前言
聚合分析是从海量数据中提取数据的基本方法,对于OLAP数据库而言,聚合分析是其关键能力之一,ClickHouse在这方面也做了很多设计和优化,正如ClickHouse在文档中所述:

本文将分析展示ClickHouse的聚合功能的工作原理、整体流程和各种优化方式。
从InterpreterSelectQuery::buildQueryPlan开始
在ClickHouse中,一条SQL语句的处理流程是:
sql -> ast -> query_plan -> pipeline -> execute
本文不关注sql解析到ast的过程(我也没看过...看其他文章,clickhouse手写了个递归下降的语法分析器),从构造query_plan开始分析。query_plan由具有执行先后顺序的query_plan_step组成,聚合操作本身作为一个query_plan_step,排在where操作之后:
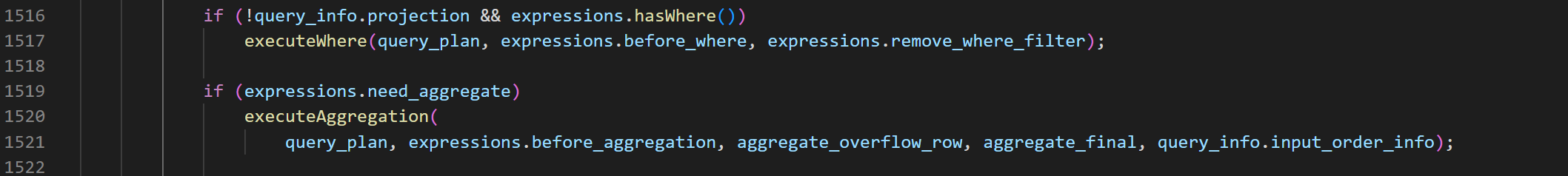
InterpreterSelectQuery::executeAggregation
void InterpreterSelectQuery::executeAggregation(QueryPlan & query_plan, const ActionsDAGPtr & expression, bool overflow_row, bool final, InputOrderInfoPtr group_by_info)
{
...
AggregateDescriptions aggregates = query_analyzer->aggregates();
...
// 我们先不关心GROUPING SETS modifier,这个配置项忽略
auto grouping_sets_params = getAggregatorGroupingSetsParams(*query_analyzer, keys);
SortDescription group_by_sort_description;
// 先不关心GROUP BY Optimization Depending on Table Sorting Key这个优化,即默认group_by_info == nullptr;
if (group_by_info && settings.optimize_aggregation_in_order && !query_analyzer->useGroupingSetKey())
group_by_sort_description = getSortDescriptionFromGroupBy(getSelectQuery());
else
group_by_info = nullptr;
auto merge_threads = max_streams;
// aggregation_memory_efficient_merge_threads这个配置项和分布式查询相关,用来降低内存使用的,先不关心。
auto temporary_data_merge_threads = settings.aggregation_memory_efficient_merge_threads
? static_cast<size_t>(settings.aggregation_memory_efficient_merge_threads)
: static_cast<size_t>(settings.max_threads);
bool storage_has_evenly_distributed_read = storage && storage->hasEvenlyDistributedRead();
// 分布式查询相关,先不关心
const bool should_produce_results_in_order_of_bucket_number
= options.to_stage == QueryProcessingStage::WithMergeableState && settings.distributed_aggregation_memory_efficient;
auto aggregating_step = std::make_unique<AggregatingStep>(
query_plan.getCurrentDataStream(),
std::move(aggregator_params),
std::move(grouping_sets_params),
final,
settings.max_block_size,
settings.aggregation_in_order_max_block_bytes,
merge_threads,
temporary_data_merge_threads,
storage_has_evenly_distributed_read,
settings.group_by_use_nulls,
std::move(group_by_info),
std::move(group_by_sort_description),
should_produce_results_in_order_of_bucket_number);
query_plan.addStep(std::move(aggregating_step));
}
executeAggregation函数的主要流程是,初始化各种配置项,构造AggregatingStep,并将其添加到query_plan中。
AggregatingStep::transformPipeline
在query_plan构造pipeline时,实际上是调用每个step的transformPipeline函数完成:
void AggregatingStep::transformPipeline(QueryPipelineBuilder & pipeline, const BuildQueryPipelineSettings & settings)
{
...
bool allow_to_use_two_level_group_by = pipeline.getNumStreams() > 1 || params.max_bytes_before_external_group_by != 0;
/// optimize_aggregation_in_order
if (group_by_info)
{
...
}
if (!allow_to_use_two_level_group_by)
{
params.group_by_two_level_threshold = 0;
params.group_by_two_level_threshold_bytes = 0;
}
/** Two-level aggregation is useful in two cases:
* 1. Parallel aggregation is done, and the results should be merged in parallel.
* 2. An aggregation is done with store of temporary data on the disk, and they need to be merged in a memory efficient way.
*/
const auto src_header = pipeline.getHeader();
auto transform_params = std::make_shared<AggregatingTransformParams>(src_header, std::move(params), final);
// 默认为空,不关心GROUPING SETS modifier
if (!grouping_sets_params.empty())
{
...
}
// 不关心GROUP BY Optimization Depending on Table Sorting Key这个优化,即默认group_by_info == nullptr;
if (group_by_info)
{
...
}
/// If there are several sources, then we perform parallel aggregation
if (pipeline.getNumStreams() > 1)
{
/// Add resize transform to uniformly distribute data between aggregating streams.
if (!storage_has_evenly_distributed_read)
pipeline.resize(pipeline.getNumStreams(), true, true);
auto many_data = std::make_shared<ManyAggregatedData>(pipeline.getNumStreams());
size_t counter = 0;
pipeline.addSimpleTransform([&](const Block & header)
{
return std::make_shared<AggregatingTransform>(header, transform_params, many_data, counter++, merge_threads, temporary_data_merge_threads);
});
/// We add the explicit resize here, but not in case of aggregating in order, since AIO don't use two-level hash tables and thus returns only buckets with bucket_number = -1.
pipeline.resize(should_produce_results_in_order_of_bucket_number ? 1 : params.max_threads, true /* force */);
aggregating = collector.detachProcessors(0);
}
else
{
pipeline.addSimpleTransform([&](const Block & header) { return std::make_shared<AggregatingTransform>(header, transform_params); });
pipeline.resize(should_produce_results_in_order_of_bucket_number ? 1 : params.max_threads, false /* force */);
aggregating = collector.detachProcessors(0);
}
}
ClickHouse中对于每个上游的数据流,会构造一个AggregatingTransform的节点进行预聚合,当所有AggregatingTransform节点预聚合完毕后,会通过ExpandPipeline扩展新的节点,这些新的节点负责将预聚合的数据进行合并(Merge)。
也就是说,ClickHouse中的聚合操作整体上分为两个阶段:预聚合阶段和合并阶段,预聚合阶段是可以并行进行的,(合并阶段在使用两层哈希的情况下也是可以并行的,详见后续)。
注意到,pipeline最后resize了一下,手动调整了output_port的数量,开始我并不明白这里resize的意义是什么,后来搜了一下issue,找到了这个 ,里面介绍了在某些情况下会产生性能问题,这里不再展开,感兴趣的朋友可以跳转过去看看。
AggregatingTransform
AggregatingTransform的工作主要分为两个阶段:
- 预聚合阶段,通过调用aggregator.executeOnBlock(...)函数执行预聚合。
- 合并阶段,当预聚合阶段结束(上游通道关闭,或者聚合行数到达了设定的上限),通过扩展pipeline替换上游节点,然后等待合并数据。
注意:
- aggregator这个对象是真正封装了具体的聚合函数、参数、预聚合操作、合并操作的对象,并提供了将聚合结果转换为Blocks的接口,我们暂且可以将aggregator当做一个黑盒子,其内部实现涉及到很多优化细节,包括内存池、针对特定类型的哈希表、单层哈希转两层哈希表等等。
- 虽然AggregatingTransform有合并阶段,但真正的合并操作不在这个节点上执行,而是由其扩展的节点执行,这个阶段它只负责传递数据。
- 只有最后一个完成第一阶段的AggregatingTransform才会扩展pipeline,见源码:
void AggregatingTransform::work()
{
if (is_consume_finished)
initGenerate();
else
{
consume(std::move(current_chunk));
read_current_chunk = false;
}
}
many_data在所有的AggregatingTransform节点中共享。
void AggregatingTransform::initGenerate()
{
...
if (many_data->num_finished.fetch_add(1) + 1 < many_data->variants.size())
return;
}
AggregatingTransform之扩展pipeline
void AggregatingTransform::initGenerate()
{
...
if (many_data->num_finished.fetch_add(1) + 1 < many_data->variants.size())
return;
if (!params->aggregator.hasTemporaryData())
{
auto prepared_data = params->aggregator.prepareVariantsToMerge(many_data->variants);
auto prepared_data_ptr = std::make_shared<ManyAggregatedDataVariants>(std::move(prepared_data));
processors.emplace_back(std::make_shared<ConvertingAggregatedToChunksTransform>(params, std::move(prepared_data_ptr), max_threads));
}
else
{
...
const auto & tmp_data = params->aggregator.getTemporaryData();
Pipe pipe;
{
Pipes pipes;
for (auto * tmp_stream : tmp_data.getStreams())
pipes.emplace_back(Pipe(std::make_unique<SourceFromNativeStream>(tmp_stream)));
pipe = Pipe::unitePipes(std::move(pipes));
}
...
addMergingAggregatedMemoryEfficientTransform(pipe, params, temporary_data_merge_threads);
processors = Pipe::detachProcessors(std::move(pipe));
}
}
void addMergingAggregatedMemoryEfficientTransform(
Pipe & pipe,
AggregatingTransformParamsPtr params,
size_t num_merging_processors)
{
pipe.addTransform(std::make_shared<GroupingAggregatedTransform>(pipe.getHeader(), pipe.numOutputPorts(), params));
if (num_merging_processors <= 1)
{
/// --> GroupingAggregated --> MergingAggregatedBucket -->
pipe.addTransform(std::make_shared<MergingAggregatedBucketTransform>(params));
return;
}
/// --> --> MergingAggregatedBucket -->
/// --> GroupingAggregated --> ResizeProcessor --> MergingAggregatedBucket --> SortingAggregated -->
/// --> --> MergingAggregatedBucket -->
pipe.resize(num_merging_processors);
pipe.addSimpleTransform([params](const Block &)
{
return std::make_shared<MergingAggregatedBucketTransform>(params);
});
pipe.addTransform(std::make_shared<SortingAggregatedTransform>(num_merging_processors, params));
}
扩展pipeline的具体逻辑在initGenerate()函数中,这里根据aggregator在预聚合过程中是否因为限制内存使用而将数据写到磁盘文件,扩展的节点是不同的,
- 如果没有写到磁盘文件,扩展ConvertingAggregatedToChunksTransform节点
- 否则扩展:
- SourceFromNativeStream节点(每个磁盘文件扩展一个SourceFromNativeStream节点)+
- GroupingAggregatedTransform(一个)+
- MergingAggregatedBucketTransform(一个或多个,如果一个则结束)+
- SortingAggregatedTransform
在进行下面的分析之前,这里需要介绍一下aggregator的两层哈希表机制:
aggregator的预聚合操作,其内部数据是通过哈希表存储的,哈希表的键是“grouping key” value(举例:如果sql语句中group by b,那么哈希表的键是表中b的所有不同的值)。这个哈希表是动态的,随着键数量的增加,ClickHouse会将其切换到两级哈希表以提升性能;另外对于不同的键类型,ClickHouse提供了很多特化版本,以针对特定类型进行优化。
对于单层哈希表,aggregator转化的block是single_level block,对于双层哈希表,aggregator转化的block是two_level block,two_level block会有一个block_num,可以认为block_num就是双层哈希表的第一层的键。使用two_level block有两个好处:
- 可以将执行预聚合的多个节点的相同block_num的block进行组合,那么不同的组合可以并行的执行合并操作
- 如果限制产生two_level block的节点必须按照block_num递增的顺序,那么可以减少内存使用量,因为需要执行合并操作的数据一定在同一个组合内,当看到一个新的block_num时,意味着所有之前的合并操作已经完成。
实际上上文将数据写到磁盘文件的分支,就是做了这样的优化。在GroupingAggregatedTransform节点中,会将single_level block转化为two_level block,并按照block_num进行组合,然后交给MergingAggregatedBucketTransform进行合并操作,因为MergingAggregatedBucketTransform可以有多个,因此合并阶段也可以是并行的。最后交给SortingAggregatedTransform节点根据block_num进行排序。(老实说不清楚为啥要排序,哈希结果乱序有啥问题呢?)
对于数据没写到磁盘文件的分支,可以看下ConvertingAggregatedToChunksTransform节点的注释:
/// Generates chunks with aggregated data.
/// In single level case, aggregates data itself.
/// In two-level case, creates `ConvertingAggregatedToChunksSource` workers:
///
/// ConvertingAggregatedToChunksSource ->
/// ConvertingAggregatedToChunksSource -> ConvertingAggregatedToChunksTransform -> AggregatingTransform
/// ConvertingAggregatedToChunksSource ->
///
/// Result chunks guaranteed to be sorted by bucket number.
class ConvertingAggregatedToChunksTransform : public IProcessor如果预聚合数据是two_level block,则扩展节点进行并行合并,然后在本节点进行sort;否则直接在本节点合并,这个分支就不详细展开了,如果熟悉了ClickHouse的套路,其实看懂就很简单了。
现在回来说说AggregatingTransform是如何从预聚合阶段切换到合并阶段的,这部分内容也是典型的运行时扩展Pipeline的案例:需要根据计算时的数据动态的判断之后需要执行的节点类型和结构。老实说之前在看Pipeline执行引擎的时候并不理解为什么需要这样的功能,ClickHouse的Pipeline执行引擎真的好强大。(这部分内容需要你理解Pipeline执行引擎的内部实现)
- 在预聚合阶段,AggregatingTransform只有一个input_port,这个是原始的上游数据流,节点执行预聚合直到这个input_port被关闭,这时设置is_consume_finished = true并返回Status::Ready;
- 下次执行work()函数的时候会调用initGenerate()函数,这个函数在上面分析过,根据预聚合的数据生成扩展的节点,并且设置is_generate_initialized=true。
- 下次执行prepare()函数的时候会返回Status::ExpandPipeline,见代码:
if (is_generate_initialized && !is_pipeline_created && !processors.empty())
return Status::ExpandPipeline;
- Pipeline执行引擎看到这个状态,调用节点的expandPipeline()函数拿到扩展的节点,并合并到初始的pipeline中:
Processors AggregatingTransform::expandPipeline()
{
if (processors.empty())
throw Exception("Can not expandPipeline in AggregatingTransform. This is a bug.", ErrorCodes::LOGICAL_ERROR);
auto & out = processors.back()->getOutputs().front();
inputs.emplace_back(out.getHeader(), this);
connect(out, inputs.back());
is_pipeline_created = true;
return std::move(processors);
}
在这个函数中,AggregatingTransform构造了一个新的input_port,和扩展节点中的最下游节点的output_port连接起来。
- 下次执行prepare()函数的时候,获取的input_port是新构造的那个,这里实际上等价于切换了上游数据流,切换完成。
aggregator
aggregator的类型是Aggregator,它封装了封装了具体的聚合和合并操作。首先来看它的构造函数:
Aggregator::Aggregator(const Block & header_, const Params & params_)
: header(header_)
, keys_positions(calculateKeysPositions(header, params_))
, params(params_)
, tmp_data(params.tmp_data_scope ? std::make_unique<TemporaryDataOnDisk>(params.tmp_data_scope, CurrentMetrics::TemporaryFilesForAggregation) : nullptr)
, min_bytes_for_prefetch(getMinBytesForPrefetch())
{
/// Use query-level memory tracker
// 记录预聚合前的内存使用,作为后续是否写入磁盘文件的依据
if (auto * memory_tracker_child = CurrentThread::getMemoryTracker())
if (auto * memory_tracker = memory_tracker_child->getParent())
memory_usage_before_aggregation = memory_tracker->get();
aggregate_functions.resize(params.aggregates_size);
for (size_t i = 0; i < params.aggregates_size; ++i)
aggregate_functions[i] = params.aggregates[i].function.get();
/// Initialize sizes of aggregation states and its offsets.
offsets_of_aggregate_states.resize(params.aggregates_size);
total_size_of_aggregate_states = 0;
all_aggregates_has_trivial_destructor = true;
// aggregate_states will be aligned as below:
// |<-- state_1 -->|<-- pad_1 -->|<-- state_2 -->|<-- pad_2 -->| .....
//
// pad_N will be used to match alignment requirement for each next state.
// The address of state_1 is aligned based on maximum alignment requirements in states
for (size_t i = 0; i < params.aggregates_size; ++i)
{
offsets_of_aggregate_states[i] = total_size_of_aggregate_states;
total_size_of_aggregate_states += params.aggregates[i].function->sizeOfData();
// aggregate states are aligned based on maximum requirement
align_aggregate_states = std::max(align_aggregate_states, params.aggregates[i].function->alignOfData());
// If not the last aggregate_state, we need pad it so that next aggregate_state will be aligned.
if (i + 1 < params.aggregates_size)
{
size_t alignment_of_next_state = params.aggregates[i + 1].function->alignOfData();
if ((alignment_of_next_state & (alignment_of_next_state - 1)) != 0)
throw Exception("Logical error: alignOfData is not 2^N", ErrorCodes::LOGICAL_ERROR);
/// Extend total_size to next alignment requirement
/// Add padding by rounding up 'total_size_of_aggregate_states' to be a multiplier of alignment_of_next_state.
total_size_of_aggregate_states = (total_size_of_aggregate_states + alignment_of_next_state - 1) / alignment_of_next_state * alignment_of_next_state;
}
if (!params.aggregates[i].function->hasTrivialDestructor())
all_aggregates_has_trivial_destructor = false;
}
method_chosen = chooseAggregationMethod();
HashMethodContext::Settings cache_settings;
cache_settings.max_threads = params.max_threads;
aggregation_state_cache = AggregatedDataVariants::createCache(method_chosen, cache_settings);
#if USE_EMBEDDED_COMPILER
compileAggregateFunctionsIfNeeded();
#endif
}
构造函数中主要做了以下几件事:
- 记录预聚合前的内存使用,作为是否将预聚合数据写入磁盘文件的依据
- 每个聚合函数有个对应的State对象,该对象作为预聚合过程中内部数据的存储点,一个sql语句中可以有多个聚合函数,ClickHouse中是将多个聚合函数的State对象分配在一整块内存上的,因此,这里需要计算每个State对象的大小和偏移量。
- 根据键类型选择合适的哈希表,代码见下:
AggregatedDataVariants::Type Aggregator::chooseAggregationMethod()
{
/// If no keys. All aggregating to single row.
if (params.keys_size == 0)
return AggregatedDataVariants::Type::without_key;
...
if (has_nullable_key)
{
if (params.keys_size == num_fixed_contiguous_keys && !has_low_cardinality)
{
...
}
if (has_low_cardinality && params.keys_size == 1)
{
...
}
}
/// No key has been found to be nullable.
/// Single numeric key.
if (params.keys_size == 1 && types_removed_nullable[0]->isValueRepresentedByNumber())
{
...
}
if (params.keys_size == 1 && isFixedString(types_removed_nullable[0]))
{
...
}
/// If all keys fits in N bits, will use hash table with all keys packed (placed contiguously) to single N-bit key.
if (params.keys_size == num_fixed_contiguous_keys)
{
...
}
/// If single string key - will use hash table with references to it. Strings itself are stored separately in Arena.
if (params.keys_size == 1 && isString(types_removed_nullable[0]))
{
...
}
return AggregatedDataVariants::Type::serialized;
}
这里根据“grouping key” 的数量、特点(lowCardinality、isNullable、isFixedString)等性质,选择合适的哈希表类型(具体细节各位可以看下源码),默认选择serialized类型的哈希表,这个哈希表的键就是将多个“grouping key”拼接。
- 针对个别类型的哈希表,构造cache,本文不关注。
这里我们总结一下,aggregator的预聚合阶段使用哈希表来存储数据,这个哈希表的键由“grouping key”决定,值就是分配有多个state对象的那块内存。根据“grouping key” 的数量和特点,Clickhouse提供了很多版本的哈希表。
Aggregator::executeOnBlock
executeOnBlock是执行预聚合的接口
bool Aggregator::executeOnBlock(Columns columns,
size_t row_begin, size_t row_end,
AggregatedDataVariants & result,
ColumnRawPtrs & key_columns,
AggregateColumns & aggregate_columns,
bool & no_more_keys) const
{
/// `result` will destroy the states of aggregate functions in the destructor
result.aggregator = this;
/// How to perform the aggregation?
if (result.empty())
{
initDataVariantsWithSizeHint(result, method_chosen, params);
result.keys_size = params.keys_size;
result.key_sizes = key_sizes;
LOG_TRACE(log, "Aggregation method: {}", result.getMethodName());
}
/** Constant columns are not supported directly during aggregation.
* To make them work anyway, we materialize them.
*/
Columns materialized_columns;
/// Remember the columns we will work with
for (size_t i = 0; i < params.keys_size; ++i)
{
materialized_columns.push_back(recursiveRemoveSparse(columns.at(keys_positions[i]))->convertToFullColumnIfConst());
key_columns[i] = materialized_columns.back().get();
...
}
NestedColumnsHolder nested_columns_holder;
AggregateFunctionInstructions aggregate_functions_instructions;
prepareAggregateInstructions(columns, aggregate_columns, materialized_columns, aggregate_functions_instructions, nested_columns_holder);
if ((params.overflow_row || result.type == AggregatedDataVariants::Type::without_key) && !result.without_key)
{
AggregateDataPtr place = result.aggregates_pool->alignedAlloc(total_size_of_aggregate_states, align_aggregate_states);
createAggregateStates(place);
result.without_key = place;
}
if (result.type == AggregatedDataVariants::Type::without_key)
{
executeWithoutKeyImpl<false>(result.without_key, row_begin, row_end, aggregate_functions_instructions.data(), result.aggregates_pool);
}
else
{
/// This is where data is written that does not fit in `max_rows_to_group_by` with `group_by_overflow_mode = any`.
AggregateDataPtr overflow_row_ptr = params.overflow_row ? result.without_key : nullptr;
executeImpl(result, row_begin, row_end, key_columns, aggregate_functions_instructions.data(), no_more_keys, overflow_row_ptr);
}
size_t result_size = result.sizeWithoutOverflowRow();
Int64 current_memory_usage = 0;
if (auto * memory_tracker_child = CurrentThread::getMemoryTracker())
if (auto * memory_tracker = memory_tracker_child->getParent())
current_memory_usage = memory_tracker->get();
/// Here all the results in the sum are taken into account, from different threads.
auto result_size_bytes = current_memory_usage - memory_usage_before_aggregation;
bool worth_convert_to_two_level = worthConvertToTwoLevel(
params.group_by_two_level_threshold, result_size, params.group_by_two_level_threshold_bytes, result_size_bytes);
/** Converting to a two-level data structure.
* It allows you to make, in the subsequent, an effective merge - either economical from memory or parallel.
*/
if (result.isConvertibleToTwoLevel() && worth_convert_to_two_level)
result.convertToTwoLevel();
/// Checking the constraints.
if (!checkLimits(result_size, no_more_keys))
return false;
/** Flush data to disk if too much RAM is consumed.
* Data can only be flushed to disk if a two-level aggregation structure is used.
*/
if (params.max_bytes_before_external_group_by
&& result.isTwoLevel()
&& current_memory_usage > static_cast<Int64>(params.max_bytes_before_external_group_by)
&& worth_convert_to_two_level)
{
size_t size = current_memory_usage + params.min_free_disk_space;
writeToTemporaryFile(result, size);
}
return true;
}
这个函数主要做了以下工作:
- initDataVariantsWithSizeHint
result(类型AggregatedDataVariants)是一个out型参数,实际的哈希表也是在这个对象中,这里会执行初始化操作,即根据aggregator选择的哈希表类型来初始化对应的哈希表,略微截图给大家看一下:

直接将各种哈希表硬编码进AggregatedDataVariants类型中,太暴力了。
- materialize columns
ClickHouse中有些列不能在聚合操作中直接使用,比如Const Column、Sparse Column等。这里对“grouping key”中这些列做了具化处理(即格式转换为普通格式)。
- prepareAggregateInstructions
这个函数内部是聚合函数的参数拼接的过程,聚合函数的参数,根据名字找到对应的列数据。
- executeWithoutKeyImpl / executeImpl
执行聚合操作,下面分析
- if convertToTwoLevel
- if writeToTemporaryFile
聚合操作之后,判断是否要将单层哈希表转换为双层,以及是否将数据写到磁盘文件中。
executeWithoutKeyImpl / executeImpl
executeWithoutKeyImpl实际上是没有group by语句时的聚合操作,比较简单,我们分析executeImpl,executeImpl实际上转发到了executeImplBatch:
template <bool no_more_keys, bool use_compiled_functions, bool prefetch, typename Method>
void NO_INLINE Aggregator::executeImplBatch(
Method & method,
typename Method::State & state,
Arena * aggregates_pool,
size_t row_begin,
size_t row_end,
AggregateFunctionInstruction * aggregate_instructions,
AggregateDataPtr overflow_row) const
{
...
/// NOTE: only row_end-row_start is required, but:
/// - this affects only optimize_aggregation_in_order,
/// - this is just a pointer, so it should not be significant,
/// - and plus this will require other changes in the interface.
std::unique_ptr<AggregateDataPtr[]> places(new AggregateDataPtr[row_end]);
/// For all rows.
for (size_t i = row_begin; i < row_end; ++i)
{
AggregateDataPtr aggregate_data = nullptr;
if constexpr (!no_more_keys)
{
...
auto emplace_result = state.emplaceKey(method.data, i, *aggregates_pool);
/// If a new key is inserted, initialize the states of the aggregate functions, and possibly something related to the key.
if (emplace_result.isInserted())
{
/// exception-safety - if you can not allocate memory or create states, then destructors will not be called.
emplace_result.setMapped(nullptr);
aggregate_data = aggregates_pool->alignedAlloc(total_size_of_aggregate_states, align_aggregate_states);
...
{
createAggregateStates(aggregate_data);
}
emplace_result.setMapped(aggregate_data);
}
else
aggregate_data = emplace_result.getMapped();
assert(aggregate_data != nullptr);
}
else
{
/// Add only if the key already exists.
auto find_result = state.findKey(method.data, i, *aggregates_pool);
if (find_result.isFound())
aggregate_data = find_result.getMapped();
else
aggregate_data = overflow_row;
}
places[i] = aggregate_data;
}
...
/// Add values to the aggregate functions.
for (size_t i = 0; i < aggregate_functions.size(); ++i)
{
AggregateFunctionInstruction * inst = aggregate_instructions + i;
if (inst->offsets)
inst->batch_that->addBatchArray(row_begin, row_end, places.get(), inst->state_offset, inst->batch_arguments, inst->offsets, aggregates_pool);
else if (inst->has_sparse_arguments)
inst->batch_that->addBatchSparse(row_begin, row_end, places.get(), inst->state_offset, inst->batch_arguments, aggregates_pool);
else
inst->batch_that->addBatch(row_begin, row_end, places.get(), inst->state_offset, inst->batch_arguments, aggregates_pool);
}
}
这个函数做了以下工作:
- 遍历需要聚合的行,对每一行我们计算其哈希表中的键,如果这个键在哈希表中不存在,则通过aggregates_pool->alignedAlloc申请一个内存块,并在内存块上初始化每个聚合函数的State对象
- 遍历聚合函数,依次执行预聚合操作(addBatchArray / addBatchSparse / addBatch)。
这部分内容分析到此为止,ClickHouse对聚合函数的封装可以参考这篇文章 。
总结
本来想再写详细一点的,但是发现现在这个程度已经2w多字了,再往下写就是一些过于细节繁杂的内容,写了估计也没耐心看,把握住框架,需要的时候再看细节吧。
聚合分析这部分代码充分说明了这样一个事实:ClickHouse之所以有如此优秀的性能,不是因为在某个或者某几个地方采用了特别牛逼的优化技巧和方法,而是作为一个软件系统,它能够将大部分常见的工程优化整合到系统的各个链路上下游中,并且还能保证一定的代码质量和合理的抽象水平,避免随着不断迭代开发导致代码完全屎山化。
参考:
ClickHouse之聚合功能源码分析 - 知乎