1. 背景
五一结束后,本qiang~又投入了LLM的技术海洋中,本期将给大家带来LLM微调神器:Unsloth。
正如Unsloth官方的对外宣贯:Easily finetune & train LLMs; Get faster with unsloth。微调训练LLM,可以显著提升速度,其次显存占用也会显著减少。
但有一点需要说明:unsloth目前开源部分只支持单机版微调,更高效微调只能交费使用unsloth pro。
2. Unsloth简介
2.1 主要特性
(1) 所有的内核均以OpenAI的Triton语言实现,并且手动实现反向传播引擎。Triton语言是面向LLM训练加速。
(2) 准确率0损失,没有近似方法,方法完全一致。
(3) 硬件层面无需变动。支持18年之后的Nvidia GPU(V100, T4, Titan V, RTX20,30,40x, A100, H100, L40等,GTX1070,1080也支撑,但比较慢),Cuda最低兼容版本是7.0
(4) 通过WSL适用于Linux和Windows
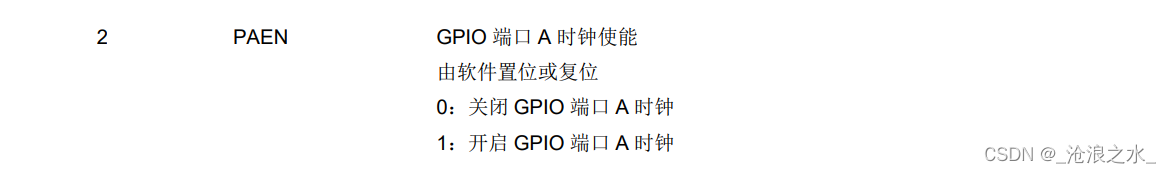
(5) 基于bisandbytes包,支持4bit和16bit的 QLoRA/LoRA微调
(6) 开源代码有5倍的训练效率提升, Unsloth Pro可以提升至30倍
2.2 目前支撑的模型
由于底层算子需要使用triton重写,因此部分开源模型的适配工作周期可能较长。当前unsloth支持的模型包含Qwen 1.5(7B, 14B, 32B, 72B), Llama3-8B, Mistral-7B, Gemma-7B, ORPO, DPO Zephyr, Phi-3(3.8B), TinyLlama
2.3 模型加速效果
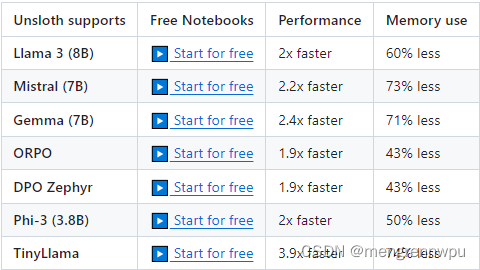
Qwen1.5-7B的集成是由Firefly作者封装并验证,性能提升30%+,显卡减少40%+,详见地址。
2.4 安装教程
conda create --name unsloth_env python=3.10
conda activate unsloth_env
conda install pytorch-cuda=<12.1/11.8> pytorch cudatoolkit xformers -c pytorch -c nvidia -c xformers
pip install "unsloth[colab-new] @ git+https://github.com/unslothai/unsloth.git"
pip install --no-deps trl peft accelerate bitsandbytes3. 实战
本着眼过千遍不如手过一遍的宗旨,本qiang~针对Unsloth做了一个对比实现。对比的实验环境分别为:P40, A40, A800,对比的模型使用的是出锅热乎的Llama3(8B)。
3.1 比对维度
| 维度 | 说明 |
| 显卡 | 是否支持bf16 |
| 最大文本长度 | max_seq_length |
| 批次大小 | per_device_train_batch_size |
| 梯度累加步长 | gradient_accumulation_steps |
| 秩 | LoRA的rank |
| dropout | lora_droput |
3.2 源码
from unsloth import FastLanguageModel
import torch
from datasets import load_dataset
from trl import SFTTrainer
from transformers import TrainingArguments, TextStreamer, AutoModelForCausalLM, set_seed, AutoTokenizer, BitsAndBytesConfig
from peft import get_peft_model, LoraConfig, prepare_model_for_kbit_training
import gc
set_seed(42)
alpaca_prompt = """Below is an instruction that describes a task, paired with an input that provides further context. Write a response that appropriately completes the request.
### Instruction:
{}
### Input:
{}
### Response:
{}"""
def train_unsloth(dtype,
max_seq_length,
per_device_train_batch_size,
gradient_accumulation_steps,
rank,
lora_alpha=16,
lora_dropout=0,
max_steps=50,
save_steps=50,
seed=42,
warmup_steps=5,
learning_rate=2e-4,
logging_steps=5):
"""
使用unsloth进行微调训练
"""
print(f'dtype:{dtype}, max_seq_length:{max_seq_length}, per_device_train_batch_size:{per_device_train_batch_size}, gradient_accumulation_steps:{gradient_accumulation_steps}, rank:{rank}, lora_dropout:{lora_dropout}')
load_in_4bit = True
model, tokenizer = FastLanguageModel.from_pretrained(
model_name='pretrain_models/llama/llama3-8B-Instruct',
max_seq_length=max_seq_length,
dtype=dtype,
load_in_4bit=load_in_4bit
)
model = FastLanguageModel.get_peft_model(
model,
r = rank,
target_modules=['q_proj', 'k_proj', 'v_proj', 'o_proj', 'gate_proj', 'up_proj', 'down_proj'],
lora_alpha=lora_alpha,
lora_dropout=lora_dropout,
bias='none',
use_gradient_checkpointing=True,
random_state=seed,
use_rslora=False
)
EOS_TOKEN = tokenizer.eos_token
def formatting_prompts_func(examples):
instructions = examples["instruction"]
inputs = examples["input"]
outputs = examples["output"]
texts = []
for instruction, input, output in zip(instructions, inputs, outputs):
# Must add EOS_TOKEN, otherwise your generation will go on forever!
text = alpaca_prompt.format(instruction, input, output) + EOS_TOKEN
texts.append(text)
return { "text" : texts}
pass
dataset = load_dataset("yahma/alpaca-cleaned", split = "train")
dataset = dataset.map(formatting_prompts_func, batched = True)
trainer = SFTTrainer(
model=model,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
train_dataset=dataset,
dataset_text_field='text',
max_seq_length=max_seq_length,
packing=False,
args = TrainingArguments(
per_device_train_batch_size=per_device_train_batch_size,
gradient_accumulation_steps=gradient_accumulation_steps,
warmup_steps=warmup_steps,
learning_rate=learning_rate,
fp16 = not torch.cuda.is_bf16_supported(),
bf16 = torch.cuda.is_bf16_supported(),
logging_steps=logging_steps,
optim='adamw_8bit',
weight_decay=0.01,
lr_scheduler_type='linear',
seed=seed,
output_dir='output/llame3-8b-instruct-unsloth',
save_steps=save_steps,
max_steps=max_steps
)
)
gpu_stats = torch.cuda.get_device_properties(0)
start_gpu_memory = round(torch.cuda.max_memory_reserved()/1024/1024/1024, 3)
max_memory = round(gpu_stats.total_memory/1024/1024/1024, 3)
print(f"GPU = {gpu_stats.name}. Max memory = {max_memory} GB.")
print(f"{start_gpu_memory} GB of memory reserved.")
trainer_stats = trainer.train()
used_memory = round(torch.cuda.max_memory_reserved()/1024/1024/1024, 3)
used_memory_for_lora = round(used_memory - start_gpu_memory)
used_percentage = round(used_memory/max_memory*100, 3)
lora_percentage = round(used_memory_for_lora/max_memory*100, 3)
print(f"{trainer_stats.metrics['train_runtime']} seconds used for training.")
print(f"{round(trainer_stats.metrics['train_runtime']/60, 2)} minutes used for training.")
print(f"Peak reserved memory = {used_memory} GB.")
print(f"Peak reserved memory for training = {used_memory_for_lora} GB.")
print(f"Peak reserved memory % of max memory = {used_percentage} %.")
print(f"Peak reserved memory for training % of max memory = {lora_percentage} %.")
model.save_pretrained("output/llame3-8b-instruct-unsloth-lora") # Local saving
tokenizer.save_pretrained("output/llame3-8b-instruct-unsloth-lora")
# model.save_pretrained_merged("model", tokenizer, save_method = "merged_16bit",) # Merge to 16bit
# model.save_pretrained_merged("model", tokenizer, save_method = "merged_4bit",) # Merge to 4bit
# model.save_pretrained_merged("model", tokenizer, save_method = "lora",) # Just LoRA adapters
# model.save_pretrained_gguf("model", tokenizer,) # Save to 8bit Q8_0
# model.save_pretrained_gguf("model", tokenizer, quantization_method = "f16") # Save to 16bit GGUF
# model.save_pretrained_gguf("model", tokenizer, quantization_method = "q4_k_m") # Save to q4_k_m GGUF
del model
del tokenizer
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
for _ in range(3):
gc.collect()
def train_trans(dtype,
max_seq_length,
per_device_train_batch_size,
gradient_accumulation_steps,
rank,
lora_alpha=16,
lora_dropout=0,
max_steps=50,
save_steps=50,
seed=42,
warmup_steps=5,
learning_rate=2e-4,
logging_steps=5):
"""
使用transformers进行微调训练
"""
print(f'dtype:{dtype}, max_seq_length:{max_seq_length}, per_device_train_batch_size:{per_device_train_batch_size}, gradient_accumulation_steps:{gradient_accumulation_steps}, rank:{rank}, lora_dropout:{lora_dropout}')
model_path = 'pretrain_models/llama/llama3-8B-Instruct'
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path, padding_side='right', model_max_length=8192)
tokenizer.add_special_tokens({"pad_token" : '<|reserved_special_token_250|>'})
tokenizer.pad_token = '<|reserved_special_token_250|>'
quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(
load_in_4bit=True,
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=dtype,
bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=True,
bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4",
llm_int8_threshold=6.0,
llm_int8_has_fp16_weight=False,
)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_path,
torch_dtype=dtype,
quantization_config=quantization_config
)
model = prepare_model_for_kbit_training(model, use_gradient_checkpointing=True)
model.enable_input_require_grads()
config = LoraConfig(
r=rank,
lora_alpha=lora_alpha,
target_modules=['q_proj', 'k_proj', 'v_proj', 'o_proj', 'gate_proj', 'up_proj', 'down_proj'],
lora_dropout=lora_dropout,
bias="none",
task_type="CAUSAL_LM",
use_rslora=False
)
model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config=config)
model.gradient_checkpointing_enable()
EOS_TOKEN = tokenizer.eos_token
def formatting_prompts_func(examples):
instructions = examples["instruction"]
inputs = examples["input"]
outputs = examples["output"]
texts = []
for instruction, input, output in zip(instructions, inputs, outputs):
# Must add EOS_TOKEN, otherwise your generation will go on forever!
text = alpaca_prompt.format(instruction, input, output) + EOS_TOKEN
texts.append(text)
return { "text" : texts}
pass
dataset = load_dataset("yahma/alpaca-cleaned", split = "train")
dataset = dataset.map(formatting_prompts_func, batched = True,)
trainer = SFTTrainer(
model=model,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
train_dataset=dataset,
dataset_text_field='text',
max_seq_length=max_seq_length,
packing=False,
args = TrainingArguments(
per_device_train_batch_size=per_device_train_batch_size,
gradient_accumulation_steps=gradient_accumulation_steps,
warmup_steps=warmup_steps,
learning_rate=learning_rate,
fp16 = not torch.cuda.is_bf16_supported(),
bf16 = torch.cuda.is_bf16_supported(),
logging_steps=logging_steps,
optim='adamw_8bit',
weight_decay=0.01,
lr_scheduler_type='linear',
seed=seed,
output_dir='output/llame3-8b-instruct-unsloth',
save_steps=save_steps,
max_steps=max_steps
)
)
gpu_stats = torch.cuda.get_device_properties(0)
start_gpu_memory = round(torch.cuda.max_memory_reserved()/1024/1024/1024, 3)
max_memory = round(gpu_stats.total_memory/1024/1024/1024, 3)
print(f"GPU = {gpu_stats.name}. Max memory = {max_memory} GB.")
print(f"{start_gpu_memory} GB of memory reserved.")
trainer_stats = trainer.train()
used_memory = round(torch.cuda.max_memory_reserved()/1024/1024/1024, 3)
used_memory_for_lora = round(used_memory - start_gpu_memory)
used_percentage = round(used_memory/max_memory*100, 3)
lora_percentage = round(used_memory_for_lora/max_memory*100, 3)
print(f"{trainer_stats.metrics['train_runtime']} seconds used for training.")
print(f"{round(trainer_stats.metrics['train_runtime']/60, 2)} minutes used for training.")
print(f"Peak reserved memory = {used_memory} GB.")
print(f"Peak reserved memory for training = {used_memory_for_lora} GB.")
print(f"Peak reserved memory % of max memory = {used_percentage} %.")
print(f"Peak reserved memory for training % of max memory = {lora_percentage} %.")
model.save_pretrained("output/llame3-8b-instruct-unsloth-lora") # Local saving
tokenizer.save_pretrained("output/llame3-8b-instruct-unsloth-lora")
del model
del tokenizer
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
for _ in range(3):
gc.collect()
def infer():
model, tokenizer = FastLanguageModel.from_pretrained(
model_name='output/llame3-8b-instruct-unsloth-lora',
max_seq_length=2048,
dtype=torch.float16,
load_in_4bit=True
)
# 2x的速率进行推理
FastLanguageModel.for_inference(model)
inputs = tokenizer([alpaca_prompt.format('Continue the fibonnaci sequence.', '1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8', '')], return_tensors = "pt").to('cuda')
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=1024, use_cache=True)
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs))
text_streamer = TextStreamer(tokenizer)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=1024, streamer=text_streamer)
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs))
if __name__ == '__main__':
train_unsloth(dtype=torch.bfloat16, max_seq_length=1024, per_device_train_batch_size=1, gradient_accumulation_steps=16, rank=8, lora_dropout=0)
train_unsloth(dtype=torch.bfloat16, max_seq_length=1024, per_device_train_batch_size=1, gradient_accumulation_steps=16, rank=64, lora_dropout=0)
train_unsloth(dtype=torch.bfloat16, max_seq_length=2048, per_device_train_batch_size=1, gradient_accumulation_steps=16, rank=64, lora_dropout=0)
train_unsloth(dtype=torch.bfloat16, max_seq_length=2048, per_device_train_batch_size=4, gradient_accumulation_steps=4, rank=64, lora_dropout=0)
train_unsloth(dtype=torch.bfloat16, max_seq_length=2048, per_device_train_batch_size=4, gradient_accumulation_steps=4, rank=64, lora_dropout=0.05)
train_unsloth(dtype=torch.bfloat16, max_seq_length=2048, per_device_train_batch_size=16, gradient_accumulation_steps=4, rank=64, lora_dropout=0.05)
train_trans(dtype=torch.bfloat16, max_seq_length=1024, per_device_train_batch_size=1, gradient_accumulation_steps=16, rank=8, lora_dropout=0)
train_trans(dtype=torch.bfloat16, max_seq_length=1024, per_device_train_batch_size=1, gradient_accumulation_steps=16, rank=64, lora_dropout=0)
train_trans(dtype=torch.bfloat16, max_seq_length=2048, per_device_train_batch_size=1, gradient_accumulation_steps=16, rank=64, lora_dropout=0)
train_trans(dtype=torch.bfloat16, max_seq_length=2048, per_device_train_batch_size=4, gradient_accumulation_steps=4, rank=64, lora_dropout=0)
train_trans(dtype=torch.bfloat16, max_seq_length=2048, per_device_train_batch_size=4, gradient_accumulation_steps=4, rank=64, lora_dropout=0.05)
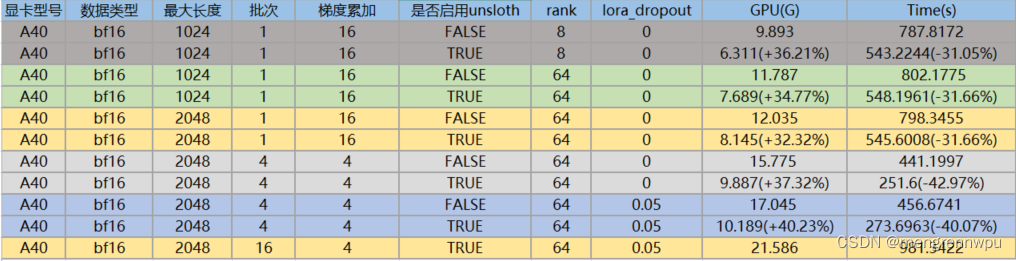
4 实验结果
4.1 P40

4.2 A40
4.3 A800

4.4 结论
针对于llama3-8B进行unsloth训练,与基于transformers框架训练进行比对,结论如下:
(1) 集成unsloth后,显卡占用确实更少,训练效率确实更快,不管是哪种维度。
(2) P40增加batch_size后,显卡的内存占用提升,但训练的时间也更长,说明P40针对大批次的数据处理,性能会降低; 但A40, A800增加batch_size后,显卡内存占用虽然提升,但训练的时间更短。
(3) A800的batch_size为1时,训练效率不如A40,当batch_size增加到16时,A800的训练效率比A40快接近一倍。因此,A800更适合处理大批次的场景,对于小batch_size,杀鸡不能用牛刀。
5. 总结
一句话足矣~
本文主要是使用unsloth框架针对llama3的高效微调实验,提供了详细的对比代码以及对比分析结果。
之后会写一篇关于Qwen1.5的对比实验,敬请期待~
6. 参考
1. unsloth: https://github.com/unslothai/unsloth
2. Qwen1.5+Unsloth: Support Qwen2 by yangjianxin1 · Pull Request #428 · unslothai/unsloth · GitHub