✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅
✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨
🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿
🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟
🌟🌟 追风赶月莫停留 🌟🌟
🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀
🌟🌟 平芜尽处是春山🌟🌟
🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟
🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿
✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨
✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅
🍋vector类
- 🍑vector介绍
- 🍑vector迭代器
- 🍑vector构造
- 🍍无参构造
- 🍍有参构造
- 🍑vector常用接口
- 🍍 size()
- 🍍capacity()
- 🍍empty()
- 🍍resize()
- 🍍reserve()
- 🍑vector增删查改
- 🍍push_back()
- 🍍pop_back()
- 🍍insert()
- 🍍erase()
- 🍍swap()
- 🍍operator[]
🍑vector介绍
-
vector是表示可变大小数组的序列容器,和我们在C语言中学习的顺序表相类似
-
vector的存储形式和数组一样,采用连续的空间存储,vector也可以用下标进行访问,但有一点和数组不同,vector空间满了,它的大小是变化的,空间满了,容器会自动扩容。
-
每当一个新的元素加入时,为了增加存储空间,vector并不会重新分配空间,而是会重新开辟一个新的vector容器,然后全部数据存储到新的vector。
-
vector相较于其它容器,它访问元素效率更高,末尾添加和删除元素相对高效。对于其它不在末尾的删除和插入操作,效率更低。
vector容器和容器string的功能相类似,增删查改都差不多,不过唯一需要注意的是使用vector容器是需要带类型,而string 不需要带类型。
🍑vector迭代器

迭代器我们掌握前面四种就可以了。
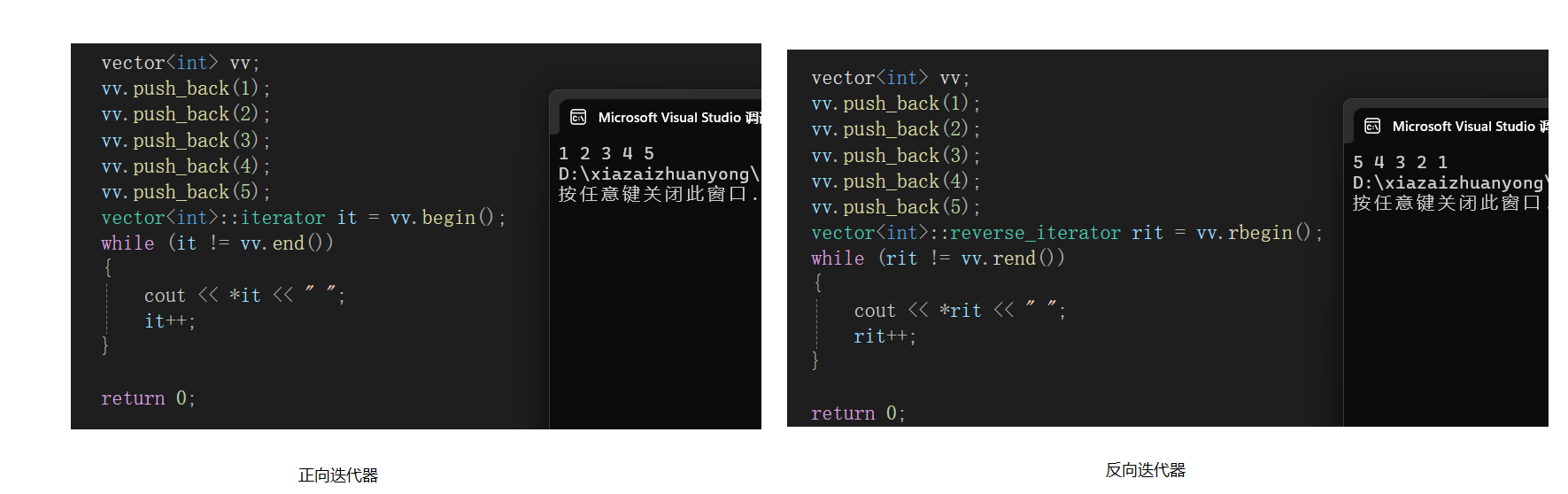
begin()和end()是正向迭代器iterator, rbegin()和rend()是反向迭代器reverse_iterator.

这幅图简单的说明了迭代器的基本使用。
用遍历来演示迭代器的用法:
vector<int> vv;
vv.push_back(1);
vv.push_back(2);
vv.push_back(3);
vv.push_back(4);
vv.push_back(5);
vector<int>::iterator it = vv.begin();
while (it != vv.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
🍑vector构造
🍍无参构造
vector<int> vv;
vector<char> cc;
vector<long long> aa;
vector<string> bb;
......
上面就是几种常见的无参构造,当然不仅仅只有这些。
vector类带的类型也可以是容器。
🍍有参构造
vector<int> vv(2,100);
vector<char> cc(2,'a');
vector<long long> aa(3,3.50);
vector<string> bb(2,"hello world");
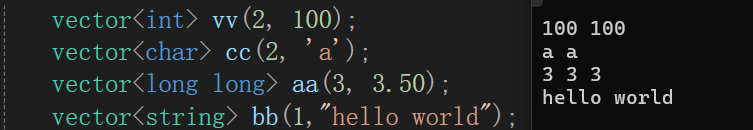
从结果可以看到vector的有参构造和string差不多,但是vector必须要带次数,也就是vector的有参构造,类型为(int, void) 。
还有一种有参构造,就是利用迭代器进行有参构造
vector<int> vv(2,100);
vector<int> aa(vv.begin(), vv.end());

🍑vector常用接口
🍍 size()
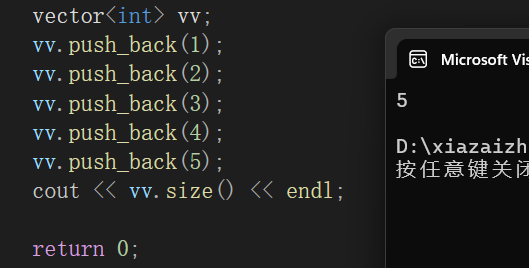
size():获取数据个数
vector<int> vv;
vv.push_back(1);
vv.push_back(2);
vv.push_back(3);
vv.push_back(4);
vv.push_back(5);
cout << vv.size() << endl;
🍍capacity()
capacity(): 获取空间容量大小
🍍empty()
empty(): 判断是否为空,返回的是布尔值
vector<int> vv;
cout << vv.empty() << endl;
vv.push_back(1);
cout << vv.empty() << endl;

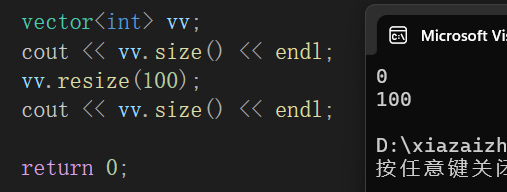
🍍resize()
resize():改变vector的数据大小
vector<int> vv;
cout << vv.size() << endl;
vv.resize(100);
cout << vv.size() << endl;
🍍reserve()
reserve():改变vector空间容量的大小
vector<int> vv;
cout << vv.capacity() << endl;
vv.reserve(100);
cout << vv.capacity() << endl;

🍑vector增删查改
🍍push_back()
push_back():对vector进行尾插
vector<int> vv;
vv.push_back(1);
vv.push_back(2);
for (auto in : vv)
{
cout << in << " ";
in++;
}
cout << endl;
vv.push_back(7);
for (auto in : vv)
{
cout << in << " ";
in++;
}
cout << endl;
vv.push_back(1);
vv.push_back(2);
for (auto in : vv)
{
cout << in << " ";
in++;
}

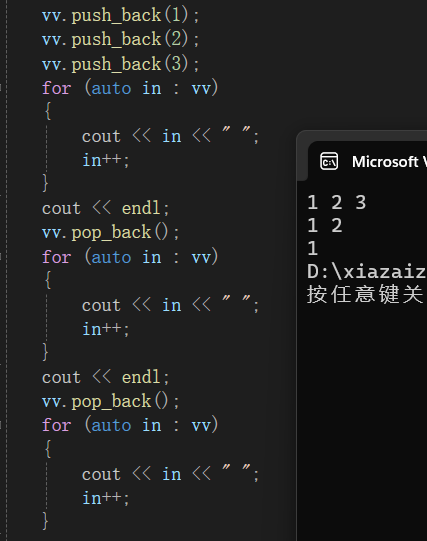
🍍pop_back()
pop_back():对vector进行尾删。
vector<int> vv;
vv.push_back(1);
vv.push_back(2);
vv.push_back(3);
for (auto in : vv)
{
cout << in << " ";
in++;
}
cout << endl;
vv.pop_back();
for (auto in : vv)
{
cout << in << " ";
in++;
}
cout << endl;
vv.pop_back();
for (auto in : vv)
{
cout << in << " ";
in++;
}
🍍insert()
insert():对vector,进行插入操作。
vector<int> vv;
vv.push_back(1);
vv.push_back(2);
vv.push_back(3);
vv.insert(vv.begin(), 44);
vv.insert(vv.end(), 99);
for (auto in : vv)
{
cout << in << " ";
}
cout << endl;

在vector中pos位置前进行插入,这幅图中vv.begin()和vv.end()代表pos。
🍍erase()
erase():对vector进行删除操作。
vector<int> vv;
vv.push_back(1);
vv.push_back(2);
vv.push_back(3);
for (auto in : vv)
{
cout << in << " ";
}
cout << endl;
vv.erase(vv.begin());
for (auto in : vv)
{
cout << in << " ";
}
cout << endl;

在vector中pos位置进行删除,vv.begin()代表的就是pos位置
🍍swap()
swap():对两个vector内容进行交换。
vector<int> vv(4, 99);
vector<int> aa(5, 1);
for (auto in : vv)
{
cout << in << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (auto in : aa)
{
cout << in << " ";
}
cout << endl;
swap(vv, aa);
for (auto in : vv)
{
cout << in << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (auto in : aa)
{
cout << in << " ";
}
cout << endl;

🍍operator[]
operator[]:让vector可以像数组一样可以对下标进行访问。
vector<int> vv;
vv.push_back(1);
vv.push_back(2);
vv.push_back(3);
vv.push_back(4);
for (int i = 0; i < vv.size(); i++)
{
cout << vv[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;

关于本章知识点如果有不足或者遗漏,欢迎大家指正,谢谢!!!



![Python文件和数据格式化-课后作业[python123题库]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/1be40852a0caba3091679c4b5aac260a.png)