本篇目标
- constructor
- operator=
- Elements access
- Iterators
- Capacity
- Modifiers
- String operations
- member contants
- 其他函数
一、constructor(对象的创建)

void StrTest1()
{
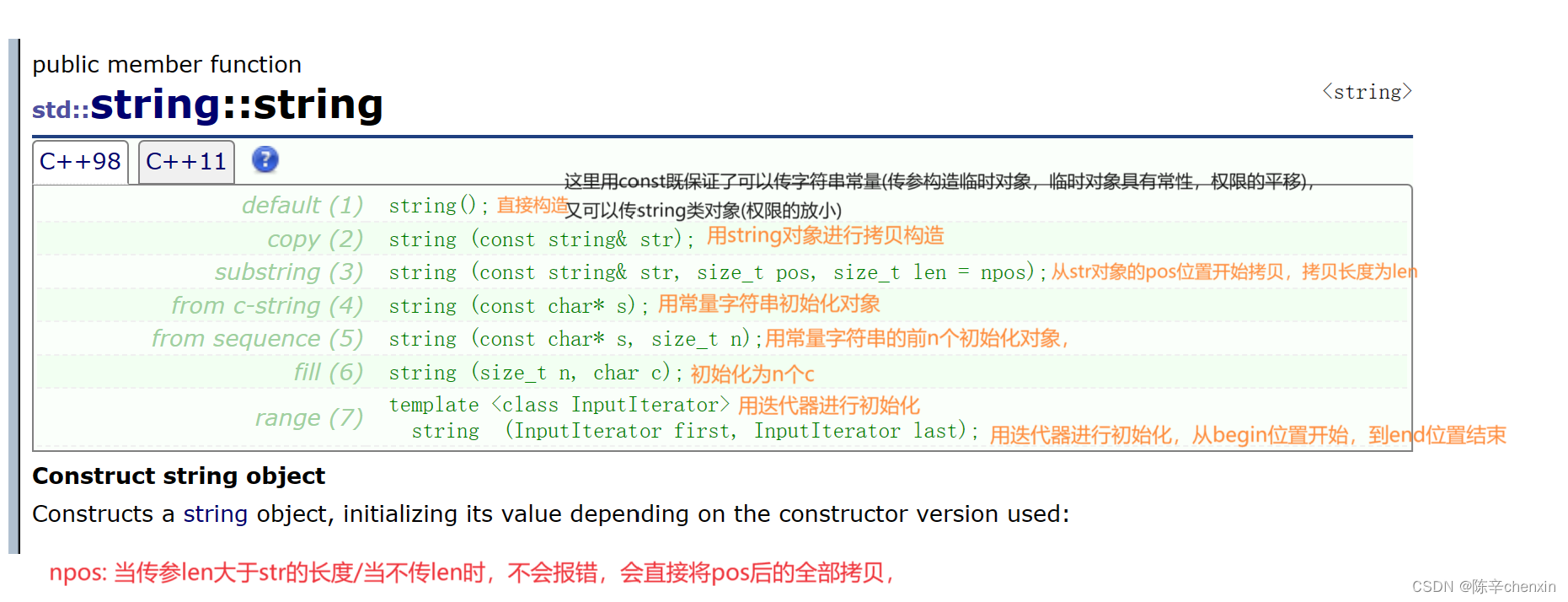
string s1;//直接构造
cout << s1 << endl;//string里内置了流插入、流提取的函数重载,可直接打印
string s2("hello world");//字符常量构造,有隐式类型转换
cout << s2 << endl;
string s3("hello world", 5);//取常量字符串的前5个进行打印
cout << s3 << endl;
string s4(s3); //拷贝构造
cout << s4 << endl;
string s5(s2, 2);//从s2的第二个字符开始(0 1 2 也就是l位置,若不给长度,直接全部拷贝)
cout << s5 << endl;
string s6(s2, 2, 4);//从第二个字符开始拷贝,到第四个字符
cout << s6 << endl;
string s7(7, 'x');//用7个x对其进行初始化
cout << s7 << endl;
string s8(s2.begin(), s2.end());//调用begin和end成员函数,其返回迭代器(迭代器很像指针,但不只指针)
cout << s8 << endl;
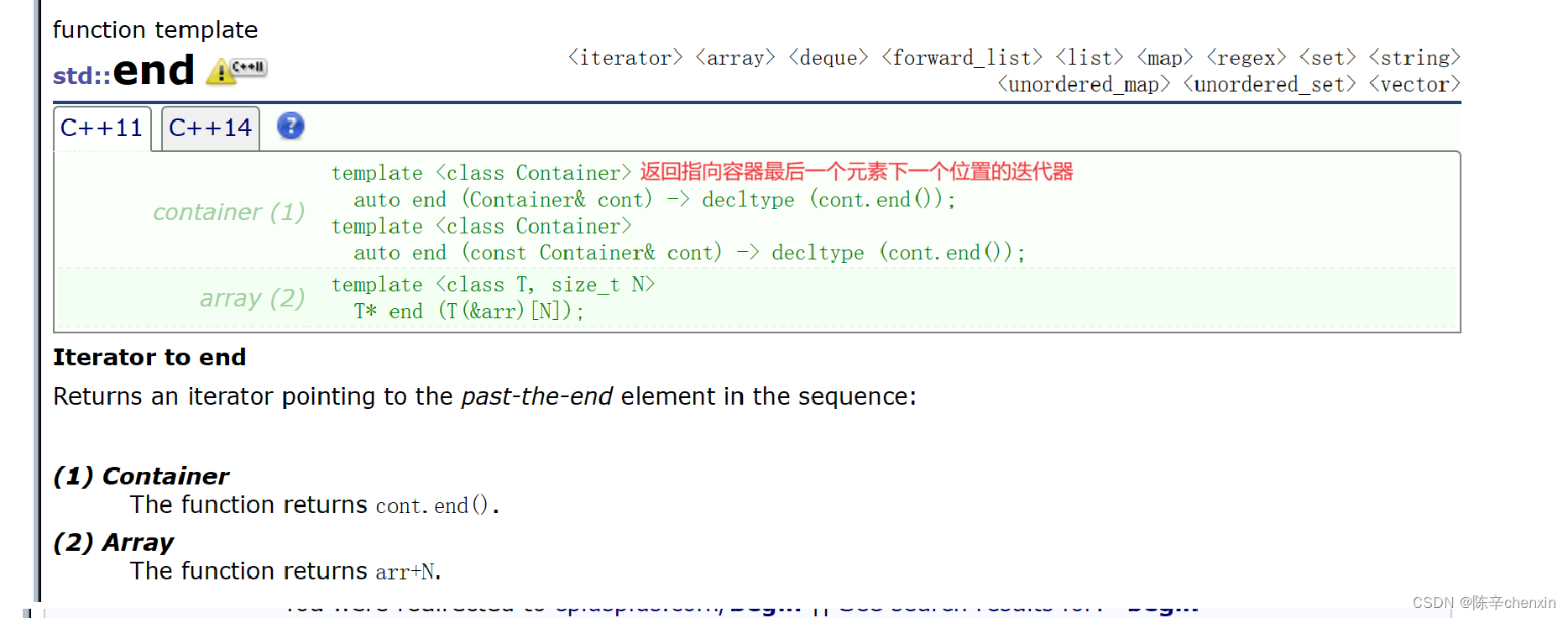
}注意:end是返回指向容器最后一个位置下一个的迭代器,所以构造s8时,他的区间是左闭右开“[ )”的.
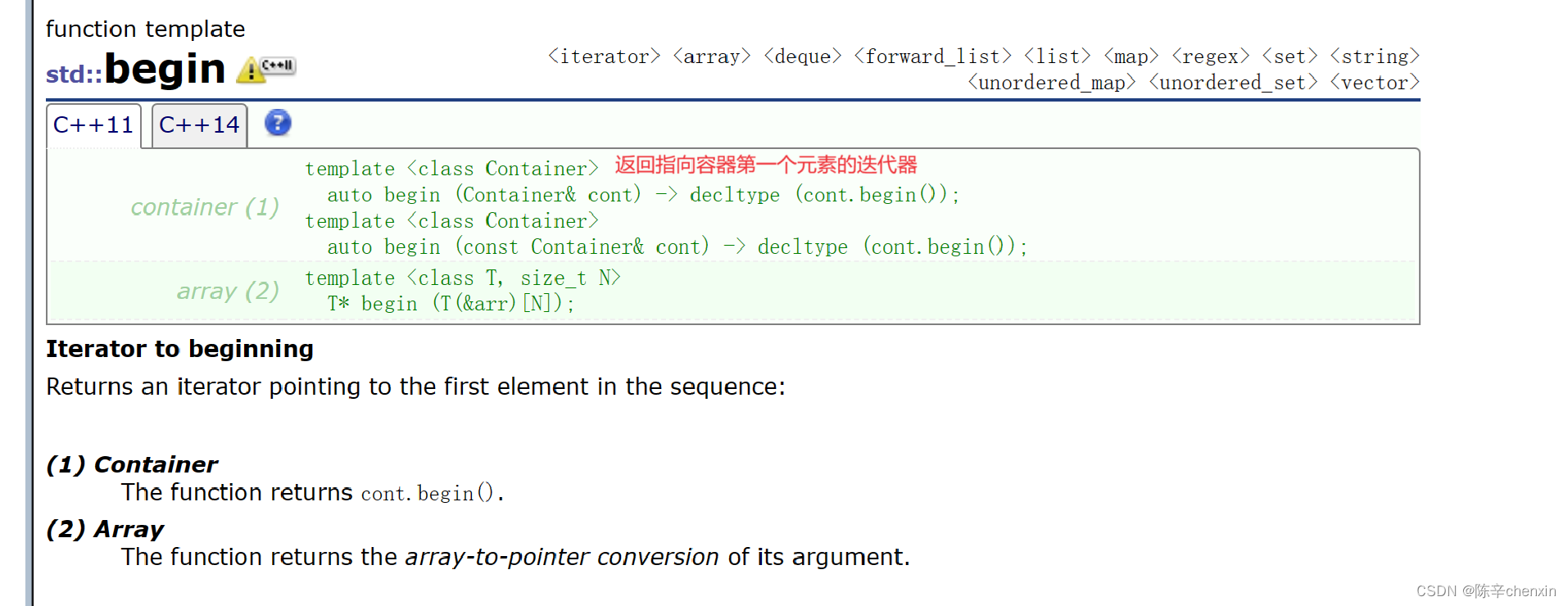
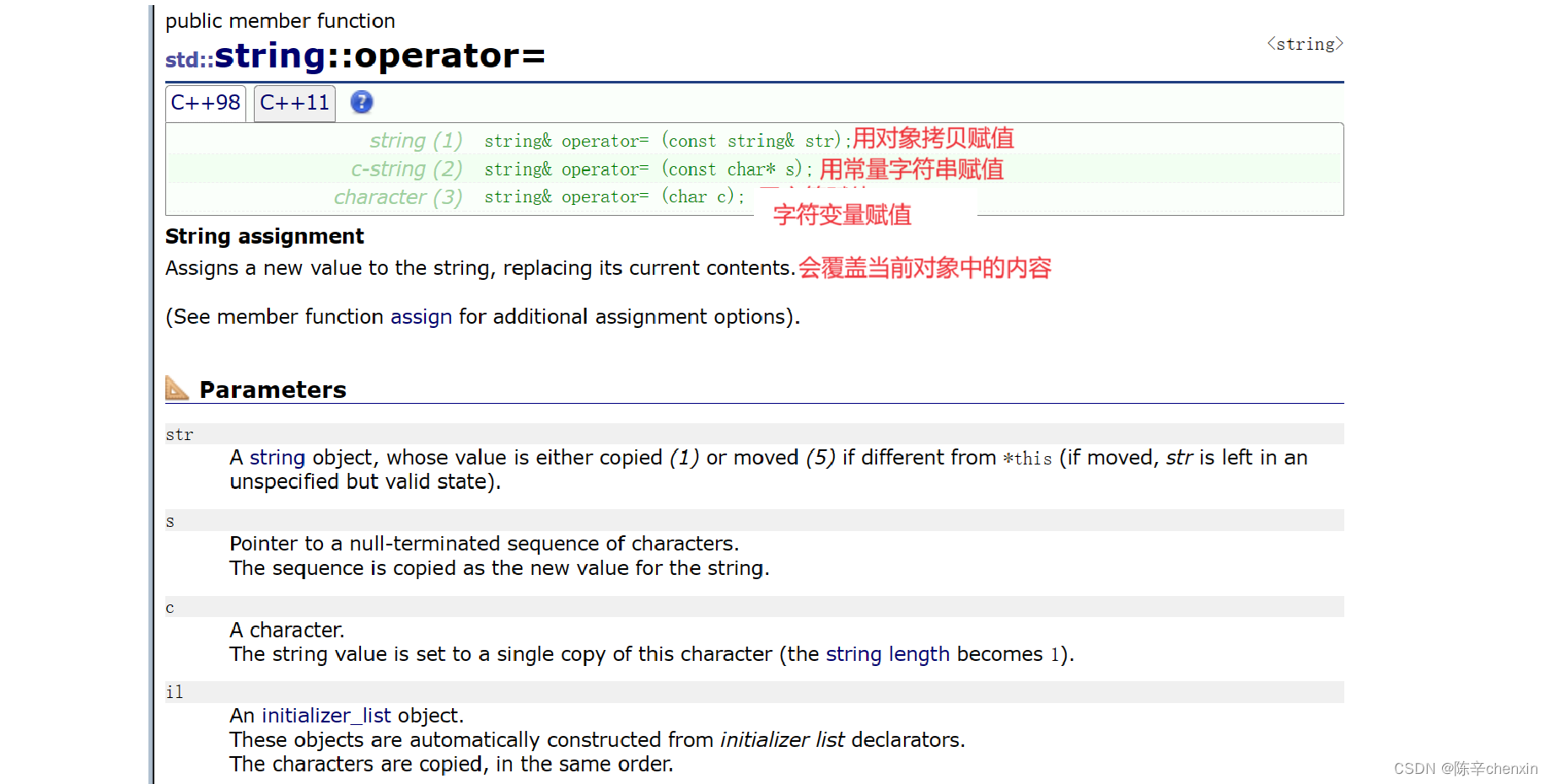
二、operator=(给对象赋值)
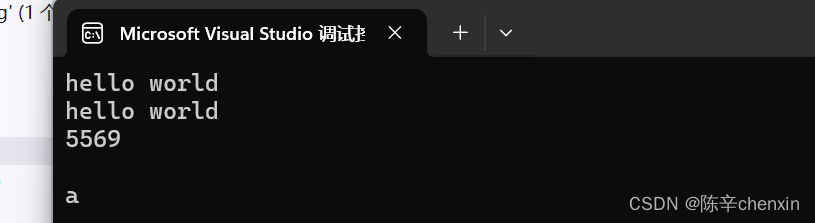
void StrTest2()
{
string s2 = "hello world";//创建对象时直接初始化 ,相当于s2("hello world")
cout << s2 << endl;
string s3 = s2;//用类对象赋值初始化
cout << s3 << endl;
s2 = "5569";
cout << s2 << endl;
//string s4 = 'c';//错误,不能在创建对象时进行赋值字符
string s4;
cout << s4 << endl;
s4 = 'a';
cout << s4 << endl;
}
三、Element access(元素访问)
3.1 oeprator[]

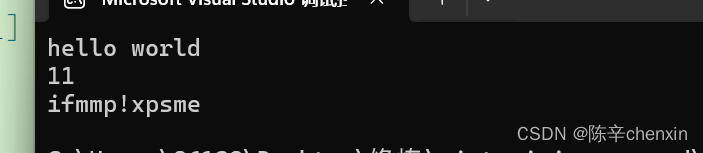
void StrTest3()
{
string s3 = "hello world";//len = 11
cout << s3 << endl;
cout << s3.size() << endl;//可以看到,size=11,size是没有把'\0'算入的
for (int i = 0; i < s3.size(); i++) {
s3[i]++;
cout << s3[i] ;
}
cout << endl;
}
若是用const修饰对象
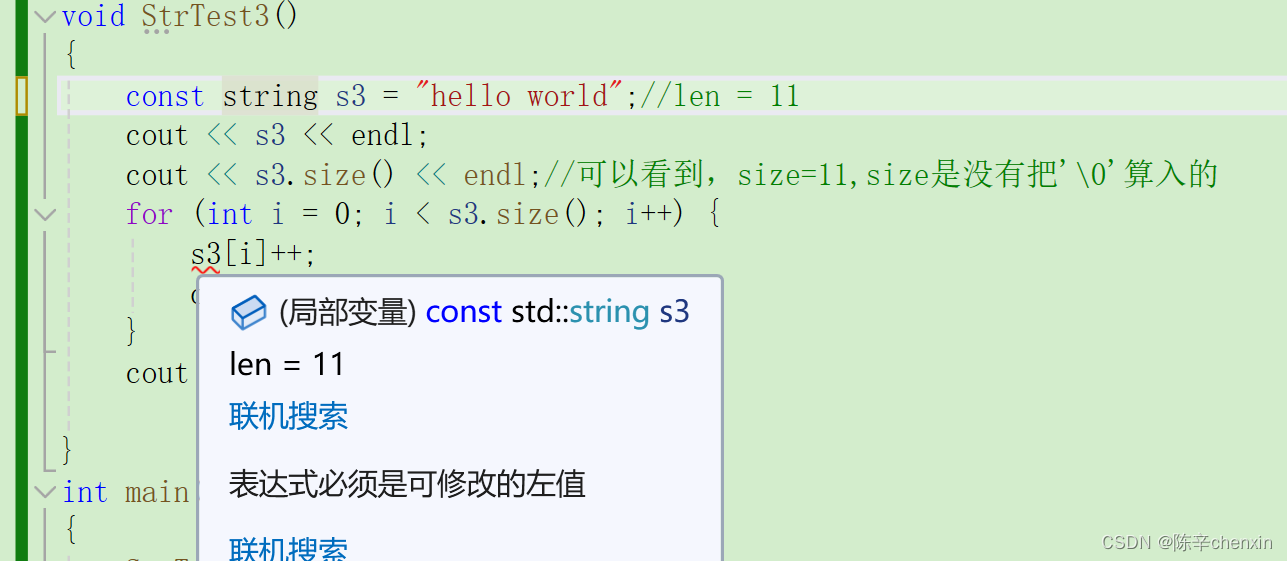
3.2 at
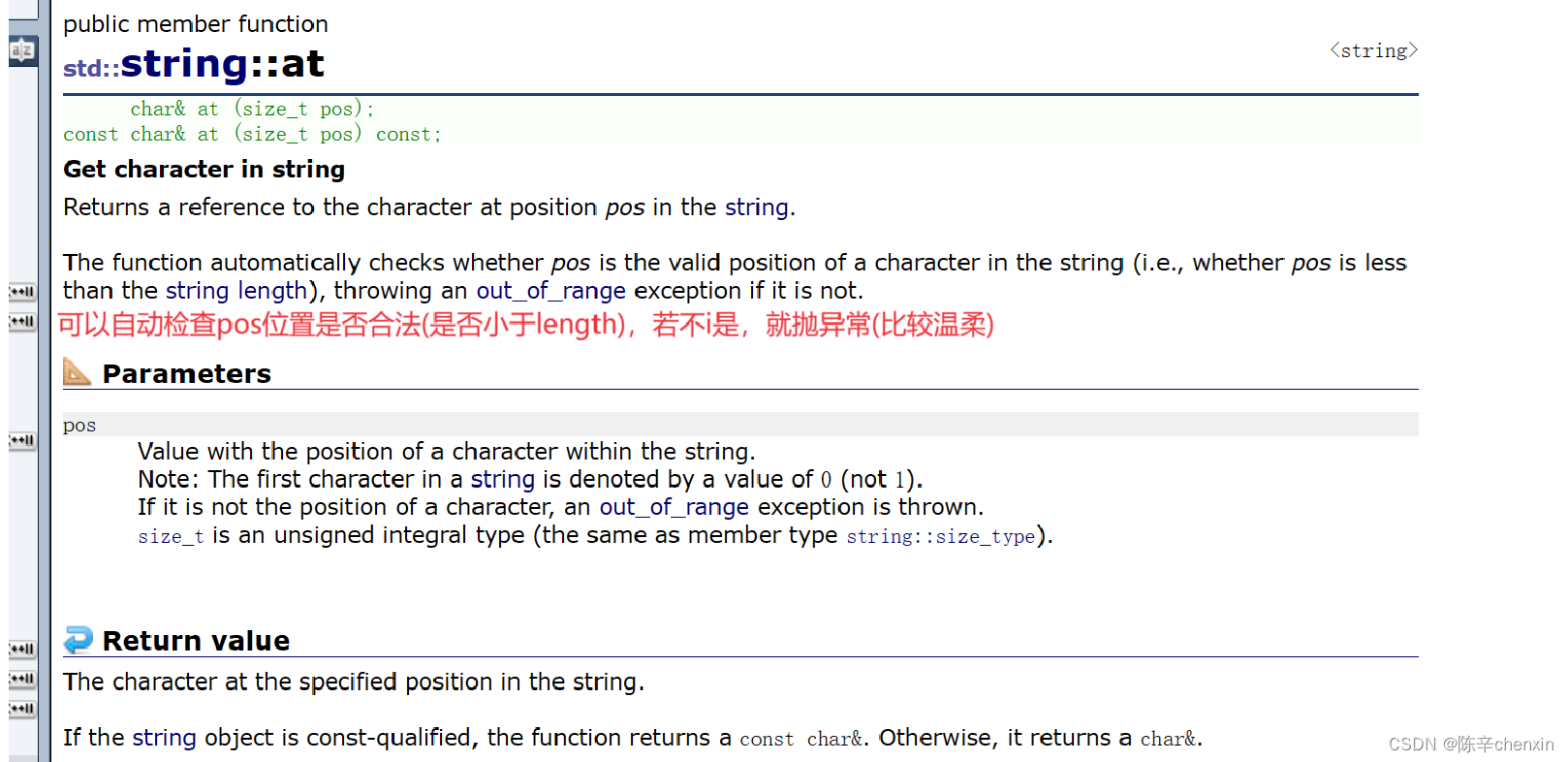
void StrTest4()
{
string s3 = "hello world";
const string s4 = "hello world";
cout << s3 << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < s3.size(); i++)
{
s3.at(i)++;
cout << s3.at(i)<<' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
3.3 back&front
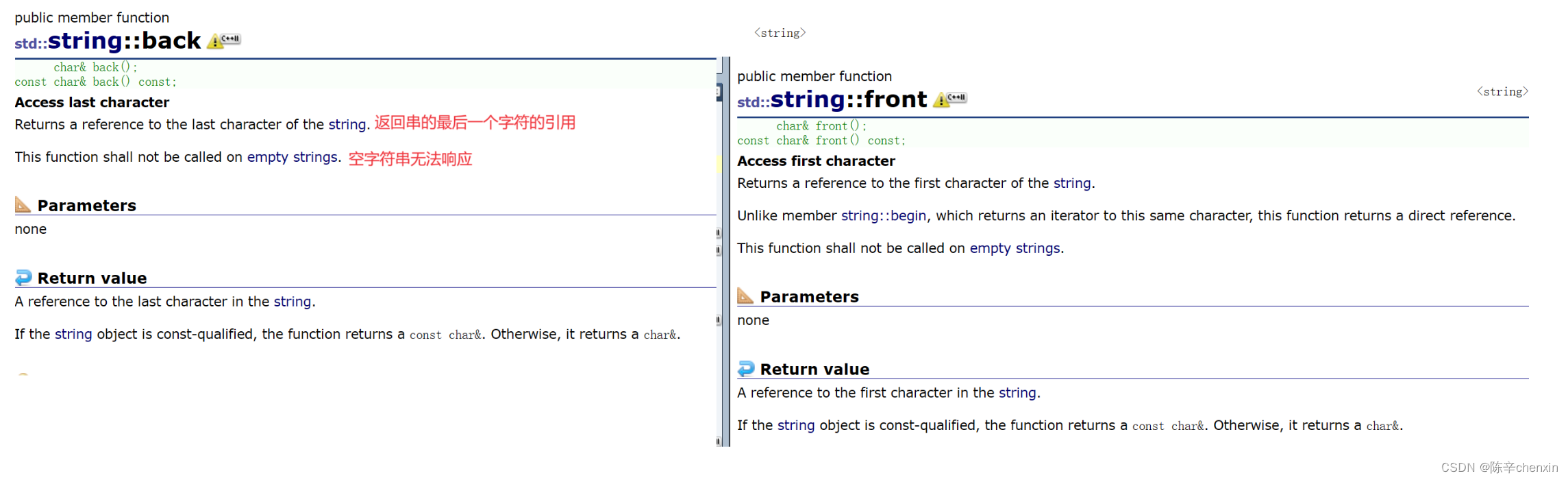
void StrTest5()
{
string s3 = "hello world";
cout << s3.back() << endl;
cout << s3.front() << endl;
} 
四、Iterator(迭代器)
4.1 begin&end
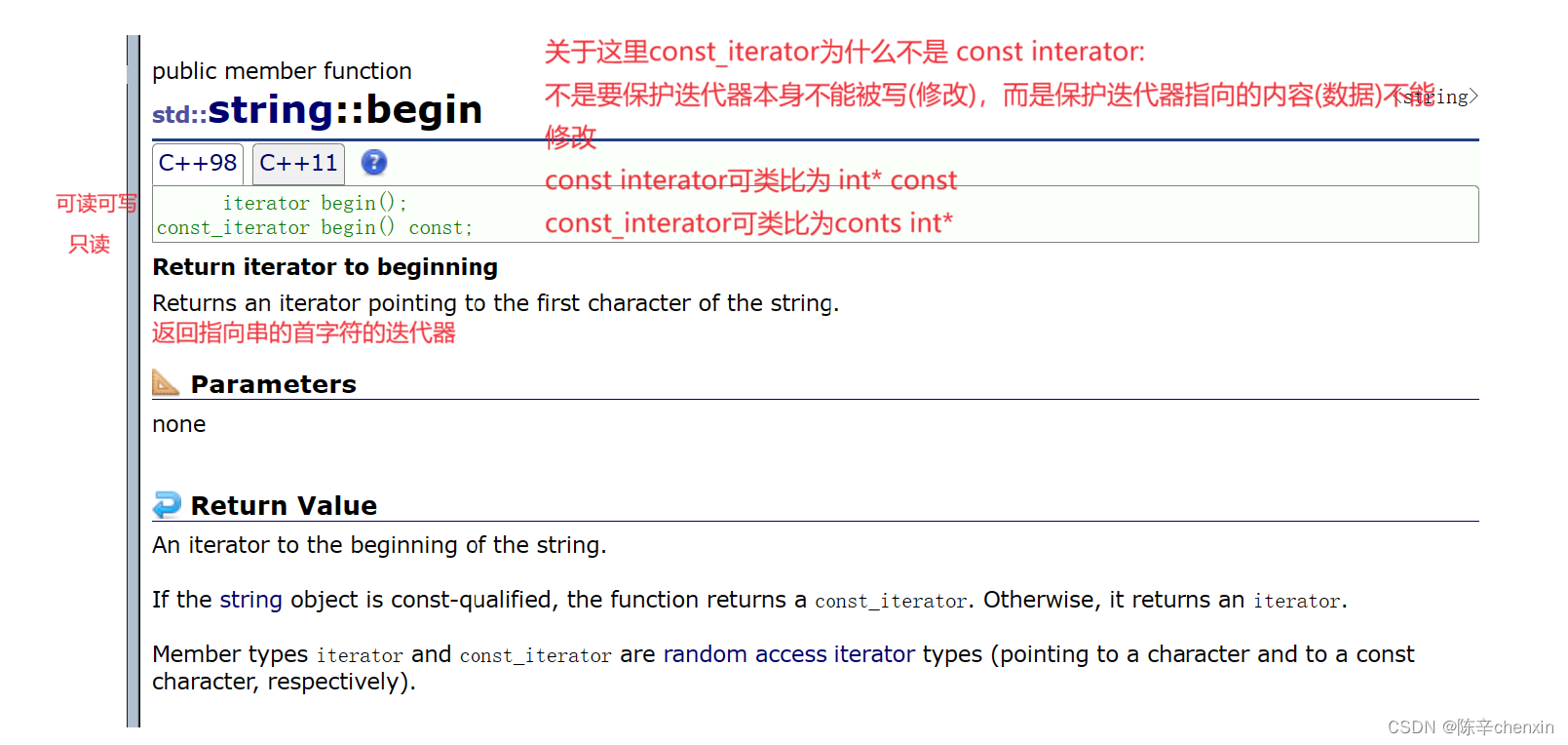
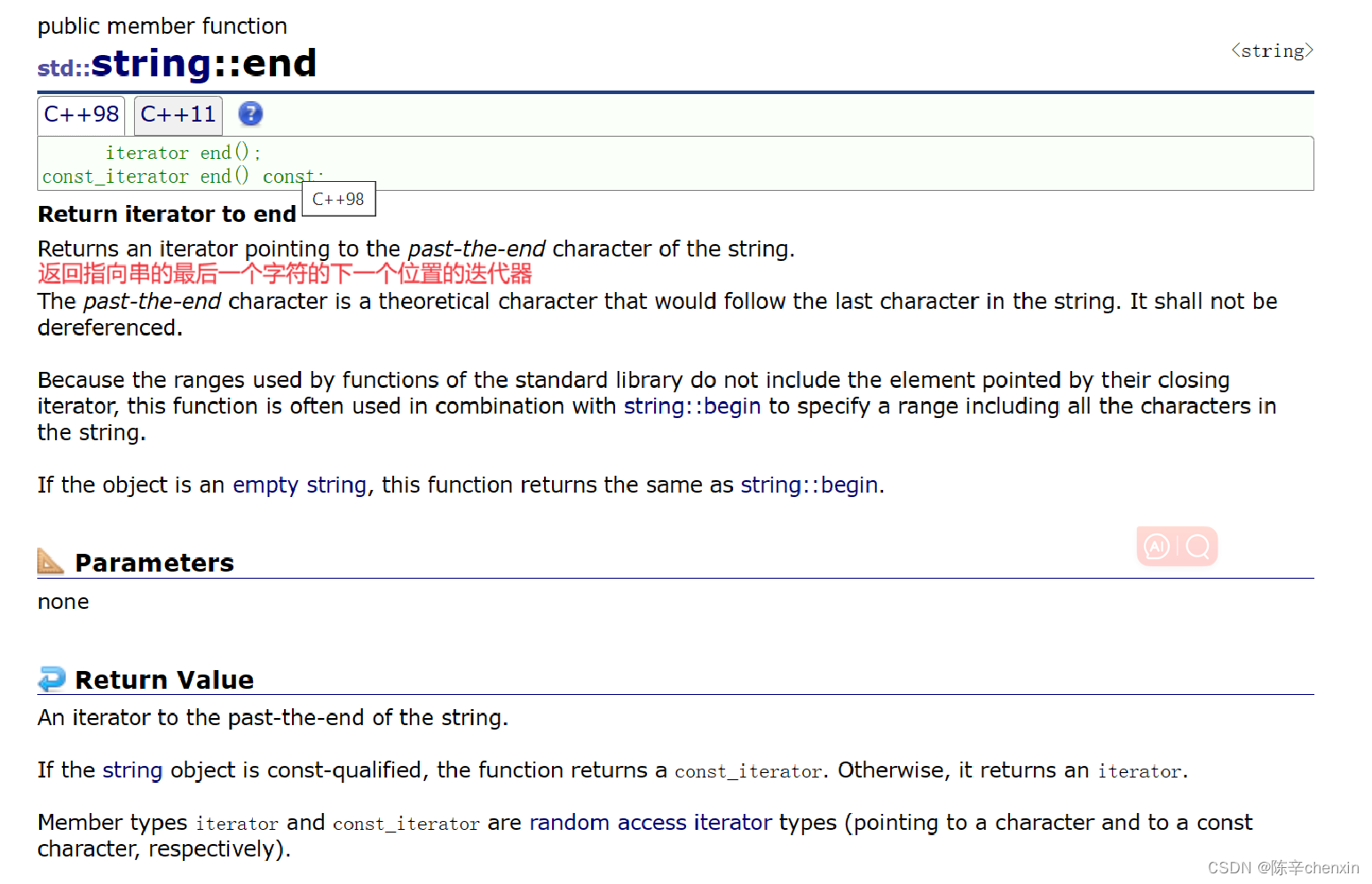
在这里我们可以认为迭代器和指针很像(当然迭代器不知包括指针),begin()返回指向首字符的指针
end返回指向最后一个字符的下一个位置的指针
下面我们将用3种不同的方式遍历串
void StrTest6()
{
string s3 = "hello world";
//方法一 operator[]
for (int i = 0; i < s3.size(); i++) {
cout << s3[i];
}
cout << endl;
//方法二 at
for (int i = 0; i < s3.size(); i++) {
cout << s3.at(i);
}
cout << endl;
//方法三 迭代器
string::iterator it1 = s3.begin();
while (it1 != s3.end())
{
*it1 += 3;
cout << *it1;
it1++;
}
cout << endl;
//方法四 遍历for循环
for (auto& e : s3) {
cout << e;
}
cout << endl;
}4.2 rbegin&rend

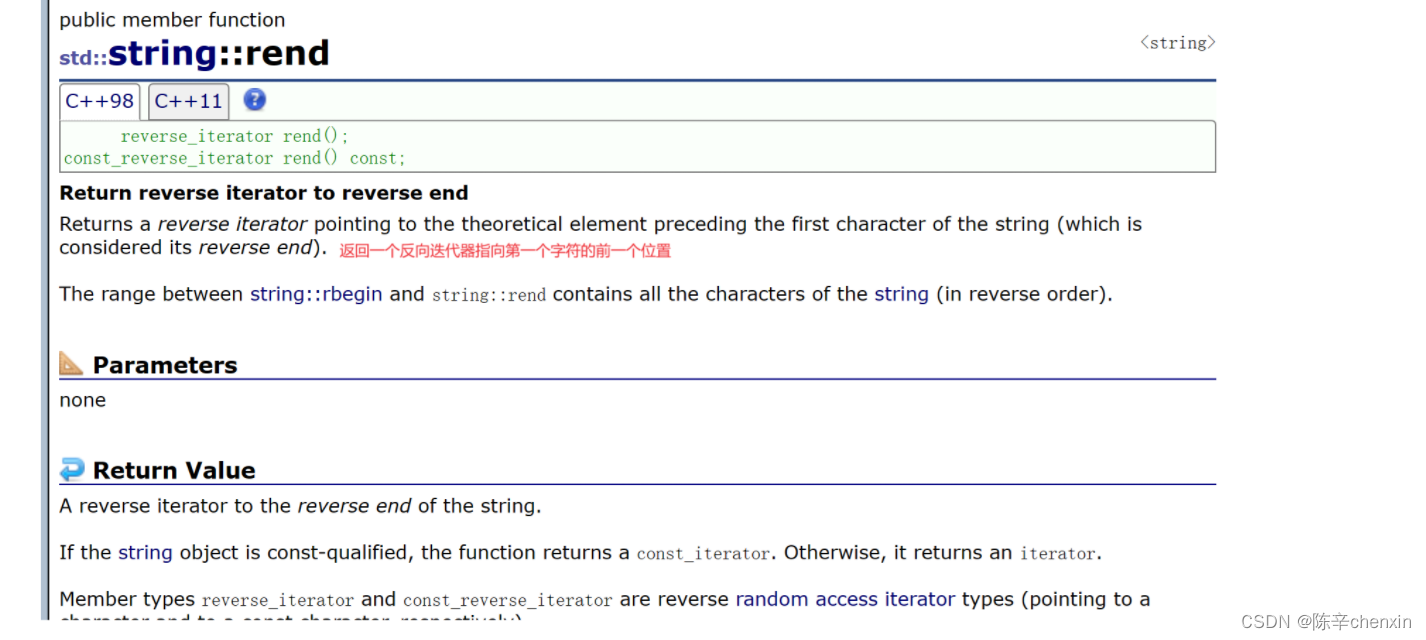 这里的r有反向的意思,reversebegin和reverseend
这里的r有反向的意思,reversebegin和reverseend
下面使用这两个函数遍历字符串
void StrTest7()
{
string s2("hello world");
//从rbegin到rend
//反向打印
string::reverse_iterator it1 = s2.rbegin();
while (it1 != s2.rend())
{
cout << *it1;
it1++;
}
cout << endl;
//正向打印
//从rend到rbegin
string::reverse_iterator it2 = s2.rend()-1;//指向第一个字符
while (it2 != s2.rbegin())
{
cout << *it2;
it2--;
}
cout << *it2;
cout << endl;
}
4.3 cbegin&cend& crbegin&crend
void StrTest8()
{
string s3 = "hello world";
string::const_iterator it1 = s3.cbegin();//这里的it1指向的内容就不能再改变了
//其余的cend 、 crend 、 crbegin 除了是_const 以外,其他和前面两个函数一摸一样,不再赘述
}五、Capacity(空间)
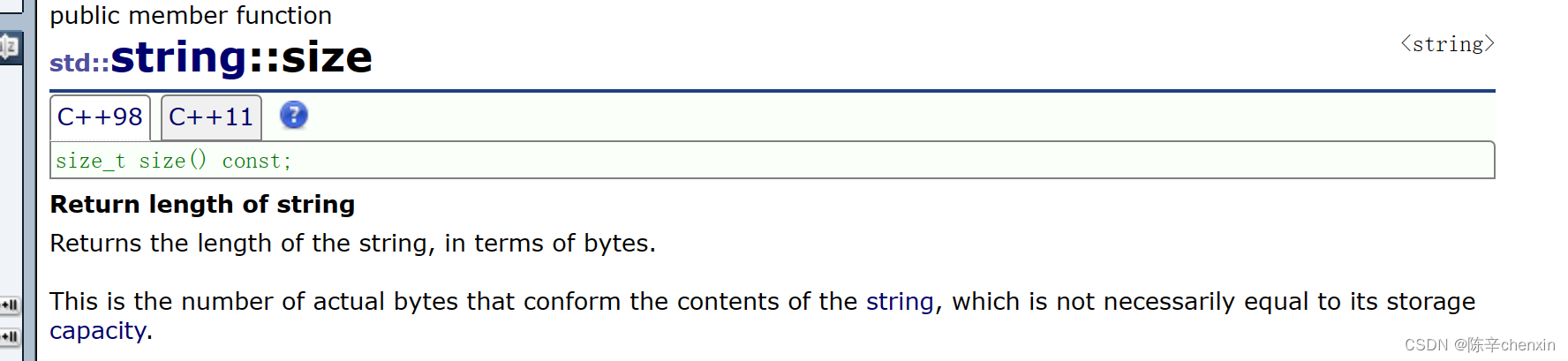
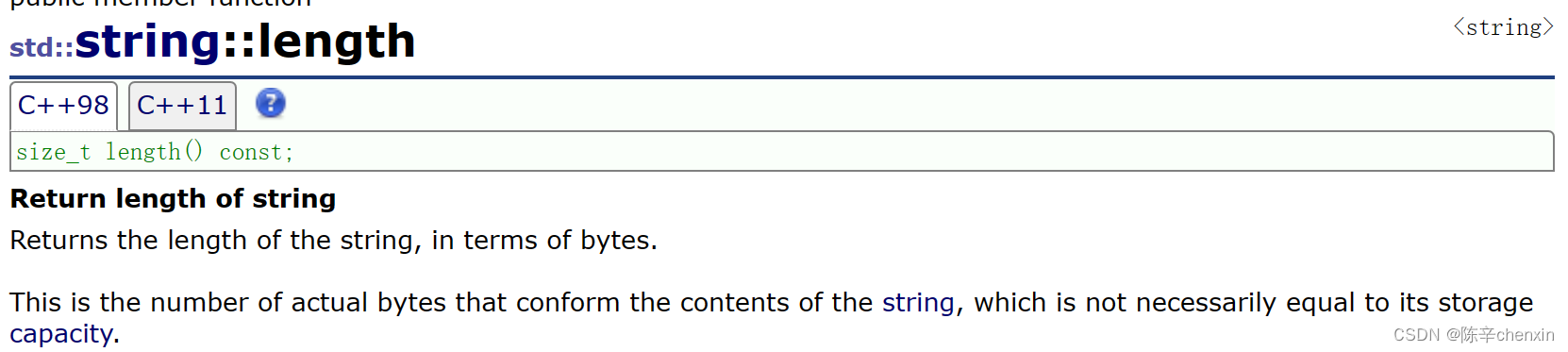
5.1 size&length&max_size
这两个都是返回字符串的长度,功能都基本相同
void StrTest9()
{
string s1 = "hello world";//实际长度为12,包含'\0'
cout << s1.length() << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl;
}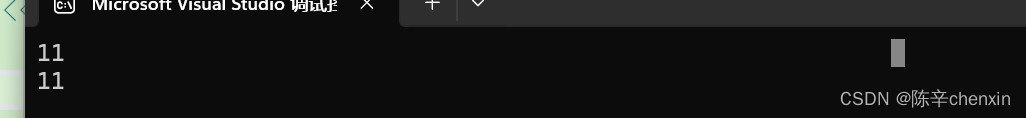
可以看出,vs编译器是不把'\0'算入size和length中的,编译器不同,得出的实际效果也就不同
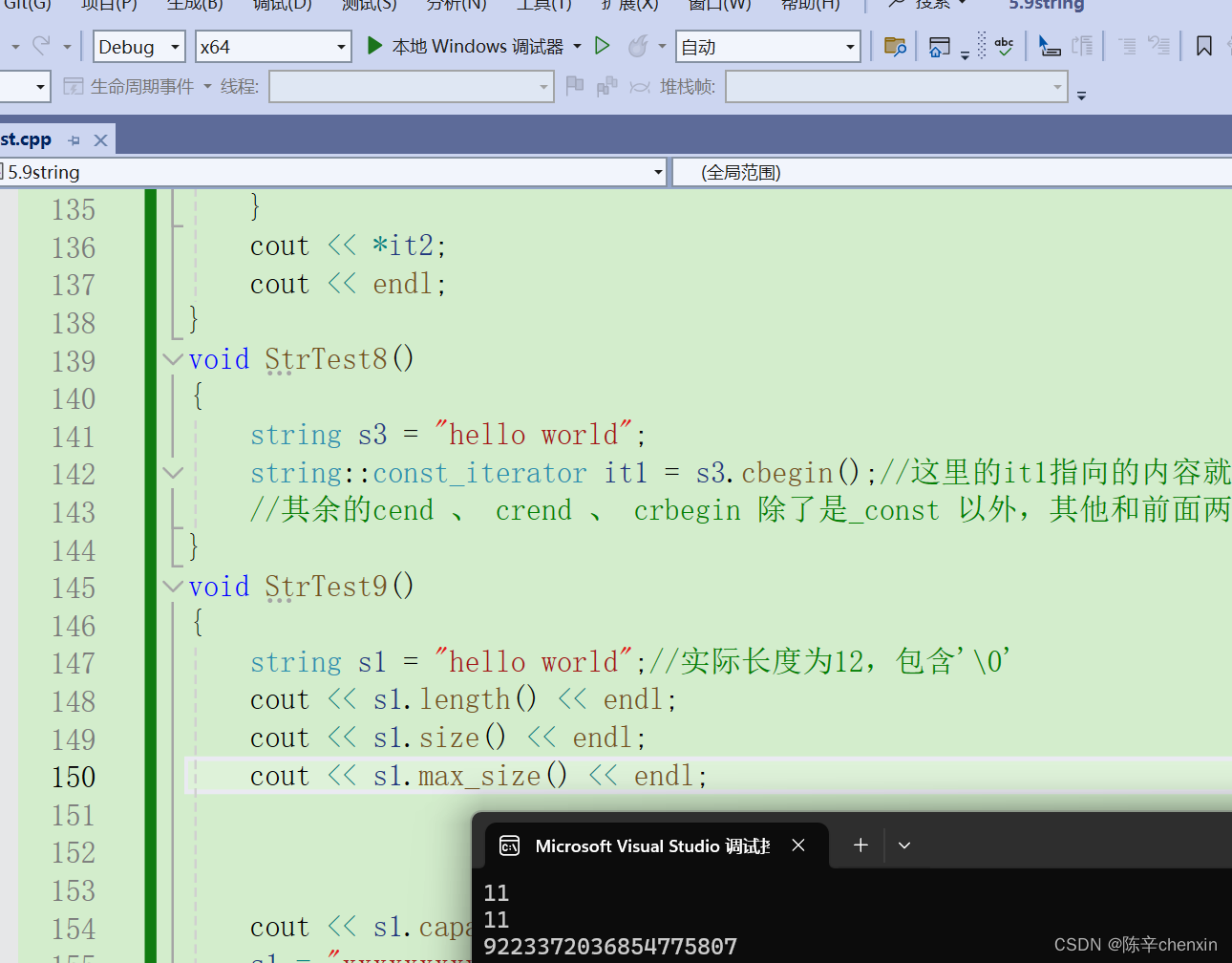
可以看到,在64位机器下,编译器能给的最大空间很大很大,但实际上却给不了这么大的空间(即便身价500亿,亦不能随时掏出1个亿)
5.2 capacity
那么当我们扩大字符串长度/缩小,capacity会有变化吗
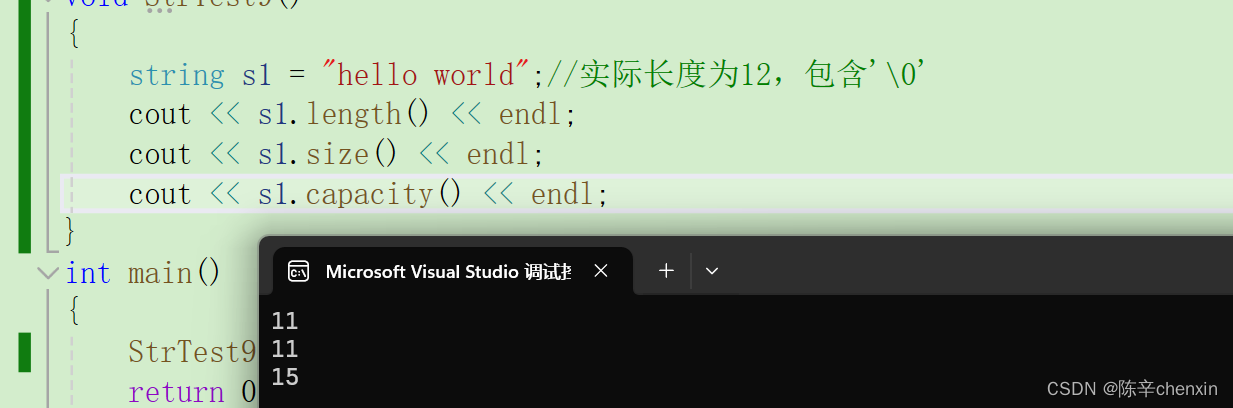
void StrTest9()
{
string s1 = "hello world";//实际长度为12,包含'\0'
cout << s1.length() << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
s1 = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx";
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
s1 = "xxx";
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
}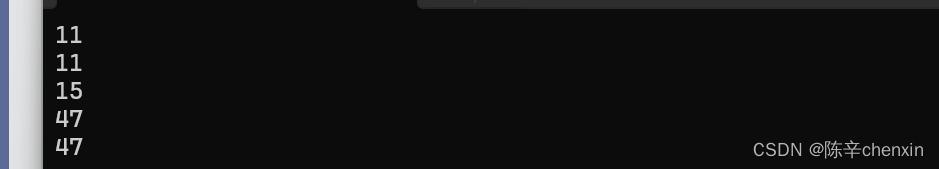
可以很明显的看出,当我们扩大字符串的长度时,capacity会自动扩大,但当我们缩小字符串长度时,capacity却不会随之变小(capacity只扩大不缩小)
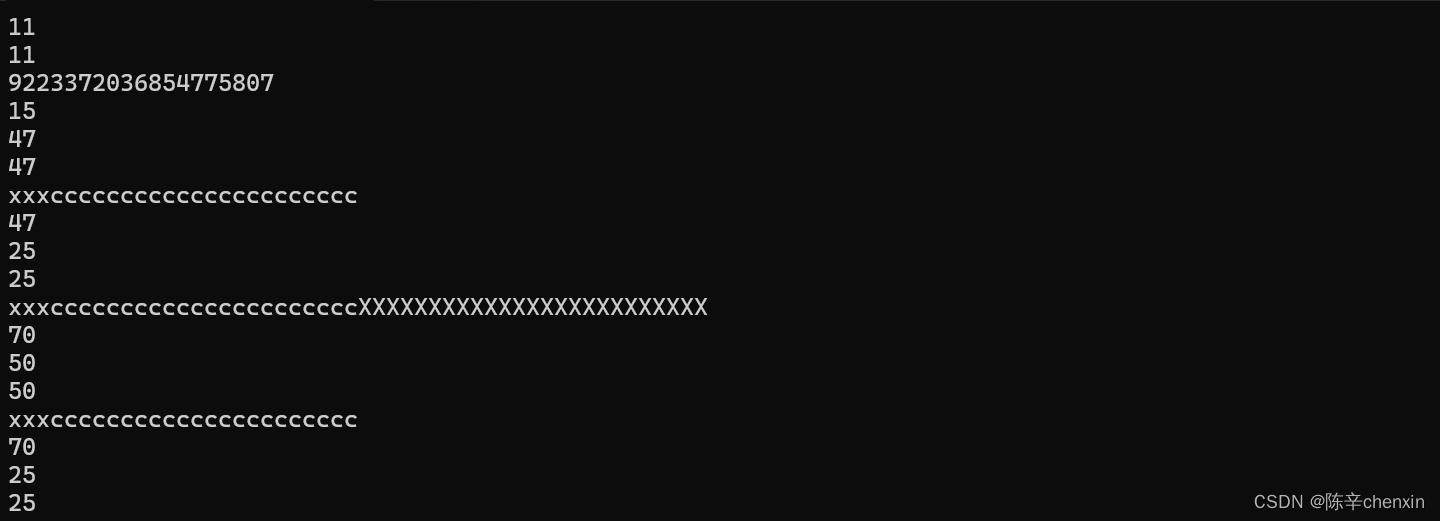
5.3 resize

void StrTest9()
{
string s1 = "hello world";//实际长度为12,包含'\0'
cout << s1.length() << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.max_size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
s1 = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx";
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
s1 = "xxx";
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
//扩容至25,其余补充为c
s1.resize(25, 'c');
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
cout << s1.length() << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl;
//扩容至50,这是会发现capacity也随之改变至70
s1.resize(50,'X');
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
cout << s1.length() << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl;
//缩容至25
s1.resize(25);//你会发现capacity不会变小,capacity只大不变小
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
cout << s1.length() << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl;
}
5.4 reserve

void StrTest10() {
string s1 = "hello world";
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;//15
cout << s1.length() << endl;//11
cout << s1.size() << endl;//11
//现在我们来扩大capacity,那么capacity就一定是50吗?
s1.reserve(50);
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;//63 ,编译器其可能觉得50不好,自动优化到63
cout << s1.length() << endl;//11
cout << s1.size() << endl;//11
//那现在我们来缩小capacity,你觉得有可能吗
s1.reserve(25);
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;//63 ,capacity还是63,根本不听你的
cout << s1.length() << endl;//11
cout << s1.size() << endl;//11
//再次缩小
s1.reserve(20);
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;//63,还是没有缩小
cout << s1.length() << endl;//11
cout << s1.size() << endl;//11
//再次缩小
s1.reserve(13);//15 ,为什么这次就缩小了呢?
//是因为其中内置了一个大小为15的数组,当空间小于15时(也就是串小于15),会先存储到这个buffer区中
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;//15,
cout << s1.length() << endl;//11
cout << s1.size() << endl;//11
}
注意:可以利用reserve提高插入数据的效率,避免增容带来的开销,一把开好,省得麻烦(如果知道要用多少)
5.5 clear&empty&shrink_to_fit
一、clear
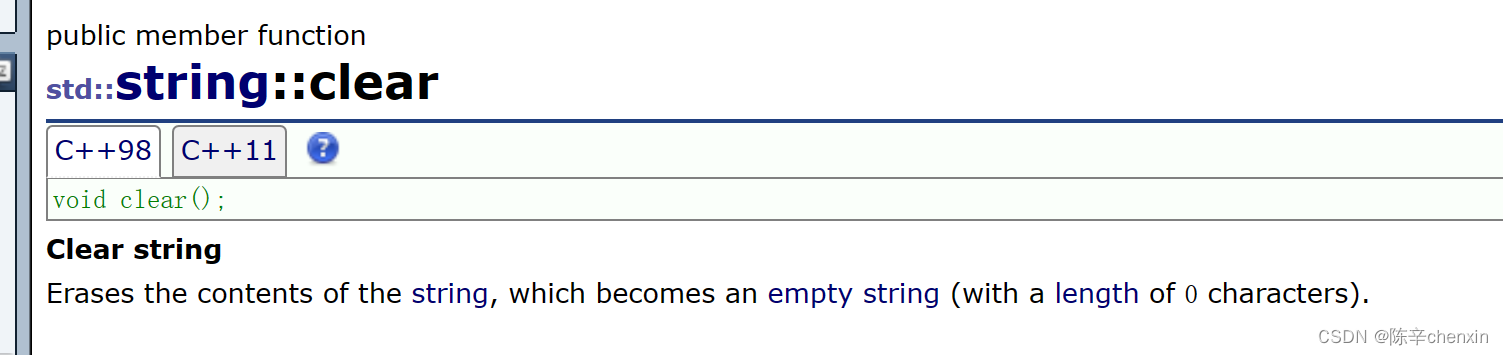
作用很直观也很简单的一个成员函数,清楚字符串中所有有效字符,使其长度变为0
void StrTest11()
{
//空间大小不变,长度变为0
string s1 = "hello world";
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;//15
cout << s1.size() << endl;
s1.clear();
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;//15
cout << s1.size() << endl;
}
二、empty
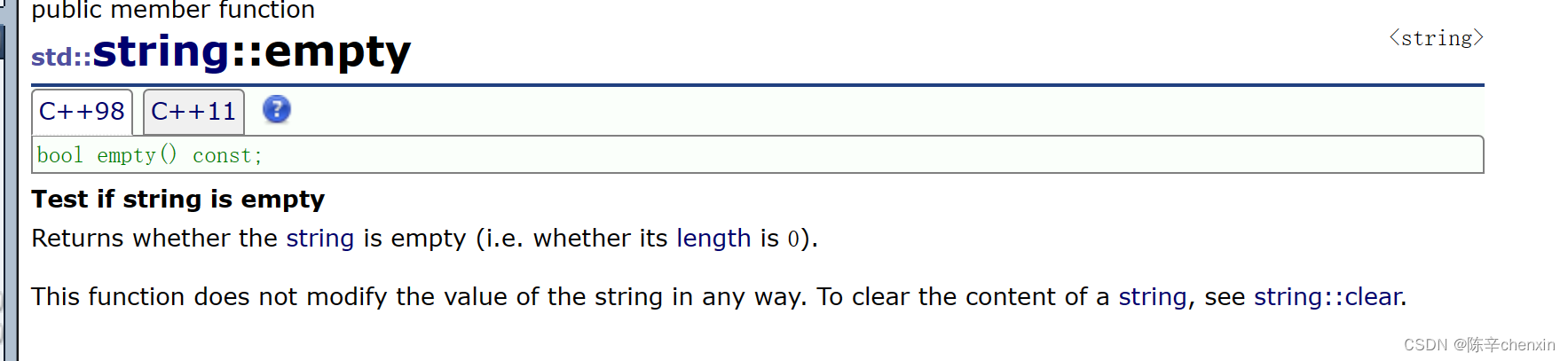
若有效字符个数为0,返回true,否则返回false
三、shrink_to_fit

void StrTest12() {
string s1 = "hello world";
cout << s1 << endl;
s1.reserve(100);
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;//111
s1.shrink_to_fit();
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;//还是15,储存在数组中
}
六、Modifiers(修改器)
6.1 oeprator+=

void StrTest13()
{
string s1 = "hello,";
string s2 = "xiaoyutongxue";
s1 += s2;
cout << s1 << endl;
string s3 = "hello,";
s3 += "xiaoyutongxue";
cout << s3 << endl;
string s4 = "ok";
s4 += 'x';
cout << s4 << endl;
}
6.2 append

void StrTest14()
{
string s3 = "hello";
string s4 = "world";
char ch[] = "good";
//添加字符串对象
s3.append(s4);
cout << s3 << endl;
//添加字符串对象的一部分
s3.append(s4, 1, 100);
cout << s3 << endl;
//添加字符数组
s3.append(ch);
cout << s3 << endl;
///添加字符数组的n个字符
s3.append(ch, 3);
cout << s3 << endl;
//追加常量字符串
s3.append("66666");
cout << s3 << endl;
///追加n个字符x
s3.append(15, 'x');
cout << s3 << endl;
//interator
string s5 = "5月12日";
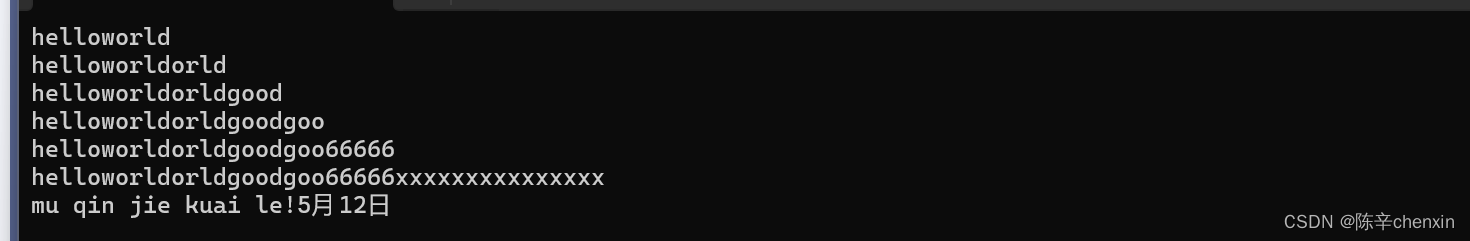
string s6 = "mu qin jie kuai le!";
s6.append(s5.begin(), s5.end());//左闭右开[ ),不用减一
cout << s6 << endl;
}
6.3 push_back
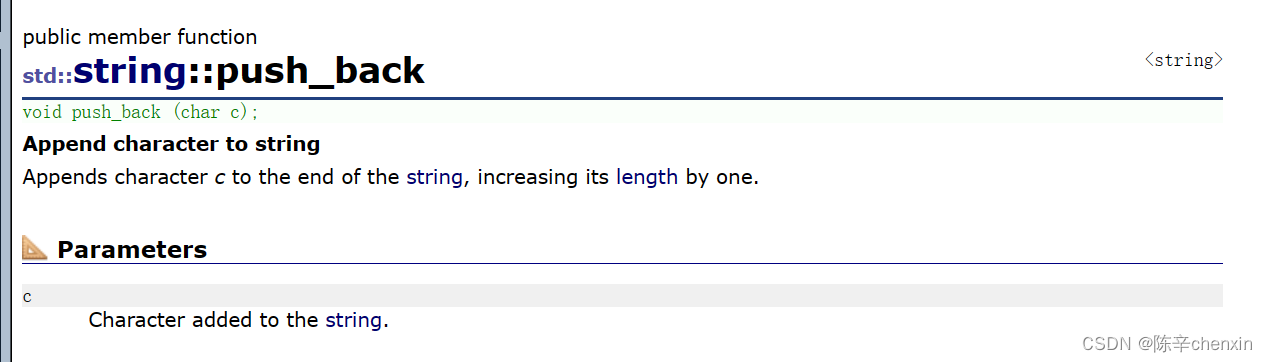
在串的尾部尾插一个字符c
6.4 assign
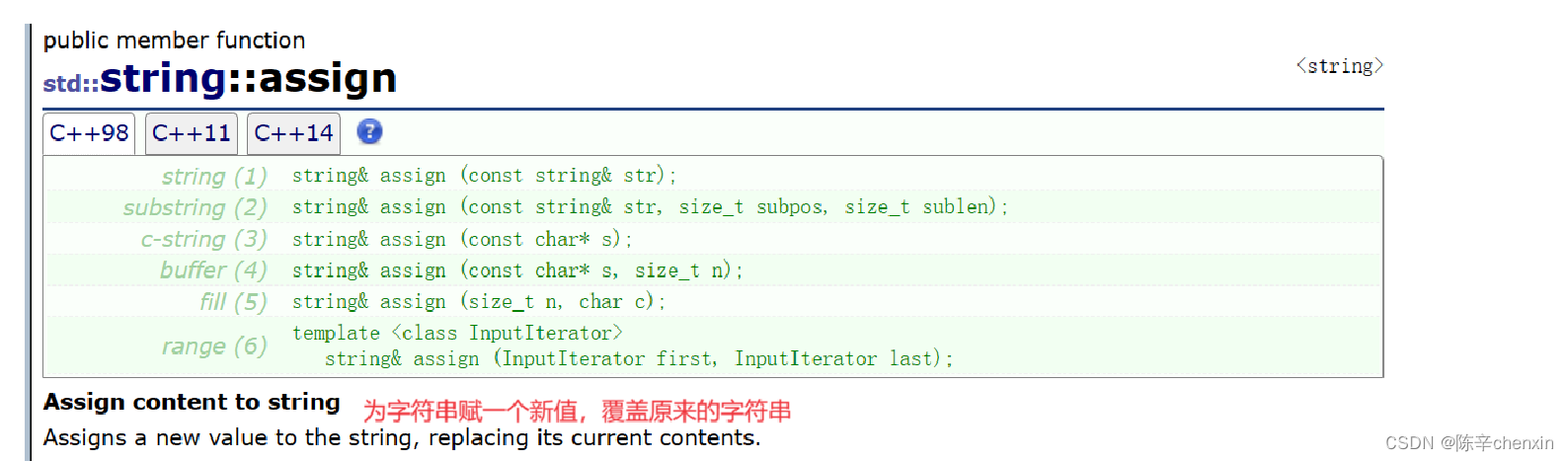
这些重载函数的参数都差不多,我就不再赘述了,直接代码呈现
void StrTest15()
{
//用字符串对象覆盖
string s1 = "hello world";
cout << s1 << endl;
string s2 = "xiaoyutongzhi";
s1.assign(s2);
cout << s1 << endl;
//用一部分字符串对象覆盖
s1.assign(s2, 6, 100);
cout << s1 << endl;
//用一个字符数组覆盖
char ch[] = "mu qin jie kuai le";
s1.assign(ch);
cout << s1 << endl;
//用字符数组的n个字符覆盖
s1.assign(ch, 5);
cout << s1 << endl;
//迭代器覆盖
s1.assign(s2.begin(), s2.end());
cout << s1 << endl;
}
6.5 insert

void StrTest16() {
string s1 = "hello ";
string s2 = "xiaoyutongzhi";
//s1.insert(6,s2);
//cout << s1 << endl;
//s1.insert(6, s2, 6, 100);
//cout << s1 << endl;
/*s1.insert(s1.end(), 6, 'x');
cout << s1 << endl;*/
/*s1.insert(s1.end(), 'x');
cout << s1 << endl;*/
s1.insert(s1.end(), s2.begin(), s2.end());
cout << s1 << endl;
}
6.6 erase
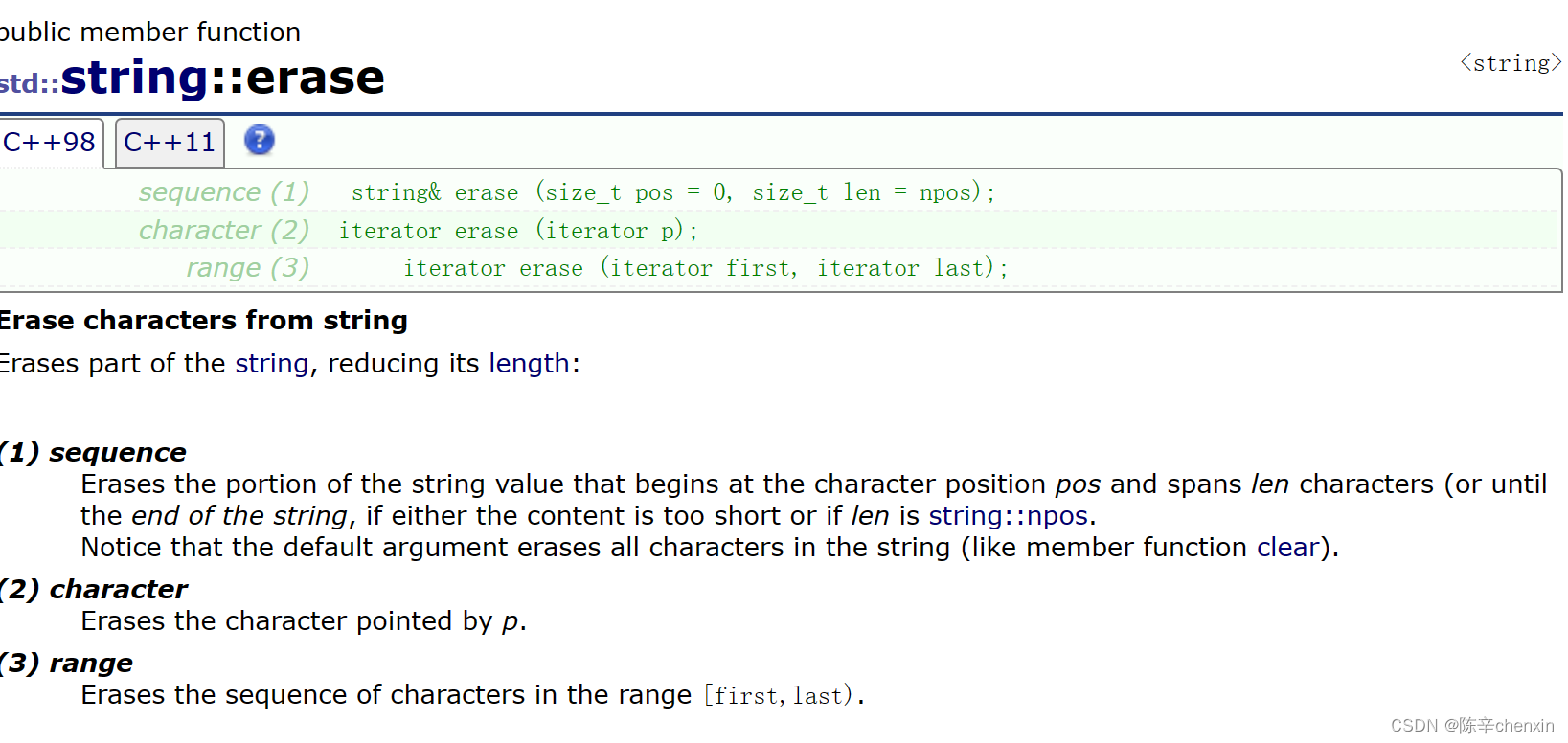
void StrTest16() {
string s1 = "hello ";
string s2 = "xiaoyutongzhi";
string s3 = "xiaoyutongzhi";
s1.erase();
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl;
s2.erase(6, 100);
cout << s2 << endl;
//删除p位置的内容
s3.erase(s3.begin());
cout << s3 << endl;
s3.erase(s3.begin(), s3.end()-2);//左闭右开
cout << s3 << endl;
}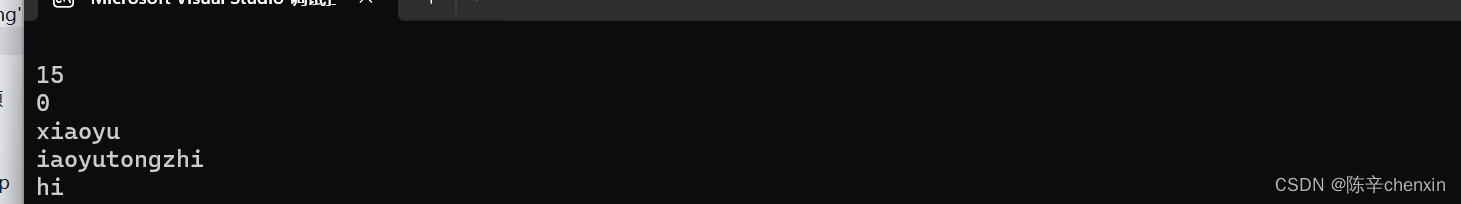 注意:若pos位置大于字符串长度,则抛异常
注意:若pos位置大于字符串长度,则抛异常
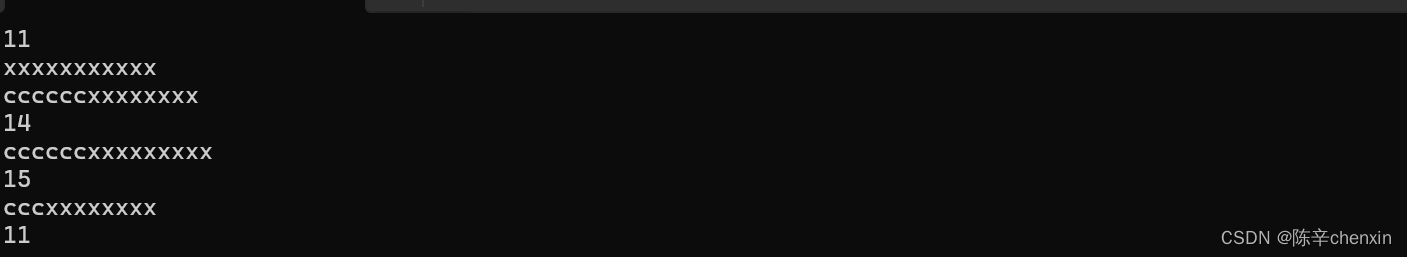
6.7 replace

void StrTest1()
{
string s1 = "xxxxxxxxxxx";
cout << s1.size() << endl;
string s2 = "cccccc";
cout << s1 << endl;
//1.类对象替换
s1.replace(0, 3, s2);
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl;
//说明会将从第0个位置开始,长度为三的字符替换,并追加s2剩余字符->size扩大
//若len>字符串长度,默认替换到字符串尾
//2.迭代器替换
s1 = "xxxxxxxxxxx";
s1.replace(s1.begin(), s1.begin()+2 , s2);
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl;
//3.固定替换长度(类对象)
s1 = "xxxxxxxxxxx";
s1.replace(0, 3, s2, 0, 3);
//若sublen大于len,则在替换的末尾追加
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl;
//
}
6.8 swap
void StrTest2()
{
//交换后,size和capacity(属性)也会交换
string s1 = "xxxxxxxx";
string s2 = "ssssssssssssssssssssss";
cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;
cout << "s1.size() = " << s1.size() << endl;
cout << "s1.capacity() = " << s1.capacity() << endl;
cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;
cout << "s2.size() = " << s2.size() << endl;
cout << "s2.capacity() = " << s2.capacity() << endl;
s1.swap(s2);
cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;
cout << "s1.size() = " << s1.size() << endl;
cout << "s1.capacity() = " << s1.capacity() << endl;
cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;
cout << "s2.size() = " << s2.size() << endl;
cout << "s2.capacity() = " << s2.capacity() << endl;
}
6.9 pop_back

七、 String operations:
7.1 c_str
void STRTest1()
{
//1.c_str函数
string s = "hello world";
//返回一个与s中存储的字符串相同的常量字符串,最后还有'\0'
char* str = new char[s.length() + 1];
//strcpy(str, s);这里直接用s是不行的,因为s是对象名,而不是一个char*
strcpy(str, s.c_str());//这样就可以,返回一个常量字符串
cout << s.c_str() << endl;
cout << str << endl;
delete[] str;
str = nullptr;
}
7.2 copy

void STRTest2()
{
string s = "hello world";
char str[20];
int length = s.copy(str, 3, 0);
//这里若是不把str的length处设置为'\0',下面打印就打印未初始化的随机值
str[length] = '\0';
cout << str << endl;
cout << length << endl;
}
7.3 find

void STRTest3()
{
string s = "hello worldho";
string s1 = "world";
char s2[5] = "ld";
size_t pos1 = s.find('h', 0);
cout << pos1 << endl;
size_t pos2 = s.find('o', 1);
cout << pos2 << endl;
size_t pos3 = s.find(s1, 0);
cout << pos3 << endl;
size_t pos4 = s.find(s2, 0);
cout << pos4 << endl;
}
7.4 rfind

void STRTest4()
{
string s1 = "hehello heorange hehe";
string s2 = "he";
size_t pos1 = s1.rfind('o',1110);
size_t pos2 = s1.rfind(s2,1110);
cout << pos1<<endl;
cout << pos2 << endl;
}
7.5 find_first_of

void STRTest5()
{
string s1 = "hello world hehe haha orange";
size_t pos = s1.find_first_of("wld", 0);
cout << pos << endl;//此处找到l下标为2
//也可以把指定元素的字符全部改为*
std::size_t found = s1.find_first_of("aeiou");
while (found != std::string::npos)
{
s1[found] = '*';
found = s1.find_first_of("aeiou", found + 1);
}
std::cout << s1 << '\n';
}
7.6 substr

void STRTest6()
{
//用find如何提取协议、域名和资源
string s1 = "https://gitee.com/chen-1/qi-training-record";
size_t pos1 = s1.find(':');
size_t pos2 = s1.find('/', pos1 + 3);
size_t pos3 = s1.find('/', pos2 + 1);
cout << s1.substr(0, pos1-0)<<endl;//左闭右开,右边减去左边是元素个数
cout << s1.substr(pos1+3, pos2-pos1-3)<<endl;//取出第二段
cout << s1.substr(pos2 + 1) << endl;//取出第三段
}
八、非成员函数
8.1 operator+
void STRTest7() {
string s1 = "hello";
string s2 = "world";
string s3 = s1 + s2;
cout << s3 << endl;
string s4 = s1 + "xxxxxx";
cout << s4 << endl;
//这就是为什么要写成全局函数而不写成成员函数的原因->要支持非对象成为第一个参数
string s5 = "xxxxx" + s1;
cout << s5 << endl;
//不能是string s5 = "xxxx"+"xxxx"; 不能对内置类型进行运算符重载,至少要有一个自定义类型
}
8.2 string类同样支持比较(用ASCLL比较)
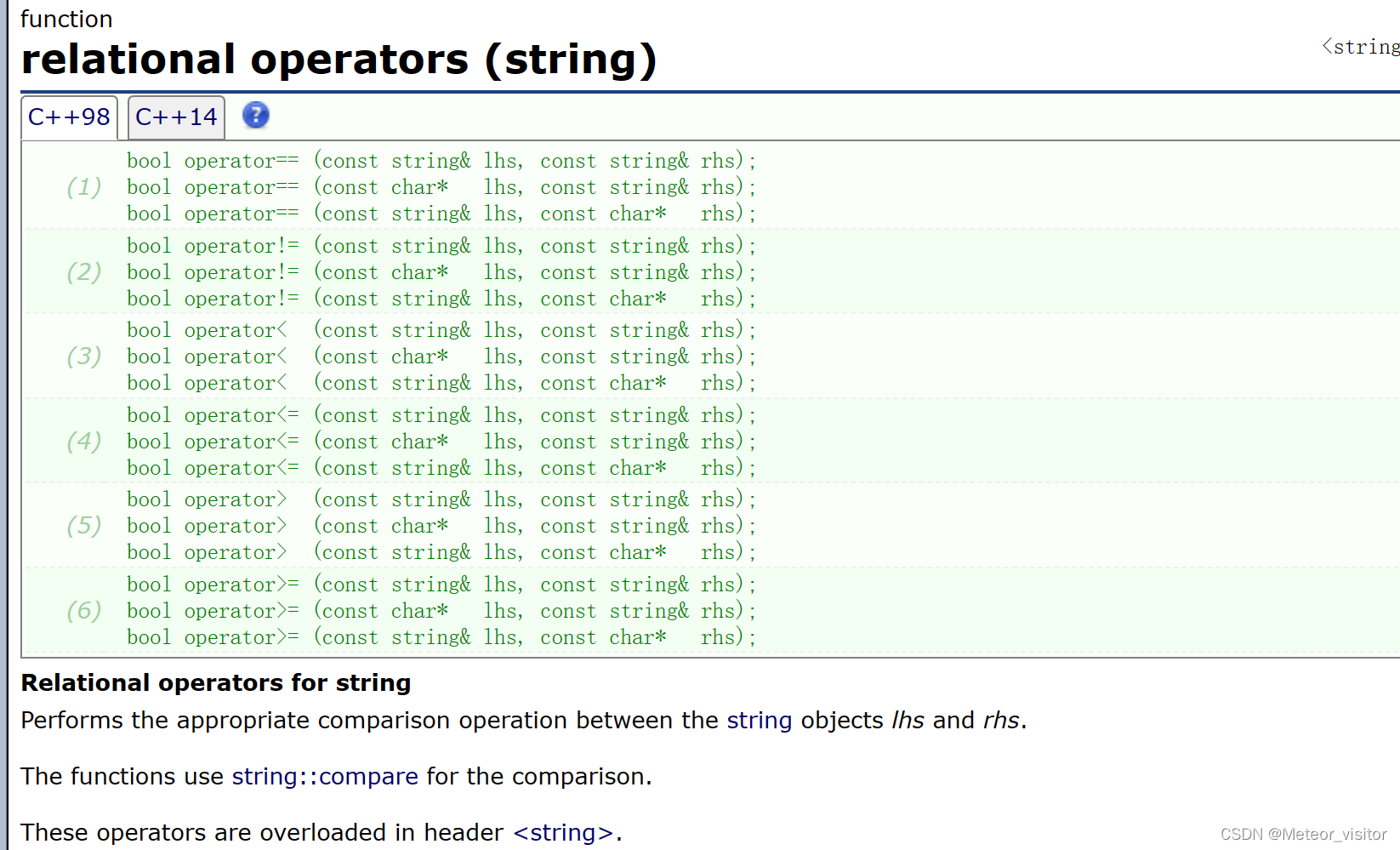
注意:运算符优先级流插入大于比较符号,注意加括号
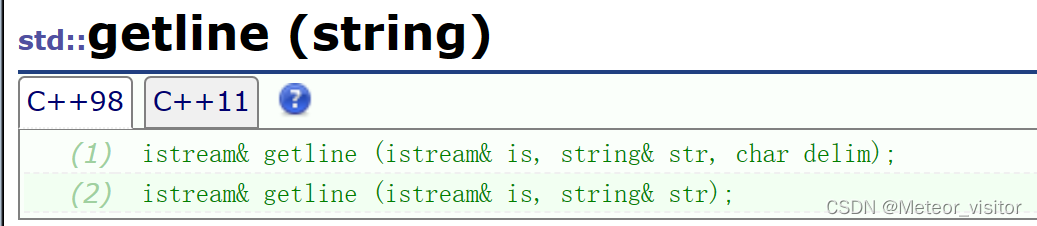
8.3 getline
可以从流中读取空格(cin就不行),读入str中
cin默认空格或换行是多个值之间的分割
getline默认换行是多个读入值之间的分割,也可以控制分隔符delim
九、其他函数
9.1 to_string、stoi

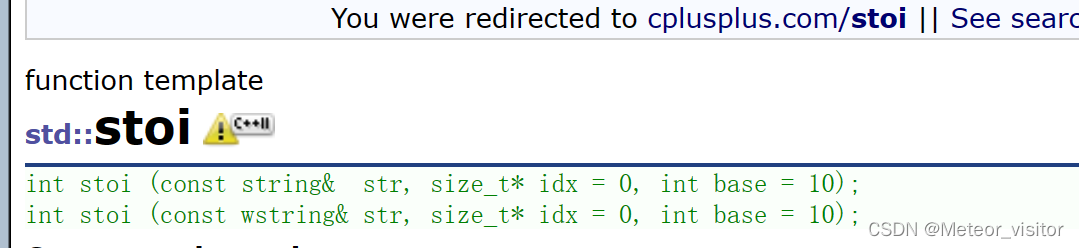
void STRTest8()
{
int x = 0, y = 90;
cin >> x >> y;
string s = to_string(x + y);
cout << s << endl;
//stoi 字符串转成整形
int ret = stoi(s);
cout << ret << endl;
}