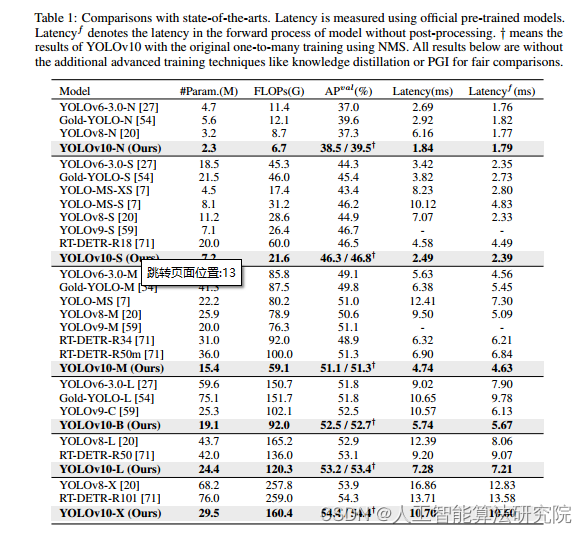
1.前言
2.剧情前透
在旧版本开发过程中,不难发现两个比较烦人的问题:
(1)设备号是静态分配的,需要我们去cat /proc/devices命令查看设备占用的设备ID号,看看哪些空闲的,而且还要看看 Documentation/devices.txt文档里面有没有占用的风险
(2)设备需要自己去创建,如:mknod /dev/chrdevbase c 200 0 创建设备节点。假如是动态分配的设备号,还得每一次通过cat /proc/devices命令查看设备占用的设备ID号,再通过mknod命令创建节点给应用层使用。
基于以上两个问题:本章就要解决这两个问题,自动分配管理设备号,自动创建设备文件。同时使用新的字符设备接口创建字符设备。
3.分配和释放设备号
3.1.没有指定设备号的申请函数
参数如:
dev:保存申请到的设备号。
baseminor:次设备号起始地址,
count:要申请的设备号数量。
name:设备名字。
使用注意:在调用之前,得通过devid = MKDEV(major, minor);生成设备ID。
3.2.给定了设备的主设备号和次设备号 的申请函数
3.3.释放设备号函数
3.4.申请函数的使用模板
int major; /* 主设备号 */
int minor; /* 次设备号 */
dev_t devid; /* 设备号 */
if (major) { /* 定义了主设备号 */
devid = MKDEV(major, minor); /* 大部分驱动次设备号都选择 0 minor可以直接给0 */
register_chrdev_region(devid, 1, "test");
} else { /* 没有定义设备号 */
alloc_chrdev_region(&devid, 0, 1, "test"); /* 申请设备号 */
major = MAJOR(devid); /* 获取分配号的主设备号 */
minor = MINOR(devid); /* 获取分配号的次设备号 */
}4.自动创建设备
4.1.自动创建设备介绍
4.2.创建和删除类
4.2.1.创建类
参数:
使用说明:
4.2.1.删除类
4.3.创建和删除设备
4.3.1.创建设备
4.3.2.删除设备
void device_destroy(struct class *class, dev_t devt)
参数 class 是要删除的设备所处的类
参数 devt 是要删除的设备号
5.新型字符设备接口
5.1.字符设备结构
struct cdev {
struct kobject kobj;
struct module *owner;
const struct file_operations *ops;
struct list_head list;
dev_t dev;
unsigned int count;
};5.2.cdev_init 函数
5.3.cdev_add 函数
int cdev_add(struct cdev *p, dev_t dev, unsigned count)
参数:
作用:cdev_add 函数用于向 Linux 系统添加字符设备(cdev 结构体变量)
5.4.cdev_del 函数
参数:
作用:cdev_del 函数从 Linux 内核中删除相应的字符设备
6.测试例子
6.1.驱动代码
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/ide.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <asm/mach/map.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#define newchr_CNT 1 /* 设备号个数 */
#define newchr_NAME "newchr" /* 名newchr */
/* newchr设备结构体 */
struct newchr_dev{
dev_t devid; /* 设备号 */
struct cdev cdev; /* cdev */
struct class *class; /* 类 */
struct device *device; /* 设备 */
int major; /* 主设备号 */
int minor; /* 次设备号 */
};
struct newchr_dev newchr; /* newchr设备 */
/*
* @description : 打开设备
* @param - inode : 传递给驱动的inode
* @param - filp : 设备文件,file结构体有个叫做private_data的成员变量
* 一般在open的时候将private_data指向设备结构体。
* @return : 0 成功;其他 失败
*/
static int newchr_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
filp->private_data = &newchr; /* 设置私有数据 */
return 0;
}
/*
* @description : 从设备读取数据
* @param - filp : 要打开的设备文件(文件描述符)
* @param - buf : 返回给用户空间的数据缓冲区
* @param - cnt : 要读取的数据长度
* @param - offt : 相对于文件首地址的偏移
* @return : 读取的字节数,如果为负值,表示读取失败
*/
static ssize_t newchr_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt)
{
printk("newchr_read \r\n");
return 0;
}
/*
* @description : 向设备写数据
* @param - filp : 设备文件,表示打开的文件描述符
* @param - buf : 要写给设备写入的数据
* @param - cnt : 要写入的数据长度
* @param - offt : 相对于文件首地址的偏移
* @return : 写入的字节数,如果为负值,表示写入失败
*/
static ssize_t newchr_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt)
{
int retvalue;
unsigned char databuf[1];
unsigned char newchrstat;
retvalue = copy_from_user(databuf, buf, cnt);
if(retvalue < 0) {
printk("kernel write fainewchr!\r\n");
return -EFAULT;
}
newchrstat = databuf[0]; /* 获取状态值 */
printk("newchr_write, %x\r\n", newchrstat);
return 0;
}
/*
* @description : 关闭/释放设备
* @param - filp : 要关闭的设备文件(文件描述符)
* @return : 0 成功;其他 失败
*/
static int newchr_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
printk("newchr_release \r\n");
return 0;
}
/* 设备操作函数 */
static struct file_operations newchr_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = newchr_open,
.read = newchr_read,
.write = newchr_write,
.release = newchr_release,
};
/*
* @description : 驱动出口函数
* @param : 无
* @return : 无
*/
static int __init newchr_init(void)
{
/* 注册字符设备驱动 */
/* 1、创建设备号 */
if (newchr.major) { /* 定义了设备号 */
newchr.devid = MKDEV(newchr.major, 0);
register_chrdev_region(newchr.devid, newchr_CNT, newchr_NAME);
} else { /* 没有定义设备号 */
alloc_chrdev_region(&newchr.devid, 0, newchr_CNT, newchr_NAME); /* 申请设备号 */
newchr.major = MAJOR(newchr.devid); /* 获取分配号的主设备号 */
newchr.minor = MINOR(newchr.devid); /* 获取分配号的次设备号 */
}
printk("newchenewchr major=%d,minor=%d\r\n",newchr.major, newchr.minor);
/* 2、初始化cdev */
newchr.cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
cdev_init(&newchr.cdev, &newchr_fops);
/* 3、添加一个cdev */
cdev_add(&newchr.cdev, newchr.devid, newchr_CNT);
/* 4、创建类 */
newchr.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, newchr_NAME);
if (IS_ERR(newchr.class)) {
return PTR_ERR(newchr.class);
}
/* 5、创建设备 */
newchr.device = device_create(newchr.class, NULL, newchr.devid, NULL, newchr_NAME);
if (IS_ERR(newchr.device)) {
return PTR_ERR(newchr.device);
}
return 0;
}
/*
* @description : 驱动出口函数
* @param : 无
* @return : 无
*/
static void __exit newchr_exit(void)
{
/* 注销字符设备驱动 */
cdev_del(&newchr.cdev);/* 删除cdev */
unregister_chrdev_region(newchr.devid, newchr_CNT); /* 注销设备号 */
device_destroy(newchr.class, newchr.devid);
class_destroy(newchr.class);
}
module_init(newchr_init);
module_exit(newchr_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("seven");
6.2.应用层测试代码
#include "stdio.h"
#include "unistd.h"
#include "sys/types.h"
#include "sys/stat.h"
#include "fcntl.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "string.h"
/*
* @description : main主程序
* @param - argc : argv数组元素个数
* @param - argv : 具体参数
* @return : 0 成功;其他 失败
*/
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int fd, retvalue;
char *filename;
unsigned char databuf[1];
if(argc != 3){
printf("Error Usage!\r\n");
return -1;
}
filename = argv[1];
/* 打开驱动的文件 */
fd = open(filename, O_RDWR);
if(fd < 0){
printf("file %s open failed!\r\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
databuf[0] = atoi(argv[2]); /* 要执行的操作:打开或关闭 */
/* 向drvier写入数据 */
retvalue = write(fd, databuf, sizeof(databuf));
if(retvalue < 0){
printf("drvier Control Failed!\r\n");
close(fd);
return -1;
}
retvalue = close(fd); /* 关闭文件 */
if(retvalue < 0){
printf("file %s close failed!\r\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
6.3.测试结果
加载驱动之后,会自动分配设备号,并且在/dev/下创建了设备节点newchr该节点。应用层就可以使用了。
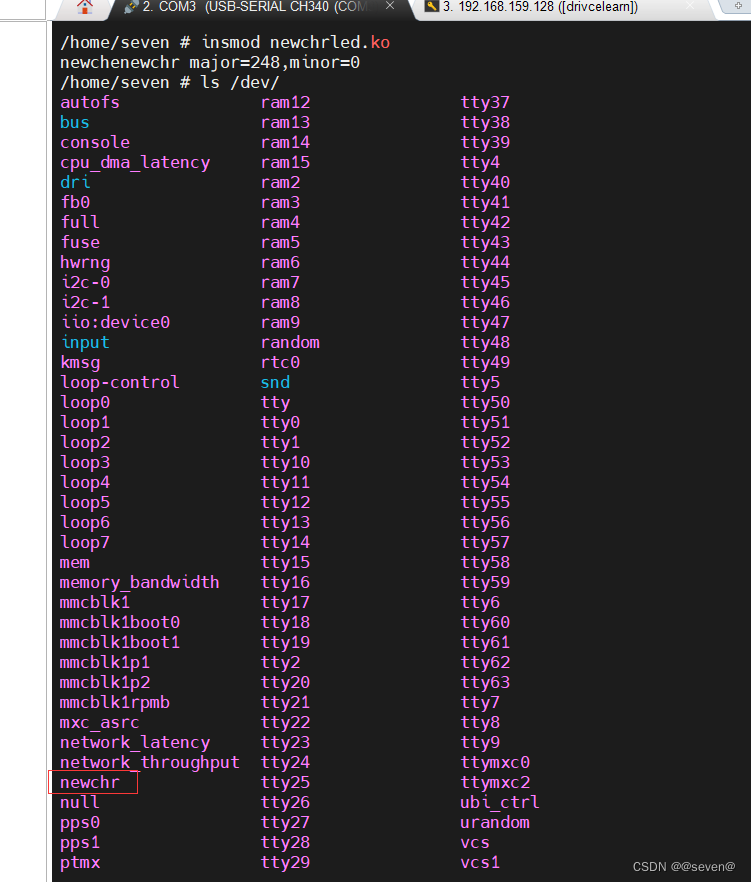
应用层操作/dev/newchr节点,符号预期效果。
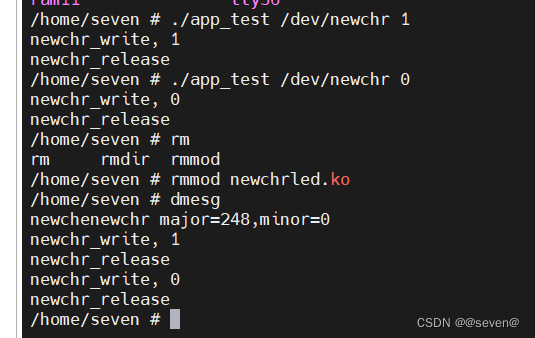
OK,到目前为止,简单字符设备已经创建完毕,下一篇,就要点灯了,点灯大师再现了。