Tips:"分享是快乐的源泉💧,在我的博客里,不仅有知识的海洋🌊,还有满满的正能量加持💪,快来和我一起分享这份快乐吧😊!
喜欢我的博客的话,记得点个红心❤️和小关小注哦!您的支持是我创作的动力!数据源存放在我的资源下载区啦!
Linux程序开发(六):进程编程和系统日志守护进程
目录
- Linux程序开发(六):进程编程和系统日志守护进程
- 1. 编程题(任选3道)
- 1.1. 编写一个程序,创建两个子进程,父进程在屏幕上输出“I am parent process.”,两个子进程分别输出” I am child process 1.”、” I am child process 2.”,要求父进程在两个子进程输出完字符后再输出自己的字符。
- 1.2. 父进程创建3个子进程,3个子进程需要打开文件a.txt并写入字符串,要求字符串能表明身份同时写明自己的进程号,最后父进程需要在该文件里面写入“I am father process, mypid is”+进程号。要求不能产生僵尸进程。
- 1.3. 有爷爷爸爸孙子三人一起工作,前两秒三人一起休息讨论工作,之后爷爷每2秒休息一次,爸爸每4秒休息一次,儿子每6秒休息一次,请按照关系创建父子进程,每人每次休息时都打印他的身份、进程pid以及当前时间,工作时间为18s。
- 1.4. 编写程序让两个子进程交替判断一个范围内的整数是不是素数。运行程序时要输入两个参数,一个是左边界,一个是右边界。比如说判断100到200之间哪些是素数,子进程1判断100是不是素数,子进程2判断101是不是素数,子进程1再判断102是不是素数,子进程2判断103是不是素数...,一直轮流下去。
- 1.5. 仿照讲义中的“系统日志守护进程”例子,写一个守护进程,每隔一段时间获取当前登录用户名,将获取到的信息加上当前时间写入系统日志。
1. 编程题(任选3道)
1.1. 编写一个程序,创建两个子进程,父进程在屏幕上输出“I am parent process.”,两个子进程分别输出” I am child process 1.”、” I am child process 2.”,要求父进程在两个子进程输出完字符后再输出自己的字符。
编写c语言程序processes.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
pid_t child1, child2;
child1 = fork(); // 创建第一个子进程
if (child1 == 0) {
// 子进程1
printf("I am child process 1.\n");
} else {
child2 = fork(); // 在父进程中创建第二个子进程
if (child2 == 0) {
// 子进程2
printf("I am child process 2.\n");
} else {
// 等待两个子进程结束
wait(NULL);
wait(NULL);
// 父进程
printf("I am parent process.\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
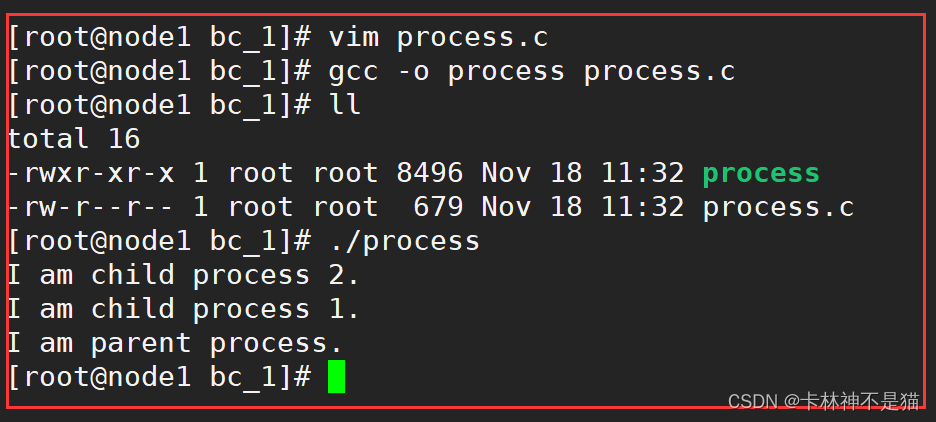
使用gcc编译器进行程序编译
gcc -o process process.c
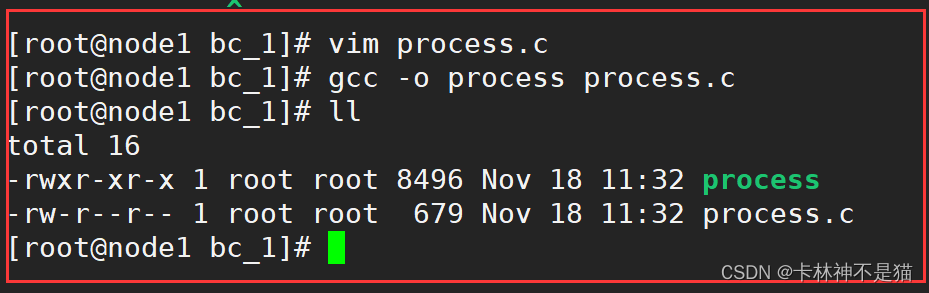
运行程序
./process
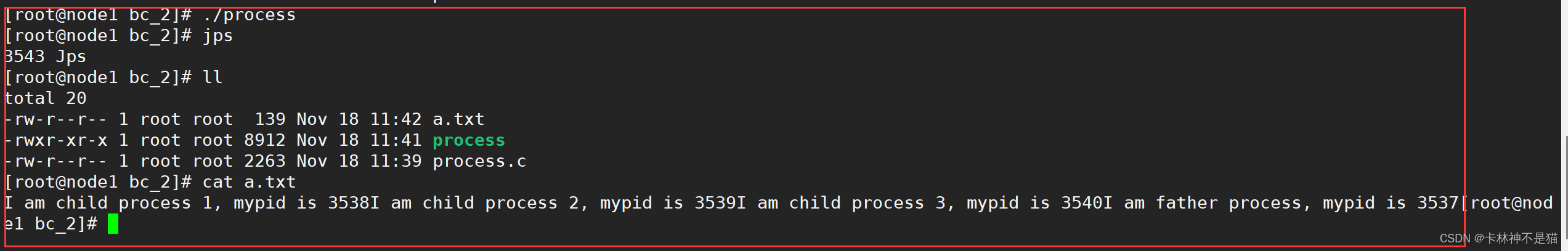
1.2. 父进程创建3个子进程,3个子进程需要打开文件a.txt并写入字符串,要求字符串能表明身份同时写明自己的进程号,最后父进程需要在该文件里面写入“I am father process, mypid is”+进程号。要求不能产生僵尸进程。
在linux上编写c语言程序process.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
// 打开文件a.txt,如果不存在则创建
int fd = open("a.txt", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0644);
if (fd == -1) {
perror("open");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
pid_t child1, child2, child3;
child1 = fork(); // 创建第一个子进程
if (child1 < 0) {
perror("fork");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} else if (child1 == 0) {
// 子进程1
char str[] = "I am child process 1, mypid is ";
char pid[10];
sprintf(pid, "%d", getpid());
strcat(str, pid);
write(fd, str, strlen(str));
close(fd);
exit(0);
} else {
child2 = fork(); // 创建第二个子进程
if (child2 < 0) {
perror("fork");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} else if (child2 == 0) {
// 子进程2
char str[] = "I am child process 2, mypid is ";
char pid[10];
sprintf(pid, "%d", getpid());
strcat(str, pid);
write(fd, str, strlen(str));
close(fd);
exit(0);
} else {
child3 = fork(); // 创建第三个子进程
if (child3 < 0) {
perror("fork");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} else if (child3 == 0) {
// 子进程3
char str[] = "I am child process 3, mypid is ";
char pid[10];
sprintf(pid, "%d", getpid());
strcat(str, pid);
write(fd, str, strlen(str));
close(fd);
exit(0);
} else {
// 等待三个子进程结束
waitpid(child1, NULL, 0);
waitpid(child2, NULL, 0);
waitpid(child3, NULL, 0);
// 父进程
char str[] = "I am father process, mypid is ";
char pid[10];
sprintf(pid, "%d", getpid());
strcat(str, pid);
write(fd, str, strlen(str));
close(fd);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
使用gcc编译器进行程序编译
gcc -o process process.c
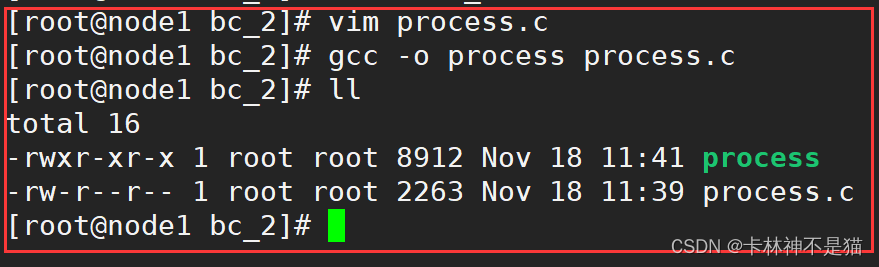
运行程序
./process
1.3. 有爷爷爸爸孙子三人一起工作,前两秒三人一起休息讨论工作,之后爷爷每2秒休息一次,爸爸每4秒休息一次,儿子每6秒休息一次,请按照关系创建父子进程,每人每次休息时都打印他的身份、进程pid以及当前时间,工作时间为18s。
在linux上编写c语言程序process.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h>
void print_info(char* role) {
time_t now;
time(&now);
printf("%s, pid: %d, time: %s", role, getpid(), ctime(&now));
}
int main() {
pid_t grandparent, parent, child;
grandparent = fork(); // 创建爷爷进程
if (grandparent < 0) {
perror("fork");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} else if (grandparent == 0) {
print_info("Grandparent");
sleep(2); // 休息两秒,与爸爸和孙子一起讨论工作
exit(0);
} else {
parent = fork(); // 创建爸爸进程
if (parent < 0) {
perror("fork");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} else if (parent == 0) {
print_info("Parent");
sleep(2); // 休息两秒,与爷爷和孙子一起讨论工作
int work_time = 18; // 设置工作时间为18秒
while (work_time > 0) {
print_info("Parent");
sleep(4); // 每4秒休息一次
work_time -= 4; // 更新剩余工作时间
}
exit(0);
} else {
child = fork(); // 创建孙子进程
if (child < 0) {
perror("fork");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} else if (child == 0) {
print_info("Child");
sleep(2); // 休息两秒,与爷爷和爸爸一起讨论工作
int work_time = 18; // 设置工作时间为18秒
while (work_time > 0) {
print_info("Child");
sleep(6); // 每6秒休息一次
work_time -= 6; // 更新剩余工作时间
}
exit(0);
} else {
// 等待子进程结束
waitpid(child, NULL, 0);
waitpid(parent, NULL, 0);
waitpid(grandparent, NULL, 0);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
使用gcc编译器进行程序编译
gcc -o process process.c
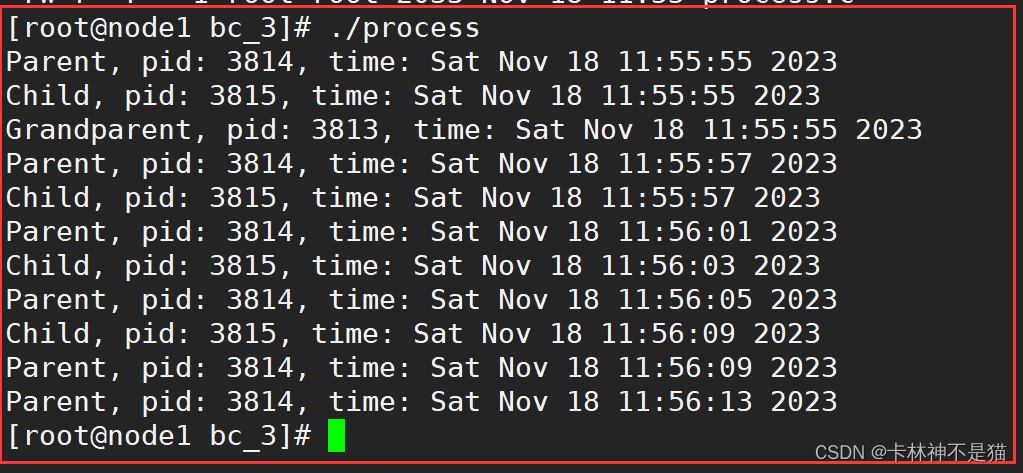
运行程序
./process
1.4. 编写程序让两个子进程交替判断一个范围内的整数是不是素数。运行程序时要输入两个参数,一个是左边界,一个是右边界。比如说判断100到200之间哪些是素数,子进程1判断100是不是素数,子进程2判断101是不是素数,子进程1再判断102是不是素数,子进程2判断103是不是素数…,一直轮流下去。
在linux上编写C语言程序process.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
// 判断一个数是否为素数
int is_prime(int num) {
if (num <= 1)
return 0;
for (int i = 2; i*i <= num; i++) {
if (num % i == 0)
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
if (argc != 3) {
printf("请提供正确的参数!\n");
printf("用法: %s 左边界 右边界\n", argv[0]);
return 1;
}
int left = atoi(argv[1]);
int right = atoi(argv[2]);
pid_t child1, child2;
int next_num = left;
child1 = fork(); // 创建子进程1
if (child1 < 0) {
perror("fork");
return 1;
} else if (child1 == 0) {
// 子进程1负责判断奇数
while (next_num <= right) {
if (next_num % 2 == 1 && is_prime(next_num))
printf("%d 是素数\n", next_num);
next_num++;
sleep(1);
}
exit(0);
} else {
child2 = fork(); // 创建子进程2
if (child2 < 0) {
perror("fork");
return 1;
} else if (child2 == 0) {
// 子进程2负责判断偶数
while (next_num <= right) {
if (next_num % 2 == 0 && is_prime(next_num))
printf("%d 是素数\n", next_num);
next_num++;
sleep(1);
}
exit(0);
} else {
// 等待子进程结束
waitpid(child1, NULL, 0);
waitpid(child2, NULL, 0);
}
}
return 0;
}
使用gcc编译器进行程序编译
gcc -std=c99 -o process process.c
编译器默认使用了较旧的 C 语言标准,而在较旧的标准下,不允许在 for 循环中声明变量。可以通过添加 -std=c99 或 -std=gnu99 选项来指定使用 C99 标准。
运行程序
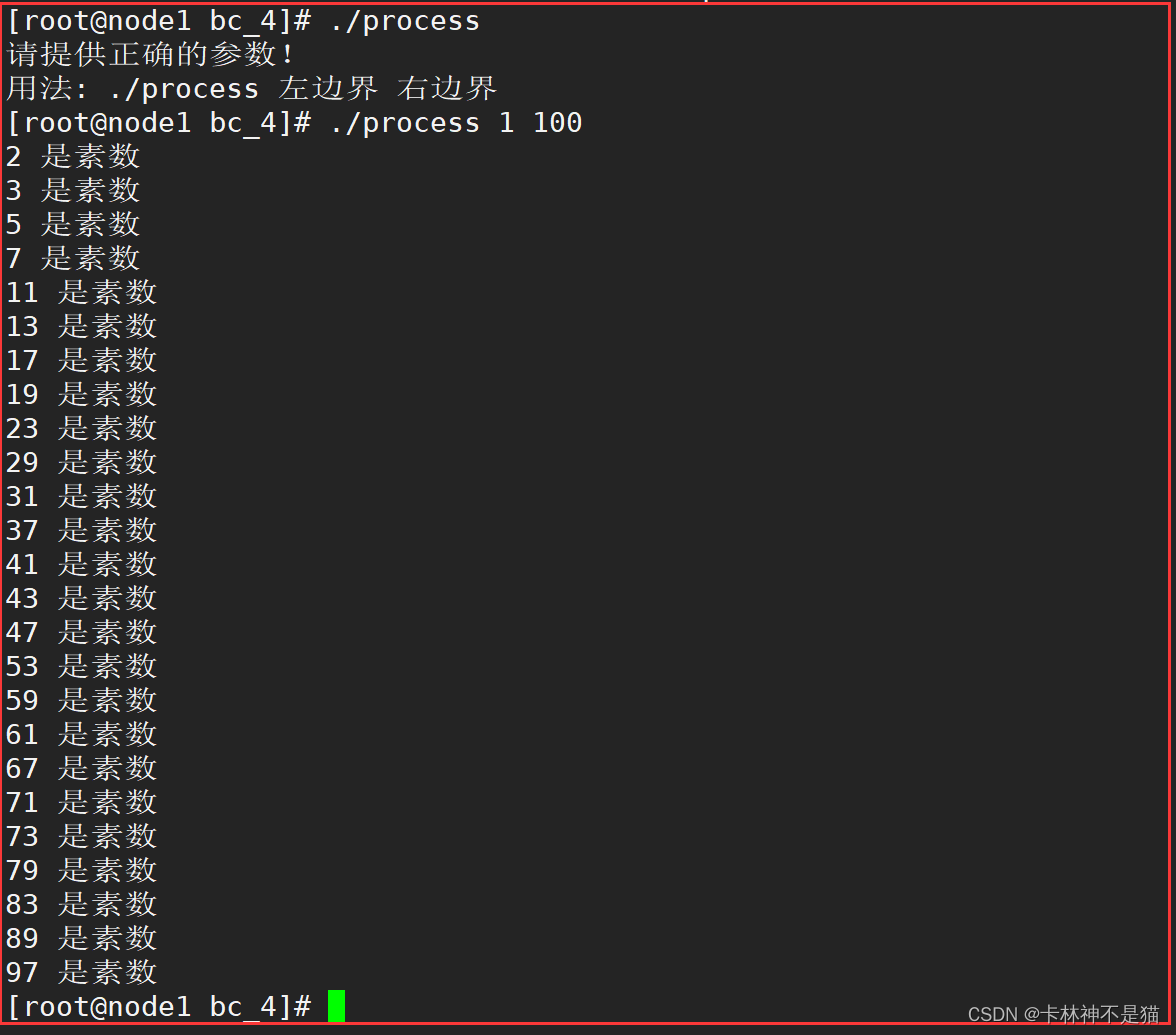
./process 1 100
解释:输出1和去100之间的素数
1.5. 仿照讲义中的“系统日志守护进程”例子,写一个守护进程,每隔一段时间获取当前登录用户名,将获取到的信息加上当前时间写入系统日志。
提示:
getlogin()、getenv()函数。
在linux上编写c语言程序daemon.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <syslog.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
int main() {
pid_t pid, sid;
time_t start_time = time(NULL); // 记录程序启动时间
// 创建子进程
pid = fork();
// 出错处理
if (pid < 0) {
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// 父进程退出
if (pid > 0) {
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
// 创建新的会话
sid = setsid();
if (sid < 0) {
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// 切换工作目录
if ((chdir("/")) < 0) {
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// 关闭标准输入、输出和错误流
close(STDIN_FILENO);
close(STDOUT_FILENO);
close(STDERR_FILENO);
// 守护进程主体
while (1) {
time_t current_time = time(NULL);
if (current_time - start_time > 60) { // 当程序运行时间超过一分钟时退出循环
break;
}
time_t rawtime;
struct tm *timeinfo;
char buffer[80];
time(&rawtime);
timeinfo = localtime(&rawtime);
strftime(buffer, 80, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", timeinfo);
char *username = getlogin();
if (username == NULL) {
username = getenv("USER");
}
openlog("MyDaemon", LOG_PID, LOG_USER);
syslog(LOG_INFO, "Current user: %s, Time: %s", username, buffer);
closelog();
sleep(10); // 每隔10秒执行一次
}
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
使用gcc编译器进行程序编译
gcc -o daemon daemon.c
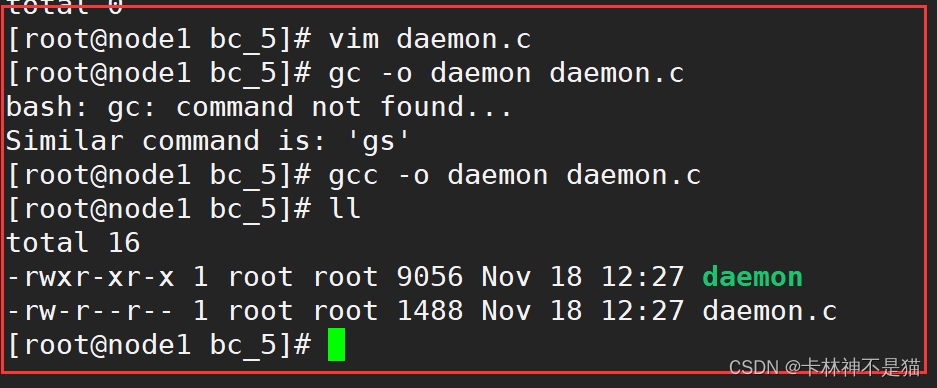
运行程序
./daemon
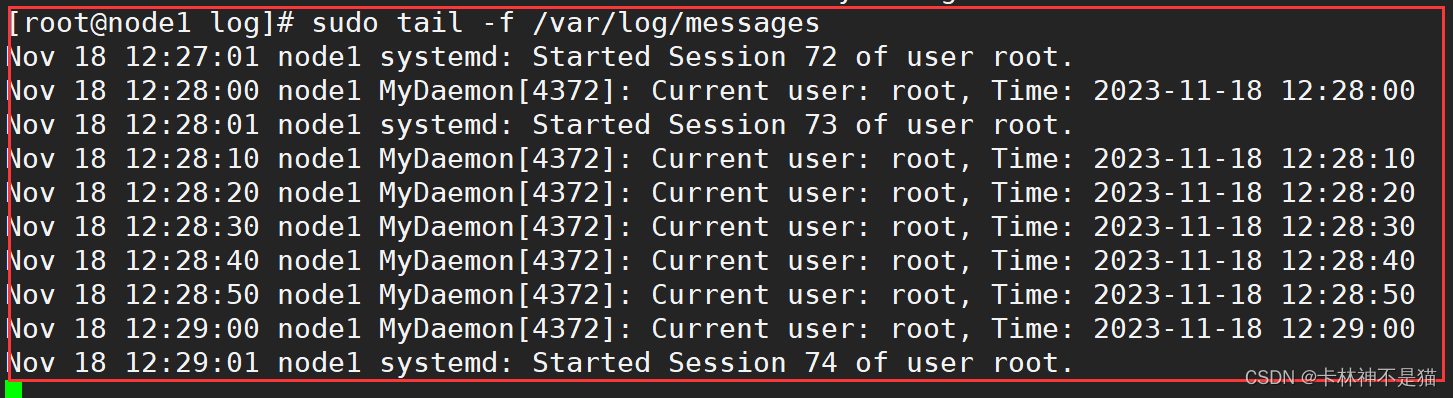
# 查看系统
sudo tail -f /var/log/messages