来源:微信公众号:EW Frontier
简介
一种能够同时对信号时域和频域分析的方法——短时傅里叶变换(STFT),可以在时频二维角度准确地描述信号 的时间、频域的局部特性,与其他算法不同,通过该算法可以得到信号的瞬时频率随时间变化的变化规律,其在雷达信号的脉内 特征分析中的效果明显。本文根据仿真结果,对不同类型信号经短时傅里叶变换后的结果进行统计,形成了基于短时傅里叶变换 的雷达信号脉内特征自动识别流程,对电子侦察情报的获取及应用有重要的意义。
电子侦察面对的电磁环境越来越复杂,这意味着雷达 信号越来越复杂,也就是说雷达信号环境中常规脉冲雷达信 号使用的比例逐渐减小。因此,对线性调频、相位编码、非 线性调频、频率捷变等雷达信号的识别已成为不可忽视重要 环节,同时,高速地对这些信号进行自动识别也是发展的需 求。本文利用短时傅里叶变换对各种复杂信号进行脉内特征 分析,以探索脉内特征自动识别流程。
STFT主要原理
短时傅里叶变换公式为:
![]()
式(1)中,m(τ-t)为窗函数在时域窗函数取截信号, 窗函数滤波出来的局部时域数据作FFT,就是在τ时刻得 到该时域窗函数对应信号的傅里叶变换,设置不同的τ值, 窗函数的中心位置会不断移动,这样就得到了不同τ下该信 号的傅里叶变换,这些不同时刻傅里叶变换的集合就是Sx (ω,t)。
从式(1)可以发现,从形式上来看,傅里叶变换和短时傅里叶变换的区别仅在于时间域上少了一个窗函 数。短时傅里叶变换通过采用滑窗处理来弥补传统傅里叶 变换的不足之处。它能够对某一小段时间滑窗内的信号做 傅里叶变换,反映该信号的频域随时间变换的大致规律。 同时,短时傅里叶变换还保留了传统傅里叶变换较好的抗 干扰能力。仿真研究表明,若时域的滑窗时间越短,则变 换后的频率分辨率会越低;若滑窗时间延长,则时域的分 辨率就会降低,这是短时傅里叶变换在时域分辨率、频域 分辨率方面存在的矛盾。
MATLAB代码
function [t, f, S] = stft1(x,N,M,Nfft,Fs,win_type)
%STFT1 Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT) - Method I.
%
% [t, f, S] = stft1(x,N,M,Nfft,Fs,win_type) calculates the Short-Time Fourier Transform
% (STFT) or in other words the spectrogram of the input signal x.
%
% Inputs:
% x is a row vector that contains the signal to be examined.
% N is the selected length of the window in samples.
% M is the selected amount of overlap between successive windows in samples.
% Nfft is the selected number of DFT calculation points (Nfft>=N).
% Fs is the signal sampling frequency in Hz.
% win_type is a string containing one of the windows shown
% below. The default value of this variable corresponds to the rectangular window.
%
% Outputs: S is a matrix that contains the complex spectrogram of x.
% i.e. S(:,k) = fft(k-th frame) computed on Nfft points.
% f is a vector of frequency points in Hz where the spectrogram is calculated.
% t is a vector of time points in sec. Each point corresponds to a
% signal frame.
%
% Copyright 2020-2030, Ilias S. Konsoulas.
%% Window selection and contruction.
switch win_type
case 'cheby'
win = chebwin(N).';
case 'blackman'
win = blackman(N).';
case 'hamm'
win = hamming(N).';
case 'hann'
win = hanning(N).';
case 'kaiser'
beta = 5;
win = kaiser(N,beta).';
case 'gauss'
win = gausswin(N).';
otherwise % otherwise use the rectangular window
win = ones(1,N);
end
%% Input Signal Segmentation Params.
x = x(:).';
L = length(x);
% Number of segments (frames) the signal is divided to.
K = floor((L-M)/(N-M));
%% DFT Matrix Construction
n = 0:Nfft-1;
w = exp(-1i*2*pi*n/Nfft);
W = zeros(Nfft,Nfft);
for k=0:Nfft-1
W(:,k+1) = w.^k;
end
%% Number of Unique FFT Points.
NUPs = Nfft;
if isreal(x)
if mod(Nfft,2) % if N is odd.
NUPs = (Nfft+1)/2;
else % if N is even.
NUPs = Nfft/2+1;
end
end
%% Input Signal Segmentation (Framing)
X = zeros(N,K);
for k=1:K
X(:,k) = x((k-1)*(N-M)+1:k*N - (k-1)*M).*win;
end
X = vertcat(X,zeros(Nfft-N,K)); % Zero-Padding each frame.
%% DFT Calculation of all frames as a single matrix product.
S = W*X;
S = S(1:NUPs,:);
%% Frame Time Points
t = (N-1)/Fs + (0:K-1)*(N-M)/Fs; % Frame Time Points.
%% Frequency Points in Hz.
f = (0:NUPs-1)*Fs/Nfft;
%% NOTES:
% When K is an integer then the following equation holds:
% (N-1)*Ts + (K-1)*(N-M)*Ts = (L-1)*Ts = total signal duration in sec.
% or (N-1) + (K-1)*(N-M) = (L-1).% Short-Time Fourier Transform - Method I (Spectrogram) Demo.
% This demo shows how the custom function stft1.m and is used to
% to produce the spectrogram of an input signal.
% Copyright 2020 - 2030, Ilias S. Konsoulas.
%% Workspace Initialization.
clc; clear; close all;
%% Select and load the signal to be analyzed.
% load('chirp','Fs','y'); x = y;
% load('gong', 'Fs','y'); x = y;
% load timit2.asc; Fs = 8000; x = timit2;
% load('train','Fs','y'); x = y;
load('splat','Fs','y'); x = y;
% load('laughter','Fs','y'); x = y;
% [x Fs] = audioread('andean-flute.wav');
%% Play Back the selected audio signal:
soundsc(x,Fs,24);
%% Signal Normalization.
x = x.'/max(abs(x));
%% STFT Parameters.
L = length(x);
N = 512; % Selected window size.
M = 450; % Selected overlap between successive segments in samples.
Nfft = 512; % Selected number of FFT points.
[t,f,S] = stft1(x,N,M,Nfft,Fs,'hamm');
%% Plot the Spectrogram.
h = figure('Name','STFT - Method I Demo');
colormap('jet');
[T,F] = meshgrid(t,f/1000); % f in KHz.
surface(T,F,10*log10(abs(S.^2) + eps),'EdgeColor','none');
axis tight;
grid on;
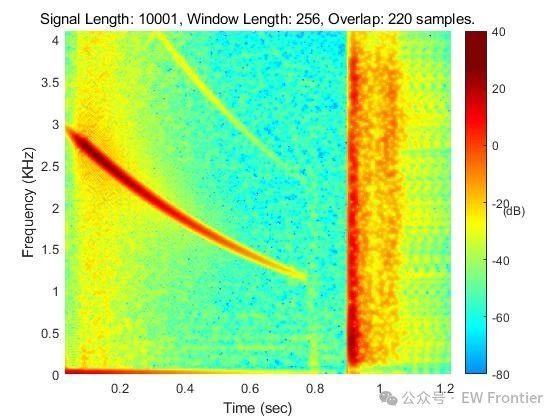
title(['Signal Length: ',num2str(L),', Window Length: ', num2str(N),', Overlap: ', num2str(M), ' samples.']);
xlabel('Time (sec)');
ylabel('Frequency (KHz)');
colorbar('Limits',[-80, 40]);
cbar_handle = findobj(h,'tag','Colorbar');
set(get(cbar_handle,'YLabel'),'String','(dB)','Rotation',0);
zlim([-80 40]);MATLAB仿真结果