近年来,心脏病已成为危害人类健康最常见的疾病。为了有效预防心脏疾病的发生,往往需要更加准确地采集与诊断心电信号,以便于更好地反映心脏情况。心电信号作为人体生理信号,对于识别心脏异常和心脏疾病具有重要的参考价值。心电信号,是由心脏的电活动引起心脏周围的导电组织和体液反映到身体表面上而产生的电压变化。正常心电信号主要由P波、QRS复合波、T波与U波组成。由于心电信号频率与振幅较低,在采集心电信号时往往伴随着不可避免的噪声,因而降噪成为心电信号处理的核心。心电信号中存在多种低频和高频噪声,常见的噪声有加性高斯白噪声(AdditiveWhiteGaussianNoise,AWGN)、基线漂移(BaselineWander,BW)、肌电干扰(MuscleArtefacts,MA)、运动伪影(ElectrodeMotion,EM)、工频干扰(PowerLineInterference,PLI)。
基线漂移(BW):BW是一种低频噪声信号,主要是由呼吸、身体运动、电极接触不良与皮肤电极阻抗所引起的。BW噪声会使心电信号中的ST段与其他低频成分失真。
工频干扰(PLI):PLI主要是由供电设备产生的,它会扭曲低振幅心电信号波(P波或T波)的振幅与形状。
肌电干扰(MA):MA作为最主要的心电噪声信号之一,是由肌肉的收缩与颤动或身体突然运动而产生的电活动。肌电信号导致心电信号的局部波失真。
运动伪影(EM):由测量心电信号的电极与皮肤之间的阻抗随着相对位移而发生改变所引起的,与P波、T波的频谱几乎完全重合。
ECG处理主要是从采集到有噪声的信号中通过技术提取纯信号,以便于更精确地分析与诊断心脏问题。因此,希望设计一种能够完全消除噪声而不影响信号的技术。然而事实上,这是不可能的。因为噪声的频率与信号的频率在一个阶段非常接近以至于重叠,会无法滤除噪声或会使信号失真。因此,尽最大可能去除噪声而不影响信号是目前最主要的技术。近年来,众多学者采用不同学科不同领域方法来研究如何降噪,取得了较满意效果。
鉴于此,提出一种基于集成经验模态分解的心电信号降噪和基于希尔伯特变换的R峰检测,运行环境为MATLAB 2018,主代码如下:
%% Data Loading
ecg=load ('ecg1.mat'); % loading the signal
ecg=struct2cell(ecg);
ecg=cell2mat(ecg);
ecg = (ecg - 1024)/200; % you have to remove "base" and "gain"
ecg1=ecg(1,:); %Noisy ecg
ecg2=ecg(2,:); %filtered ecg
Fs =500; % sampling frequecy
t =linspace(0,length(ecg1)/Fs,length(ecg1)); %time vector
%% ECG signal denoising
imf=eemd(ecg1,.2,70); %Apply the EEMD to the noisy signal .2->ratio of the standard deviation 70->ensemble number
imfs=imf'; %transpose the imf's matrix
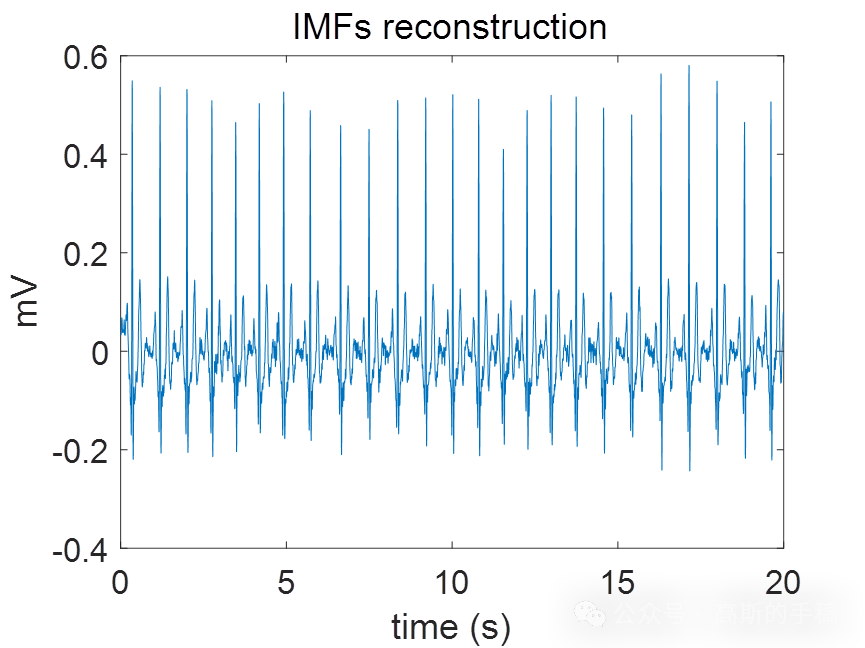
reconstruction=imfs(4,:)+imfs(5,:)+imfs(6,:); %We consider that these 3 imf's possess the important information
%4 order Butterworth filter bandpass .05-230Hz.
fclowpass=230; % Low pass cut-off frequency 230Hz
fchighpass=.05; % Low pass cut-off frequency .05Hz
filterorder=4; %filter order
[b,a]=butter(filterorder,[filterorder*fchighpass/Fs,2*fclowpass/Fs]);
filtered_ECG=filter(b,a,reconstruction);
%% Emphasizing R peaks of the ECG
%Getting the maxima and minima of the ECG signal, to emphasize the R peaks
decg=(1/Fs)*(diff(filtered_ECG)); %derivative of the ecg
hecg=hilbert(decg); %hilbert transform of the derivative.
envelope=abs(hecg); %It returns the envelope of the ecg
%% R peaks detection
maximum=(max(envelope));
Threshold=.6*(maximum);
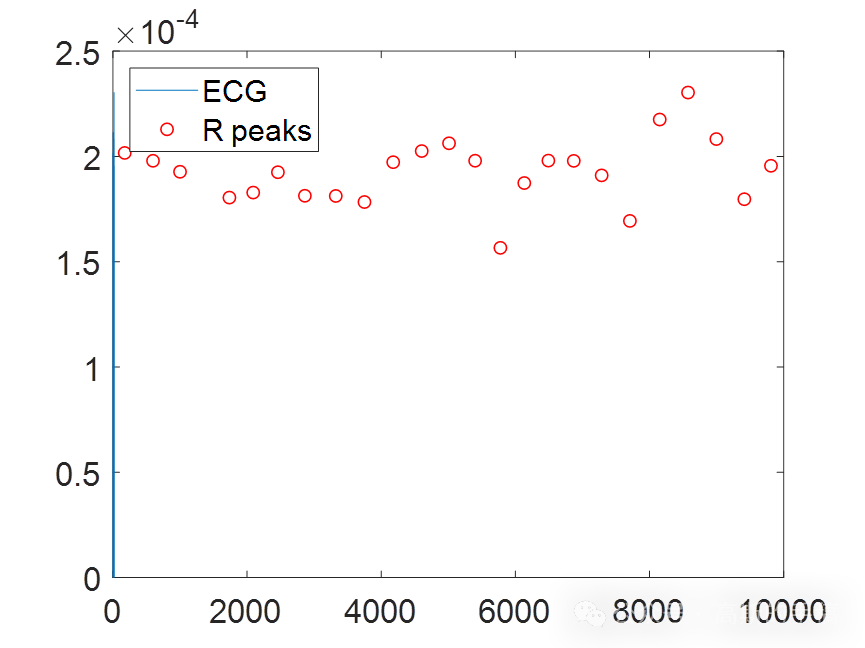
[pks,locs] = findpeaks(envelope,'MinPeakHeight',Threshold);
time=(1/Fs)*length(ecg1);
timefactor=60/time;
cardiacFreq=round(timefactor*length(pks));
%% Plots
figure (1)
plot(t,ecg1); xlabel('time (s)'); ylabel('mV'); title('Raw ECG');
figure(2)
subplot(7,1,1);
plot(t,imfs(1,:)); xlabel('time (s)'); ylabel('mV'); title('Original ECG');
subplot(7,1,2);
plot(t,imfs(2,:)); xlabel('time (s)'); ylabel('mV'); title('1st IMF');
subplot(7,1,3);
plot(t,imfs(3,:)); xlabel('time (s)'); ylabel('mV'); title('2nd IMF');
subplot(7,1,4);
plot(t,imfs(4,:)); xlabel('time (s)'); ylabel('mV'); title('3rd IMF');
subplot(7,1,5);
plot(t,imfs(5,:)); xlabel('time (s)'); ylabel('mV'); title('4th IMF');
subplot(7,1,6);
plot(t,imfs(6,:)); xlabel('time (s)'); ylabel('mV'); title('5th IMF');
subplot(7,1,7);
plot(t,imfs(7,:)); xlabel('time (s)'); ylabel('mV'); title('6th IMF');
figure (3)
subplot(7,1,1);
plot(t,imfs(8,:)); xlabel('time (s)'); ylabel('mV'); title('7th IMF');
subplot(7,1,2);
plot(t,imfs(9,:)); xlabel('time (s)'); ylabel('mV'); title('8th IMF');
subplot(7,1,3);
plot(t,imfs(10,:)); xlabel('time (s)'); ylabel('mV'); title('9th IMF');
subplot(7,1,4);
plot(t,imfs(11,:)); xlabel('time (s)'); ylabel('mV'); title('10th IMF');
subplot(7,1,5);
plot(t,imfs(12,:)); xlabel('time (s)'); ylabel('mV'); title('11th IMF');
subplot(7,1,6);
plot(t,imfs(13,:)); xlabel('time (s)'); ylabel('mV'); title('12th IMF');
subplot(7,1,7);
plot(t,imfs(14,:)); xlabel('time (s)'); ylabel('mV'); title('13th IMF');
figure (4)
plot(t,reconstruction); xlabel('time (s)'); ylabel('mV'); title('IMFs reconstruction');
figure(5)
plot(t,filtered_ECG); xlabel('time (s)'); ylabel('mV'); title('Filtered ECG (IMF+bandPass)');
figure(6)
plot(t(1:9999),decg); xlabel('time (s)'); ylabel('d(ECG)/dt'); title('ECG derivative');
figure(7)
plot(t(1:9999),hecg); xlabel('time (s)'); ylabel('H(d(ECG)/dt)'); title('Hilbert Transform of derivate');
figure(8)
plot(t(1:9999),envelope); xlabel('time (s)'); ylabel('B(d(ECG)/dt)'); title('Envelope');
figure (9)
plot(t(1:9999),envelope,locs,pks,'or');
%完整代码:mbd.pub/o/bread/mbd-ZJablZ5x
legend('ECG','R peaks','Location','NorthWest');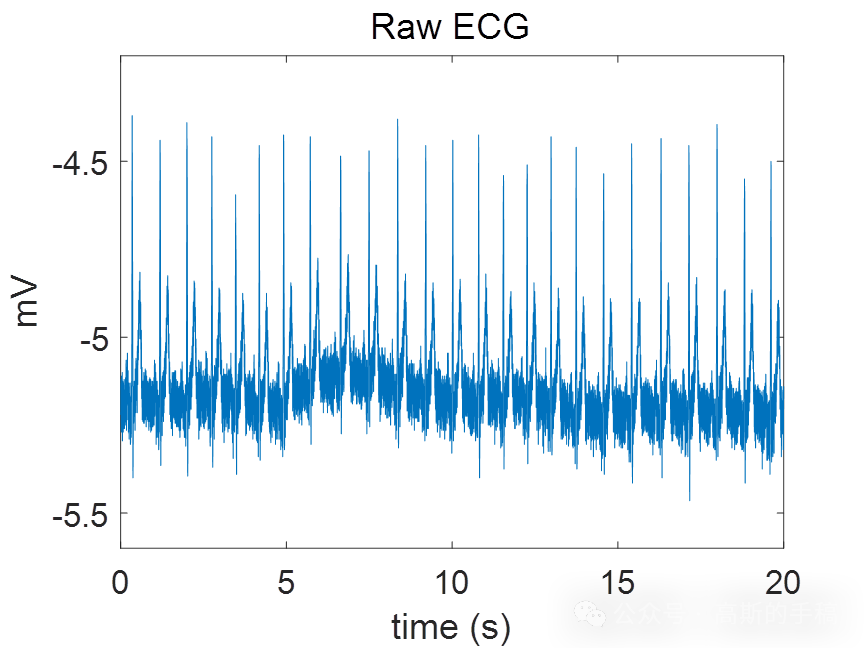




工学博士,担任《Mechanical System and Signal Processing》《中国电机工程学报》《控制与决策》等期刊审稿专家,擅长领域:现代信号处理,机器学习,深度学习,数字孪生,时间序列分析,设备缺陷检测、设备异常检测、设备智能故障诊断与健康管理PHM等。