文章目录
- 1. MongoDB相关概念
- 1.1 业务应用场景
- 1.2 MongoDB简介
- 1.3 体系结构
- 1.4 数据模型
- 1.5 MongoDB的特点
- 2. docker安装mongodb
- 3. springboot集成
- 3.1 文件结构
- 3.2 增删改查
- 3.2.1 增加insert
- 3.2.2 保存save
- 3.2.3 更新update
- 3.2.4 查询
- 3.2.5 删除
1. MongoDB相关概念
1.1 业务应用场景
传统的关系型数据库(如MySQL),在数据操作的“三高”需求以及应对Web2.0的网站需求面前,显得力不从心。
解释:“三高”需求:
• High performance - 对数据库高并发读写的需求。
• Huge Storage - 对海量数据的高效率存储和访问的需求。
• High Scalability && High Availability- 对数据库的高可扩展性和高可用性的需求。
而MongoDB可应对“三高”需求。
具体的应用场景如:
1)社交场景,使用 MongoDB 存储存储用户信息,以及用户发表的朋友圈信息,通过地理位置索引实现附近的人、地点等功能。
2)游戏场景,使用 MongoDB 存储游戏用户信息,用户的装备、积分等直接以内嵌文档的形式存储,方便查询、高效率存储和访问。
3)物流场景,使用 MongoDB 存储订单信息,订单状态在运送过程中会不断更新,以 MongoDB 内嵌数组的形式来存储,一次查询就能将订单所有的变更读取出来。
4)物联网场景,使用 MongoDB 存储所有接入的智能设备信息,以及设备汇报的日志信息,并对这些信息进行多维度的分析。
5)视频直播,使用 MongoDB 存储用户信息、点赞互动信息等。
这些应用场景中,数据操作方面的共同特点是:
(1)数据量大
(2)写入操作频繁(读写都很频繁)
(3)价值较低的数据,对事务性要求不高
对于这样的数据,我们更适合使用MongoDB来实现数据的存储。
什么时候选择MongoDB
在架构选型上,除了上述的三个特点外,如果你还犹豫是否要选择它?可以考虑以下的一些问题:
应用不需要事务及复杂 join 支持
新应用,需求会变,数据模型无法确定,想快速迭代开发
应用需要2000-3000以上的读写QPS(更高也可以)
应用需要TB甚至 PB 级别数据存储
应用发展迅速,需要能快速水平扩展
应用要求存储的数据不丢失
应用需要99.999%高可用
应用需要大量的地理位置查询、文本查询
如果上述有1个符合,可以考虑 MongoDB,2个及以上的符合,选择 MongoDB 绝不会后悔。
思考:如果用MySQL呢?
答:相对MySQL,可以以更低的成本解决问题(包括学习、开发、运维等成本)
1.2 MongoDB简介
MongoDB是一个开源、高性能、无模式的文档型数据库,当初的设计就是用于简化开发和方便扩展,是NoSQL数据库产品中的一种。是最像关系型数据库(MySQL)的非关系型数据库。
它支持的数据结构非常松散,是一种类似于 JSON 的 格式叫BSON,所以它既可以存储比较复杂的数据类型,又相当的灵活。
MongoDB中的记录是一个文档,它是一个由字段和值对(field:value)组成的数据结构。MongoDB文档类似于JSON对象,即一个文档认为就是一个对象。字段的数据类型是字符型,它的值除了使用基本的一些类型外,还可以包括其他文档、普通数组和文档数组。
1.3 体系结构
MySQL和MongoDB对比

| SQL术语/概念 | MongoDB术语/概念 | 解释/说明 |
|---|---|---|
| database | database | 数据库 |
| table | collection | 数据库表/集合 |
| row | document | 数据记录行/文档 |
| column | field | 数据字段/域 |
| index | index | 索引 |
| table joins | 表连接,MongoDB不支持 | |
| 嵌入文档 | MongoDB通过嵌入式文档来替代多表连接 | |
| primary key | primary key | 主键,MongoDB自动将_id字段设置为主键 |
1.4 数据模型
MongoDB的最小存储单位就是文档(document)对象。文档(document)对象对应于关系型数据库的行。数据在MongoDB中以BSON(Binary-JSON)文档的格式存储在磁盘上。
BSON(Binary Serialized Document Format)是一种类json的一种二进制形式的存储格式,简称Binary JSON。BSON和JSON一样,支持内嵌的文档对象和数组对象,但是BSON有JSON没有的一些数据类型,如Date和BinData类型。
BSON采用了类似于 C 语言结构体的名称、对表示方法,支持内嵌的文档对象和数组对象,具有轻量性、可遍历性、高效性的三个特点,可以有效描述非结构化数据和结构化数据。这种格式的优点是灵活性高,但它的缺点是空间利用率不是很理想。
Bson中,除了基本的JSON类型:string,integer,boolean,double,null,array和object,mongo还使用了特殊的数据类型。这些类型包括date,object id,binary data,regular expression 和code。每一个驱动都以特定语言的方式实现了这些类型,查看你的驱动的文档来获取详细信息。
BSON数据类型参考列表:
| 数据类型 | 描述 | 举例 |
|---|---|---|
| 字符串 | UTF-8字符串都可表示为字符串类型的数据 | {“x” : “foobar”} |
| 对象id | 对象id是文档的12字节的唯一 ID | {“X” :ObjectId() } |
| 布尔值 | 真或者假:true或者false | {“x”:true}+ |
| 数组 | 值的集合或者列表可以表示成数组 | {“x” : [“a”, “b”, “c”]} |
| 32位整数 | 类型不可用。JavaScript仅支持64位浮点数,所以32位整数会被自动转换。 | shell是不支持该类型的,shell中默认会转换成64位浮点数 |
| 64位整数 | 不支持这个类型。shell会使用一个特殊的内嵌文档来显示64位整数 | shell是不支持该类型的,shell中默认会转换成64位浮点数 |
| 64位浮点数 | shell中的数字就是这一种类型 | {“x”:3.14159,“y”:3} |
| null | 表示空值或者未定义的对象 | {“x”:null} |
| undefined | 文档中也可以使用未定义类型 | {“x”:undefined} |
| 符号 | shell不支持,shell会将数据库中的符号类型的数据自动转换成字符串 | |
| 正则表达式 | 文档中可以包含正则表达式,采用JavaScript的正则表达式语法 | {“x” : /foobar/i} |
| 代码 | 文档中还可以包含JavaScript代码 | {“x” : function() { /* …… */ }} |
| 二进制数据 | 二进制数据可以由任意字节的串组成,不过shell中无法使用 | |
| 最大值/最小值 | BSON包括一个特殊类型,表示可能的最大值。shell中没有这个类型。 |
提示:
shell默认使用64位浮点型数值。{“x”:3.14}或{“x”:3}。对于整型值,可以使用NumberInt(4字节符号整数)或NumberLong(8字节符号整数),{“x”:NumberInt(“3”)}{“x”:NumberLong(“3”)}
1.5 MongoDB的特点
MongoDB主要有如下特点:
(1)高性能:
MongoDB提供高性能的数据持久性。特别是,
对嵌入式数据模型的支持减少了数据库系统上的I/O活动。
索引支持更快的查询,并且可以包含来自嵌入式文档和数组的键。(文本索引解决搜索的需求、TTL索引解决历史数据自动过期的需求、地理位置索引可用于构建各种 O2O 应用)
mmapv1、wiredtiger、mongorocks(rocksdb)、in-memory 等多引擎支持满足各种场景需求。
Gridfs解决文件存储的需求。
(2)高可用性:
MongoDB的复制工具称为副本集(replica set),它可提供自动故障转移和数据冗余。
(3)高扩展性:
MongoDB提供了水平可扩展性作为其核心功能的一部分。
分片将数据分布在一组集群的机器上。(海量数据存储,服务能力水平扩展)
从3.4开始,MongoDB支持基于片键创建数据区域。在一个平衡的集群中,MongoDB将一个区域所覆盖的读写只定向到该区域内的那些片。
(4)丰富的查询支持:
MongoDB支持丰富的查询语言,支持读和写操作(CRUD),比如数据聚合、文本搜索和地理空间查询等。
(5)其他特点:如无模式(动态模式)、灵活的文档模型
2. docker安装mongodb
单机安装
1. 拉取镜像
docker pull mongo:latest
//2. 创建挂载目录
//mkdir -p /root/data/mongodata 可以不用,直接用~/data/mongodata
2. 运行容器
docker run -di --name mongo-service \
--restart=always \
-p 27017:27017 \
-v ~/data/mongodata:/data mongo:latest
连接mongodb
studio3t是mongodb优秀的客户端工具。官方地址在https://studio3t.com/
3. springboot集成
3.1 文件结构
工程结构
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.ganz</groupId>
<artifactId>mongodb-demo</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<!-- 继承Spring boot -->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.5.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- mongodb -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- lombok -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.8</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
application.yml
server:
port: 9998
spring:
data:
mongodb:
host: 192.168.200.131
port: 27017
database: test-db
# username: root
# password: root
# authentication-database: admin
pojo
@Data
@Document("ap_associate_words")
public class ApAssociateWords implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String id;
/**
* 联想词
*/
private String associateWords;
/**
* 创建时间
*/
private Date createdTime;
/**
* 得分
*/
private Integer score;
}
测试类
@SpringBootTest(classes = MongoApplication.class)
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class MongoTest {
@Autowired
private MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;
/**
* 单个增加
*/
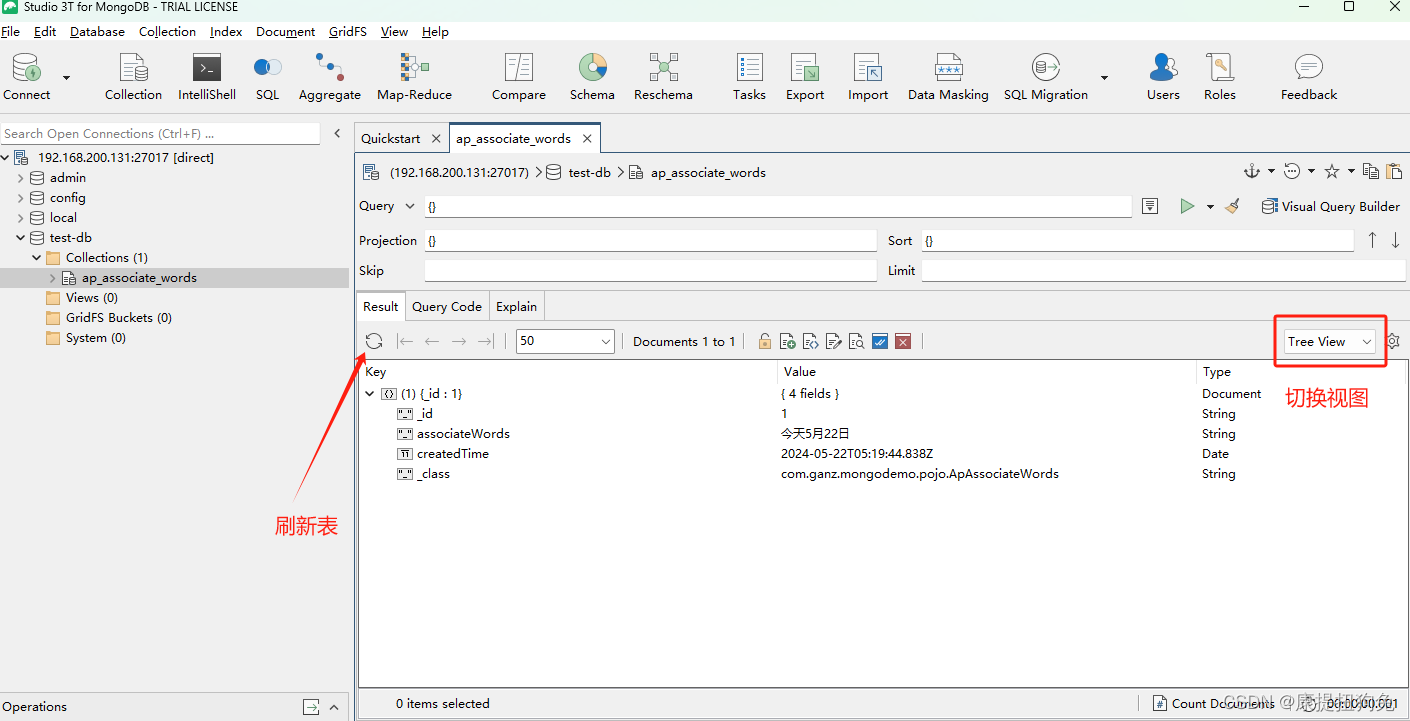
@Test
public void testInsert(){
ApAssociateWords apAssociateWords =new ApAssociateWords();
apAssociateWords.setId("1");
apAssociateWords.setAssociateWords("今天5月22日");
apAssociateWords.setCreatedTime(new Date());
mongoTemplate.insert(apAssociateWords);
}
}
3.2 增删改查
3.2.1 增加insert
- 单个增加
@Test
public void testInsert(){
ApAssociateWords apAssociateWords =new ApAssociateWords();
apAssociateWords.setId("1");
apAssociateWords.setAssociateWords("今天5月22日");
apAssociateWords.setCreatedTime(new Date());
mongoTemplate.insert(apAssociateWords);
}
运行结果
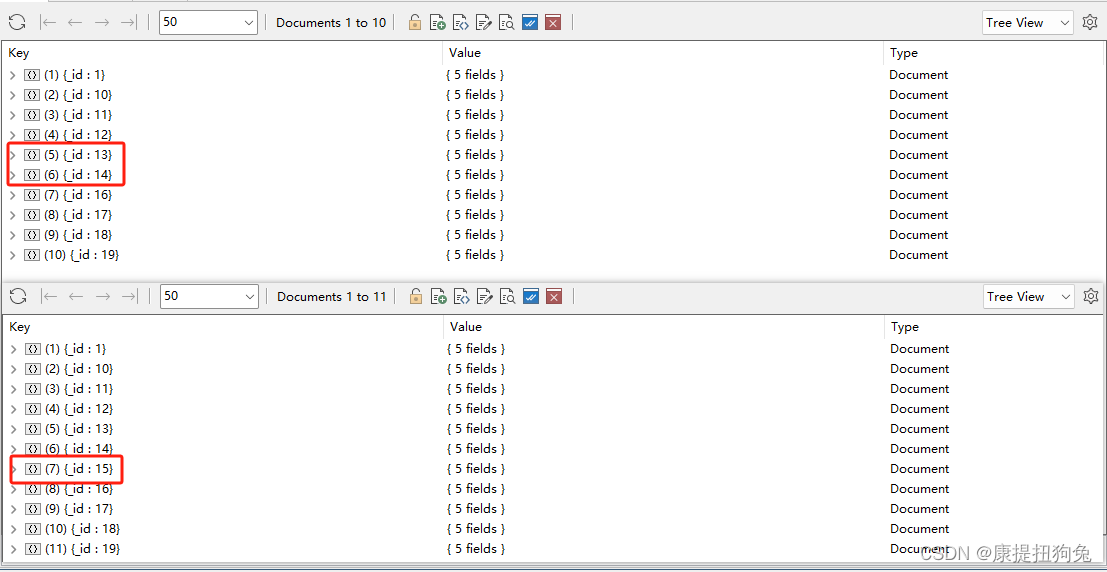
- 批量增加
@Test
public void testBatchInsert(){
ArrayList<ApAssociateWords> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
ApAssociateWords apAssociateWords = new ApAssociateWords();
apAssociateWords.setId((i+10)+"");
apAssociateWords.setAssociateWords("今天是这学期第"+i+"天");
apAssociateWords.setCreatedTime(new Date());
int score =(int)Math.random()*100;
apAssociateWords.setScore(score);
list.add(apAssociateWords);
}
mongoTemplate.insertAll(list);
}
运行结果
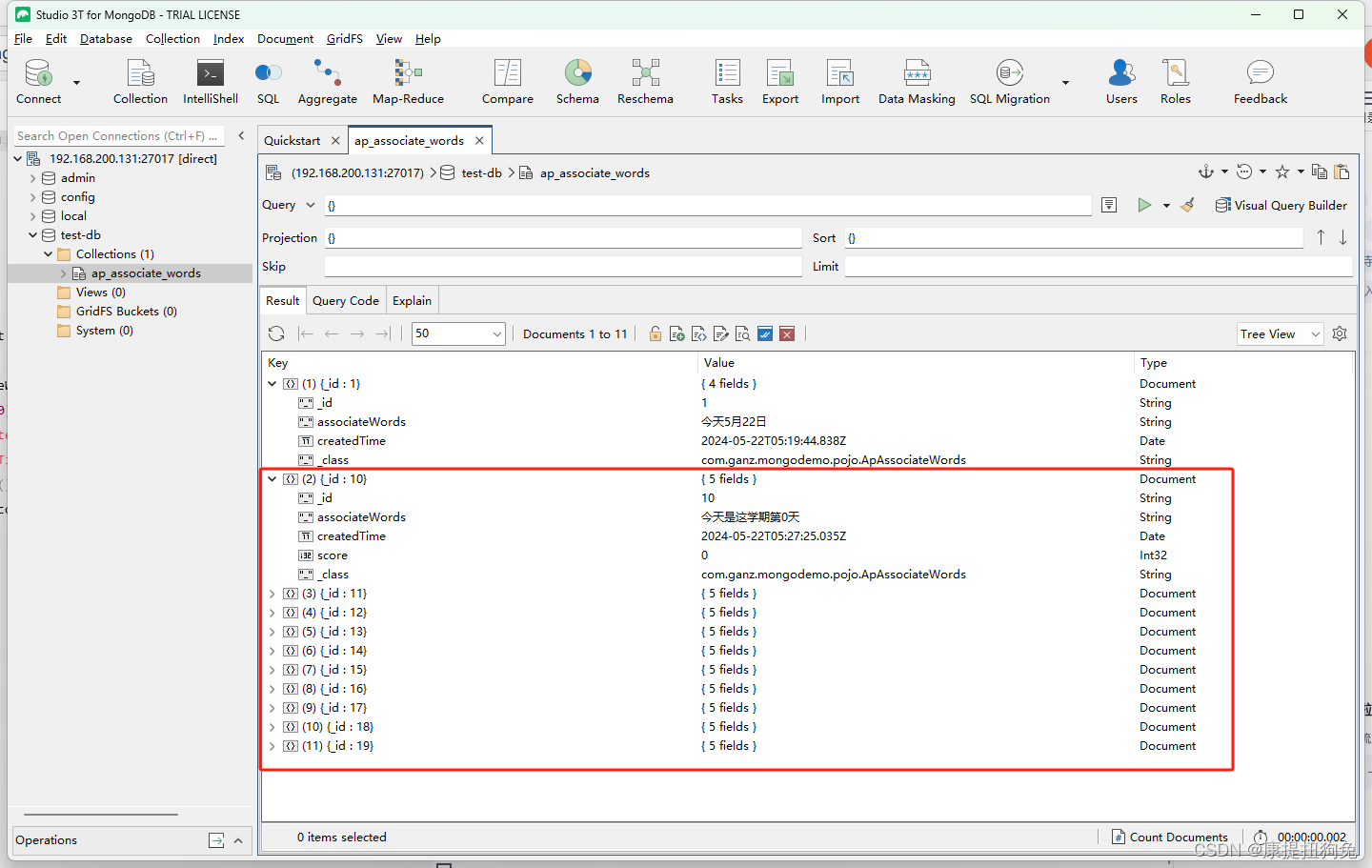
3.2.2 保存save
不同于insert和update
当id不存在的时候,insert;当id存在的时候,update
/**
* 保存:当id不存在的时候,插入
* 当id存在的时候,修改
*/
@Test
public void testSave(){
ApAssociateWords apAssociateWords = new ApAssociateWords();
apAssociateWords.setId("1");
apAssociateWords.setAssociateWords("今天5月22日");
apAssociateWords.setCreatedTime(new Date());
apAssociateWords.setScore(65);
mongoTemplate.save(apAssociateWords);
}
运行结果
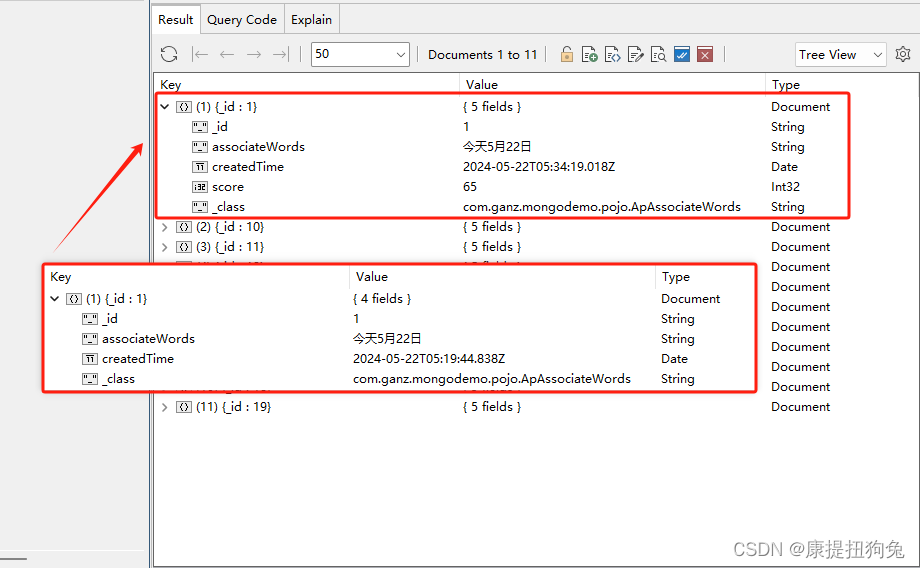
3.2.3 更新update
/**
* 修改
*/
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
//Query 相当于mysql中update的where后的条件
Query query = Query.query(Criteria.where("score").gt(60));
//update 相当于mysql中update的set后的新数据
Update update = new Update();
update.set("associateWords","分数大于60");
//updateFirst 修改符合条件的第一条
//mongoTemplate.updateFirst(query,update,ApAssociateWords.class);
//updateMulti 修改所有符合条件的
mongoTemplate.updateMulti(query,update,ApAssociateWords.class);
}
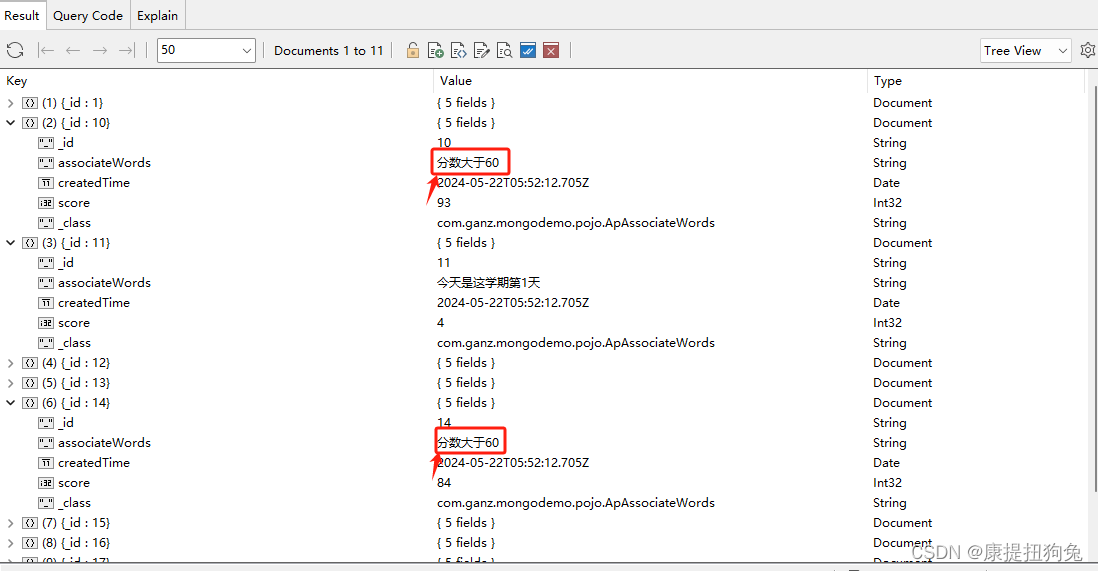
3.2.4 查询
/**
* 查询
*/
@Test
public void testFind(){
Query query =Query.query(Criteria.where("associateWords")
// 模糊查询
.regex("今天")
// 10 < score < 30
.and("score").gt(10).lt(50)
);
// 排序 相当于order by score asc
query.with(Sort.by(Sort.Direction.ASC,"score"));
// 分页 相当于 limit 0, 2
query.with(PageRequest.of(0,2));
List<ApAssociateWords> result = mongoTemplate.find(query, ApAssociateWords.class);
for (ApAssociateWords apAssociateWords:result){
System.out.println(apAssociateWords);
}
}
运行结果
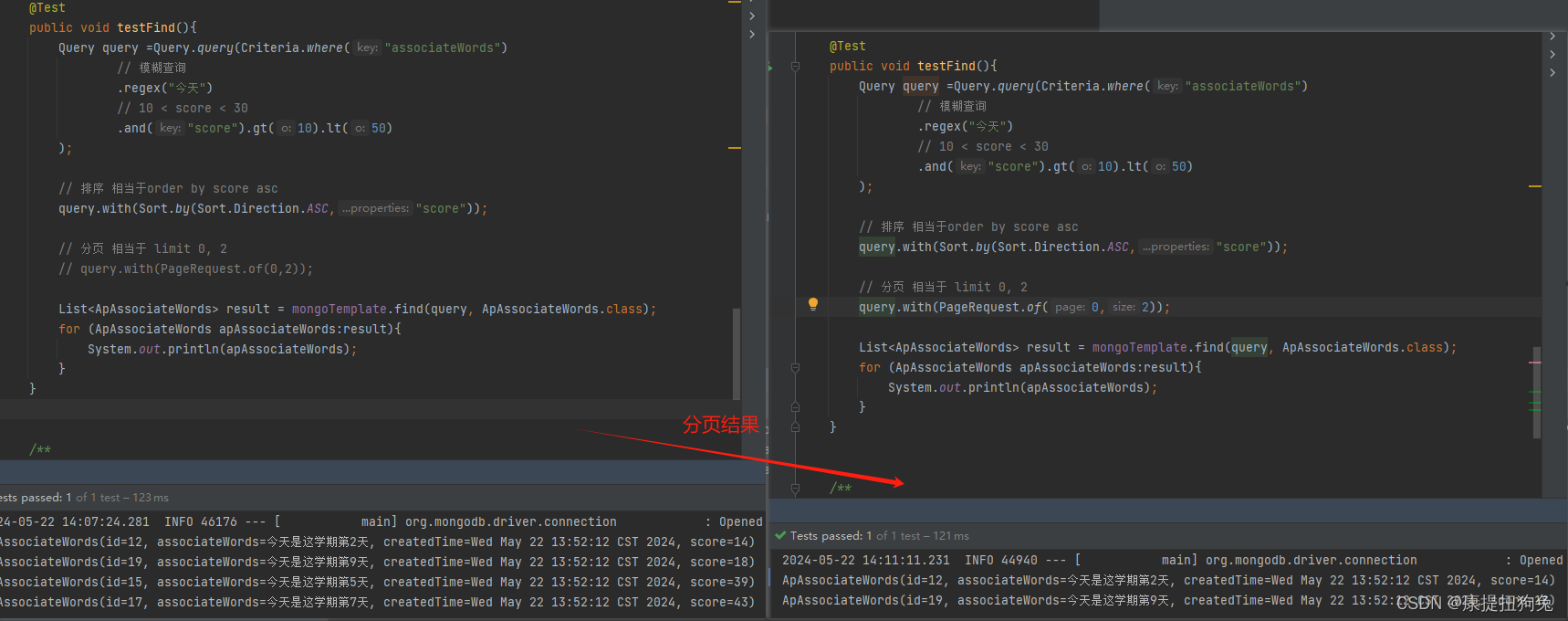
3.2.5 删除
/**
* 删除
*/
@Test
public void testRemove(){
// _id = "15"
Query query = Query.query(Criteria.where("_id").is("15"));
mongoTemplate.remove(query, ApAssociateWords.class);
}
运行结果,删掉了_id为"15"的文档