文章目录
- 一、什么是RNN?
- 二、准备环境和数据
- 2.1 导入数据
- 三、构建模型
- 四、训练和预测
- 五、其他
- (1)sklearn模块导入报错:`ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'sklearn'`
- (2)优化器改为SGD,accuracy=25.81%
- (3)使用训练acc最高的模型进行预测
- 🍨 本文为🔗365天深度学习训练营 中的学习记录博客
- 🍖 原作者:K同学啊 | 接辅导、项目定制
一、什么是RNN?
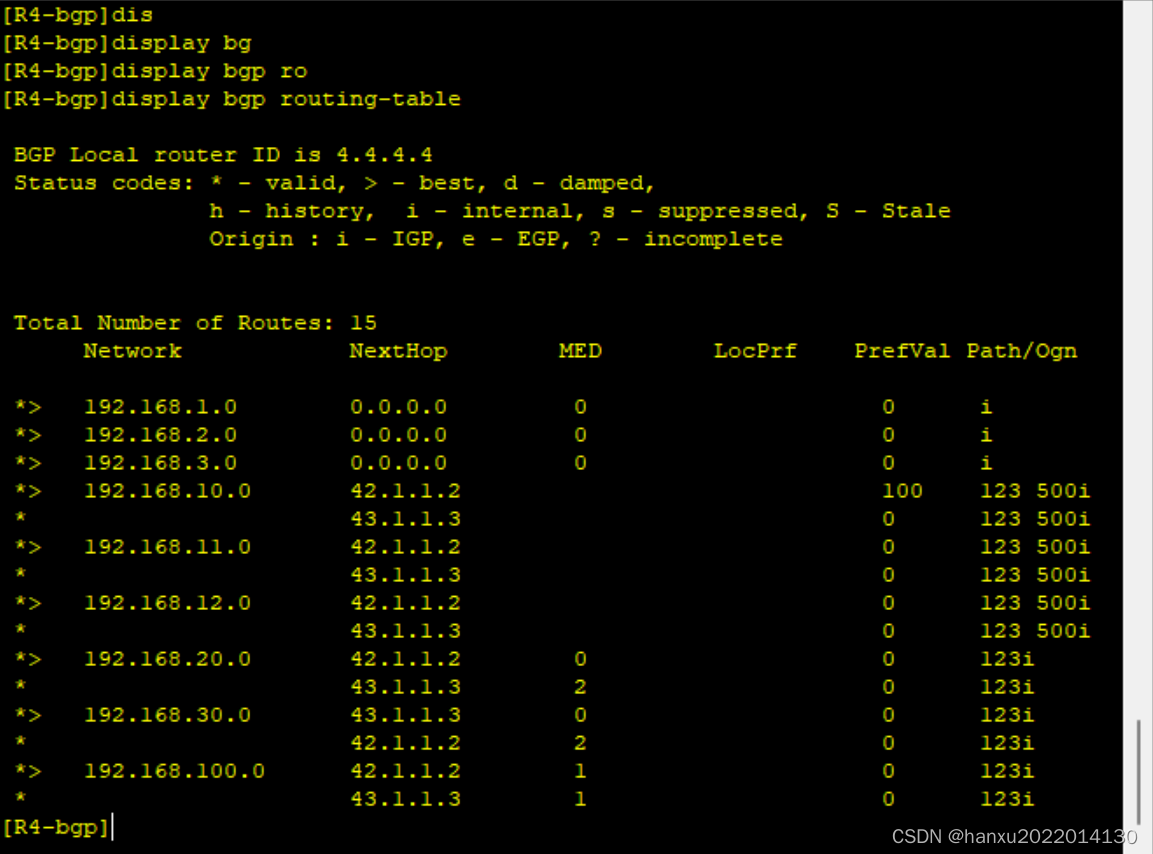
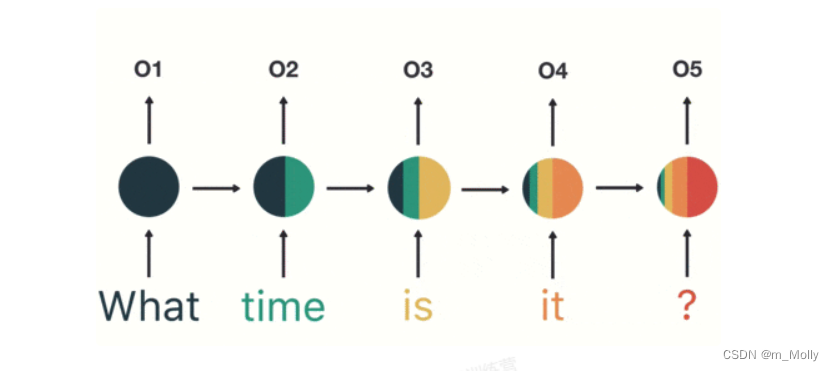
RNN:Recurrent Neural Network,用于处理序列数据。和传统神经网络不同的点在于,当前一层的输出会被当做输入,带到下一个隐藏层中,进行训练,于是除了第一层,RNN中每一个隐藏层的输入都包含两个部分【上一层的输出和当前层的输入】,如教案中给出的简易示意图,每个单词用一种颜色表示,01~05为不同的隐藏层,到达最后一层得到的输出为 05,也是神经网络需要判断的层。
二、准备环境和数据
环境:tensorflow框架,py312,cpu
编译:VSCode
使用CPU进行编译,就无需再设置GPU
2.1 导入数据
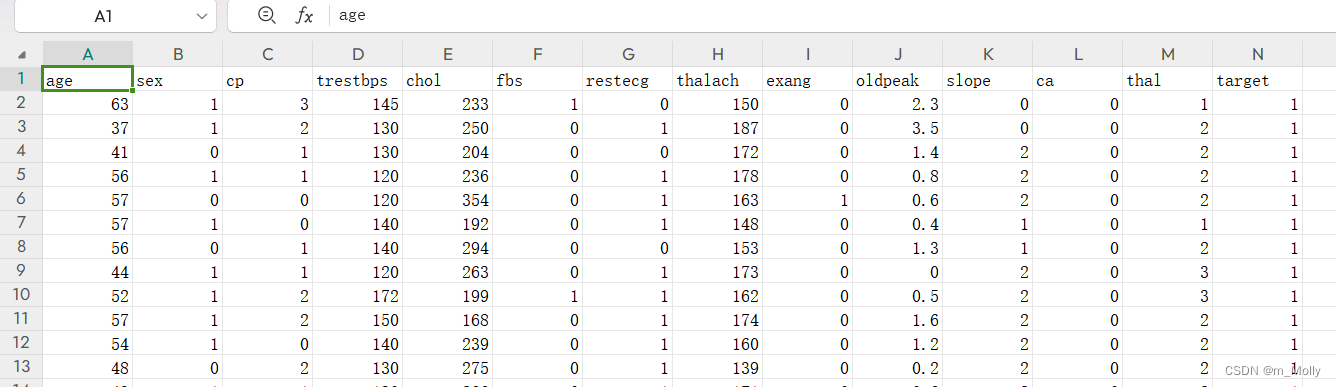
根据给出的数据集文件,分析如下:

import tensorflow as tf
gpus = tf.config.list_physical_devices("GPU")
if gpus:
gpu0 = gpus[0]
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(gpu0,true)
tf.config.set_visible_devices([gpu0],"GPU")
print("GPU: ",gpus)
else:
print("CPU:")
# 2.1 导入数据
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
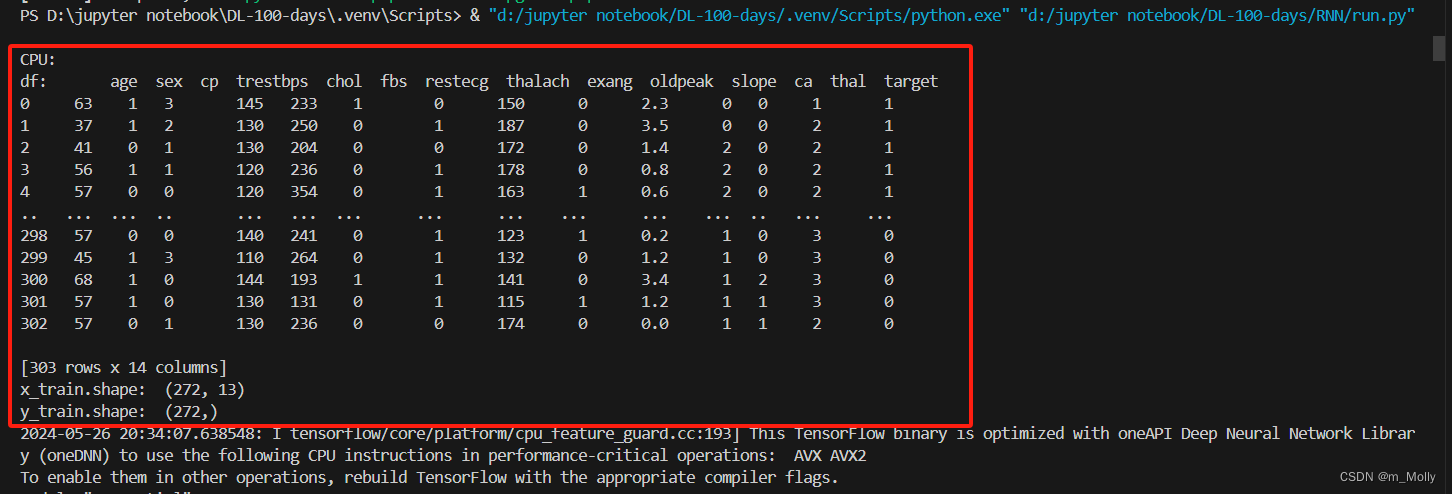
df = pd.read_csv("D:\\jupyter notebook\\DL-100-days\\RNN\\heart.csv")
print("df: ", df)
# 2.2 检查是否有空值
df.isnull().sum()
#3.1 划分训练集与测试集
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x = df.iloc[:, :-1]
y = df.iloc[:, -1]
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x,y,test_size=0.1,random_state=1)
print("x_train.shape: ", x_train.shape)
print("y_train.shape: ", y_train.shape)
# 3.2 标准化: 针对每一列进行标准化
sc = StandardScaler()
x_train = sc.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = sc.transform(x_test)
x_train = x_train.reshape(x_train.shape[0], x_train.shape[1], 1)
x_test = x_test.reshape(x_test.shape[0], x_test.shape[1], 1)
三、构建模型
tf官方教程 Keras中的循环神经网络RNN 一文中有提到:


本次学习使用的是SimpleRNN内置层,其关键参数说明:
● units: 正整数,输出空间的维度。
● activation: 要使用的激活函数。 默认:双曲正切(tanh)。 如果传入 None,则不使用激活函数 (即 线性激活:a(x) = x)。
● use_bias: 布尔值,该层是否使用偏置向量。
● kernel_initializer: kernel 权值矩阵的初始化器, 用于输入的线性转换 (详见 initializers)。
● recurrent_initializer: recurrent_kernel 权值矩阵 的初始化器,用于循环层状态的线性转换 (详见 initializers)。
● bias_initializer:偏置向量的初始化器 (详见initializers).
● dropout: 在 0 和 1 之间的浮点数。 单元的丢弃比例,用于输入的线性转换。
# 4.1 构建RNN模型
import keras
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense,LSTM,SimpleRNN
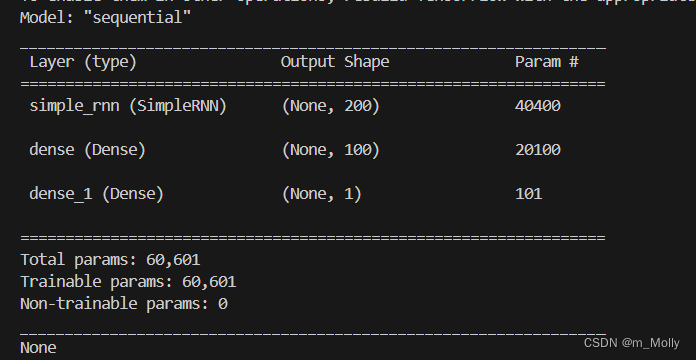
model = Sequential()
model.add(SimpleRNN(200, input_shape=(13,1), activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(100, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
print(model.summary())
四、训练和预测
#4.2 编译模型
opt = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=1e-4)
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
optimizer = opt,
metrics="accuracy")
# 4.3 训练模型
epochs = 100
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train,
epochs=epochs,
batch_size=128,
validation_data=(x_test,y_test),
verbose=1)
#4.4 评估模型
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
acc = history.history['accuracy']
val_acc = history.history['val_accuracy']
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
epochs_range = range(epochs)
plt.figure(figsize=(14,4))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.plot(epochs_range, acc, label='Training Acuuracy')
plt.plot(epochs_range, val_acc, label='Validation Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.title('Training & Validation Accuracy')
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.plot(epochs_range, loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(epochs_range, val_loss, label='Validation Losss')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.title('Training & Validation Loss')
plt.savefig("D:\\jupyter notebook\\DL-100-days\\RNN\\result.png")
plt.show()
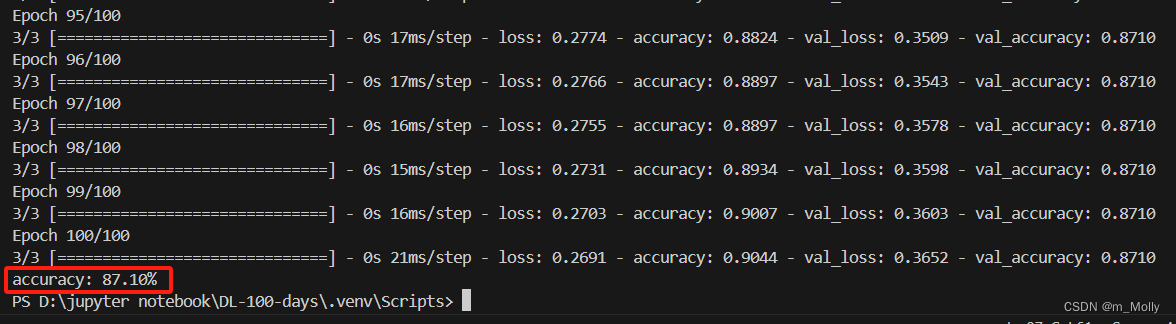
scores = model.evaluate(x_test,y_test,verbose=0)
print("%s: %.2f%%" % (model.metrics_names[1], scores[1]*100))
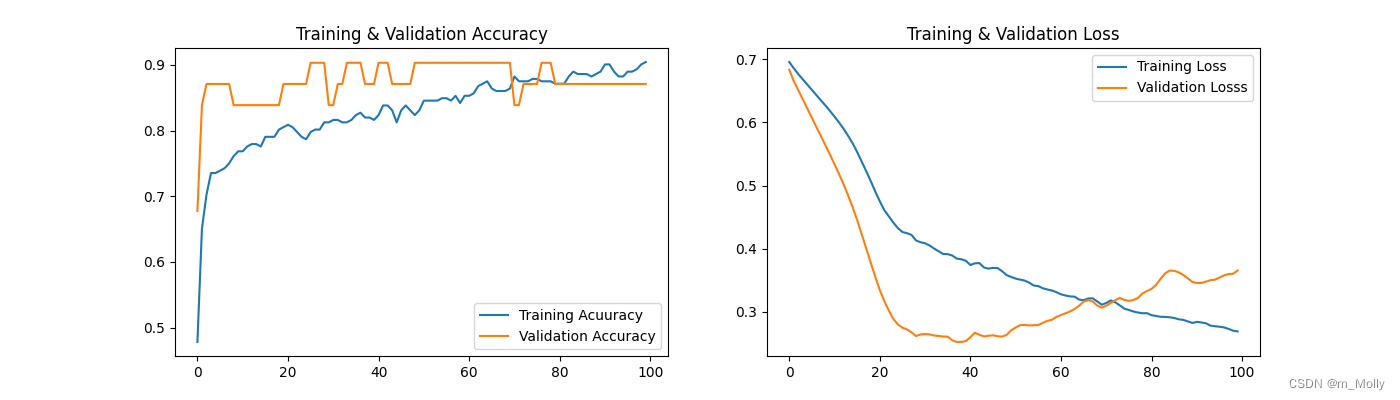
五、其他
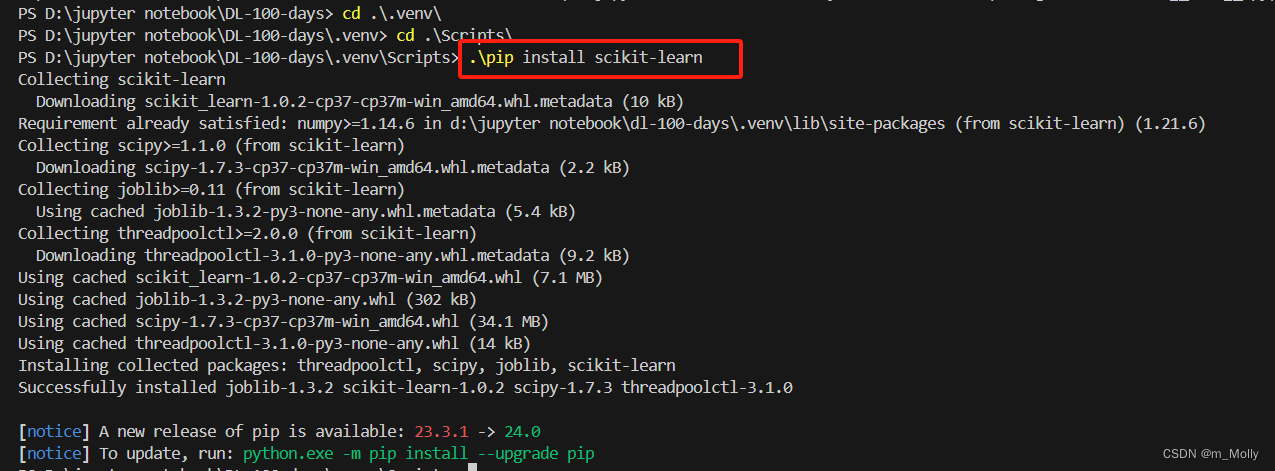
(1)sklearn模块导入报错:ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'sklearn'
解决办法:在VSCode终端中,cd到.venv/Script路径下,执行.\pip install scikit-learn,等待安装完成,如下:
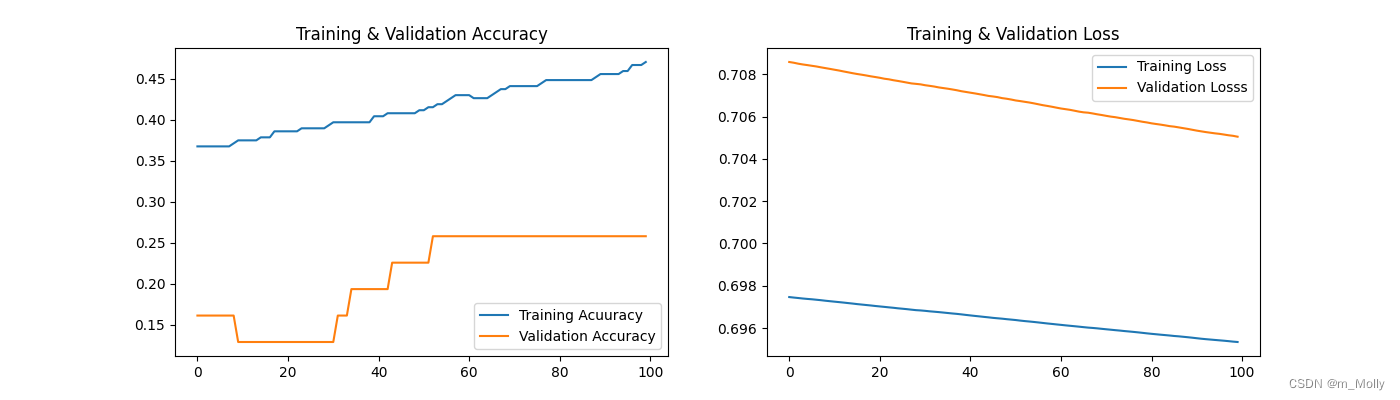
(2)优化器改为SGD,accuracy=25.81%

(3)使用训练acc最高的模型进行预测
观察100个epoch输出的训练结果,可以看到最高的val_accuracy=0.9032,可以把这次的模型保存出来,作为预测模型。
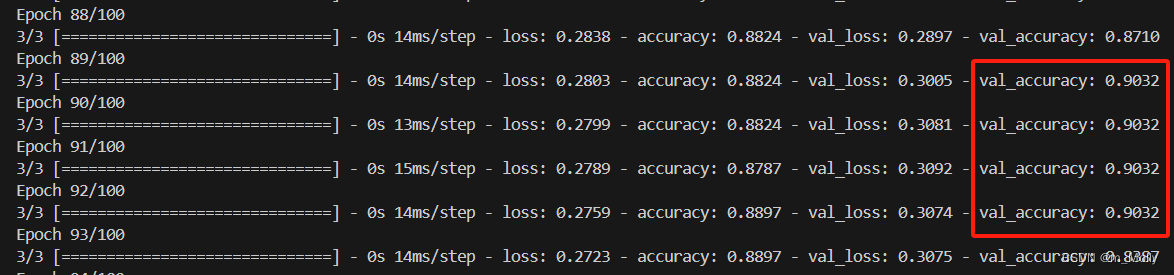
修改代码如下:
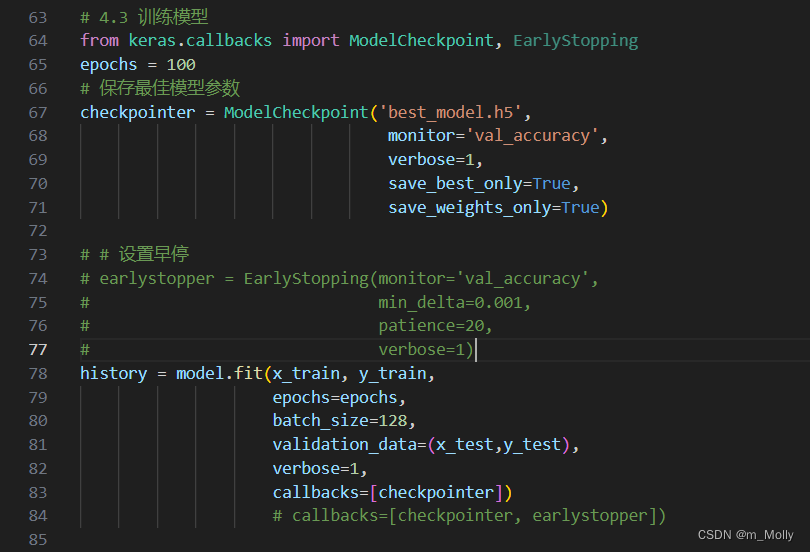
得到结果: