目录
一,MVC定义
二,SpringMVC的基本使用
2.1建立连接 - @RequestMapping("/...")
编辑
2.2请求
1.传递单个参数
2.传递多个参数
3.传递对象
4.参数重命名
5.传递数组
6. 传递集合
7.传递JSON数据
8. 获取url中数据
9. 传递文件
10.获取Cookie
11.获取session
12.获取header
编辑
2.3响应
1.返回静态页面
2.返回html片段
3. 返回JSON
4.设置状态码
5.设置Header
一,MVC定义
MVC,英文名Model-View-Controller,是软件工程中的一种软件架构模式。MVC模式分离了应用程序的数据访问,用户界面,和处理逻辑。
- Model(模型):模型是用来处理数据和业务逻辑,在MVC 模式中,模型与视图是分离的,模型并不知道视图的存在。
- View(视图):视图是用户看到和交互的界面,例如网页,窗口等。视图通常是动态生成的。
- Controller(控制器):控制器接收用户的请求,并调用模型和视图去完成用户的需求。控制器本身不输出任何东西和做任何处理,它只是接收请求并决定调用哪个模型构件和哪个视图来处理请求。
二,SpringMVC的基本使用
学习Spring MVC 就是学习如何通过浏览器和用户程序进行交互,主要分为一下三个方面:
- 建立连接:将浏览器于Java程序连接起来,就是访问一个网址能调用Spring程序
- 接收请求:用户请求可能会带一些参数,要学会在程序中接收这些参数
- 返回响应:直接完业务逻辑后,要将程序运行的结果返回给用户
2.1建立连接 - @RequestMapping("/...")
@RequestMapping 注解是用来注册接口的路由映射的。表示服务接收到请求时,路径为 /... 的请求会调用对应的方法。
该注释既可以修饰方法也可以修饰类,如果两者同时加注释的话,它的访问地址就是 类路径 + 方法路径,举个例子:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class Test {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String test1(){
return "hello world!";
}
}
//这里的路径是指:类路径(/test)+ 方法路径(/hello)@RequestMapping注释既支持post请求也支持get请求,也可以限定只支持其中一个请求方式,代码如下:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class Test {
//如果只有一个参数,就会默认赋值给value这个属性,如果有多个参数,就需要属性名 = ...
//此处表示只支持post请求
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String test1(){
return "hello world!";
}
}2.2请求
一般的参数名要与请求中给的数据一致
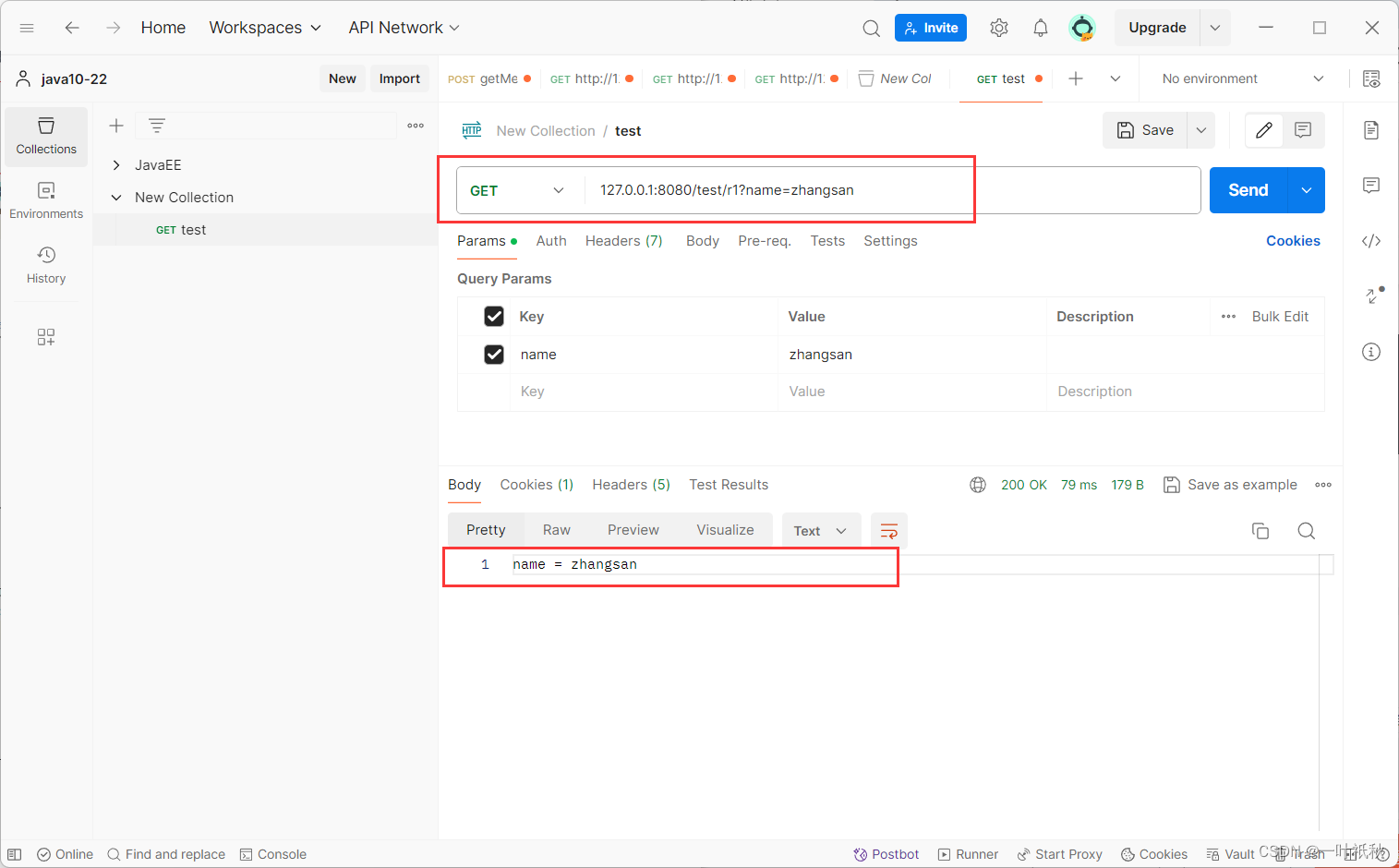
1.传递单个参数
@RequestMapping("/r1")
public String r1(String name){
return "name = " + name;
}
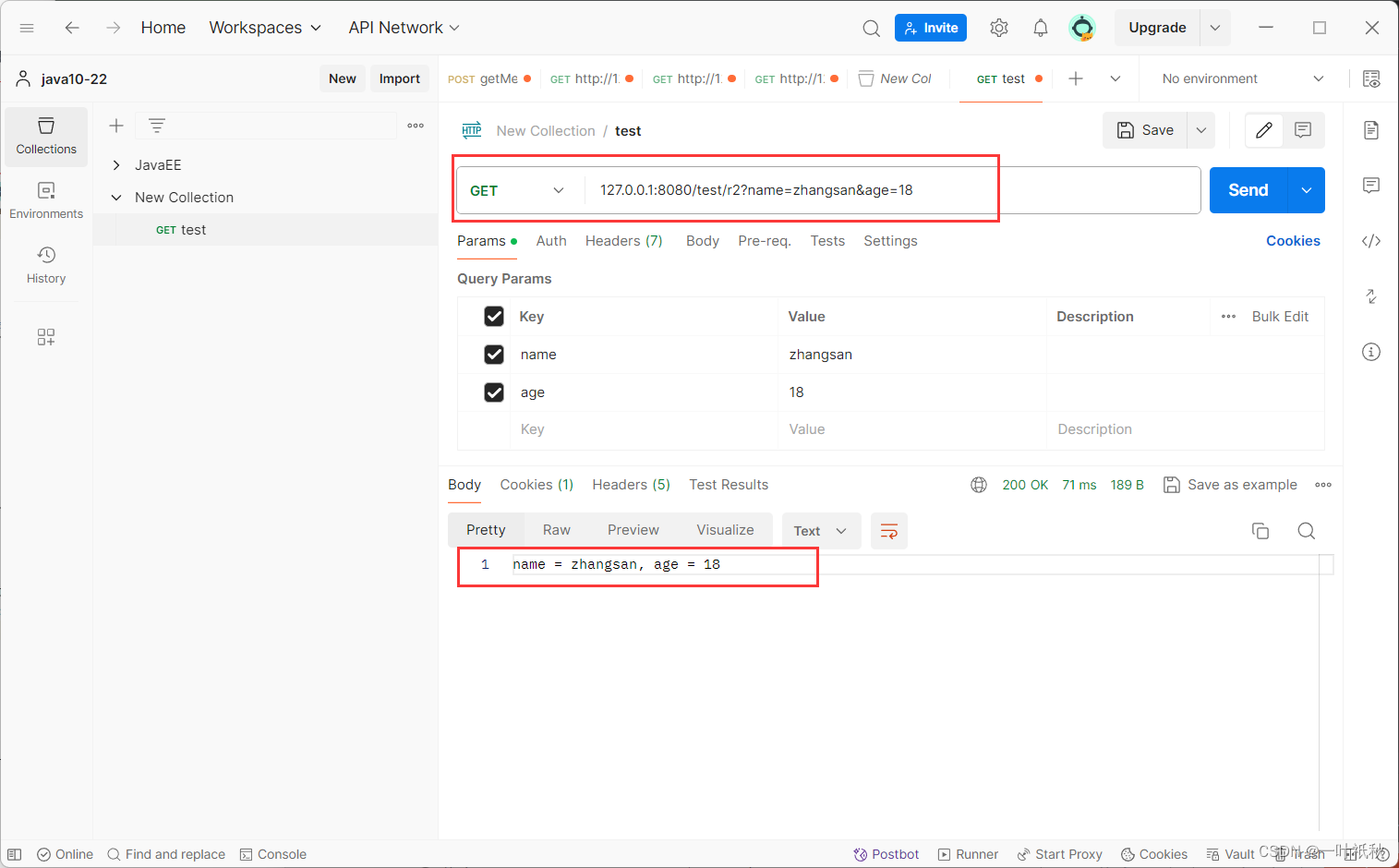
2.传递多个参数
@RequestMapping("/r2")
public String r2(String name, Integer age){
return "name = " + name+", age = " + age;
}
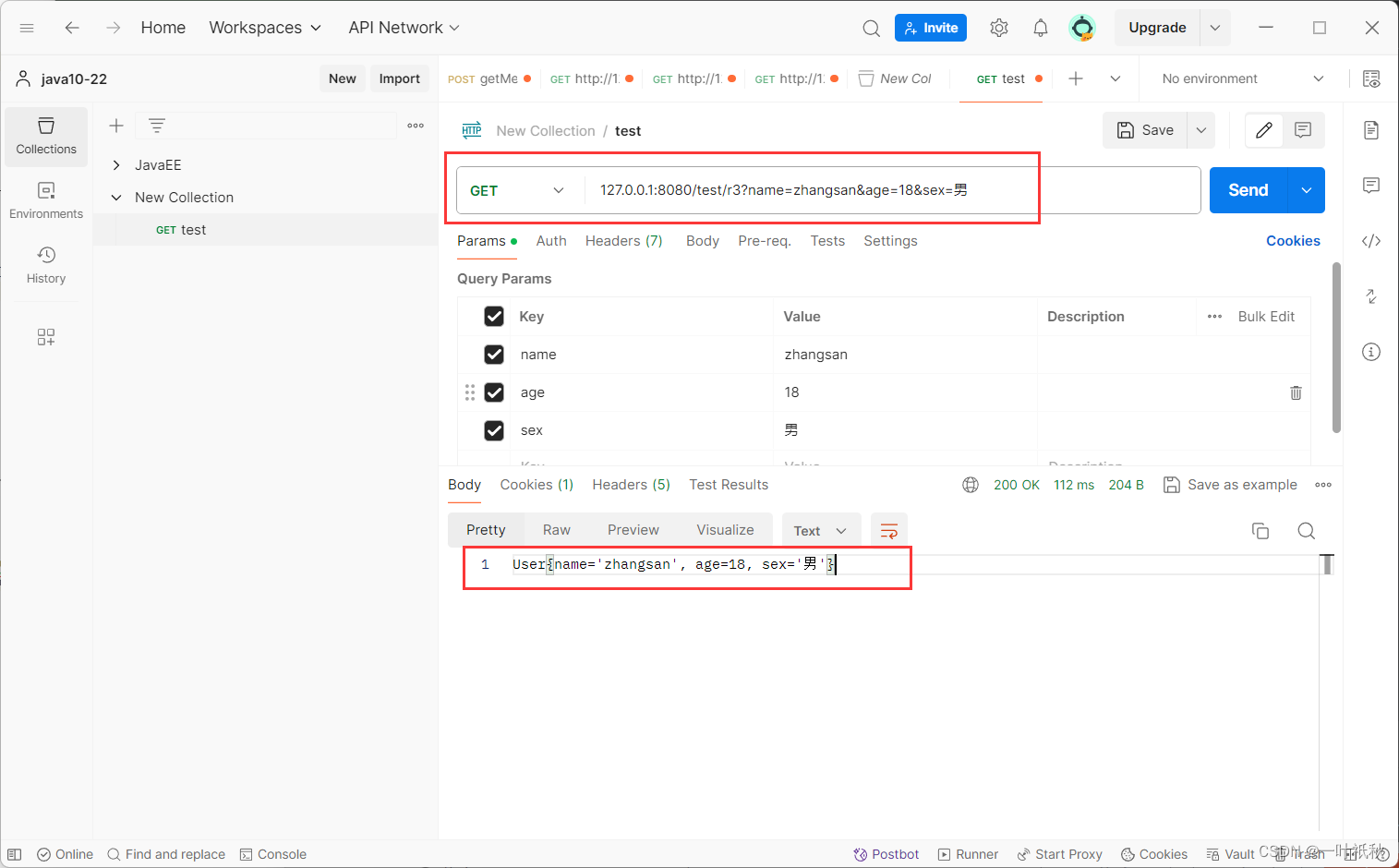
3.传递对象
@RequestMapping("/r3")
public String r3(User user){
//User是单独创建的一个对象,需要有构造方法和get()
return user.toString();
}
4.参数重命名
当请求中的给的名称与参数名不一致时,可以使用 @RequestParam注解
@RequestMapping("/r4")
public String r4(@RequestParam("name") String username, Integer age){
return "name = " + username+", age = " + age;
}
使用@RequestParam注解还有一点需要注意:它修饰的参数默认是必须传值的,如果没有传值,就会报错。当然也可以设置为非必传,代码如下:
@RequestMapping("/r4")
public String r4(@RequestParam(value = "name", required = false) String username, Integer age){
return "name = " + username+", age = " + age;
}5.传递数组
@RequestMapping("/r5")
public String r5(int[] arr){
return Arrays.toString(arr);
}有两种请求方式 :
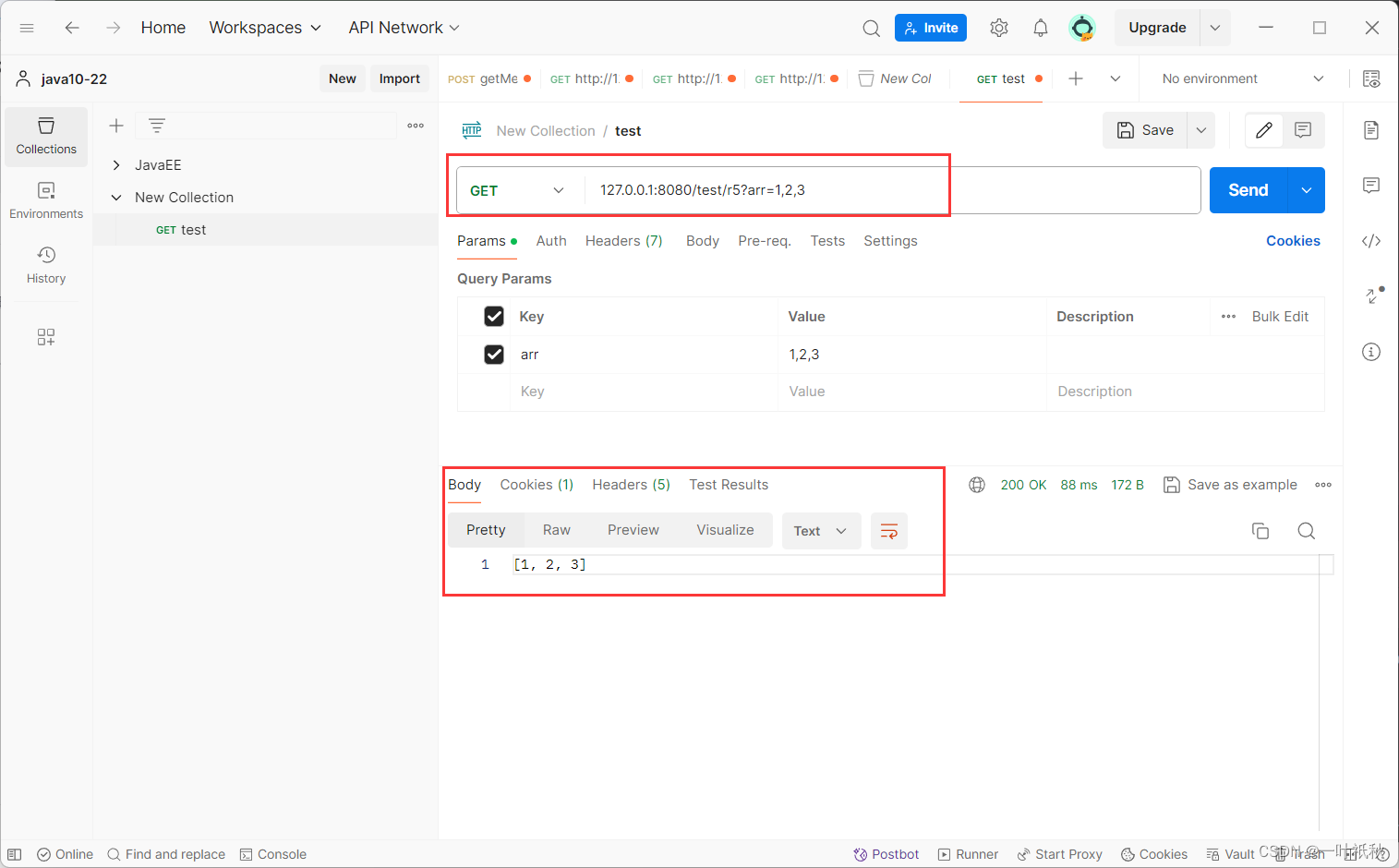
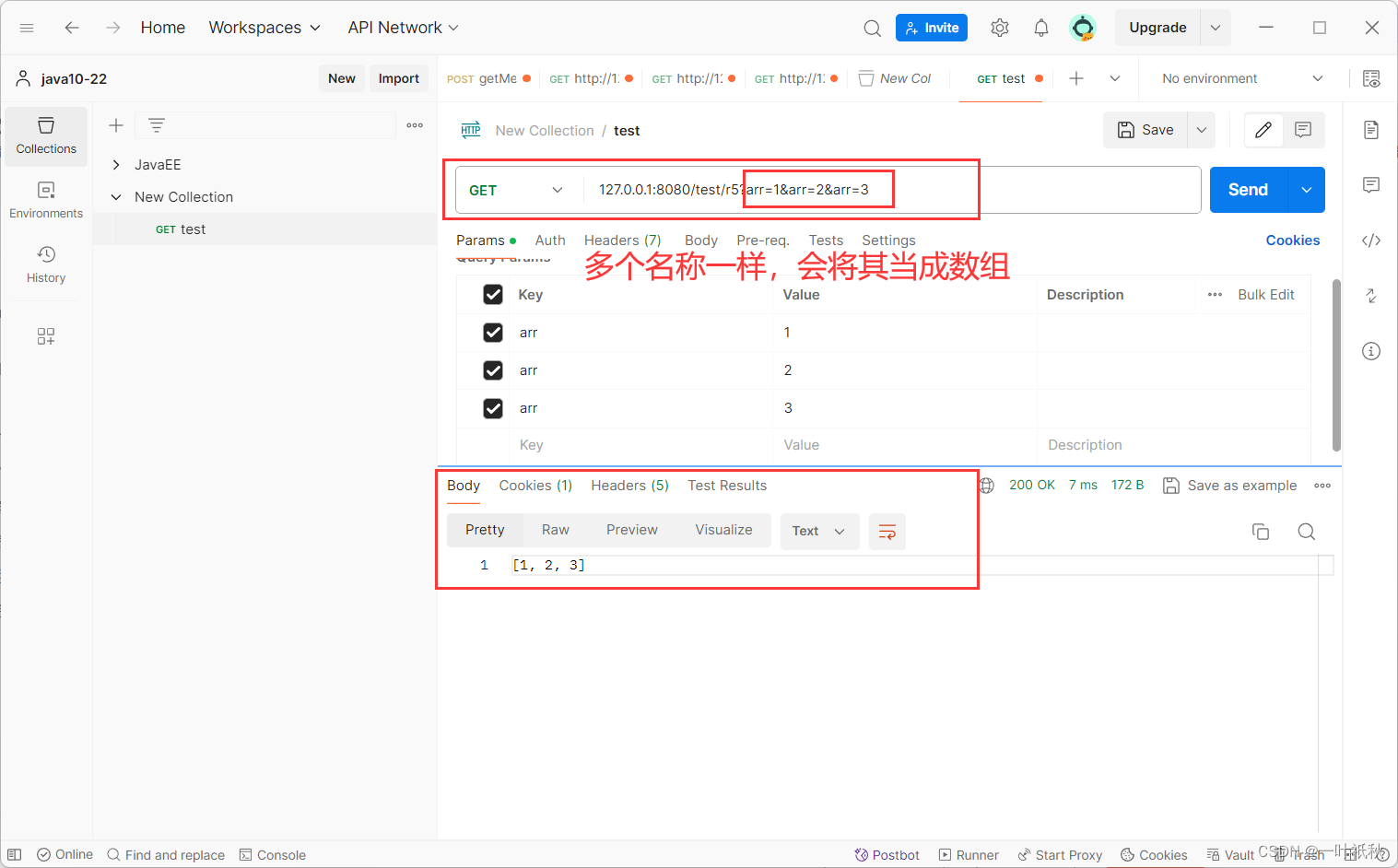
6. 传递集合
@RequestMapping("/r6")
public String r6(@RequestParam List<Integer> lst){
return lst.toString();
}7.传递JSON数据
@RequestMapping("/r7")
public String r7(@RequestBody User user){
return user.toString();
}
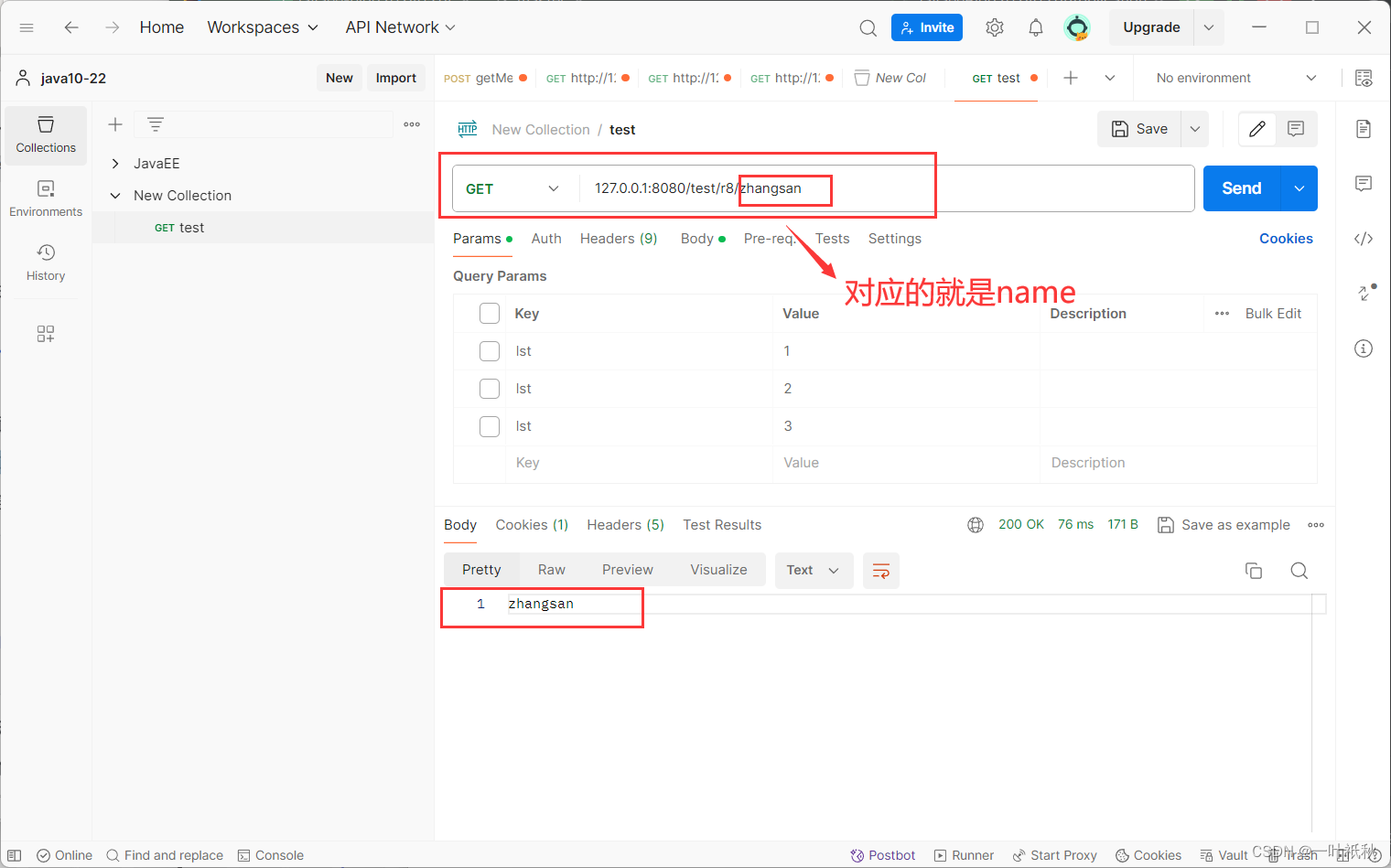
8. 获取url中数据
这里需要使用@PathVariable,该注释主要作用在url路径的数据绑定上,即默认参数写在url上。该注释也可以设置成非必传,但是一般都是默认的。
@RequestMapping("/r8/{name}")
public String r8(@PathVariable String name){
return name;
}
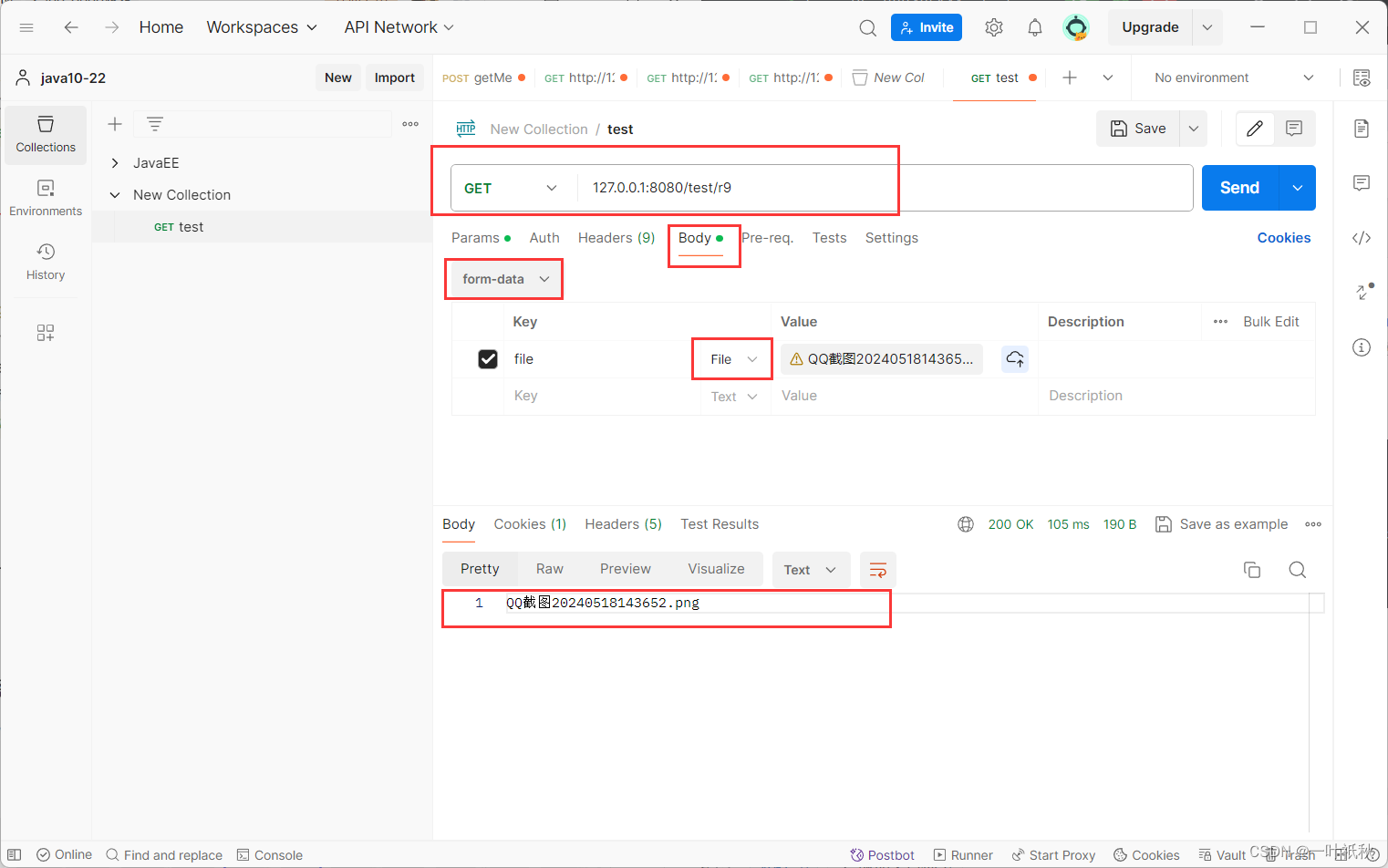
9. 传递文件
@RequestMapping("/r9")
public String r9(@RequestPart MultipartFile file) throws IOException {
String filename = file.getOriginalFilename();//获取文件名
file.transferTo(new File("D:/二次元/"+filename));//将文件上传到指定的路径
return filename;
}
10.获取Cookie
@RequestMapping("/r10")//这里的两个参数,是spring内置的,用到的时候可以直接加上
public String r10(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
}
//获取cookie的第一种写法,能得到所有的cookie
@RequestMapping("/r10")
public String r10(HttpServletRequest request) {
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
String res = "";
for(Cookie x : cookies){
res = res + x.getName() + ":" + x.getValue();
}
return res;
}
//第二种写法,获取名为Cookie_2对应value
@RequestMapping("/r11")
public String r11(@CookieValue("Cookie_2") String value) {
return value;
}11.获取session
//三种方式都行
@RequestMapping("/r12")
public String r12(HttpServletRequest request) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
String username = (String)session.getAttribute("username");
return username;
}
@RequestMapping("/r13")
public String r13(HttpSession session) {
String username = (String)session.getAttribute("username");
return username;
}
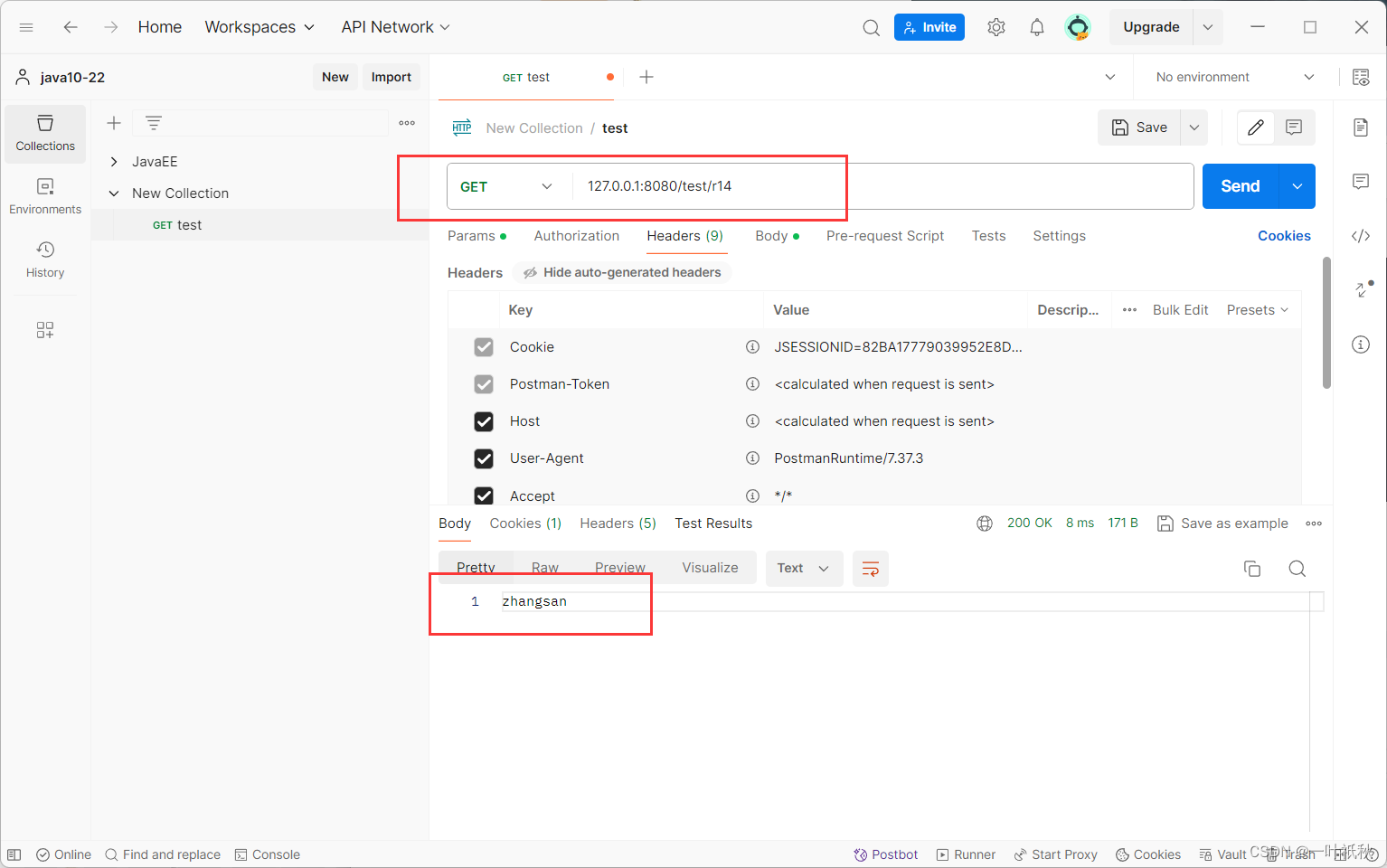
@RequestMapping("/r14")
public String r14(@SessionAttribute("username") String name) {
return name;
}
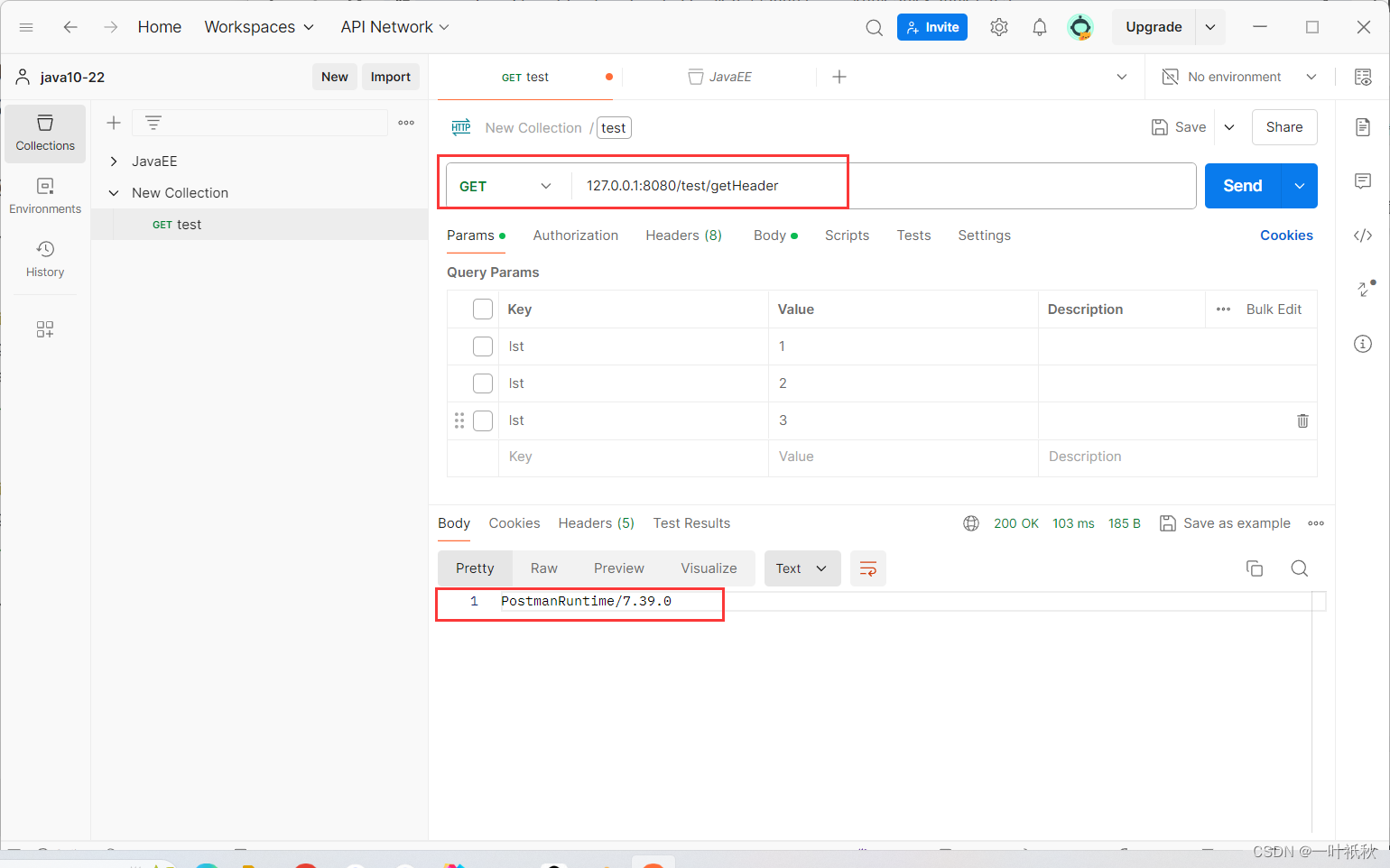
12.获取header
@RequestMapping("/getHeader")
public String getHeader(HttpServletRequest request){
//请求头中的数据是以键值对的形式存储,所以和map的用法差不多
String userAgent = request.getHeader("User-Agent");
return userAgent;
}
@RequestMapping("/getHeader2")
public String getHeader2(@RequestHeader("User-Agent") String userAgent){
return userAgent;
}2.3响应
1.返回静态页面
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class Demo {
@RequestMapping("/r1")
public String r1(){
return "/index.html";
}
}
这里需要讲解一下@RequestController注解与@Controller注解的区别,先看一下它们的源码:
//@Controller
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})//表示能作用的目标(比如:类,方法)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//表示生命周期
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Controller {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Component.class
)
String value() default "";
}//@ResquestController
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Controller
@ResponseBody
public @interface RestController {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Controller.class
)
String value() default "";
}我们可以发现,@RequestController = @Controller + @ResponseBody,而@Controller注释只负责告诉Spring帮我们管理哪些程序,所以关键是@ResponsBody注释,它的作用是保证返回的一定是数据,如果不加该注释,那么默认返回的是一个网页。
@ResponsBody注解既可以修饰类,也可以修饰方法,修饰类,那么该类中的所有方法都返回数据;修饰方法,表示该方法返回的数数据,当一个类中的方法既要返回数据也要返回页面时,要给该类使用@Controller注解,再给返回数据的方法加上@ResponseBody注解。
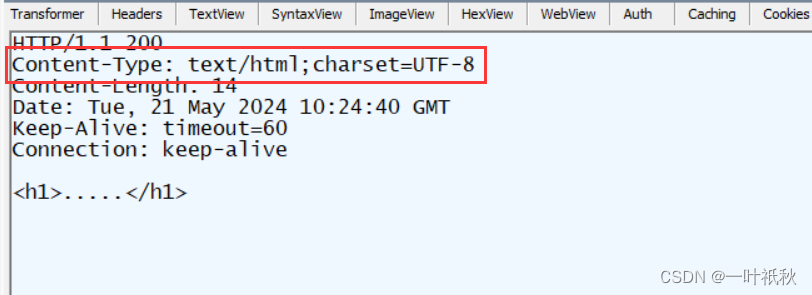
2.返回html片段
直接返回数据,spring会根据返回的结果,动态设置response的content-type
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/r2")
public String r2(){
return "<h1>.....</h1>";
}
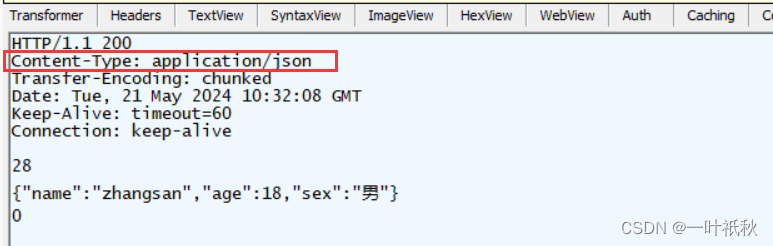
3. 返回JSON
类和哈希都会自动转换成 json格式来返回
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/r3")
public User r3(){
User user = new User();
user.setName("zhangsan");
user.setAge(18);
user.setSex("男");
return user;
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/r4")
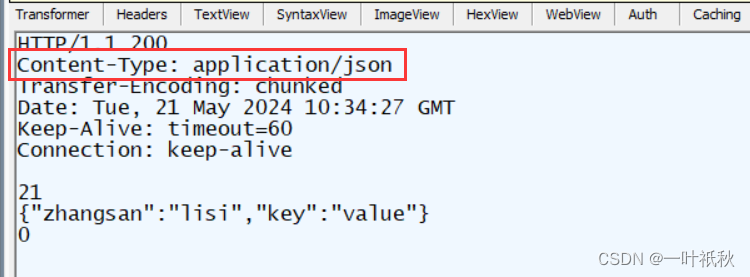
public Map<String, String> r4(){
HashMap map = new HashMap();
map.put("key", "value");
map.put("zhangsan", "lisi");
return map;
}
4.设置状态码
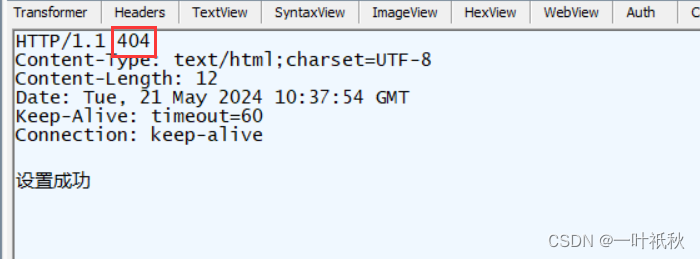
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/r7")
public String r7(HttpServletResponse response){
response.setStatus(404);
return "设置成功";
}
5.设置Header
Http响应报头也会向客户端传递一些信息,比如服务程序的名称,请求资源已移动到新地址等,如:Content-Type,Local等。这些信息通过@RequestMapping注解来实现,先看看它的源码:
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Mapping
public @interface RequestMapping {
String name() default "";
@AliasFor("path")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] path() default {};
RequestMethod[] method() default {};
String[] params() default {};
String[] headers() default {};
String[] consumes() default {};
String[] produces() default {};
}
- value:指映射的URL
- method:指请求的method类型,比如:post,get,put...
- consumes:指处理请求(request)的提交内容类型(Content-Type)
- produces:指返回提交内容类型,仅当request请求头中的Accept类型包含该指定类型才返回
- params:request中必须包含某参数值时,才让该方法处理
- header:request中必须包含某指定的header参数值时,才让该方法处理
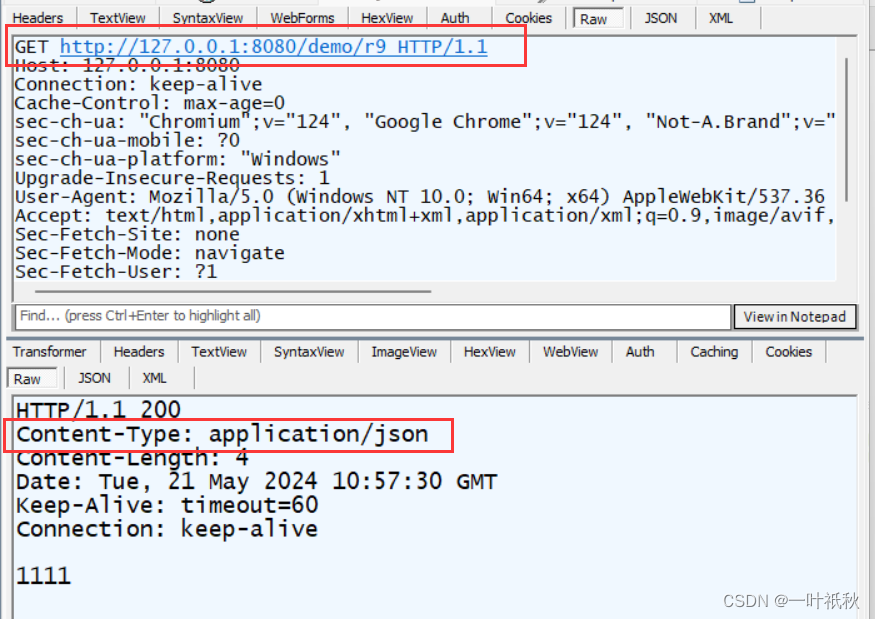
设置Content-Type
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "/r9",produces = "application/json")
public String r9(){
return "1111";
}
自定义Header:这里的key和value是可以自己随意指定的
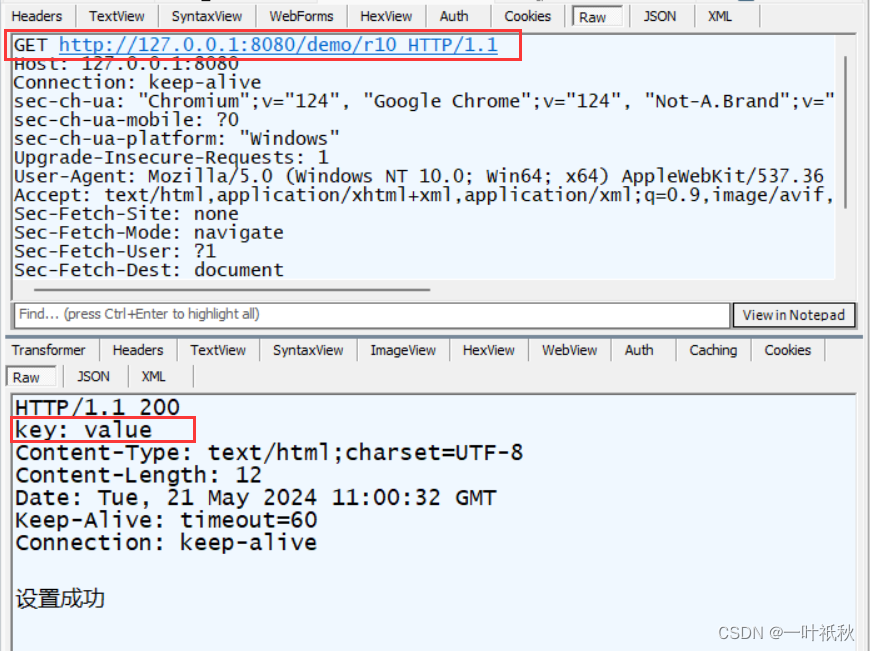
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/r10")
public String r10(HttpServletResponse response) {
response.setHeader("key","value");
return "设置成功";
}