写这篇文章让我头大了好几天,书中描述的内容倒是不多,可能也是那会Tomcat的现状。如今Tomcat发展了好多代,加上springboot的广泛应用,导致现在的类加载的步骤和Tomcat资料中描述的大相径庭。可能也是由于微服务的发展,导致Tomcat中原来可以部署多个应用的特性正在淡化,Tomcat与springboot结合后的启动流程精简了许多。下面我将我了解到的知识介绍一下,有不对的请指出,有新发现我也会继续补充。
进入正文
首先,搞清楚两个词语的含义,载入器与类加载器。实现了org.apache.catalina.Loader接口的类为载入器,容器直接持有的是载入器,比如我们前面提到的容器基础类 ContainerBase 中持有一个 Loader 对象的引用。类加载器被载入器持有,作为载入器的一个属性存在。
载入器
这是Loader接口的定义
package org.apache.catalina;
import java.beans.PropertyChangeListener;
public interface Loader {
// 持有一个类加载器
public ClassLoader getClassLoader();
// 与此载入器关联的容器对象
public Container getContainer();
public void setContainer(Container container);
// 存储 Host 在创建 Context 时将使用的默认配置
public DefaultContext getDefaultContext();
public void setDefaultContext(DefaultContext defaultContext);
// 配合类加载器使用,设置类加载的流程是否遵循双亲委派机制
public boolean getDelegate();
public void setDelegate(boolean delegate);
public String getInfo();
// 是否支持热部署(动态重新加载类)
public boolean getReloadable();
public void setReloadable(boolean reloadable);
// --------------------------------------------------------- Public Methods
// 设置属性变化监听器
public void addPropertyChangeListener(PropertyChangeListener listener);
public void removePropertyChangeListener(PropertyChangeListener listener);
// 添加一个类加载器的存储库(该载入器持有的类加载器只能去指定的存储库中加载类)
public void addRepository(String repository);
public String[] findRepositories();
// 与此载入器关联的内部库中是否有类文件被修改了?这将会成为是否需要重新加载类(启动热部署)的依据
public boolean modified();
}
由此接口的定义可以看出:载入器大概有两大功能
- 持有一个类加载器,并管理类加载器的一些行为:是否遵循双亲委派机制、包含哪些类库
- 拥有热部署的功能,并可设定是否开启。开启后,当class文件或jar包发生更改时,会触发自动重载操作
Tomcat的载入器通常会与一个Context级别的servlet容器相关联,而Context容器代表的是一个Web应用程序,所以载入器的作用就是加载这个Web应用程序下的类,并支持自动重载(当然也可以关闭自动重载)。
类加载器
类加载器其实是jdk中定义的东西,继承了java.lang.ClassLoader的类叫做类加载器。jdk中关于类加载器的实现有很多,Tomcat主要使用URLClassLoader这个类加载器,URLClassLoader可以通过url的形式添加该类加载器的存储库,该类加载器只会去它的存储库中查找并加载类。
了解过JVM类加载的同学应该都知道双亲委派机制。这里再简单阐述下这个机制。
双亲委派机制
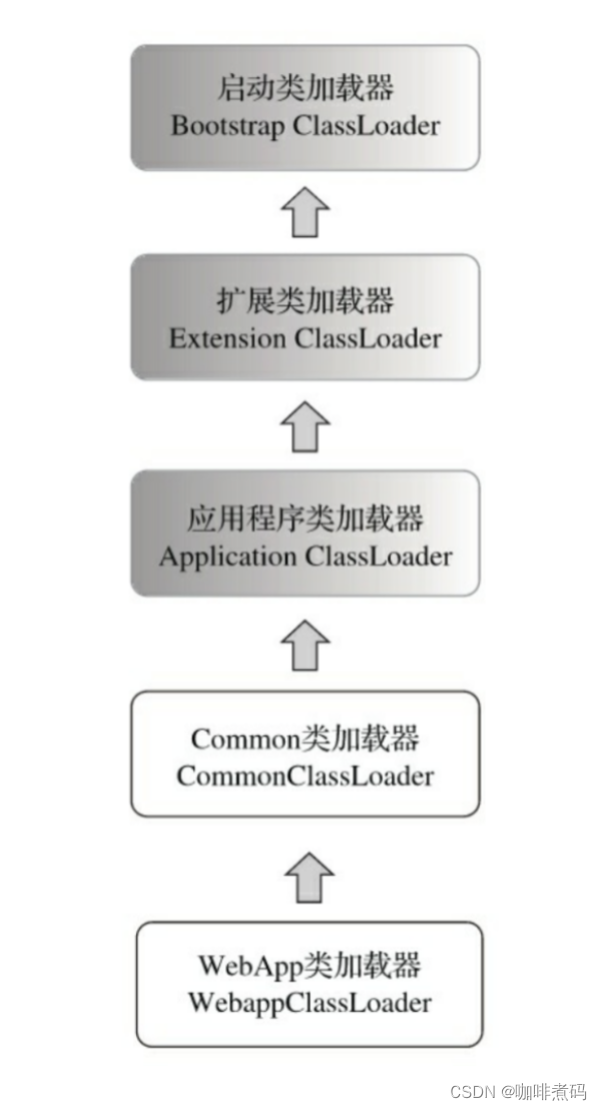
jdk定义了三种类加载器
- 启动类加载器(Bootstrap Class Loader ):负责加载<JAVA_HOME>\lib目录中 rt.jar、tools.jar 等包中的基础类
- 扩展类加载器(Extension Class Loader):负责加载<JAVA_HOME>\lib\ext目录中的类
- 应用程序类加载器(Application Class Loader):也称系统类加载器,system class loader ,它负责加载用户类路径(ClassPath)上的所有类,如果应用程序中没有自定义类加载器的话,一般情况下这个就是程序默认的类加载器。
用户也可以自定义类加载器,以实现类库的隔离与重载。
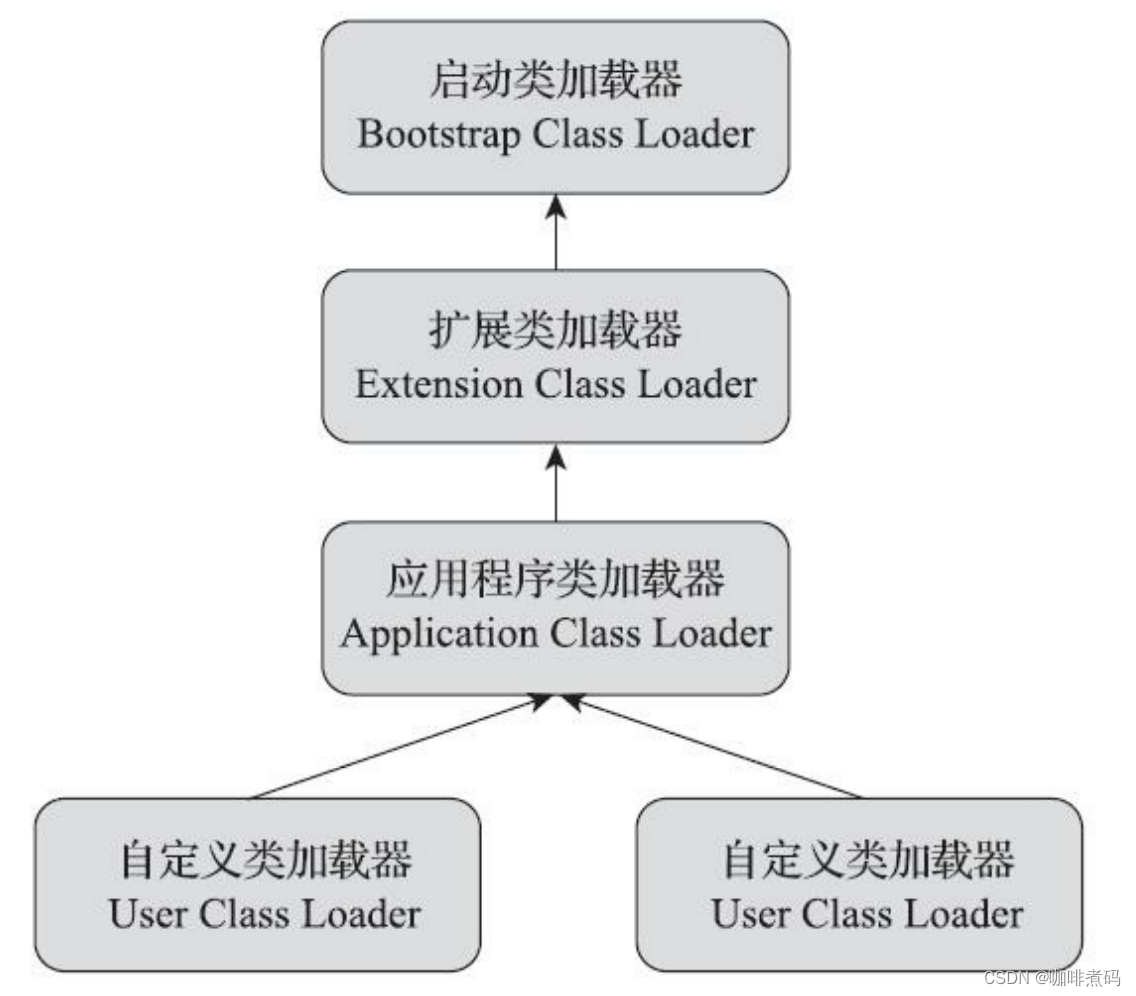
类加载器的双亲委派模型如上图,每个类加载器在收到类加载请求时,都会优先交给它的父类加载器来执行,直到这个加载请求到达启动类加载器,如果父类加载器加载不了,自己才会尝试加载。这种父类优先的模式就形成了如下图所示的这种规则(假如当前场景是应用程序类加载器要加载一个类)
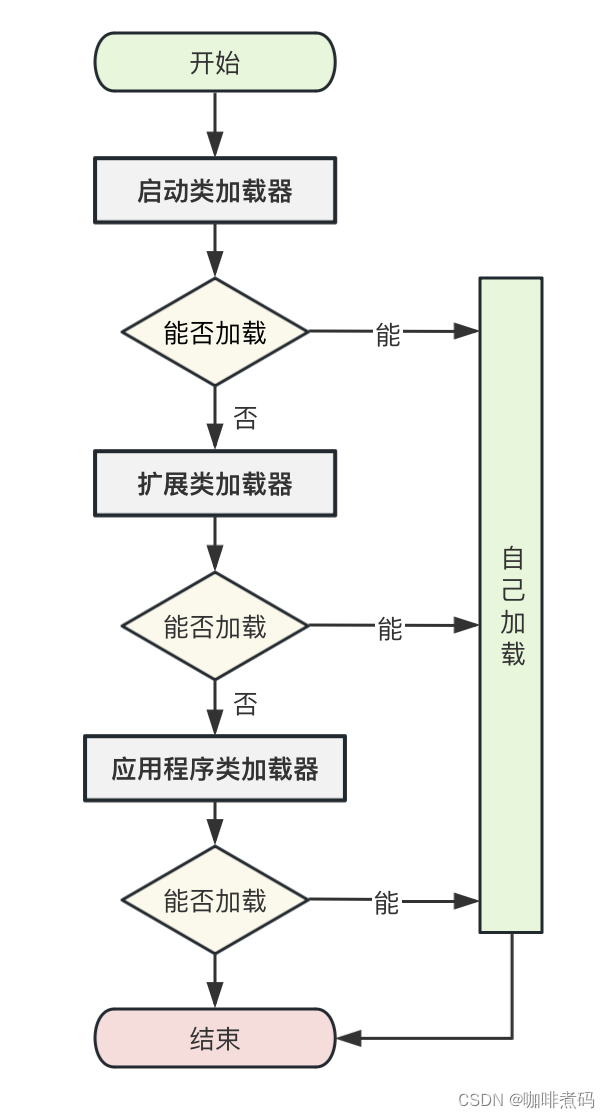
这种机制保证了JDK中的基础类,如java.lang.Object,java.lang.String等永远只会被启动类加载器加载,不会被用户在项目中编写的同包同名类影响。
另外,JVM中判断一个Class唯一性的标准为:加载该Class的类加载器+该Class本身。所以双亲委派机制也维护了这一标准,同一个类不会被不同的类加载器加载。
至于为什么叫双亲委派,我想大概是因为jdk中只定义了三种类加载器,而我们编写的工程类一般使用“应用程序类加载器”,在这个类加载器上面还有两代亲,所以就叫“双亲委派”了。
Tomcat的自定义类加载器
Tomcat在诞生之处就实现了一个目标:我不仅是一个Web服务,我还是一个支持部署多个应用的Web服务。Tomcat有一个webapps目录,这个目录下要放的就是我们的项目应用,可以放多个应用,客户端访问时带上应用名就能访问到指定应用。
这个多应用的支持就对jdk的类加载机制带来了挑战,不同的应用可能会有同包同名的类,或者引用了一个第三方包的不同版本。如果所有应用的类都用系统类加载器来加载的话,那么肯定就会产生冲突了,所以需要一个机制,将不同应用的类加载过程隔离开来,因此,Tomcat自定义了自己的类加载器,来实现自己自定义的类加载逻辑。
早期的Tomcat的目录结构是下面这样的,(我下载了一个5.0.28版本的Tomcat工程)
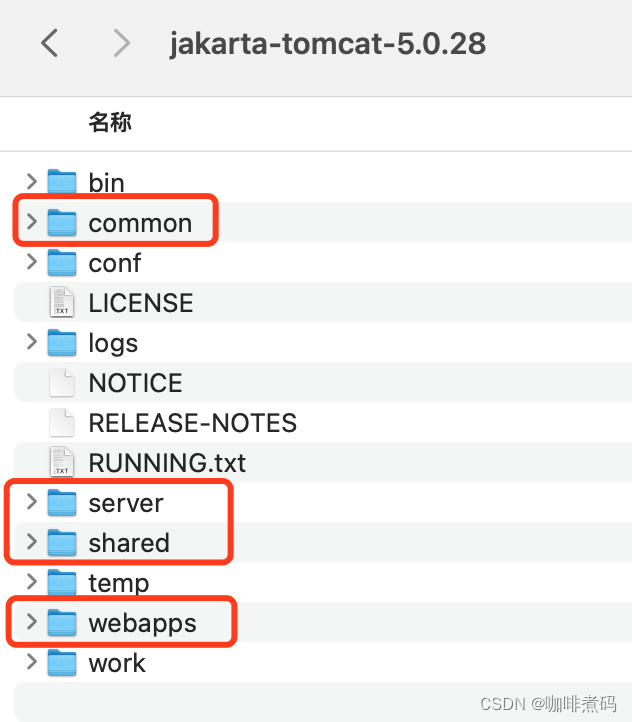
我圈起来的四个包,Tomcat用了四个类加载器来分别加载
- common目录下的类库可以被Tomcat和所有Web应用共同使用,使用Common类加载器来加载。
- server目录下的类库可被Tomcat使用,对所有Web应用不可见,使用Catalina类加载器(server类加载器)来加载。
- shared目录下的类库可被所有Web应用使用,对Tomcat自己不可见,使用 Shared类加载加载。
- webapps目录下放了1到多个应用目录,每个应用目录的类库仅对该应用自己可见,每个应用使用一个WebApp类加载器实例来加载自己的类。
所以这四个自定义类加载器结合jdk的三个类加载器就形成了这个关系
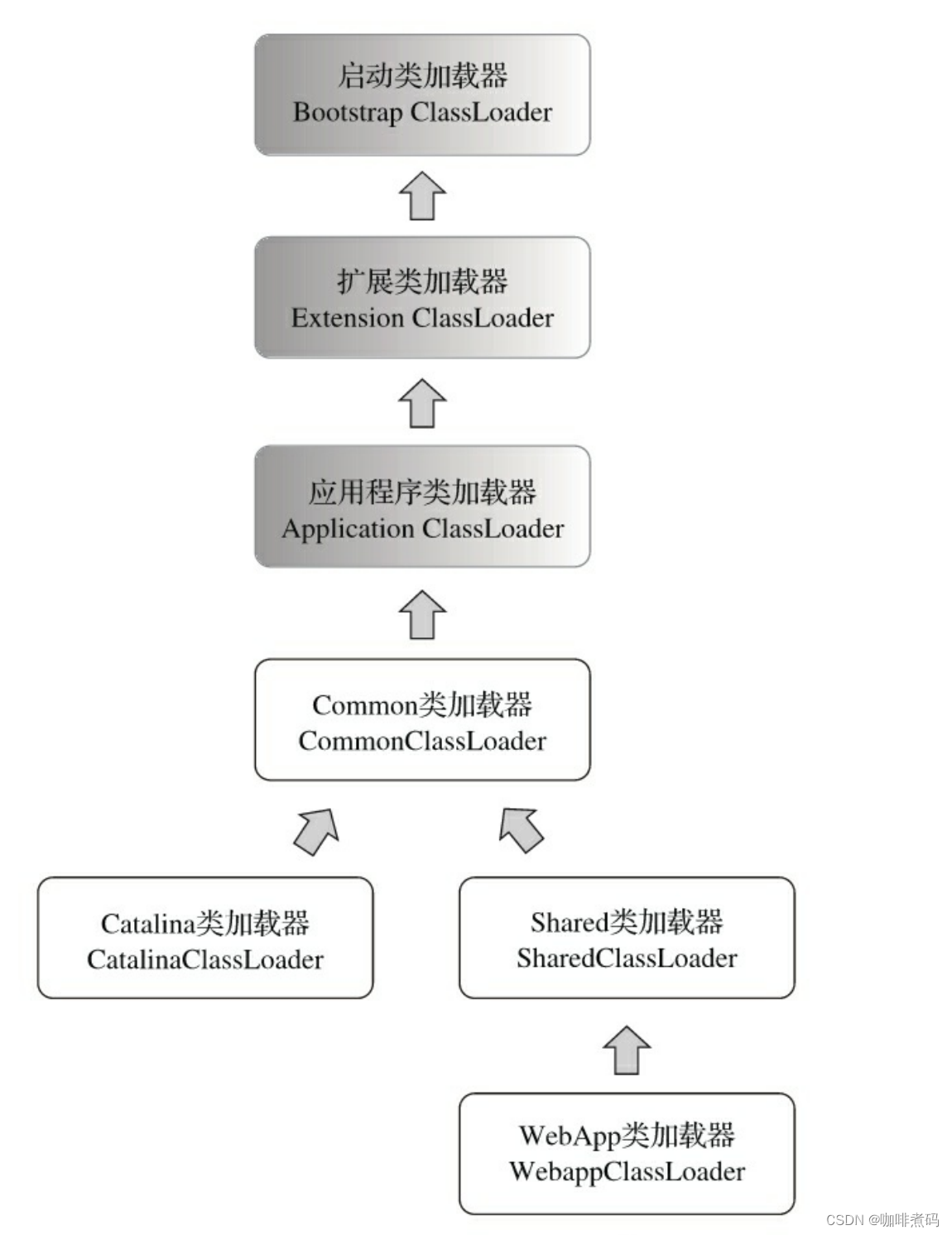
不同的类加载器分别加载各自目录下的类库,也就将各个类库隔离开来了。
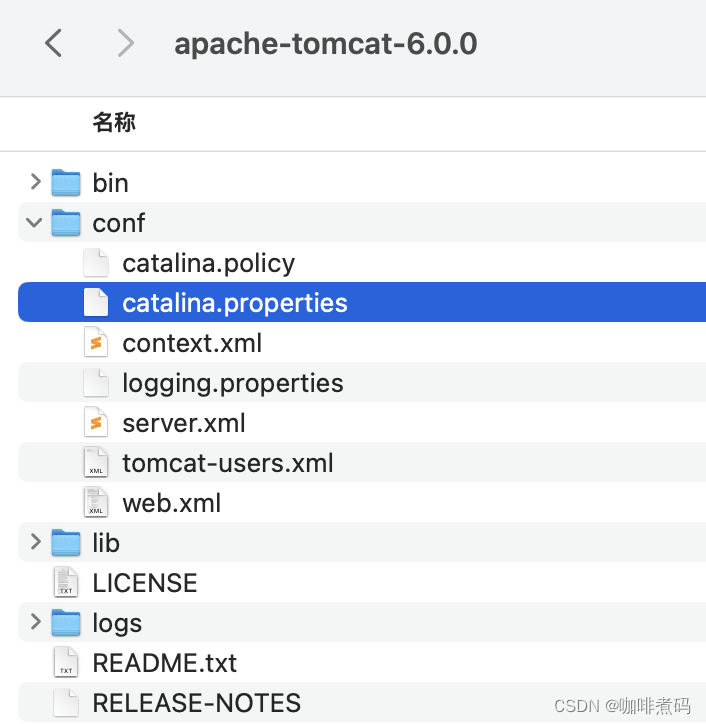
随着Tomcat的发展,在升级到版本6后,它默认的目录结构发生了变化(我下载了一个6.0.0版本的Tomcat工程)
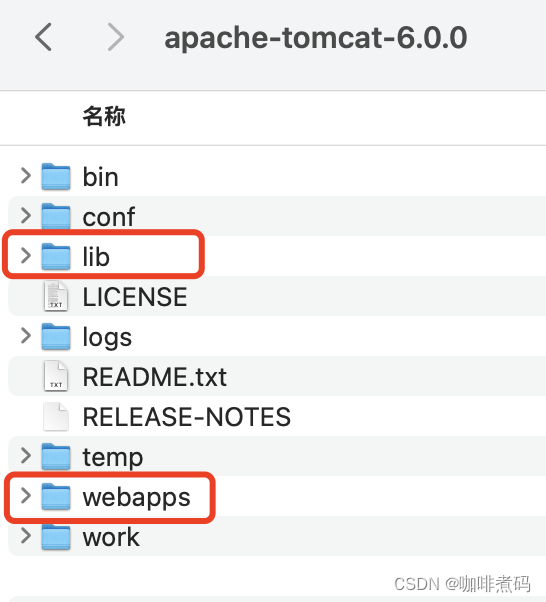
common、server、shared三个目录没有了,多了一个lib目录,这个lib目录的作用相当于之前common目录的作用,用Common类加载器进行加载。Tomcat这么做说明它也发现了用户实际使用过程中,对server和shared的使用场景很少,所以干脆将它们从默认配置中移除了。如果我升级到了Tomcat高版本,还想用server或shared目录怎么办?那就自己在catalina.properties文件中配置 server.loader与shared.loader两个属性的属性值即可
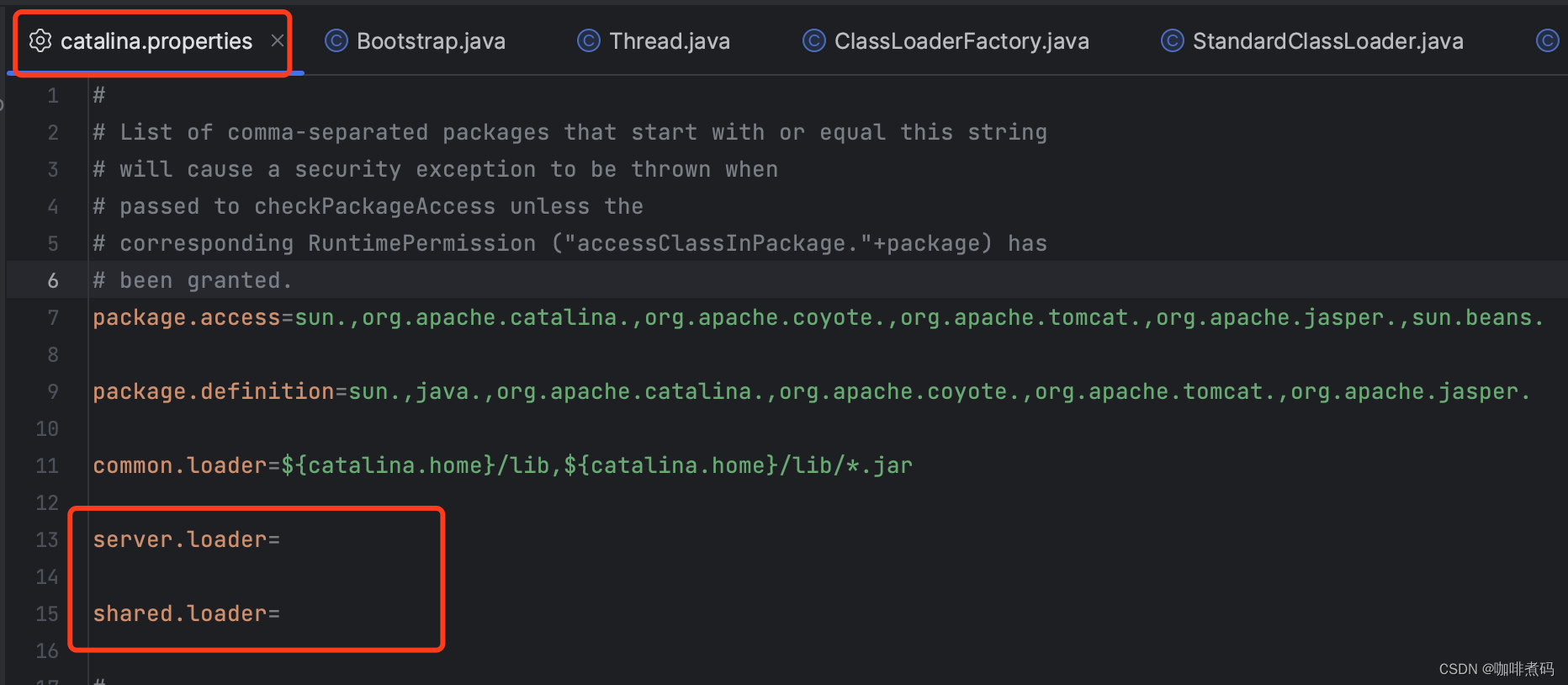
由于少了server与shared两个目录,所以默认情况下Tomcat的类加载器的关系又成了这样
了解了Tomcat的载入器与类加载器的情况,现在来看看它们的代码实现
载入器的代码实现
Tomcat提供的载入器实现类为 org.apache.catalina.loader.WebappLoader。
WebappLoader类中创建了一个自定义类加载器(org.apache.catalina.loader.WebappClassLoader类的实例)。
WebappLoader类实现了Runnable接口,并开启一个线程来支持类的自动重载。
WebappLoader类实现了Lifecycle接口,它的start()方法中的主要逻辑为
- 创建一个类载入器;
- 设置仓库;
- 设置类路径;
- 设置访问权限;
- 启动一个新线程来支持自动重载。
接下来分别说一下start方法中的这几件事
创建一个类载入器
WebappLoader中有一个loaderClass属性,来存放类加载器的全限定名,默认是org.apache.catalina.loader.WebappClassLoader,也支持修改。
WebappLoader根据loaderClass来反射创建一个类加载器。
private String loaderClass = "org.apache.catalina.loader.WebappClassLoader";
设置仓库
如果载入器关联的Context容器需要引入额外的类库作为该应用的类库,则将额外的类库设置到WebappLoader的 repositories 属性中(通过addRepository方法),在start()方法中 会首先将repositories中的类库添加到类加载器中,然后调用 setRepositories() 方法将WEB-INF/classes 与 WEB-INF/lib两个类库添加到类加载器中。
private String[] repositories = new String[0];
设置类路径
这是jsp相关的内容,考虑到jsp基本已经不再使用,所以这里不再研究。
设置访问权限
访问权限的内容将在第十章进行介绍,这些不做研究。
启动一个新线程来支持自动重载
WebappLoader类实现了Runnable接口,在 start 方法中,会启动这个线程,用来不断检查该载入器对应的Context容器中的类(也就是应用程序中的类)是否发生了变更,如果发生了变更则要通知Context进行类重载。
其中检查类是否发生变更,是调用的类加载器的modified()方法,逻辑由类加载器实现。
检查到类发生变更后,Tomcat另起了一个线程来调用Context中的reload方法。至于为什么要另起一个线程,我暂时没有理解,如果你知道,还请评论赐教。
下面是WebappLoader的代码,我省略了一些代码,保留了主要逻辑代码
public class WebappLoader implements Lifecycle, Loader, PropertyChangeListener, Runnable {
// ----------------- 构造方法
public WebappLoader() {
this(null);
}
public WebappLoader(ClassLoader parent) {
super();
this.parentClassLoader = parent;
}
// 热部署线程,巡检的时间间隔
private int checkInterval = 15;
// 类加载器
private WebappClassLoader classLoader = null;
private Container container = null;
protected DefaultContext defaultContext = null;
// 是否遵循双亲委派模型
private boolean delegate = false;
protected LifecycleSupport lifecycle = new LifecycleSupport(this);
// 类加载器的全限定名
private String loaderClass = "org.apache.catalina.loader.WebappClassLoader";
// classLoader的父 类加载器
private ClassLoader parentClassLoader = null;
// 是否支持热重载
private boolean reloadable = false;
// 类加载器关联的类库,这是除了WEB-INF/classes与WEB-INF/lib外的额外类库
private String repositories[] = new String[0];
private boolean started = false;
protected PropertyChangeSupport support = new PropertyChangeSupport(this);
// 热部署巡检线程
private Thread thread = null;
// 巡检线程是否停止了
private boolean threadDone = false;
// 巡检线程的name
private String threadName = "WebappLoader";
// ------------------ Properties
public void setReloadable(boolean reloadable) {
// Process this property change
boolean oldReloadable = this.reloadable;
this.reloadable = reloadable;
support.firePropertyChange("reloadable", new Boolean(oldReloadable), new Boolean(this.reloadable));
// Start or stop our background thread if required
if (!started) return;
if (!oldReloadable && this.reloadable) threadStart();
else if (oldReloadable && !this.reloadable) threadStop();
}
// ------------------ Public Methods
/**
* Has the internal repository associated with this Loader been modified,
* such that the loaded classes should be reloaded?
*/
public boolean modified() {
return (classLoader.modified());
}
// ------------------ Lifecycle Methods
public void start() throws LifecycleException {
if (started) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("webappLoader.alreadyStarted"));
}
lifecycle.fireLifecycleEvent(START_EVENT, null);
started = true;
if (container.getResources() == null) {
return;
}
try {
// 创建类加载器
classLoader = createClassLoader();
classLoader.setResources(container.getResources());
classLoader.setDebug(this.debug);
classLoader.setDelegate(this.delegate);
// 如果载入器额外设置了类库,则将这些类库添加到类加载器的类库中
for (int i = 0; i < repositories.length; i++) {
classLoader.addRepository(repositories[i]);
}
// 设置仓库,WEB_INF/classes 与 WEB_INF/lib 两个目录
setRepositories();
// 设置类路径,与JSP相关,不再研究
setClassPath();
// 设置访问权限,这块内容后面章节再介绍
setPermissions();
if (classLoader instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) classLoader).start();
}
// Binding the Webapp class loader to the directory context
DirContextURLStreamHandler.bind((ClassLoader) classLoader, this.container.getResources());
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new LifecycleException("start: ", t);
}
// 验证所有必需的包都是实际可用的,这个方法这里暂不研究
validatePackages();
// 如果支持重载的话,开启一个守护线程来巡检,在线程内完成重载的触发流程
if (reloadable) {
log(sm.getString("webappLoader.reloading"));
try {
threadStart();
} catch (IllegalStateException e) {
throw new LifecycleException(e);
}
}
}
public void stop() throws LifecycleException {
// Validate and update our current component state
if (!started) throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("webappLoader.notStarted"));
lifecycle.fireLifecycleEvent(STOP_EVENT, null);
started = false;
// Stop our background thread if we are reloadable
if (reloadable) threadStop();
// Remove context attributes as appropriate
if (container instanceof Context) {
ServletContext servletContext = ((Context) container).getServletContext();
servletContext.removeAttribute(Globals.CLASS_PATH_ATTR);
}
// Throw away our current class loader
if (classLoader instanceof Lifecycle) ((Lifecycle) classLoader).stop();
DirContextURLStreamHandler.unbind((ClassLoader) classLoader);
classLoader = null;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------- Private Methods
/**
* 创建一个类加载器
*/
private WebappClassLoader createClassLoader() throws Exception {
Class clazz = Class.forName(loaderClass);
WebappClassLoader classLoader = null;
// 根据 parentClassLoader 有没有值来使用 WebappClassLoader 的不同构造函数
if (parentClassLoader == null) {
classLoader = (WebappClassLoader) clazz.newInstance();
} else {
Class[] argTypes = {ClassLoader.class};
Object[] args = {parentClassLoader};
Constructor constr = clazz.getConstructor(argTypes);
classLoader = (WebappClassLoader) constr.newInstance(args);
}
return classLoader;
}
/**
* 基于关联的Context,为我们的类加载器配置类库。主要是 WEB-INF/classes 和 WEB-INF/lib 两个目录
*/
private void setRepositories() {
if (!(container instanceof Context)) return;
ServletContext servletContext = ((Context) container).getServletContext();
if (servletContext == null) return;
// Loading the work directory
File workDir = (File) servletContext.getAttribute(Globals.WORK_DIR_ATTR);
if (workDir == null) return;
log(sm.getString("webappLoader.deploy", workDir.getAbsolutePath()));
DirContext resources = container.getResources();
// Setting up the class repository (/WEB-INF/classes), if it exists
String classesPath = "/WEB-INF/classes";
DirContext classes = null;
try {
Object object = resources.lookup(classesPath);
if (object instanceof DirContext) {
classes = (DirContext) object;
}
} catch (NamingException e) {
// Silent catch: it's valid that no /WEB-INF/classes collection
// exists
}
if (classes != null) {
File classRepository = null;
String absoluteClassesPath = servletContext.getRealPath(classesPath);
if (absoluteClassesPath != null) {
classRepository = new File(absoluteClassesPath);
} else {
classRepository = new File(workDir, classesPath);
classRepository.mkdirs();
copyDir(classes, classRepository);
}
log(sm.getString("webappLoader.classDeploy", classesPath, classRepository.getAbsolutePath()));
// Adding the repository to the class loader
classLoader.addRepository(classesPath + "/", classRepository);
}
// Setting up the JAR repository (/WEB-INF/lib), if it exists
String libPath = "/WEB-INF/lib";
classLoader.setJarPath(libPath);
DirContext libDir = null;
// Looking up directory /WEB-INF/lib in the context
try {
Object object = resources.lookup(libPath);
if (object instanceof DirContext) libDir = (DirContext) object;
} catch (NamingException e) {
// Silent catch: it's valid that no /WEB-INF/lib collection
// exists
}
if (libDir != null) {
boolean copyJars = false;
String absoluteLibPath = servletContext.getRealPath(libPath);
File destDir = null;
if (absoluteLibPath != null) {
destDir = new File(absoluteLibPath);
} else {
copyJars = true;
destDir = new File(workDir, libPath);
destDir.mkdirs();
}
// Looking up directory /WEB-INF/lib in the context
try {
NamingEnumeration myEnum = resources.listBindings(libPath);
while (myEnum.hasMoreElements()) {
Binding binding = (Binding) myEnum.nextElement();
String filename = libPath + "/" + binding.getName();
if (!filename.endsWith(".jar")) continue;
// Copy JAR in the work directory, always (the JAR file
// would get locked otherwise, which would make it
// impossible to update it or remove it at runtime)
File destFile = new File(destDir, binding.getName());
log(sm.getString("webappLoader.jarDeploy", filename, destFile.getAbsolutePath()));
Resource jarResource = (Resource) binding.getObject();
if (copyJars) {
if (!copy(jarResource.streamContent(), new FileOutputStream(destFile))) continue;
}
JarFile jarFile = new JarFile(destFile);
classLoader.addJar(filename, jarFile, destFile);
}
} catch (NamingException e) {
// Silent catch: it's valid that no /WEB-INF/lib directory
// exists
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// 开启一个巡检线程
private void threadStart() {
// Has the background thread already been started?
if (thread != null) return;
// Validate our current state
if (!reloadable) throw new IllegalStateException(sm.getString("webappLoader.notReloadable"));
if (!(container instanceof Context)) throw new IllegalStateException(sm.getString("webappLoader.notContext"));
// Start the background thread
threadDone = false;
threadName = "WebappLoader[" + container.getName() + "]";
thread = new Thread(this, threadName);
thread.setDaemon(true);
thread.start();
}
// 让当前线程睡一会
private void threadSleep() {
try {
Thread.sleep(checkInterval * 1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
;
}
}
// 停止巡检线程
private void threadStop() {
if (thread == null) return;
threadDone = true;
thread.interrupt();
try {
thread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
;
}
thread = null;
}
// 巡检线程的run方法
public void run() {
// 循环检查,直到 threadDone 为 true
while (!threadDone) {
// 睡一会再检查
threadSleep();
if (!started) break;
try {
// 检查类是否被更改过
if (!classLoader.modified()) {
continue;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log(sm.getString("webappLoader.failModifiedCheck"), e);
continue;
}
// 检查到类被更改过,通知Context去重载类
notifyContext();
break;
}
}
/**
* 另外开启一个线程来通知Context容器需要进行类重载了
*/
private void notifyContext() {
WebappContextNotifier notifier = new WebappContextNotifier();
(new Thread(notifier)).start();
}
// -------------------- WebappContextNotifier 内部类
/**
* 私有线程类来通知关联Context,需要重新加载类了。
*/
protected class WebappContextNotifier implements Runnable {
public void run() {
// 类重载的逻辑实际在Context容器类中
((Context) container).reload();
}
}
}
自定义类加载器的代码实现
Tomcat为Web应用程序做的类加载器为org.apache.catalina.loader.WebappClassLoader类的实例,WebappClassLoader继承自URLClassLoader。
WebappClassLoader中主要是对类加载的逻辑做了自定义,用来隔离各个Web应用的类库。同时它也做了一些缓存,来提升类加载的效率。
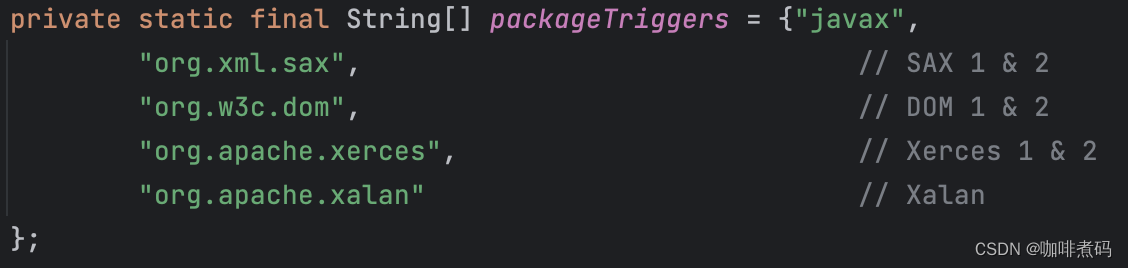
考虑到安全性,WebappClassLoader 类不允许载入指定的某些类,这些类的名字存储在一个字符串数组变量triggers 中,当前只有一个元素

此外,某些特殊的包及其子包下的类也是不允许WebApp类加载器直接加载的,需要先委托父类加载器去加载。
每个由 WebappClassLoader载入的类(无论是在WEB-INF/classes 目录下还是从某个JAR文件内作为类文件部署 ), 都视为“资源”。资源是 org.apache.catalina.loader.ResourceEntry类的实 例 。ResourceEntry 实例会保存其所代表的class 文件的字节流、最后一次修改日期、Manifest 信息(如果资源来自与一个JAR 文件的话)等。
为了达到更好的新能,WebappClassLoader会缓存已经加载过的类,放到 resourceEntries 这个map中。
protected HashMap<String,ResourceEntry> resourceEntries = new HashMap<>();
另外,如果WebappClassLoader在尝试加载某类时,没有找到此类并报了ClassNotFoundException,那么WebappClassLoader也会将这个不存在的类记录下来,下次再需要加载时直接抛异常就行。
protected HashMap<String,String> notFoundResources = new HashMap<>();
本章应用程序中没有定义common类加载类,所以本章代码中类加载器的结构如下

WebappClassLoader中有两个类加载器属性
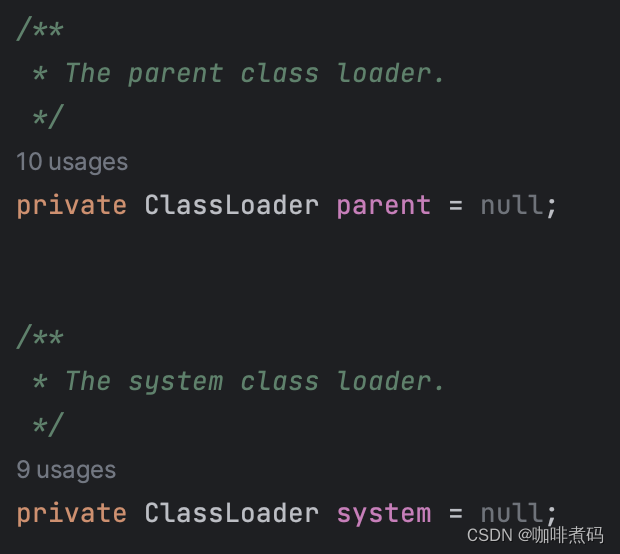
parent是它的父类加载器,正常来说这个值应该是common类加载器,但是我们本次代码并没有创建common类加载器,所以parent属性为null。
sytem就是系统类加载器,也就是应用程序类加载器。
WebappClassLoader类重写了loadClass方法,自定义的类加载逻辑如下图
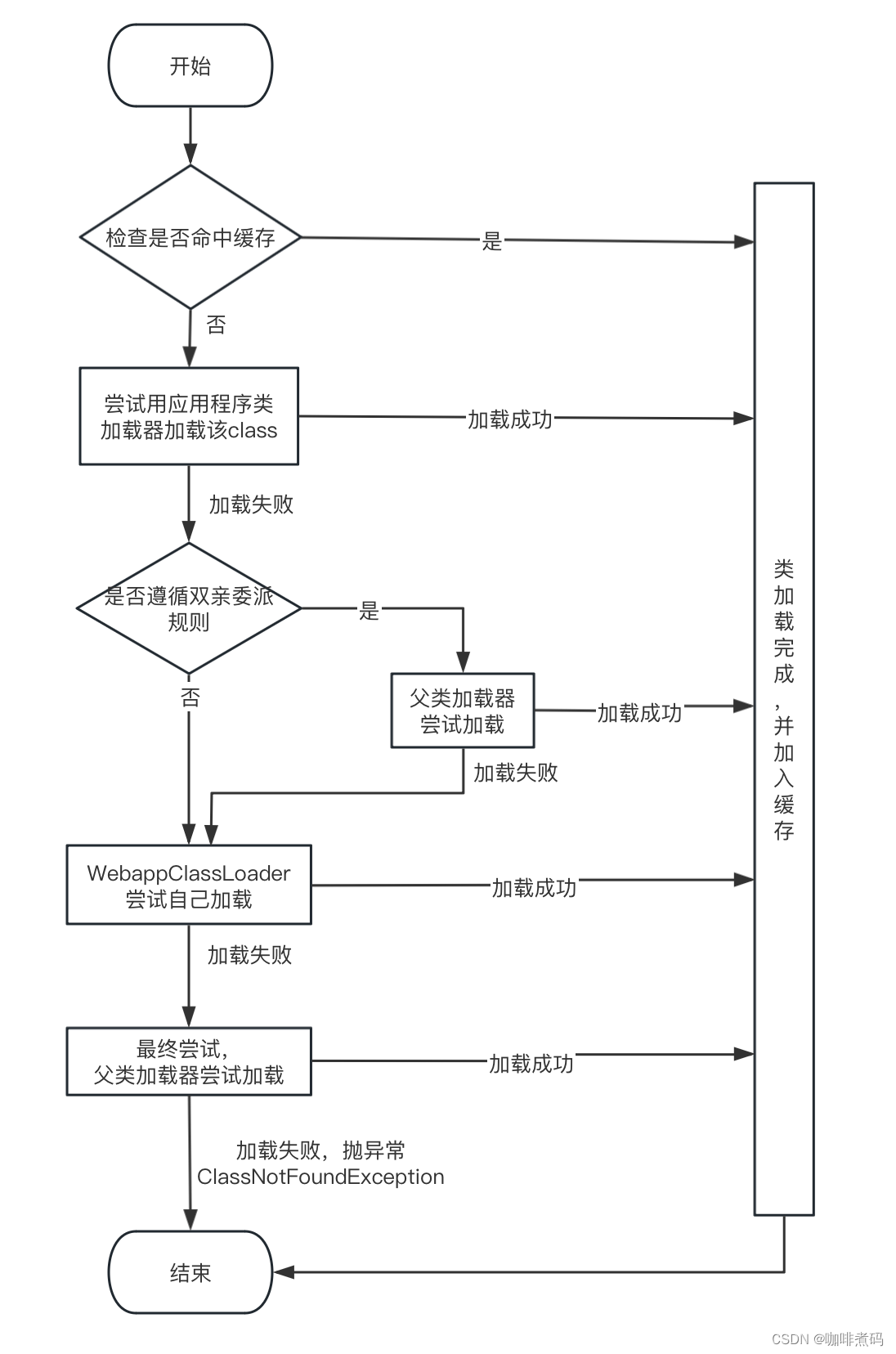
WebappClassLoader在加载类时会首先委托应用程序类加载器去加载,应用程序类加载器能加载哪些类呢?
应用程序类加载器默认加载以下目录和文件中的类:
1.通过 -classpath 或 -cp 参数指定的路径:
当启动Java应用程序时,可以使用 -classpath 或 -cp 参数来指定一个或多个目录和JAR文件,作为类的搜索路径。
例如:java -classpath /path/to/classes:/path/to/lib/some-library.jar com.example.Main
2.环境变量 CLASSPATH 指定的路径:
如果没有使用 -classpath 或 -cp 参数,系统类加载器会使用环境变量 CLASSPATH 中指定的路径。
例如,CLASSPATH=/path/to/classes:/path/to/lib/some-library.jar
3.当前工作目录:
如果 CLASSPATH 没有指定,系统类加载器会默认包含当前工作目录(.),即应用程序启动时的工作目录。
在通过WebappClassLoader加载的一个应用程序中的类中,如果依赖了其他类,这些其他类也会通过WebappClassLoader来加载,后面我会通过一个MyObject的例子来验证。
WebappClassLoader 中含有 modified() 方法,用来判断该类加载器对应的类库中有没有class文件或jar包被修改了。这个方法会被WebappLoader中的热加载巡检线程不断调用。
下面是WebappClassLoader的部分代码,完整代码请看源码
public class WebappClassLoader extends URLClassLoader implements Reloader, Lifecycle {
private static final String[] triggers = {"javax.servlet.Servlet" // Servlet API
};
private static final String[] packageTriggers = {"javax", // Java extensions
"org.xml.sax", // SAX 1 & 2
"org.w3c.dom", // DOM 1 & 2
"org.apache.xerces", // Xerces 1 & 2
"org.apache.xalan" // Xalan
};
public WebappClassLoader() {
super(new URL[0]);
this.parent = getParent();
system = getSystemClassLoader();
}
public WebappClassLoader(ClassLoader parent) {
super(new URL[0], parent);
this.parent = getParent();
system = getSystemClassLoader();
}
// 缓存已经加载过的类
protected HashMap<String,ResourceEntry> resourceEntries = new HashMap<>();
// 缓存找不到的那些类的类名
protected HashMap<String,String> notFoundResources = new HashMap<>();
// 是否遵循双亲委派模型
protected boolean delegate = false;
// 该类加载器的类库
protected String[] repositories = new String[0];
// 该类加载器的jar包类库
protected JarFile[] jarFiles = new JarFile[0];
// jar包名字的集合
protected String[] jarNames = new String[0];
// jar包类库中各jar包的最后修改日期
protected long[] lastModifiedDates = new long[0];
// modify方法需要检查的所有资源路径
protected String[] paths = new String[0];
// 父 类加载器
private ClassLoader parent = null;
// 系统类加载器
private ClassLoader system = null;
public Class loadClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
return loadClass(name, false);
}
public Class loadClass(String name, boolean resolve) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class clazz = null;
// Don't load classes if class loader is stopped
if (!started) {
log("Lifecycle error : CL stopped");
throw new ClassNotFoundException(name);
}
// (0) 检查该类加载器的缓存中存在
clazz = findLoadedClass0(name);
if (clazz != null) {
if (resolve) {
resolveClass(clazz);
}
return clazz;
}
// (0.1) 检查JVM提供的类加载缓存中是否存在
clazz = findLoadedClass(name);
if (clazz != null) {
if (resolve) {
resolveClass(clazz);
}
return clazz;
}
// (0.2) 尝试使用系统类加载器进行加载,方式应用程序中类覆盖 J2SE 中的类
try {
clazz = system.loadClass(name);
if (clazz != null) {
if (resolve) resolveClass(clazz);
return (clazz);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// Ignore
}
// (0.5) Permission to access this class when using a SecurityManager
if (securityManager != null) {
int i = name.lastIndexOf('.');
if (i >= 0) {
try {
securityManager.checkPackageAccess(name.substring(0, i));
} catch (SecurityException se) {
String error = "Security Violation, attempt to use " + "Restricted Class: " + name;
System.out.println(error);
se.printStackTrace();
log(error);
throw new ClassNotFoundException(error);
}
}
}
boolean delegateLoad = delegate || filter(name);
// (1) 如果遵循双亲委派机制的话,要先交给父类加载器去加载
if (delegateLoad) {
ClassLoader loader = parent;
if (loader == null) loader = system;
try {
clazz = loader.loadClass(name);
if (clazz != null) {
if (debug >= 3) log(" Loading class from parent");
if (resolve) resolveClass(clazz);
return (clazz);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
;
}
}
// (2) WebappClassLoader自己加载,从自己的类库中加载
try {
clazz = findClass(name);
if (clazz != null) {
if (debug >= 3) log(" Loading class from local repository");
if (resolve) resolveClass(clazz);
return (clazz);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
;
}
// (3) 强制使用父类加载器进行加载
if (!delegateLoad) {
if (debug >= 3) log(" Delegating to parent classloader");
ClassLoader loader = parent;
if (loader == null) loader = system;
try {
clazz = loader.loadClass(name);
if (clazz != null) {
if (debug >= 3) log(" Loading class from parent");
if (resolve) resolveClass(clazz);
return (clazz);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
;
}
}
// This class was not found
throw new ClassNotFoundException(name);
}
public Class findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
if (debug >= 3) {
log(" findClass(" + name + ")");
}
// (1) Permission to define this class when using a SecurityManager
if (securityManager != null) {
int i = name.lastIndexOf('.');
if (i >= 0) {
try {
if (debug >= 4) log(" securityManager.checkPackageDefinition");
securityManager.checkPackageDefinition(name.substring(0, i));
} catch (Exception se) {
if (debug >= 4) log(" -->Exception-->ClassNotFoundException", se);
throw new ClassNotFoundException(name);
}
}
}
// Ask our superclass to locate this class, if possible
// (throws ClassNotFoundException if it is not found)
Class clazz = null;
try {
if (debug >= 4) log(" findClassInternal(" + name + ")");
try {
clazz = findClassInternal(name);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cnfe) {
if (!hasExternalRepositories) {
throw cnfe;
}
} catch (AccessControlException ace) {
ace.printStackTrace();
throw new ClassNotFoundException(name);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
if (debug >= 4) log(" -->RuntimeException Rethrown", e);
throw e;
}
if ((clazz == null) && hasExternalRepositories) {
try {
clazz = super.findClass(name);
} catch (AccessControlException ace) {
throw new ClassNotFoundException(name);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
if (debug >= 4) log(" -->RuntimeException Rethrown", e);
throw e;
}
}
if (clazz == null) {
if (debug >= 3) log(" --> Returning ClassNotFoundException");
throw new ClassNotFoundException(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
if (debug >= 3) log(" --> Passing on ClassNotFoundException", e);
throw e;
}
// Return the class we have located
if (debug >= 4) log(" Returning class " + clazz);
if ((debug >= 4) && (clazz != null)) log(" Loaded by " + clazz.getClassLoader());
return (clazz);
}
/**
* 添加一个类库到类加载器的类库集合中,该类加载器将加载这些类库中的类。
* 这个方法只接受一个参数,即类库的路径名。它的作用是向 WebappClassLoader 中添加一个新的类库路径;
* 这个方法假设类库路径指向的是一个有效的 URL,并且不进行文件存在性检查。
*/
public void addRepository(String repository) {
// 忽略标准库,他们已经被其他方法加载过了
if (repository.startsWith("/WEB-INF/lib") || repository.startsWith("/WEB-INF/classes")) {
return;
}
// Add this repository to our underlying class loader
try {
URL url = new URL(repository);
super.addURL(url);
hasExternalRepositories = true;
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e.toString());
}
}
/**
* 同addRepository(String repository),第二个参数file是类库的绝对路径file
* 这个方法接受两个参数,第一个参数是类库的路径名,第二个参数是表示类库文件的 File对象。与第一个方法不同的是,这个方法会将类库路径名和对应的文件对象一一对应地添加到内部的数组中。这种方式更为灵活,因为它可以将路径名和文件对象关联起来,便于后续的管理和使用。
*/
synchronized void addRepository(String repository, File file) {
if (repository == null) return;
int i;
// Add this repository to our internal list
String[] result = new String[repositories.length + 1];
for (i = 0; i < repositories.length; i++) {
result[i] = repositories[i];
}
result[repositories.length] = repository;
repositories = result;
// Add the file to the list
File[] result2 = new File[files.length + 1];
for (i = 0; i < files.length; i++) {
result2[i] = files[i];
}
result2[files.length] = file;
files = result2;
}
/**
* 将一个jar包加到类库中
*/
synchronized void addJar(String jar, JarFile jarFile, File file) throws IOException {
if (jar == null) return;
if (jarFile == null) return;
if (file == null) return;
int i;
if ((jarPath != null) && (jar.startsWith(jarPath))) {
String jarName = jar.substring(jarPath.length());
while (jarName.startsWith("/")) jarName = jarName.substring(1);
String[] result = new String[jarNames.length + 1];
for (i = 0; i < jarNames.length; i++) {
result[i] = jarNames[i];
}
result[jarNames.length] = jarName;
jarNames = result;
}
try {
// Register the JAR for tracking
long lastModified = ((ResourceAttributes) resources.getAttributes(jar)).getLastModified();
String[] result = new String[paths.length + 1];
for (i = 0; i < paths.length; i++) {
result[i] = paths[i];
}
result[paths.length] = jar;
paths = result;
long[] result3 = new long[lastModifiedDates.length + 1];
for (i = 0; i < lastModifiedDates.length; i++) {
result3[i] = lastModifiedDates[i];
}
result3[lastModifiedDates.length] = lastModified;
lastModifiedDates = result3;
} catch (NamingException e) {
// Ignore
}
// If the JAR currently contains invalid classes, don't actually use it
// for classloading
if (!validateJarFile(file)) return;
JarFile[] result2 = new JarFile[jarFiles.length + 1];
for (i = 0; i < jarFiles.length; i++) {
result2[i] = jarFiles[i];
}
result2[jarFiles.length] = jarFile;
jarFiles = result2;
// Add the file to the list
File[] result4 = new File[jarRealFiles.length + 1];
for (i = 0; i < jarRealFiles.length; i++) {
result4[i] = jarRealFiles[i];
}
result4[jarRealFiles.length] = file;
jarRealFiles = result4;
// Load manifest
Manifest manifest = jarFile.getManifest();
if (manifest != null) {
Iterator extensions = Extension.getAvailable(manifest).iterator();
while (extensions.hasNext()) {
available.add(extensions.next());
}
extensions = Extension.getRequired(manifest).iterator();
while (extensions.hasNext()) {
required.add(extensions.next());
}
}
}
/**
* 是否有类文件或jar包被修改了?
*/
public boolean modified() {
// Checking for modified loaded resources
int length = paths.length;
// A rare race condition can occur in the updates of the two arrays
// It's totally ok if the latest class added is not checked (it will
// be checked the next time
int length2 = lastModifiedDates.length;
if (length > length2) length = length2;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
try {
long lastModified = ((ResourceAttributes) resources.getAttributes(paths[i])).getLastModified();
if (lastModified != lastModifiedDates[i]) {
log(" Resource '" + paths[i] + "' was modified; Date is now: " + new java.util.Date(lastModified) + " Was: " + new java.util.Date(lastModifiedDates[i]));
return (true);
}
} catch (NamingException e) {
log(" Resource '" + paths[i] + "' is missing");
return (true);
}
}
length = jarNames.length;
// Check if JARs have been added or removed
if (getJarPath() != null) {
try {
NamingEnumeration myEnum = resources.listBindings(getJarPath());
int i = 0;
while (myEnum.hasMoreElements() && (i < length)) {
NameClassPair ncPair = (NameClassPair) myEnum.nextElement();
String name = ncPair.getName();
// Ignore non JARs present in the lib folder
if (!name.endsWith(".jar")) continue;
if (!name.equals(jarNames[i])) {
// Missing JAR
log(" Additional JARs have been added : '" + name + "'");
return (true);
}
i++;
}
if (myEnum.hasMoreElements()) {
while (myEnum.hasMoreElements()) {
NameClassPair ncPair = (NameClassPair) myEnum.nextElement();
String name = ncPair.getName();
// Additional non-JAR files are allowed
if (name.endsWith(".jar")) {
// There was more JARs
log(" Additional JARs have been added");
return (true);
}
}
} else if (i < jarNames.length) {
// There was less JARs
log(" Additional JARs have been added");
return (true);
}
} catch (NamingException e) {
if (debug > 2) log(" Failed tracking modifications of '" + getJarPath() + "'");
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
log(" Failed tracking modifications of '" + getJarPath() + "' : " + e.getMessage());
}
}
// No classes have been modified
return (false);
}
}
StandardContext类
StandardContext类的具体内容将放到第十二章来讲,这里仅列出它的 reload() 方法,即类重载的方法。看上去其实就是一个Context容器的重启过程:先将容器实例及其相关组件实例stop掉,然后在start起来。
public synchronized void reload() {
// Validate our current component state
if (!started) throw new IllegalStateException(sm.getString("containerBase.notStarted", logName()));
// Make sure reloading is enabled
// if (!reloadable)
// throw new IllegalStateException
// (sm.getString("standardContext.notReloadable"));
log(sm.getString("standardContext.reloadingStarted"));
// Stop accepting requests temporarily
setPaused(true);
// Binding thread
ClassLoader oldCCL = bindThread();
// Shut down our session manager
if ((manager != null) && (manager instanceof Lifecycle)) {
try {
((Lifecycle) manager).stop();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log(sm.getString("standardContext.stoppingManager"), e);
}
}
// Shut down the current version of all active servlets
Container children[] = findChildren();
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
Wrapper wrapper = (Wrapper) children[i];
if (wrapper instanceof Lifecycle) {
try {
((Lifecycle) wrapper).stop();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log(sm.getString("standardContext.stoppingWrapper", wrapper.getName()), e);
}
}
}
// Shut down application event listeners
listenerStop();
// Clear all application-originated servlet context attributes
if (context != null) context.clearAttributes();
// Shut down filters
filterStop();
if (isUseNaming()) {
// Start
namingContextListener.lifecycleEvent(new LifecycleEvent(this, Lifecycle.STOP_EVENT));
}
// Binding thread
unbindThread(oldCCL);
// Shut down our application class loader
if ((loader != null) && (loader instanceof Lifecycle)) {
try {
((Lifecycle) loader).stop();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log(sm.getString("standardContext.stoppingLoader"), e);
}
}
// Binding thread
oldCCL = bindThread();
// Restart our application class loader
if ((loader != null) && (loader instanceof Lifecycle)) {
try {
((Lifecycle) loader).start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log(sm.getString("standardContext.startingLoader"), e);
}
}
// Binding thread
unbindThread(oldCCL);
// Create and register the associated naming context, if internal
// naming is used
boolean ok = true;
if (isUseNaming()) {
// Start
namingContextListener.lifecycleEvent(new LifecycleEvent(this, Lifecycle.START_EVENT));
}
// Binding thread
oldCCL = bindThread();
// Restart our application event listeners and filters
if (ok) {
if (!listenerStart()) {
log(sm.getString("standardContext.listenerStartFailed"));
ok = false;
}
}
if (ok) {
if (!filterStart()) {
log(sm.getString("standardContext.filterStartFailed"));
ok = false;
}
}
// Restore the "Welcome Files" and "Resources" context attributes
postResources();
postWelcomeFiles();
// Restart our currently defined servlets
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
if (!ok) break;
Wrapper wrapper = (Wrapper) children[i];
if (wrapper instanceof Lifecycle) {
try {
((Lifecycle) wrapper).start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log(sm.getString("standardContext.startingWrapper", wrapper.getName()), e);
ok = false;
}
}
}
// Reinitialize all load on startup servlets
loadOnStartup(children);
// Restart our session manager (AFTER naming context recreated/bound)
if ((manager != null) && (manager instanceof Lifecycle)) {
try {
((Lifecycle) manager).start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log(sm.getString("standardContext.startingManager"), e);
}
}
// Unbinding thread
unbindThread(oldCCL);
// Start accepting requests again
if (ok) {
log(sm.getString("standardContext.reloadingCompleted"));
} else {
setAvailable(false);
log(sm.getString("standardContext.reloadingFailed"));
}
setPaused(false);
// Notify our interested LifecycleListeners
lifecycle.fireLifecycleEvent(Context.RELOAD_EVENT, null);
}Web应用程序
下面来构建两个应用程序,作为Tomcat中存放的应用程序,他们分别由不同的载入器实例来加载。我们仍然使用前面章节用到的ModernServlet与PrimitiveServlet来作为应用程序的servlet。至于lib包下的simple-project-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar则是只提供了一个MyObject类

MyObject类中打印了加载该类的类加载器,并提供了一个print方法
public class MyObject {
public MyObject() {
ClassLoader classLoader = this.getClass().getClassLoader();
System.out.println("=======MyObject's classLoader is: "+classLoader.toString());
}
public void print() {
System.out.println("=======MyObject print [AAAAAA]");
}
}ModernServlet的doGet方法末尾使用了MyObject类,创建了一个MyObject对象并调用其print方法。
public class ModernServlet extends HttpServlet {
public void init(ServletConfig config) {
System.out.println("ModernServlet -- init");
}
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
//先输出HTTP的头部信息
String msg = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n" +
"Content-Type: text/html\r\n" +
"Transfer-Encoding: chunked\r\n" +
"\r\n";
out.print(msg);
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
//再输出HTTP的消息体
builder.append("<html>");
builder.append("<head>");
builder.append("<title>Modern Servlet</title>");
builder.append("</head>");
builder.append("<body>");
builder.append("<h2>Headers</h2>");
Enumeration headers = request.getHeaderNames();
while (headers.hasMoreElements()) {
String header = (String) headers.nextElement();
builder.append("<br>" + header + " : " + request.getHeader(header));
}
builder.append("<br><h2>Method</h2>");
builder.append("<br>" + request.getMethod());
builder.append("<br><h2>Parameters</h2>");
Enumeration parameters = request.getParameterNames();
while (parameters.hasMoreElements()) {
String parameter = (String) parameters.nextElement();
builder.append("<br>" + parameter + " : " + request.getParameter(parameter));
}
builder.append("<br><h2>Query String</h2>");
builder.append("<br>" + request.getQueryString());
builder.append("<br><h2>Request URI</h2>");
builder.append("<br>" + request.getRequestURI());
builder.append("</body>");
builder.append("</html>");
// 这里是与原书中代码不一样的地方,原代码没有加chunked块的长度,浏览器不能正常解析
out.print(Integer.toHexString(builder.length()) + "\r\n");
out.print(builder.toString() + "\r\n");
out.print("0\r\n\r\n");
out.flush();
out.close();
MyObject myObject = new MyObject();
myObject.print();
}
}这里我加入MyObject这个类,是有两种用途
- 检测WebappClassLoader是否能加载 WEB-INF/lib 包下的jar包中的类。
- 在ModernServlet执行doGet方法时,发现其依赖MyObject,测试MyObject类是否是和ModernServlet用的同一个类加载实例来加载的。
另外我构建了两个应用程序 myApp与myApp2,使用了同一套代码,我们可以来检查下,这两个应用程序下相同的类是否是由不同的WebappClassLoader实例来加载的。
我写了一段检测不同类的类加载器的代码,放在了Wrapper容器的基础阀SimpleWrapperValve中,在Wrapper实例获取到对应的servlet后,打印了一下加载该servlet的类加载器;这里还打印了一下HttpServlet类的类加载器,HttpServlet类在项目最外层的lib包中,是我设置的整个项目的lib依赖,这个lib包理应会被加入到应用程序类加载器的类库中,所以HttpServlet类的类加载器应该是 sun.misc.Launcher.AppClassLoader
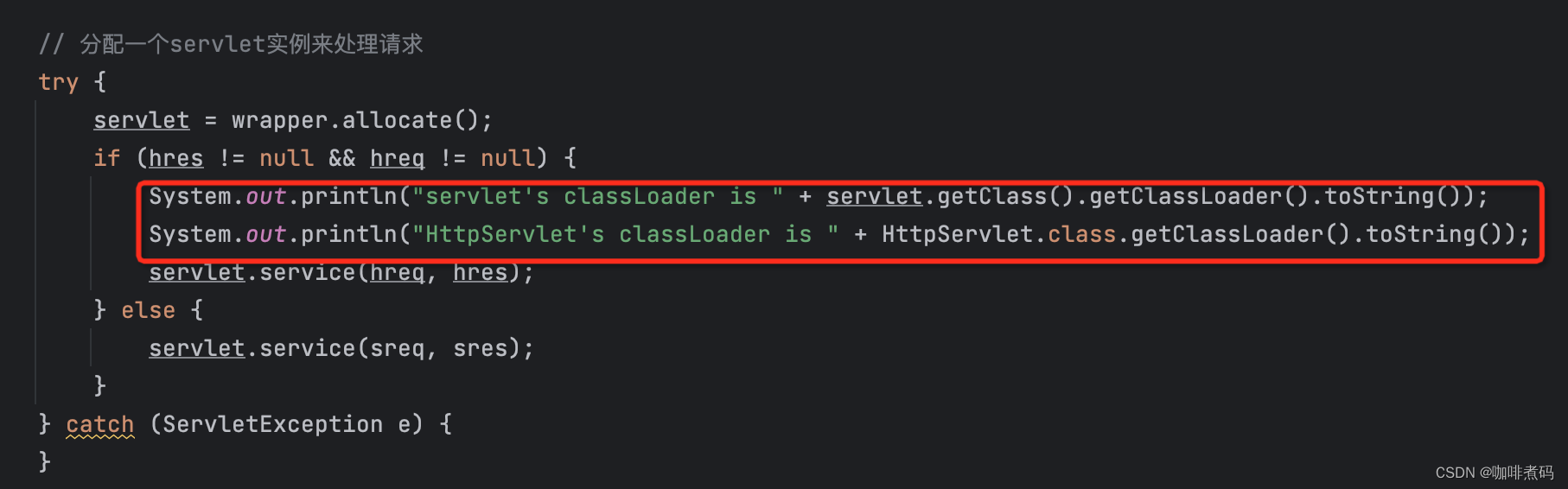
public class SimpleWrapperValve implements Valve, Contained {
protected Container container;
public void invoke(Request request, Response response, ValveContext valveContext)
throws IOException, ServletException {
SimpleWrapper wrapper = (SimpleWrapper) getContainer();
ServletRequest sreq = request.getRequest();
ServletResponse sres = response.getResponse();
Servlet servlet = null;
HttpServletRequest hreq = null;
if (sreq instanceof HttpServletRequest) {
hreq = (HttpServletRequest) sreq;
}
HttpServletResponse hres = null;
if (sres instanceof HttpServletResponse) {
hres = (HttpServletResponse) sres;
}
// 分配一个servlet实例来处理请求
try {
servlet = wrapper.allocate();
if (hres != null && hreq != null) {
System.out.println("servlet's classLoader is " + servlet.getClass().getClassLoader().toString());
System.out.println("HttpServlet's classLoader is " + HttpServlet.class.getClassLoader().toString());
servlet.service(hreq, hres);
} else {
servlet.service(sreq, sres);
}
} catch (ServletException e) {
}
}
public String getInfo() {
return null;
}
public Container getContainer() {
return container;
}
public void setContainer(Container container) {
this.container = container;
}
}wrapper.allocate()这个方法是调用的SimpleWrapper的allocate方法,allocate会调用loadServlet方法来进行servlet类的类加载,我把代码放这,你可以再看下
public class SimpleWrapper implements Wrapper, Pipeline, Lifecycle {
public SimpleWrapper() {
pipeline.setBasic(new SimpleWrapperValve());
}
// the servlet instance
private Servlet instance = null;
private String servletClass;
private Loader loader;
private String name;
protected LifecycleSupport lifecycle = new LifecycleSupport(this);
private SimplePipeline pipeline = new SimplePipeline(this);
protected Container parent = null;
protected boolean started = false;
public synchronized void addValve(Valve valve) {
pipeline.addValve(valve);
}
public Servlet allocate() throws ServletException {
// Load and initialize our instance if necessary
if (instance == null) {
try {
instance = loadServlet();
} catch (ServletException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new ServletException("Cannot allocate a servlet instance", e);
}
}
return instance;
}
public Servlet loadServlet() throws ServletException {
if (instance != null) return instance;
Servlet servlet = null;
String actualClass = servletClass;
if (actualClass == null) {
throw new ServletException("servlet class has not been specified");
}
Loader loader = getLoader();
// Acquire an instance of the class loader to be used
if (loader == null) {
throw new ServletException("No loader.");
}
ClassLoader classLoader = loader.getClassLoader();
// Load the specified servlet class from the appropriate class loader
Class classClass = null;
try {
if (classLoader != null) {
classClass = classLoader.loadClass(actualClass);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new ServletException("Servlet class not found");
}
// Instantiate and initialize an instance of the servlet class itself
try {
servlet = (Servlet) classClass.newInstance();
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate servlet");
}
// Call the initialization method of this servlet
try {
servlet.init(null);
} catch (Throwable f) {
throw new ServletException("Failed initialize servlet.");
}
return servlet;
}
public Loader getLoader() {
if (loader != null) return (loader);
if (parent != null) return (parent.getLoader());
return (null);
}
}SimpleWrapper的getLoader方法会主动去寻找父容器的Loader,所以本次程序我们只要给Context容器设置好Loader就行(WebappLoader)。
通过loader就能获取到对应的类加载器,也就是WebappClassLoader的实例,然后通过WebappClassLoader去加载该servlet类。
如果浏览器访问 http://localhost:8080/myApp/Modern,WebappClassLoader实例先加载了 ModernServlet 类,然后ModernServlet的doGet方法被调用,发现需要使用MyObject类,于是JVM拿到ModernServlet的类加载器(即WebappClassLoader实例)去加载MyObject类。
接下来我们写个启动类,启动一个简易Tomcat,来验证上述说法
Bootstrap启动类
本次context容器类使用Tomcat内置的StandardContext,为了验证两个应用的类加载隔离性,这次还将用上StandardHost作为Host容器,Host容器的内容将在第十三章介绍。
我将构建两个一模一样的StandardContext实例,唯一不同是就是它们加载的应用程序目录不同,一个是myApp,一个是myApp2。理论上来讲,两个应用程序内的类应该由不同的类加载器来加载,接下来启动服务来验证看看
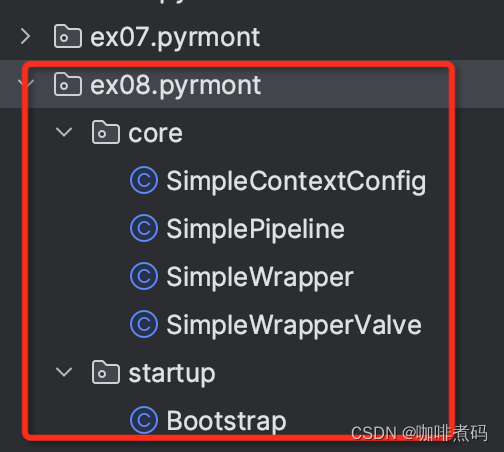
package ex08.pyrmont.startup;
import ex08.pyrmont.core.SimpleWrapper;
import ex08.pyrmont.core.SimpleContextConfig;
import org.apache.catalina.*;
import org.apache.catalina.connector.http.HttpConnector;
import org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext;
import org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHost;
import org.apache.catalina.loader.WebappClassLoader;
import org.apache.catalina.loader.WebappLoader;
import org.apache.naming.resources.ProxyDirContext;
public final class Bootstrap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.setProperty("catalina.base", System.getProperty("user.dir"));
Connector connector = new HttpConnector();
Host host = new StandardHost();
host.setName("localhost");
host.setAppBase("");
{
Wrapper wrapper1 = new SimpleWrapper();
wrapper1.setName("Primitive");
wrapper1.setServletClass("PrimitiveServlet");
Wrapper wrapper2 = new SimpleWrapper();
wrapper2.setName("Modern");
wrapper2.setServletClass("ModernServlet");
Context context = new StandardContext();
// StandardContext's start method adds a default mapper
context.setPath("/myApp");
context.setDocBase("myApp");
context.addChild(wrapper1);
context.addChild(wrapper2);
// context.addServletMapping(pattern, name);
context.addServletMapping("/Primitive", "Primitive");
context.addServletMapping("/Modern", "Modern");
// add ContextConfig. This listener is important because it configures
// StandardContext (sets configured to true), otherwise StandardContext
// won't start
LifecycleListener listener = new SimpleContextConfig();
((Lifecycle) context).addLifecycleListener(listener);
// here is our loader
Loader loader = new WebappLoader();
// associate the loader with the Context
context.setLoader(loader);
host.addChild(context);
}
{
Wrapper wrapper1 = new SimpleWrapper();
wrapper1.setName("Primitive");
wrapper1.setServletClass("PrimitiveServlet");
Wrapper wrapper2 = new SimpleWrapper();
wrapper2.setName("Modern");
wrapper2.setServletClass("ModernServlet");
Context context = new StandardContext();
// StandardContext's start method adds a default mapper
context.setPath("/myApp2");
context.setDocBase("myApp2");
context.addChild(wrapper1);
context.addChild(wrapper2);
// context.addServletMapping(pattern, name);
context.addServletMapping("/Primitive", "Primitive");
context.addServletMapping("/Modern", "Modern");
// add ContextConfig. This listener is important because it configures
// StandardContext (sets configured to true), otherwise StandardContext
// won't start
LifecycleListener listener = new SimpleContextConfig();
((Lifecycle) context).addLifecycleListener(listener);
// here is our loader
Loader loader = new WebappLoader();
// associate the loader with the Context
context.setLoader(loader);
host.addChild(context);
}
connector.setContainer(host);
try {
connector.initialize();
((Lifecycle) connector).start();
((Lifecycle) host).start();
// make the application wait until we press a key.
System.in.read();
((Lifecycle) host).stop();
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}启动服务,浏览器访问两下
1. http://localhost:8080/myApp/Modern
2. http://localhost:8080/myApp2/Modern
浏览器的结果与前几章的一样,不再贴了,主要看后端日志
Connected to the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:64327', transport: 'socket'
HttpConnector Opening server socket on all host IP addresses
HttpConnector[8080] Starting background thread
WebappLoader[/myApp2]: Deploying class repositories to work directory /Users/hml/IdeaProjects/demo/HowTomcatWorks/work/_/localhost/myApp2
WebappLoader[/myApp2]: Deploy class files /WEB-INF/classes to /Users/hml/IdeaProjects/demo/HowTomcatWorks/myApp2/WEB-INF/classes
WebappLoader[/myApp2]: Deploy JAR /WEB-INF/lib/simple-project-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar to /Users/hml/IdeaProjects/demo/HowTomcatWorks/myApp2/WEB-INF/lib/simple-project-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar
Starting Wrapper Primitive
Starting Wrapper Modern
StandardManager[/myApp2]: Seeding random number generator class java.security.SecureRandom
StandardManager[/myApp2]: Seeding of random number generator has been completed
WebappLoader[/myApp]: Deploying class repositories to work directory /Users/hml/IdeaProjects/demo/HowTomcatWorks/work/_/localhost/myApp
WebappLoader[/myApp]: Deploy class files /WEB-INF/classes to /Users/hml/IdeaProjects/demo/HowTomcatWorks/myApp/WEB-INF/classes
WebappLoader[/myApp]: Deploy JAR /WEB-INF/lib/simple-project-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar to /Users/hml/IdeaProjects/demo/HowTomcatWorks/myApp/WEB-INF/lib/simple-project-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar
Starting Wrapper Primitive
Starting Wrapper Modern
StandardManager[/myApp]: Seeding random number generator class java.security.SecureRandom
StandardManager[/myApp]: Seeding of random number generator has been completed
ModernServlet -- init
=======servlet's classLoader is org.apache.catalina.loader.WebappClassLoader@4bf558aa
=======HttpServlet's classLoader is sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2
=======MyObject's classLoader is: org.apache.catalina.loader.WebappClassLoader@4bf558aa
=======MyObject print [AAAAAA]
ModernServlet -- init
=======servlet's classLoader is org.apache.catalina.loader.WebappClassLoader@7cca494b
=======HttpServlet's classLoader is sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2
=======MyObject's classLoader is: org.apache.catalina.loader.WebappClassLoader@7cca494b
=======MyObject print [AAAAAA]
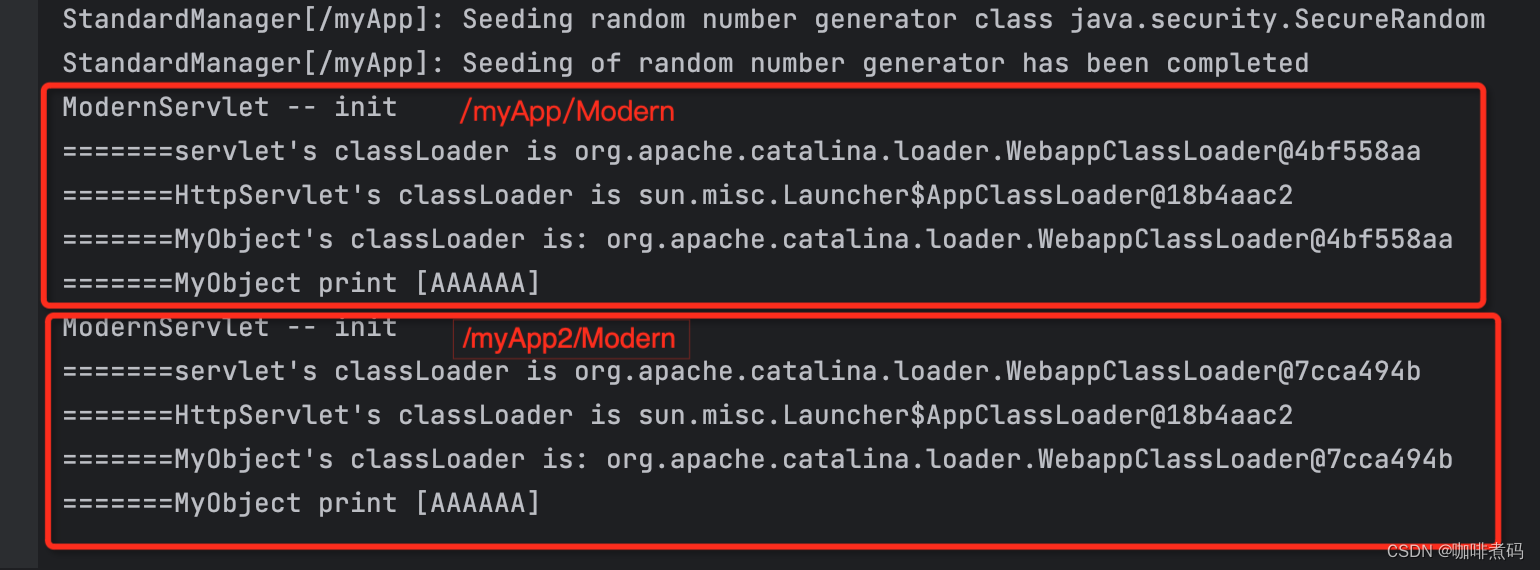
可以看到 HttpServlet的类加载是应用程序类加载器 AppClassLoader ,并且myApp与myApp2两个应用的AppClassLoader是同一个对象。说明Tomcat中的应用程序类加载器是唯一的,多应用公用的。
而加载ModernServlet与MyObject两个类的类加载为WebappClassLoader,并且myApp与myApp2两个应用的WebappClassLoader是不同的对象,说明两个应用的类加载是隔离的。
MyObject类与ModernServlet类使用的类加载相同,也证实了上面的说法,当JVM检测到某类依赖的另外的类需要还没加载时,会拿当前类的类加载器去加载。
好,Tomcat的载入器内容就到这里,Tomcat的自定义类加载器是一个经典的打破双亲委派机制的案例,目的是为了实现各应用程序之间的类库隔离。
另外,关于 common、server、shared三个类加载器并不像 WebApp类加载器一样有特定的类(WebappClassLoader)来支撑。Tomcat中并没有类似的诸如CommonClassLoader、ServerClassLoader等类,而是提供了StandardClassLoader类,这三个类加载器都是一个StandardClassLoader类实例,不同的是,他们可加载的类库不同,这个类库就定义在 catalina.properties 文件中,这三个类加载的创建逻辑在org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap#initClassLoaders方法中(基于apache-tomcat-6.09版本)
org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap部分代码
private void initClassLoaders() {
try {
commonLoader = createClassLoader("common", null);
if( commonLoader == null ) {
// no config file, default to this loader - we might be in a 'single' env.
commonLoader=this.getClass().getClassLoader();
}
catalinaLoader = createClassLoader("server", commonLoader);
sharedLoader = createClassLoader("shared", commonLoader);
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.error("Class loader creation threw exception", t);
System.exit(1);
}
}
private ClassLoader createClassLoader(String name, ClassLoader parent)
throws Exception {
String value = CatalinaProperties.getProperty(name + ".loader");
if ((value == null) || (value.equals("")))
return parent;
ArrayList repositoryLocations = new ArrayList();
ArrayList repositoryTypes = new ArrayList();
int i;
StringTokenizer tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(value, ",");
while (tokenizer.hasMoreElements()) {
String repository = tokenizer.nextToken();
// Local repository
boolean replace = false;
String before = repository;
while ((i=repository.indexOf(CATALINA_HOME_TOKEN))>=0) {
replace=true;
if (i>0) {
repository = repository.substring(0,i) + getCatalinaHome()
+ repository.substring(i+CATALINA_HOME_TOKEN.length());
} else {
repository = getCatalinaHome()
+ repository.substring(CATALINA_HOME_TOKEN.length());
}
}
while ((i=repository.indexOf(CATALINA_BASE_TOKEN))>=0) {
replace=true;
if (i>0) {
repository = repository.substring(0,i) + getCatalinaBase()
+ repository.substring(i+CATALINA_BASE_TOKEN.length());
} else {
repository = getCatalinaBase()
+ repository.substring(CATALINA_BASE_TOKEN.length());
}
}
if (replace && log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Expanded " + before + " to " + replace);
// Check for a JAR URL repository
try {
URL url=new URL(repository);
repositoryLocations.add(repository);
repositoryTypes.add(ClassLoaderFactory.IS_URL);
continue;
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
// Ignore
}
if (repository.endsWith("*.jar")) {
repository = repository.substring
(0, repository.length() - "*.jar".length());
repositoryLocations.add(repository);
repositoryTypes.add(ClassLoaderFactory.IS_GLOB);
} else if (repository.endsWith(".jar")) {
repositoryLocations.add(repository);
repositoryTypes.add(ClassLoaderFactory.IS_JAR);
} else {
repositoryLocations.add(repository);
repositoryTypes.add(ClassLoaderFactory.IS_DIR);
}
}
String[] locations = (String[]) repositoryLocations.toArray(new String[0]);
Integer[] types = (Integer[]) repositoryTypes.toArray(new Integer[0]);
ClassLoader classLoader = ClassLoaderFactory.createClassLoader
(locations, types, parent);
// Retrieving MBean server
MBeanServer mBeanServer = null;
if (MBeanServerFactory.findMBeanServer(null).size() > 0) {
mBeanServer =
(MBeanServer) MBeanServerFactory.findMBeanServer(null).get(0);
} else {
mBeanServer = MBeanServerFactory.createMBeanServer();
}
// Register the server classloader
ObjectName objectName =
new ObjectName("Catalina:type=ServerClassLoader,name=" + name);
mBeanServer.registerMBean(classLoader, objectName);
return classLoader;
}org.apache.catalina.startup.ClassLoaderFactory#createClassLoader方法
public static ClassLoader createClassLoader(String locations[],
Integer types[],
ClassLoader parent)
throws Exception {
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Creating new class loader");
// Construct the "class path" for this class loader
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
if (locations != null && types != null && locations.length == types.length) {
for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) {
String location = locations[i];
if ( types[i] == IS_URL ) {
URL url = new URL(location);
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug(" Including URL " + url);
list.add(url);
} else if ( types[i] == IS_DIR ) {
File directory = new File(location);
directory = new File(directory.getCanonicalPath());
if (!directory.exists() || !directory.isDirectory() ||
!directory.canRead())
continue;
URL url = directory.toURL();
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug(" Including directory " + url);
list.add(url);
} else if ( types[i] == IS_JAR ) {
File file=new File(location);
file = new File(file.getCanonicalPath());
if (!file.exists() || !file.canRead())
continue;
URL url = file.toURL();
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug(" Including jar file " + url);
list.add(url);
} else if ( types[i] == IS_GLOB ) {
File directory=new File(location);
if (!directory.exists() || !directory.isDirectory() ||
!directory.canRead())
continue;
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug(" Including directory glob "
+ directory.getAbsolutePath());
String filenames[] = directory.list();
for (int j = 0; j < filenames.length; j++) {
String filename = filenames[j].toLowerCase();
if (!filename.endsWith(".jar"))
continue;
File file = new File(directory, filenames[j]);
file = new File(file.getCanonicalPath());
if (!file.exists() || !file.canRead())
continue;
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug(" Including glob jar file "
+ file.getAbsolutePath());
URL url = file.toURL();
list.add(url);
}
}
}
}
// Construct the class loader itself
URL[] array = (URL[]) list.toArray(new URL[list.size()]);
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
log.debug(" location " + i + " is " + array[i]);
}
StandardClassLoader classLoader = null;
if (parent == null)
classLoader = new StandardClassLoader(array);
else
classLoader = new StandardClassLoader(array, parent);
return (classLoader);
}关于Tomcat与SpringBoot
如今我们在用java写Web应用程序时多使用SpringBoot框架,SpringBoot默认集成了Tomcat,这也导致了一个Tomcat中只会部署一个应用程序,自定义类加载器的存在感就大大降低了。
我写了个测试类来测试了一下
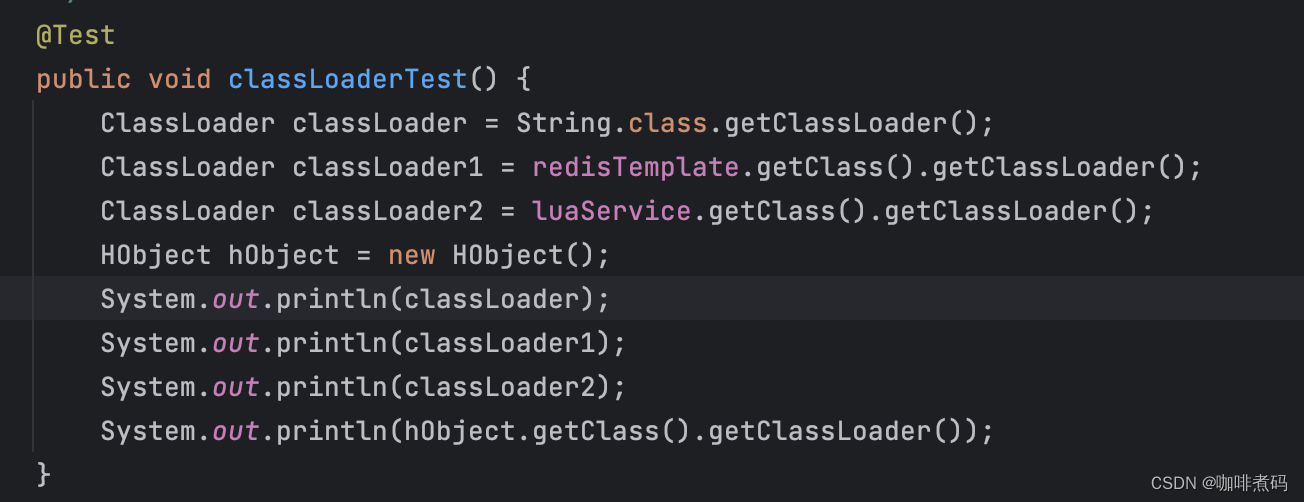
输出结果
null
sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2
sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2
sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2redisTemplate就是我们熟知的那个RedisTemplate,luaService是我自己写的标注了@Service的类,HObject就是一个普普通通不带任何注解的pojo类。
实验结果就是除了String被启动类加载器加载了,其他的类都是被jdk自带的应用程序类加载器加载的,并且我在这个springboot自带的tomcat的 WebappClassLoaderBase#loadClass 方法上打了断点,发现项目启动后压根没有进入到过这个方法中,也就是WebappClassLoader压根没用上。
springboot的东西再深挖又得烧脑了,容我休息一下,这里暂且告一段落,后续再做研究。
源码分享
https://gitee.com/huo-ming-lu/HowTomcatWorks
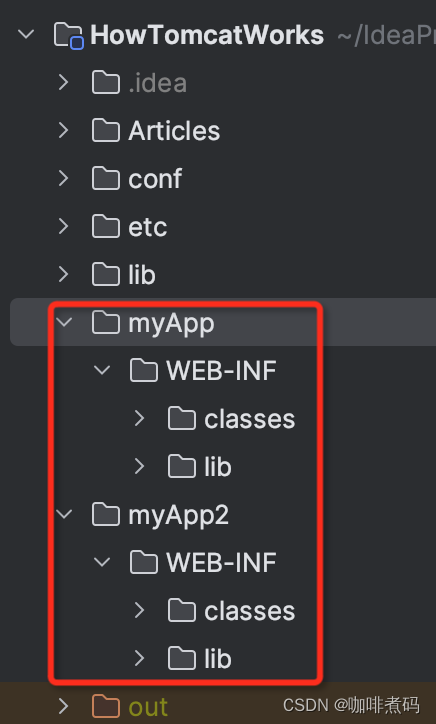
基于原书源码,我改造了Bootstrap以支持启动一个多应用的简易Tomcat。
我改造了ModernServlet类并加入simple-project-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar包来验证WebApp应用程序中除servlet类外的其他类的类加载过程。并复制了myApp工程得到myApp2工程,来验证多应用间的类加载隔离。
另附Tomcat各版本源码的下载目录
https://archive.apache.org/dist/tomcat/