一,播放器框架

二 常用音视频术语
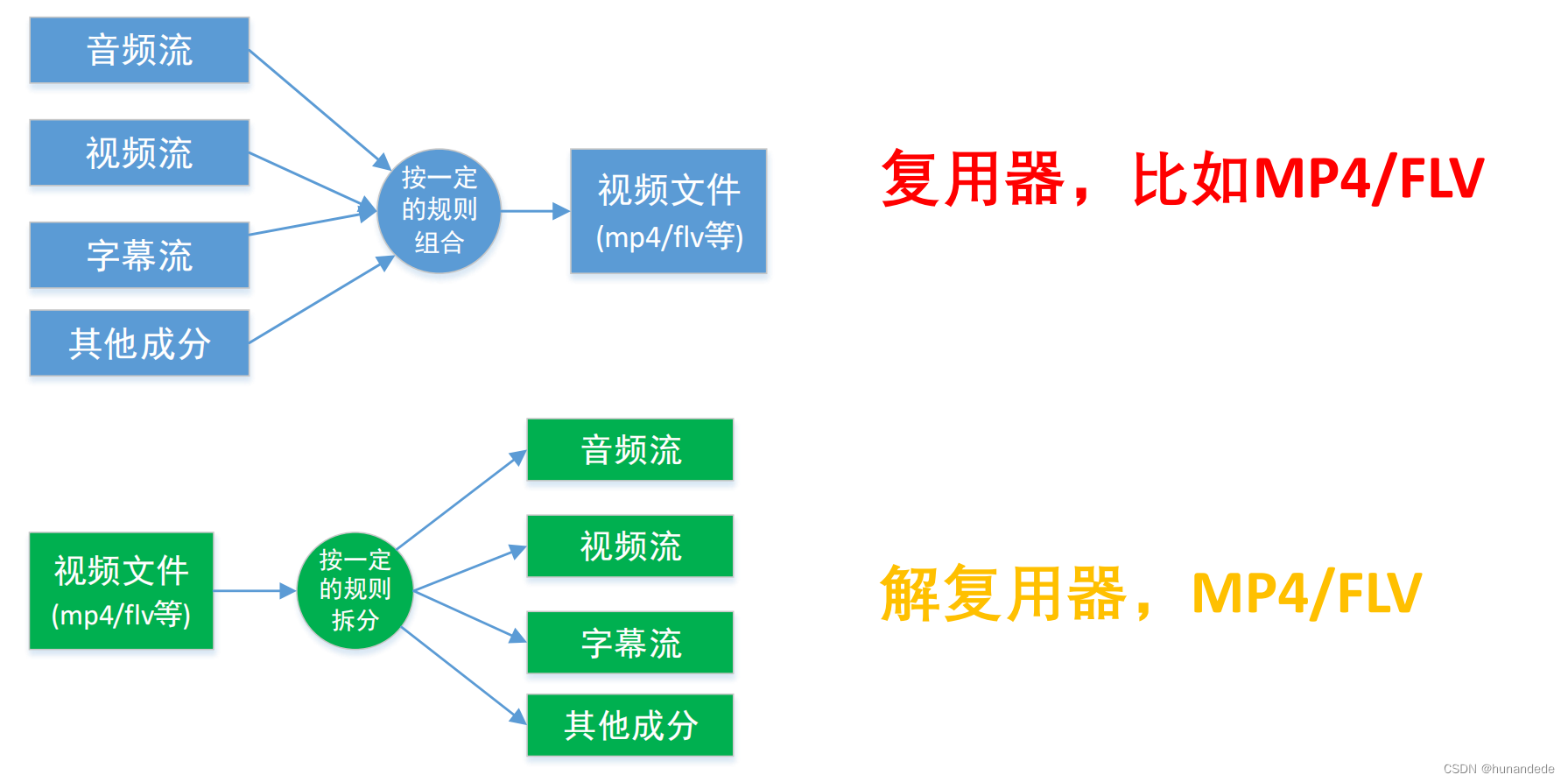
三 常用概念-复用器
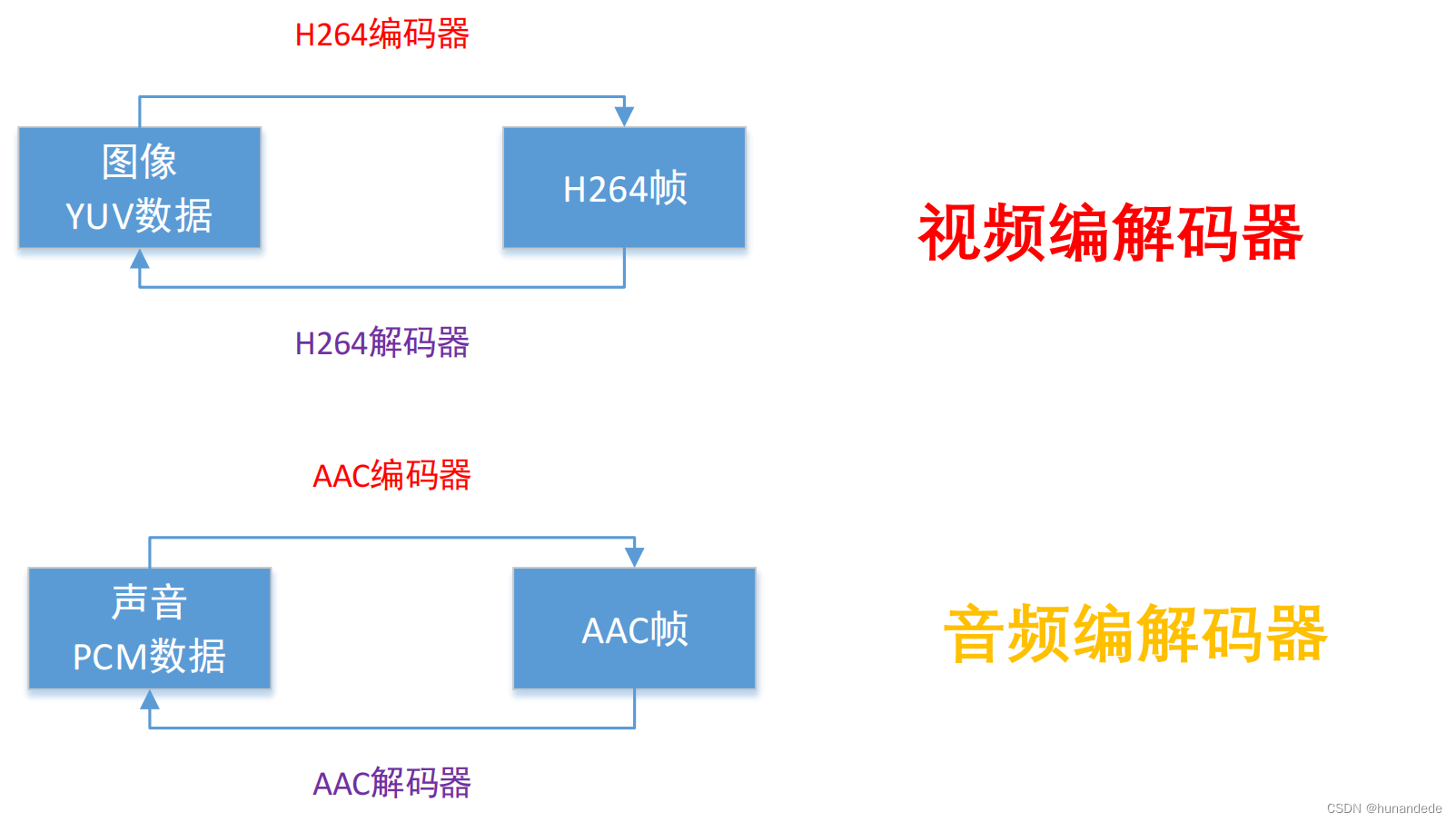
四 常用概念-编解码器
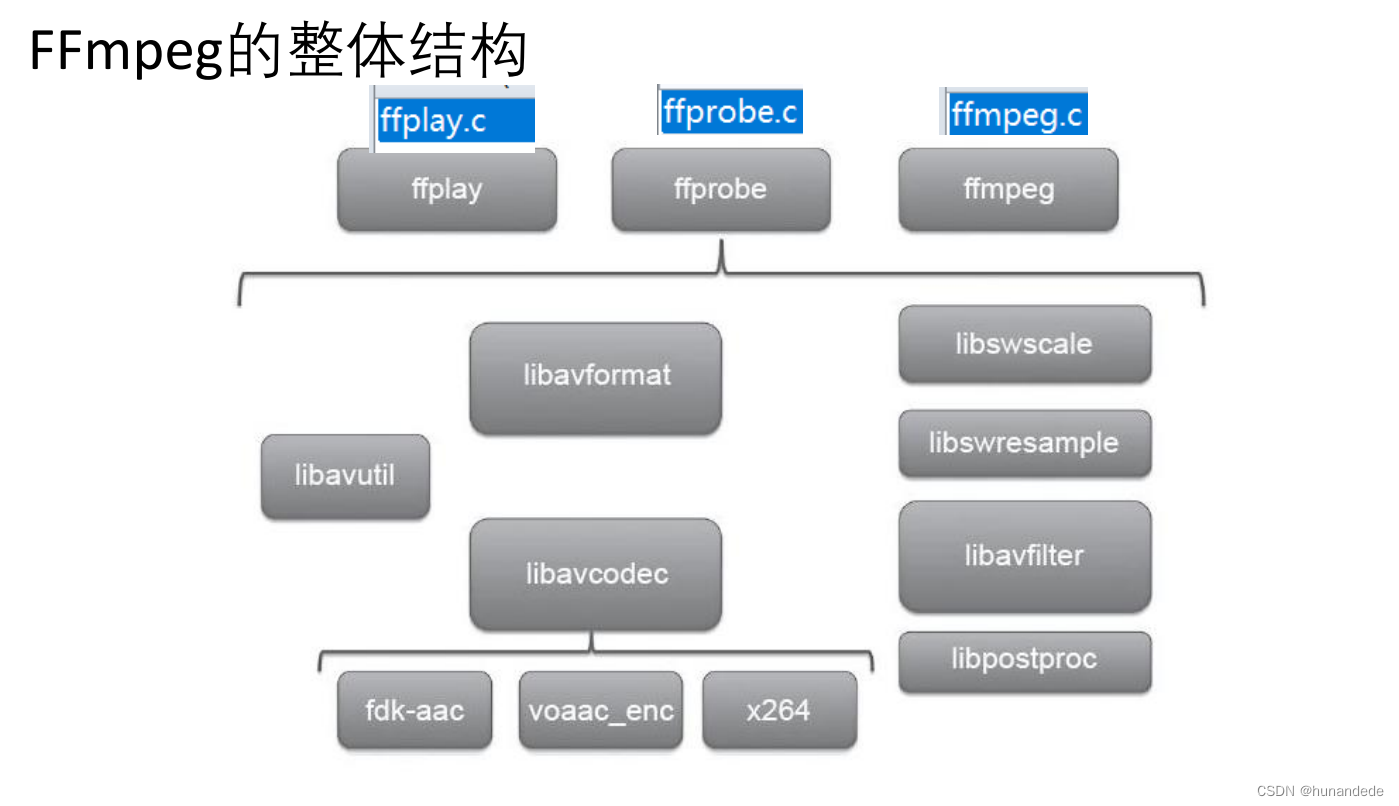
五 FFmpeg库简介
六 FFmpeg函数简介
◼ av_register_all():注册所有组件,4.0已经弃用
◼ avdevice_register_all()对设备进行注册,比如V4L2等。
#include <libavdevice/avdevice.h>
/**
* Initialize libavdevice and register all the input and output devices.
*/
void avdevice_register_all(void);◼ avformat_network_init();初始化网络库以及网络加密协议相关 的库(比如openssl)
#include <libavformat/avformat.h>
int avformat_network_init(void);七 FFmpeg函数简介-封装格式相关
◼ avformat_alloc_context();负责申请一个AVFormatContext 结构的内存,并进行简单初始化
#include <libavformat/avformat.h>
/**
* Allocate an AVFormatContext.
* avformat_free_context() can be used to free the context and everything
* allocated by the framework within it.
*/
AVFormatContext *avformat_alloc_context(void);
## AVFormatContext:它是FFMPEG解封装(flv,mp4,rmvb,avi)功能的结构体,
其中比较重要的几个如下解释:
typedef struct AVFormatContext {
const AVClass *av_class; // 一个类,用于保存指向父对象的链接,用于日志记录
struct AVInputFormat *iformat; // 用于指定输入文件的格式以及文件读取的操作函数
struct AVOutputFormat *oformat; // 用于指定输出文件的格式以及文件写入的操作函数
void *priv_data; // 指向 AVFormatContext(容器上下文)的私有数据
AVIOContext *pb; // 用于读取和写入媒体数据的 I/O 上下文
int nb_streams; // 流的数量,包括音频、视频、字幕等
AVStream **streams; // 指向 AVStream 结构体的指针,用于存储所有流的信息
char *filename; // 用于存储文件名的字符串
int64_t start_time, duration;// 媒体文件的起始时间戳和持续时间
int64_t bit_rate; // 比特率,以 bit/s 计算
uint8_t *buffer; // 用于暂存数据的缓冲区
int buffer_size; // 缓冲区的大小
} AVFormatContext;
AVFormatContext 结构体的各个成员变量的作用详见以下介绍。
成员变量介绍
AVClass *av_class: 一个类,用于保存指向父对象的链接,用于日志记录;
AVClass是FFmpeg中libavutil库中的一个结构体,用于在FFmpeg中实现类及其对象的日志和调试功能。AVClass提供了一种标准的方式来管理类及其对象,在不同的库和插件之间提供了统一的日志记录和调试接口。
AVInputFormat *iformat:用于指定输入文件的格式以及文件读取的操作函数;
AVOutputFormat *oformat: 用于指定输出文件的格式以及文件写入的操作函数;
void *priv_data: 指向 AVFormatContext(容器上下文)的私有数据;
priv_data成员可以用于存储和传递特定协议下使用的私有数据,常见的使用场景是实现自定义输入或输出协议。
AVIOContext *pb:用于读取和写入媒体数据的 I/O 上下文;
AVIOContext 是libavformat库中一个表示访问媒体文件的I/O环境的结构体。它封装了对媒体文件的读取和写入操作,提供了和具体I/O操作系统相关的操作的抽象接口,实现了独立于实际操作系统的媒体文件访问接口。
int nb_streams: 流的数量,包括音频、视频、字幕等;
AVStream **streams:指向 AVStream 结构体的指针,用于存储所有流的信息;
AVStream是FFmpeg中libavformat库中的一个数据结构,用于表示媒体文件中的一个音频或视频流。在FFmpeg中,一个媒体文件通常包含多个音视频流,每个流对应着媒体文件中的一个轨道。AVStream通过存储音视频流的各种属性信息,方便解码和编码,对于多媒体处理和视频编辑有着至关重要的作用。
AVStream包含了一个媒体流的所有基本信息,如类型、编解码器、时间戳、时长、帧率、码率等等。常用的成员变量有:
char *filename: 用于存储文件名的字符串;
int64_t start_time: 媒体文件的起始时间戳;
int64_t duration: 媒体文件的持续时间;
int64_t bit_rate: 比特率,以 bit/s 计算;
uint8_t *buffer: 用于暂存数据的缓冲区;
int buffer_size: 缓冲区的大小。
◼ avformat_free_context();释放该结构里的所有东西以及该 结构本身
#include <libavformat/avformat.h>
/**
* Free an AVFormatContext and all its streams.
* @param s context to free
*/
void avformat_free_context(AVFormatContext *s);◼ avformat_close_input();关闭解复用器。关闭后就不再需要 使用avformat_free_context 进行释放。
/**
* Close an opened input AVFormatContext. Free it and all its contents
* and set *s to NULL.
*/
void avformat_close_input(AVFormatContext **s);◼ avformat_open_input();打开媒体文件并获取媒体文件信息的函数
* The input container format.
*
* Demuxing only, set by avformat_open_input().
*/
const struct AVInputFormat *iformat;
avformat_open_input() 函数是用于打开媒体文件并获取媒体文件信息的函数,该函数定义在libavformat/avformat.h中。
该函数的参数含义如下:
ps:AVFormatContext结构体的指针。该参数用于存储打开的媒体文件的信息。当该函数成功返回时,AVFormatContext结构体中将存储媒体文件的相关信息。
url:要打开的媒体文件的URL。可以是本地文件路径,也可以是HTTP URL或其他协议的URL。
fmt:AVInputFormat结构体的指针,用于指定媒体文件的格式。如果该参数为NULL,则根据文件扩展名自动选择输入格式。
options:AVDictionary结构体的指针,用于传递打开媒体文件时的选项。
/**
* Open an input stream and read the header. The codecs are not opened.
* The stream must be closed with avformat_close_input().
*
* @param ps Pointer to user-supplied AVFormatContext (allocated by
* avformat_alloc_context). May be a pointer to NULL, in
* which case an AVFormatContext is allocated by this
* function and written into ps.
* Note that a user-supplied AVFormatContext will be freed
* on failure.
* @param url URL of the stream to open.
* @param fmt If non-NULL, this parameter forces a specific input format.
* Otherwise the format is autodetected.
* @param options A dictionary filled with AVFormatContext and demuxer-private
* options.
* On return this parameter will be destroyed and replaced with
* a dict containing options that were not found. May be NULL.
*
* @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR on failure.
*
* @note If you want to use custom IO, preallocate the format context and set its pb field.
*/
int avformat_open_input(AVFormatContext **ps, const char *url,
const AVInputFormat *fmt, AVDictionary **options);◼avformat_find_stream_info():获取音视频文件信息
当我们使用avformat_open_input打开一个文件后,下来就应该将这个文件的每个音视频流获取出来,就是通过avformat_find_stream_info方法完成的,因此第一个参数要传递 avformatcontext,第二个参数已经不在使用,直接填写NULL,就好
avformat_find_stream_info()函数是用于获取媒体文件中每个音视频流的详细信息的函数,包括解码器类型、采样率、声道数、码率、关键帧等信息。该函数定义在libavformat/avformat.h中。
函数原型为:
int avformat_find_stream_info(AVFormatContext *fmt_ctx, AVDictionary **options);
该函数的参数含义如下:
fmt_ctx:AVFormatContext结构体指针,表示媒体文件的格式上下文,其中包含已经打开的媒体文件的信息和媒体文件中每个音视频流的信息。
options:AVDictionary结构体指针,用于传递选项。目前已经不使用,传NULL即可。
◼ av_read_frame(); 从文件中读取数据包,
int av_read_frame(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt);
参数说明:
AVFormatContext *s // 文件格式上下文,输入的AVFormatContext
AVPacket *pkt // 这个值不能传NULL,必须是一个空间,输出的AVPacket
// 返回值:return 0 is OK, <0 on error or end of file
ffmpeg中的av_read_frame()的作用是读取码流中的音频若干帧或者视频一帧。例如,解码视频的时候,每解码一个视频帧,需要先调用 av_read_frame()获得一帧视频的压缩数据,然后才能对该数据进行解码(例如H.264中一帧压缩数据通常对应一个NAL)。
对于视频的编解码来说,要对数据进行解码,那么首先要获取视频帧的压缩数据。 av_read_frame()的作用就是获取视频的数据。
注:av_read_frame()获取视频的一帧,不存在半帧说法。但可以获取音频的若干帧。
说明①:av_read_frame()函数是ffmpeg新型的用法,旧用法之所以被抛弃,就是因为以前获取的数据可能不是完整的,而av_read_frame()保证了视频数据一帧的完整性。
说明②:查看API的改变可以看到,从2012-03-20开始,Deprecate av_read_packet(), use
av_read_frame()
返回流的下一帧。
*此函数返回存储在文件中的内容,但不验证解码器是否有有效帧。 它将把文件中存储的内容拆分为帧,并为每个调用返回一个帧。 它不会省略有效帧之间的无效数据,以便给解码器最大可能的解码信息。
如果pkt->buf为NULL,那么直到下一个av_read_frame()或直到avformat_close_input(),包都是有效的。
否则数据包将无限期有效。在这两种情况下,当不再需要包时,必须使用av_free_packet释放包。 对于视频,数据包只包含一帧。
对于音频,如果每个帧具有已知的固定大小(例如PCM或ADPCM数据),则它包含整数帧数。
如果音频帧有一个可变的大小(例如MPEG音频),那么它包含一帧。
在AVStream中,pkt->pts、pkt->dts和pkt->持续时间总是被设置为恰当的值。
time_base单元(猜测格式是否不能提供它们)。
如果视频格式为B-frames,pkt->pts可以是AV_NOPTS_VALUE,所以如果不解压缩有效负载,最好依赖pkt->dts。
/**
* 返回流的下一帧。
* 此函数返回文件中存储的内容,不进行验证
* 什么是解码器的有效帧。它会分裂什么是
* 将文件存储为帧并为每次调用返回一个。它不会
* 省略有效帧之间的无效数据,以便给解码器最大
* 可用于解码的信息。
*
* 如果 pkt->buf 为 NULL,则数据包在下一次之前有效
* av_read_frame() 或直到 avformat_close_input()。否则包
* 无限期有效。在这两种情况下,必须使用以下命令释放数据包
* av_free_packet 不再需要时。对于视频,数据包包含
*正好一帧。对于音频,它包含整数个帧,如果每个
* 帧具有已知的固定大小(例如 PCM 或 ADPCM 数据)。如果音频帧
* 具有可变大小(例如 MPEG 音频),则它包含一帧。
*
* pkt->pts、pkt->dts 和 pkt->duration 始终设置为正确
* AVStream.time_base 单位中的值(如果格式不能,则猜测
* 提供它们)。 pkt->pts 可以是 AV_NOPTS_VALUE 如果视频格式
* 有 B 帧,所以如果你没有,最好依靠 pkt->dts
* 解压有效载荷。
* @return 0 如果正常,< 0 错误或文件结束
*
* s:输入的AVFormatContext
* pkt:输出的AVPacket
*/
int av_read_frame(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt);
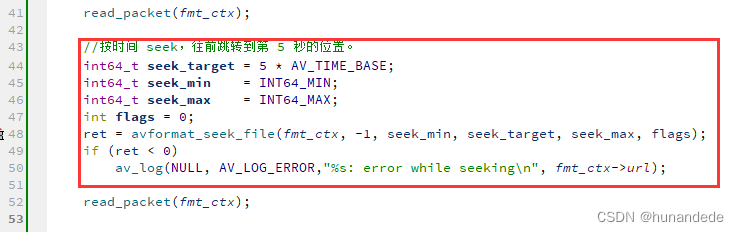
◼ avformat_seek_file(); 定位文件
在做音视频数据分析的时候,经常会遇到这样的需求,每隔5分钟抽取一帧数据进行分析。
在做播放器开发的时候,也会遇到这种情况,就是拖动进度条跳转到某个位置进行播放。
如果直接用 av_read_frame() 不断读数据,读到第 5 分钟的 AVPacket 才开始处理,其他读出来的 AVPacket 丢弃,这样做会带来非常大的磁盘IO。
其实上面两种场景,都可以用同一个函数解决,那就是 avformat_seek_file(),这个函数类似于 Linux 的 lseek() ,设置文件的读取位置。
只不过 avformat_seek_file() 是用于音视频文件的。
/**
* Seek to timestamp ts.
* Seeking will be done so that the point from which all active streams
* can be presented successfully will be closest to ts and within min/max_ts.
* Active streams are all streams that have AVStream.discard < AVDISCARD_ALL.
*
* If flags contain AVSEEK_FLAG_BYTE, then all timestamps are in bytes and
* are the file position (this may not be supported by all demuxers).
* If flags contain AVSEEK_FLAG_FRAME, then all timestamps are in frames
* in the stream with stream_index (this may not be supported by all demuxers).
* Otherwise all timestamps are in units of the stream selected by stream_index
* or if stream_index is -1, in AV_TIME_BASE units.
* If flags contain AVSEEK_FLAG_ANY, then non-keyframes are treated as
* keyframes (this may not be supported by all demuxers).
* If flags contain AVSEEK_FLAG_BACKWARD, it is ignored.
*
* @param s media file handle
* @param stream_index index of the stream which is used as time base reference
* @param min_ts smallest acceptable timestamp
* @param ts target timestamp
* @param max_ts largest acceptable timestamp
* @param flags flags
* @return >=0 on success, error code otherwise
*
* @note This is part of the new seek API which is still under construction.
*/
int avformat_seek_file(AVFormatContext *s, int stream_index, int64_t min_ts, int64_t ts, int64_t max_ts, int flags);参数解释如下:
1,AVFormatContext *s,已经打开的容器示例。
2,int stream_index,流索引,但是只有在 flags 包含 AVSEEK_FLAG_FRAME 的时候才是 设置某个流的读取位置。其他情况都只是把这个流的 time_base (时间基)作为参考。
3,int64_t min_ts,跳转到的最小的时间,但是这个变量不一定是时间单位,也有可能是字节单位,也可能是帧数单位(第几帧)。
4,int64_t ts,要跳转到的读取位置,单位同上。
5,int64_t max_ts,跳转到的最大的时间,单位同上,通常填 INT64_MAX 即可。
6,int flags,跳转的方式,有 4 个 flags,如下:
AVSEEK_FLAG_BYTE,按字节大小进行跳转。
AVSEEK_FLAG_FRAME,按帧数大小进行跳转。
AVSEEK_FLAG_ANY,可以跳转到非关键帧的读取位置,但是解码会出现马赛克。
AVSEEK_FLAG_BACKWARD,往 ts 的后面找关键帧,默认是往 ts 的前面找关键帧。
avformat_seek_file() 函数默认是把文件的读取位置,设置到离 ts 参数最近的关键帧的地方。
而且默认情况,是容器里面所有流的读取位置都会被设置,包括 音频流,视频流,字幕流。
只要流的 discard 属性小于 AVDISCARD_ALL 就会被设置。
AVStream.discard < AVDISCARD_ALL
min_ts 跟 max_ts 变量有一些设置的技巧。
如果是快进的时候,min_ts 可以设置得比 当前位置 大一点,例如加 2。 而 max_ts 可以填 INT64_MAX
min_ts = 当前位置 + 2
max_ts = INT64_MAX
+2 是为了防止某些情况,avformat_seek_file() 会把读取位置往后挪一点。
如果是后退的时候,min_ts 可以填 INT64_MIN,max_ts 可以设置得比 当前位置 小一点,例如减 2。
min_ts = INT64_MIN
max_ts = 当前位置 - 2
-2 是为了防止某些情况,avformat_seek_file() 会把读取位置往前挪一点。
当 flags 为 0 的时候,默认情况,是按时间来 seek 的,而时间基是根据 stream_index 来确定的。
如果 stream_index 为 -1 ,那 ts 的时间基就是 AV_TIME_BASE,
如果stream_index 不等于 -1 ,那 ts 的时间基就是 stream_index 对应的流的时间基。
这种情况,avformat_seek_file() 会导致容器里面所有流的读取位置都发生跳转,包括音频流,视频流,字幕流。
当 flags 包含 AVSEEK_FLAG_BYTE,ts 参数就是字节大小,代表 avformat_seek_file() 会把读取位置设置到第几个字节。用 av_read_frame() 读出来的 pkt 里面有一个字段 pos,代表当前读取的字节位置。可以用pkt->pos 辅助设置 ts 参数,
AVSEEK_FLAG_BYTE 是否是对所有流都生效,我后面测试一下再补充。
当 flags 包含 AVSEEK_FLAG_FRAME,ts 参数就是帧数大小,代表 avformat_seek_file() 会把读取位置设置到第几帧。这时候 stream_index 可以指定只设置某个流的读取位置,如果 stream_index 为 -1 ,代表设置所有的流。
当 flags 包含 AVSEEK_FLAG_ANY,那就代表 seek 可以跳转到非关键帧的位置,但是非关键帧解码会出现马赛克。如果不设置 AVSEEK_FLAG_ANY, 默认是跳转到离 ts 最近的关键帧的位置的。
当 flags 包含 AVSEEK_FLAG_BACKWARD,代表 avformat_seek_file() 在查找里 ts 最近的关键帧的时候,会往 ts 的后面找,默认是往 ts 的前面找关键帧。
提醒:AVSEEK_FLAG_BYTE ,AVSEEK_FLAG_FRAME,AVSEEK_FLAG_ANY 这 3 种方式,有些封装格式是不支持的。
下面通过一个例子来演示 avformat_seek_file() 函数的用法。
————————————————
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/u012117034/article/details/127760798
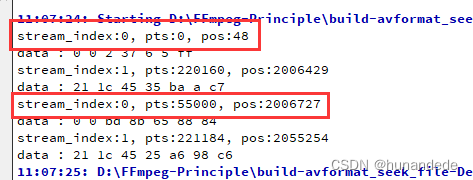
可以看到,跳转之后,后面 av_read_frame() 读取到的 AVPacket 的 pts 跟 pos 都有很大的偏移了。
avformat_seek_file() 函数介绍完毕。
扩展知识:avformat_seek_file() 对应的旧版函数是 av_seek_frame()
————————————————
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/u012117034/article/details/127760798◼ av_seek_frame():定位文件
功能 :该函数可以将音/视频seek到指定的位置。
参数说明:
AVFormatContext *s // 封装格式上下文
int streamIndex // 流的索引。默认值为-1,因为媒体文件中可能既包含视频又包含音频,可以通过streamIndex来指定究竟是以视频还是音频来移。
int64_t timestamp. // 时间戳。你要移动到哪个时间位置。
int flag // 标识位。表示我们移动的策略(究竟是向前移,还是向后移)。
参数 timestamp:
时间戳以AVStream.time_base为单位,如果未指定流,则以AV_time_base为单位
PS:参数flag
#define AVSEEK_FLAG_BACKGROUND 1 ///<<Seek Background 往后移,
#define AVSEEK_FALG_BYTE ///<<<seeking based on position in bytes 让时间戳 变成一个byte, 按照文件的大小位置跳到那个位置
#define AVSEEK_FLAG_ANY ///<<<seek to any frame, even non-keyframes // 移动到任意帧的位置,不去找前面的关键帧,
#define AVSEEK_FLAG_FRAME ///<<<seeking based on frame number // 找关键帧,一般与AVSEEK_FLAG_BACKGROUND一起使用
/**
* Seek to the keyframe at timestamp.
* 'timestamp' in 'stream_index'.
*
* @param s media file handle
* @param stream_index If stream_index is (-1), a default stream is selected,
* and timestamp is automatically converted from
* AV_TIME_BASE units to the stream specific time_base.
* @param timestamp Timestamp in AVStream.time_base units or, if no stream
* is specified, in AV_TIME_BASE units.
* @param flags flags which select direction and seeking mode
*
* @return >= 0 on success
*/
int av_seek_frame(AVFormatContext *s, int stream_index, int64_t timestamp,
int flags);// 读取一帧数据
AVPacket *packet = av_packet_alloc();
for (;;) {
int ret = av_read_frame(ic, packet);
if (ret != 0) {
LOGI("读取到结尾处");
int pos = 20 * r2d(ic->streams[videoStream]->time_base);
// 改变播放进度
av_seek_frame(ic, videoStream, pos, AVSEEK_FLAG_BACKWARD | AVSEEK_FLAG_FRAME);
continue;
}
LOGI("streamIndex=%d, size=%d, pts=%lld, flag=%d",
packet->stream_index,
packet->size,
packet->pts,
packet->flags
);
av_packet_unref(packet);
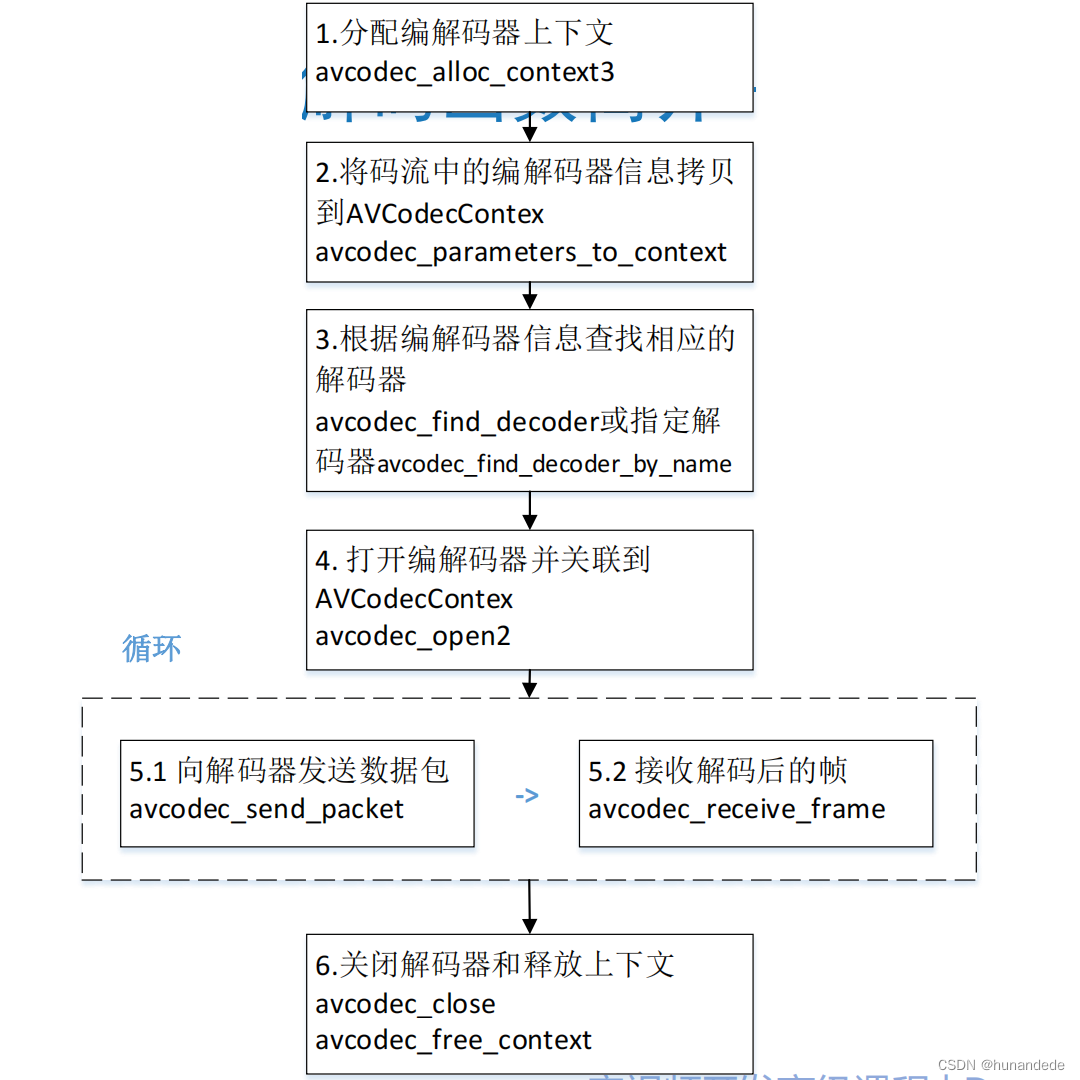
}FFmpeg函数简介-封装格分式配解相复用关器上下文,整体流程图
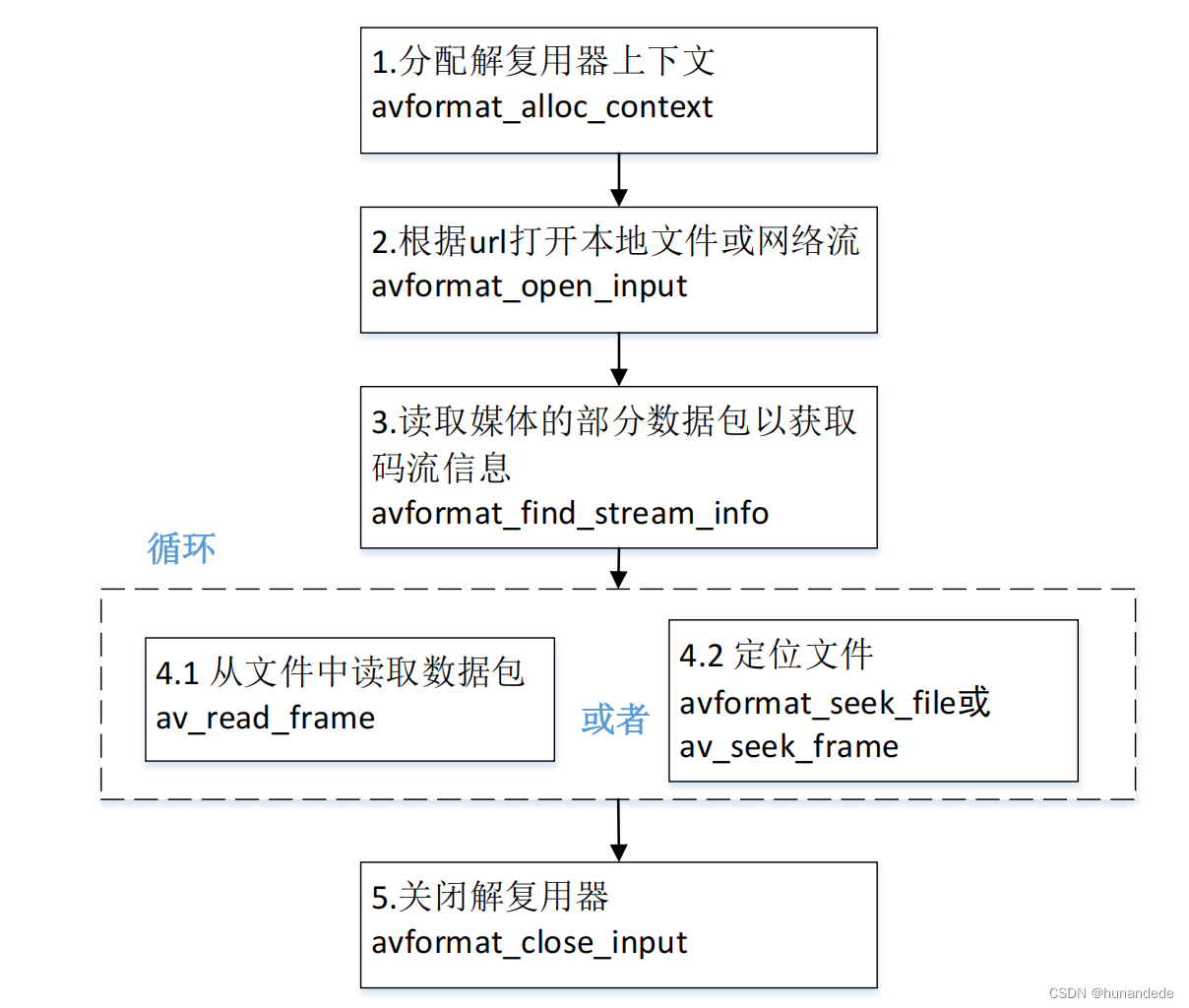
当解封装完成,我们目前的进度是这样的
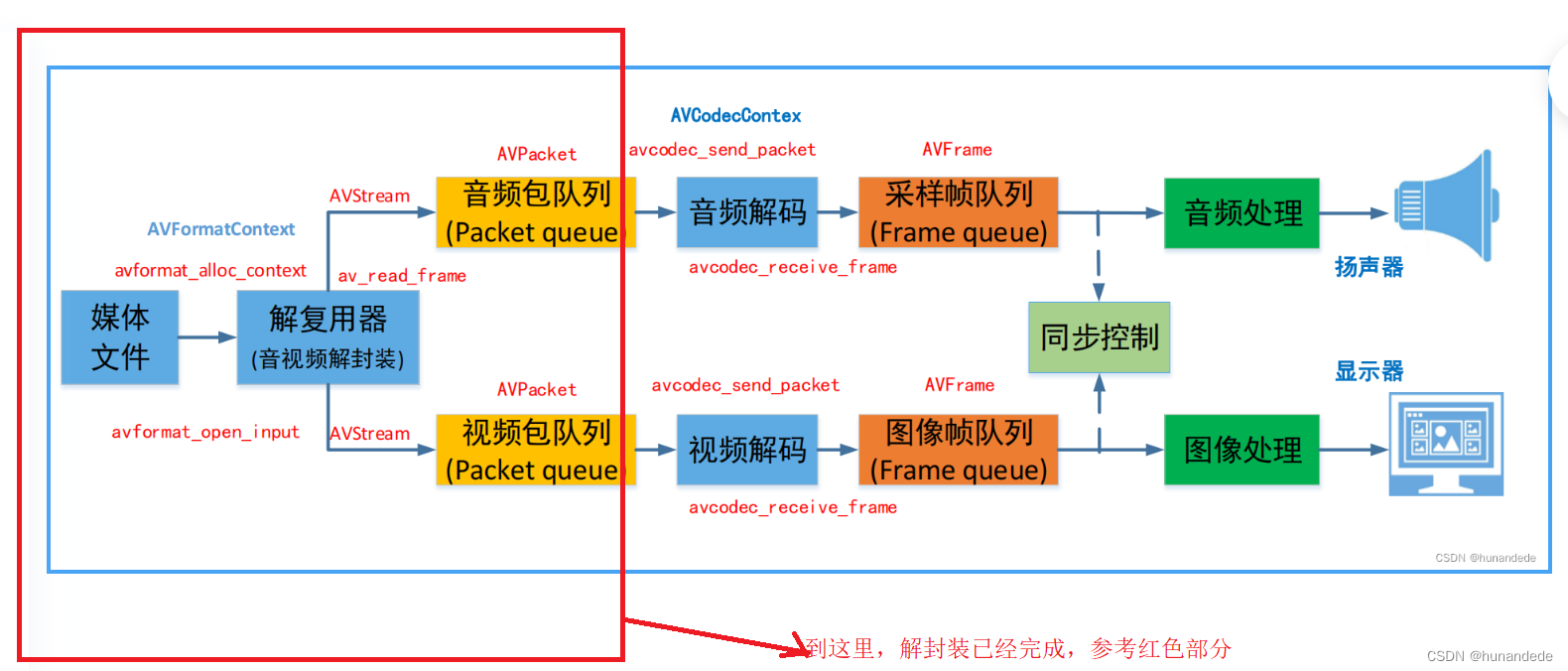
八 FFmpeg解码函数简介-解码器相关
那么我们下来就需要将从前面解封装得到的avpacket 进行处理。进行解码。
首先,我们要指定一个解码器,告诉ffmpeg 代码,我用这个解码器来解码。方法有两种,avcodec_find_decoder() 和 avcodec_find_decoder_by_name();
• avcodec_find_decoder():根据ID查找解码器
/**
* Find a registered decoder with a matching codec ID.
*
* @param id AVCodecID of the requested decoder
* @return A decoder if one was found, NULL otherwise.
*/
const AVCodec *avcodec_find_decoder(enum AVCodecID id);详情请参考 enum AVCodecID,这个enum AVCodecID 太大了,这里写不下,用的时候要具体查看,我们举例说明一下,就好
const AVCodec *codec;
codec = avcodec_find_decoder(AV_CODEC_ID_AAC);
const AVCodec *codec;
codec = avcodec_find_decoder(AV_CODEC_ID_H264);但是这里有一个问题,就是我们一般在解析一个文件的时候,并不知道这个文件的音频和视频用的什么编码,也就不知道用什么解码器解码比较好,因此,这里一种通用的写法是使用如下的api从得到流中 最合适的
int av_find_best_stream(AVFormatContext *ic,
enum AVMediaType type,
int wanted_stream_nb,
int related_stream,
const struct AVCodec **decoder_ret,
int flags);
•avcodec_find_decoder_by_name():根据解码器名字
• avcodec_alloc_context3(): 分配解码器上下文
#include <libavcodec/avcodec.h>• avcodec_open2(): 打开编解码器
• avcodec_decode_video2():解码一帧视频数据
• avcodec_decode_audio4():解码一帧音频数据
• avcodec_send_packet(): 发送编码数据包
• avcodec_receive_frame(): 接收解码后数据
• avcodec_free_context():释放解码器上下文,包含了 avcodec_close()
• avcodec_close():关闭解码器