Response的,因此这里的主要属性是基于NettyClient构造的ExchangeChannel。
public class HeaderExchangeClient implements ExchangeClient {
private final Client client; private final ExchangeChannel channel;
public HeaderExchangeClient(Client client) { if (client == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("client == null"); } this.client = client; this.channel = new HeaderExchangeChannel(client); }}
3.4 ExchangeServer
ExchangeServer接口仅仅继承了Server接口,并新增了对Exchange层的ExchangeChannel的管理,仅此而已。
public interface ExchangeServer extends Server {
/** * get channels. * * @return channels */ Collection<ExchangeChannel> getExchangeChannels();
/** * get channel. * * @param remoteAddress * @return channel */ ExchangeChannel getExchangeChannel(InetSocketAddress remoteAddress);
}
下面我们看下HeaderExchangeServer的简单实现,我们可以看到在构造的时候,会启动一个心跳的任务去检测客户端的连接是否正常。
public class HeaderExchangeServer implements ExchangeServer {
private final ScheduledExecutorService scheduled = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1, new NamedThreadFactory("dubbo-remoting-server-heartbeat", true)); // 心跳定时器 private ScheduledFuture<?> heatbeatTimer; // 心跳超时,毫秒。缺省0,不会执行心跳。 private int heartbeat; private int heartbeatTimeout; private final Server server; private volatile boolean closed = false;
public HeaderExchangeServer(Server server) { if (server == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("server == null"); } this.server = server; this.heartbeat = server.getUrl().getIntParameter(Constants.HEARTBEAT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_HEARTBEAT); this.heartbeatTimeout = server.getUrl().getIntParameter(Constants.HEARTBEAT_TIMEOUT_KEY, heartbeat * 3); if (heartbeatTimeout < heartbeat * 2) { throw new IllegalStateException("heartbeatTimeout < heartbeatInterval * 2"); } startHeatbeatTimer(); }}
4. 总结
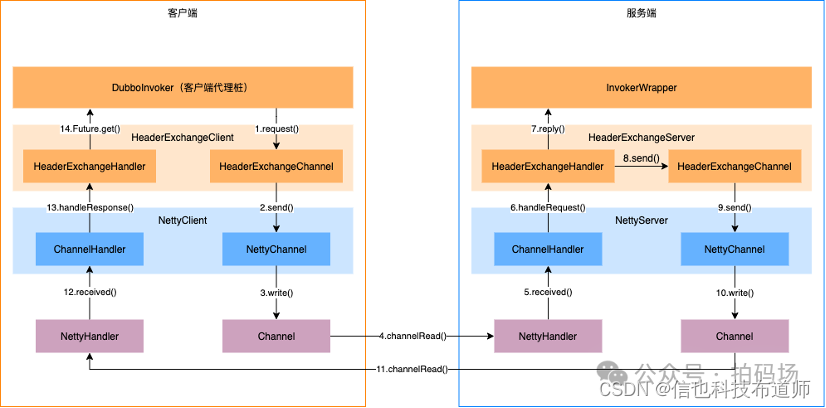
从图上我们可以看出,一共分为4层。最下面一层是通信框架层,也就是直接和Netty组件交互的一层。其中Channel 指的是 Netty 框架的Channel,也就是直接发送数据的通道。另外,NettyHandler 是继承Netty框架的Handler组件,而NettyHandler 本身又组合了上层的Handler,最终完成对底层网络事件的上层业务逻辑处理。其类的组合形式见如下示意图:

最下面的一层是Transport层,这一层的NettyServer 和 NettyClient(Dubbo的NettyChannel的子类) 接口都是Dubbo自定义的。对于Channel而言,是组合了底层Netty框架的Channel,并在此基础上增加了attributes 的属性。对于ChannelHandler 最终的实现由 NettyClient / NettyServer 承载,而最终NettyClient / NettyServer 又会作为ChannelHandler的形式,作为客户端 / 服务端启动的入参,传入底层的Netty框架层,就如上图所示的那样。除此之外,这一层还有对于ChannelHandler的异步处理的封装层,也就是ChannelHandlerWrapper。
再往上的一层是Exchange层,这一层可以认为就是应用层了。其中收发的数据都是Dubbo协议对应的 Request / Response对象,并且对于发送的请求有异步转同步的处理等等。最上层是Protocol层,这一层主要是实现了ExchangeHandler的reply() 方法,通常用来实现,当Server端接收到了客户端的请求后,用来返回响应报文的(Response)。
对于HeaderExchangeChannel,组合了下层的 NettyChannel,并对上层发过来的 Object message 原始对象做了Dubbo的Request对象封装,也就是Dubbo请求协议的封装。然后再发送出去。由此看来对于 Channel 的封装,相对于ChannelHandler的封装嵌套是反着的,如下所示:

5. 作者介绍
风度玉门,现任后端研发资深专家