目录
一、用栈实现队列
1.1 题目
1.2 思路
1.3 C语言题解
1.3.1 栈接口
1.3.2 代码实现
二、用队列实现栈
2.1 题目
2.2 思路
2.2.1 如何设计出栈
2.2.2 如何设计入栈
2.3 C语言题解
2.3.1 队列接口
2.3.2 代码实现
三、括号匹配问题
3.1 题目
3.2 思路
3.3 C语言题解
3.3.1 栈接口
3.3.2 主函数
一、用栈实现队列
1.1 题目
LeetCode原题链接:. - 力扣(LeetCode)
1.2 思路
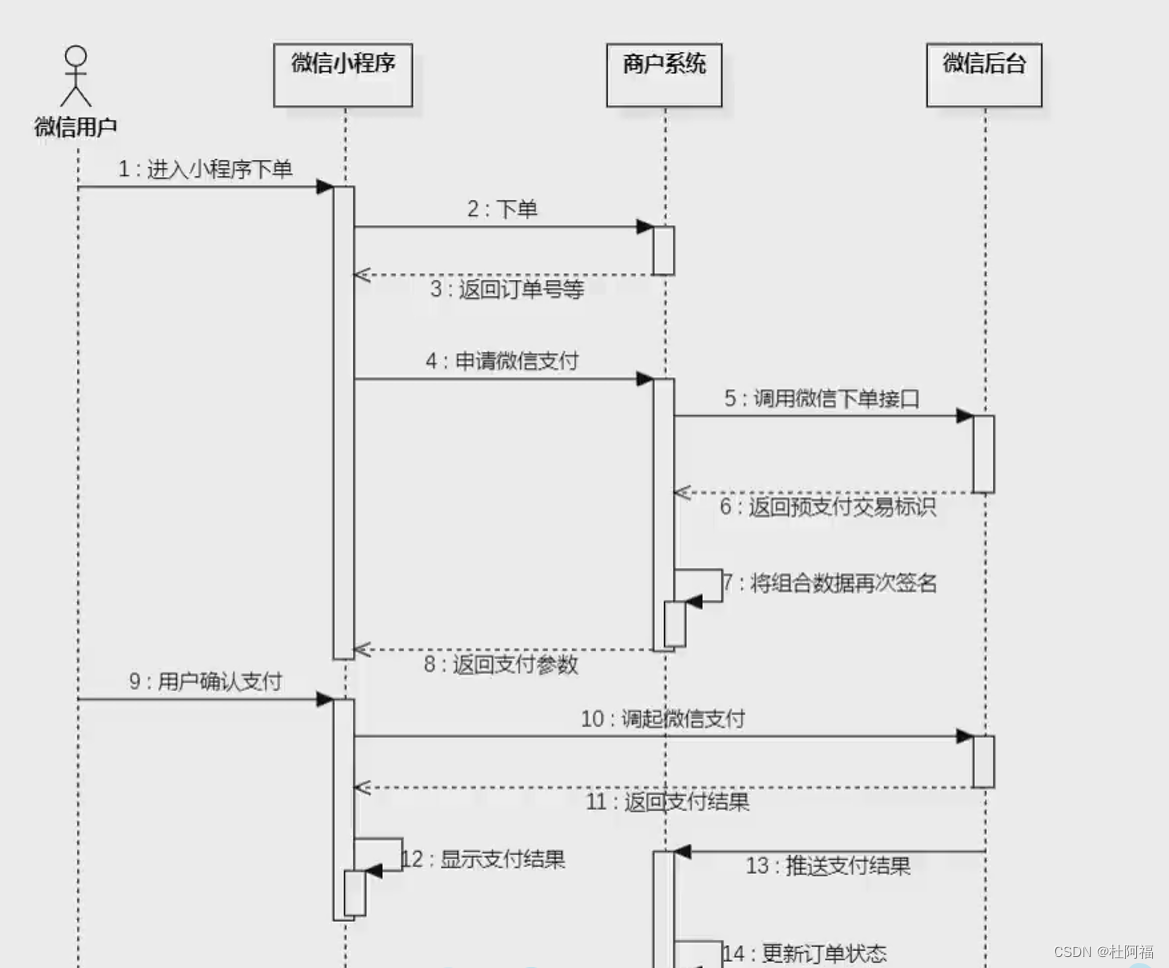
栈的特点是后进先出,要通过栈实现队列的先进先出。可以将所有数据压入一个栈中,再一个个出栈压入另一个空栈中,这样原先的栈底就变成了现在的栈顶。现在的栈的顺序就完美符合队列的顺序。
综上,设计一个入栈,一个出栈即可完成此问题。
1.3 C语言题解
1.3.1 栈接口
- 基于自己用C语言编写的接口进行题目的求解
- 关于栈的知识详见博主的另一篇博客:http://t.csdnimg.cn/SHAxi
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a; //数组
int top; //栈顶元素
int capacity; //数据个数
}ST;
void STInit(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = 0;
//top指向栈顶元素的下一个位置
pst->top = 0;
top指向栈顶元素的位置
//pst->top = -1;
}
void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = pst->top = 0;
}
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
//扩容
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = 0;
if (pst->capacity == 0)
{
newcapacity = 4;
}
else
{
newcapacity = pst->capacity * 2;
}
STDataType* temp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (temp == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
exit(1);
}
pst->a = temp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
void STPop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst > 0);
pst->top--;
}
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst > 0);
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top == 0;
}
int STSize(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}1.3.2 代码实现
typedef struct {
ST pushstack;
ST popstack;
} MyQueue;
//创建队列
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* obj = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
if (obj == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
exit(1);
}
STInit(&(obj->pushstack));
STInit(&(obj->popstack));
return obj;
}
//将元素 x 推到队列的末尾
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
STPush(&(obj->pushstack), x);
}
//从队列的开头移除并返回元素
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
if (STEmpty(&(obj->popstack)))
{
while (!STEmpty(&(obj->pushstack)))
{
int front = STTop(&(obj->pushstack));
STPush(&(obj->popstack), front);
STPop(&(obj->pushstack));
}
}
int temp = STTop(&(obj->popstack));
STPop(&(obj->popstack));
return temp;
}
//返回队列开头的元素
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
if (STEmpty(&(obj->popstack)))
{
while (!STEmpty(&(obj->pushstack)))
{
int front = STTop(&(obj->pushstack));
STPush(&(obj->popstack), front);
STPop(&(obj->pushstack));
}
}
return STTop(&(obj->popstack));
}
//如果队列为空,返回 true ;否则,返回 false
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
if (STEmpty(&(obj->popstack)) == 1 && STEmpty(&(obj->pushstack)) == 1)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
//销毁队列
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
STDestroy(&(obj->pushstack));
STDestroy(&(obj->pushstack));
free(obj);
}二、用队列实现栈
2.1 题目
LeetCode原题链接:. - 力扣(LeetCode)
2.2 思路
2.2.1 如何设计出栈
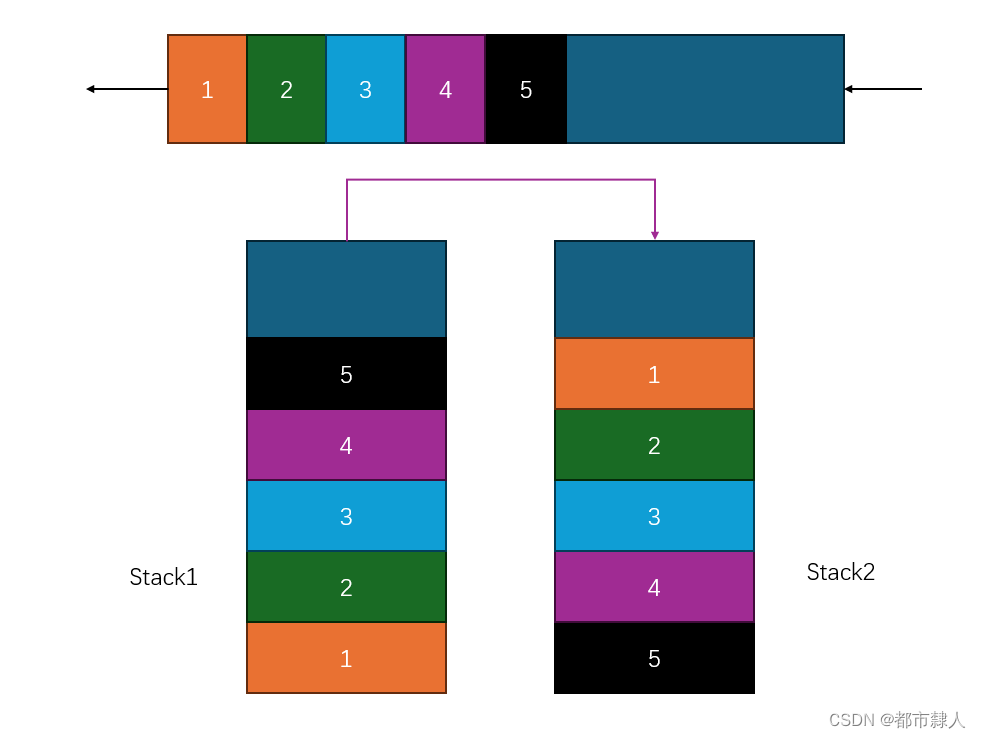
队列的特点是先进先出,要想实现栈的后进先出。核心就是要实现后进的元素先出栈。使用两个队列。先将所有元素全部压入其中一个队列,将队列中最后一个元素之前的所有元素全部出队到另一个空的队列,那么剩下的元素便是最后的元素,从而实现了后进先出。
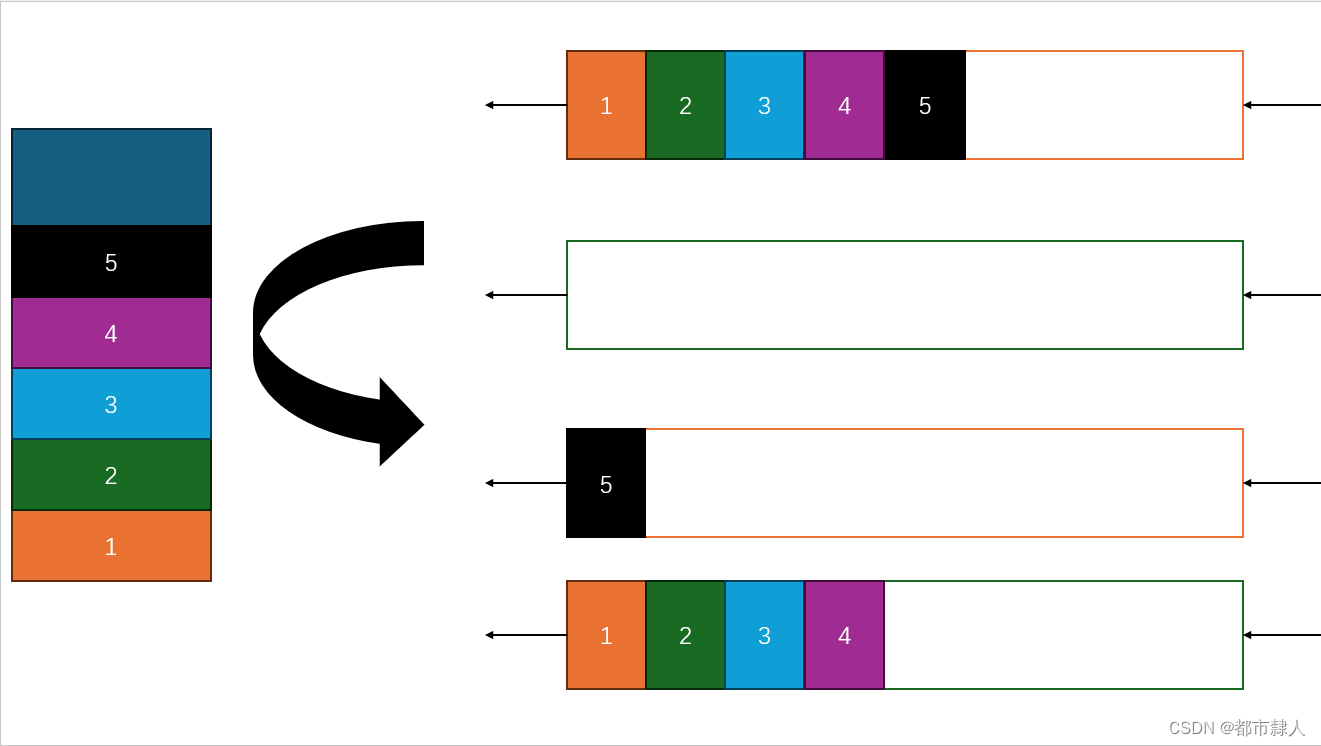
2.2.2 如何设计入栈
出栈的问题解决了以后,我们再来看如何入栈。入栈的问题就在于在空的栈入栈还是在非空的栈入栈。理论上讲两种方式都可以实现。但是从代码的编写角度看,如果在空栈中继续压栈,那么就导致没有空栈的存在,意味着判断的困难,所以一律采取从非空栈入栈。
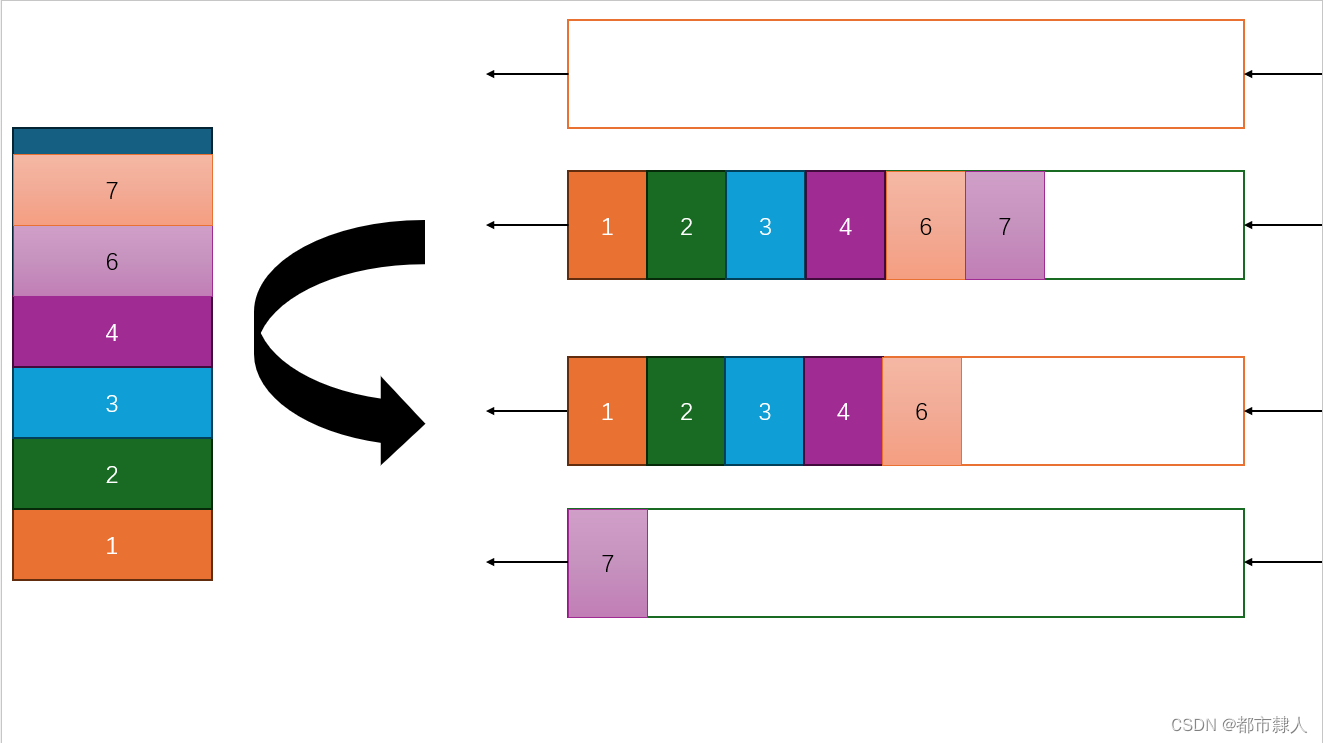
2.3 C语言题解
2.3.1 队列接口
- 基于自己用C语言编写的接口进行题目的求解
- 关于队列的知识详见博主的另一篇博客:http://t.csdnimg.cn/afeBF
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType val;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;
//队列初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
//队列销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* pcur = pq->phead;
while (pcur)
{
QNode* temp = pcur->next;
free(pcur);
pcur = temp;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
//创建节点封装
QNode* InitNewnode(QDataType x)
{
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
exit(1);
}
newnode->val = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
//入队
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = InitNewnode(x);
if (pq->phead == NULL)
{
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
//出队
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->size != 0);
assert(pq);
assert(pq->size != 0);
if (pq->phead->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* temp = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = temp;
}
pq->size--;
}
//队列大小
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
return pq->size;
}
//判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size == 0;
}
//返回队头元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->phead);
return pq->phead->val;
}
//返回队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->ptail);
return pq->ptail->val;
}2.3.2 代码实现
typedef struct {
Queue queue1;
Queue queue2;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* obj = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
if (obj == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
exit(1);
}
QueueInit(&(obj->queue1));
QueueInit(&(obj->queue2));
return obj;
}
//将元素 x 压入栈顶。
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
if (QueueEmpty(&(obj->queue1))) //如果队1为空
{
QueuePush(&(obj->queue2), x); //往队2插入
}
else
{
QueuePush(&(obj->queue1), x);
}
}
//移除并返回栈顶元素。
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
Queue* full = &(obj->queue1);
Queue* non = &(obj->queue2);
if (QueueEmpty(&(obj->queue1)))
{
full = &(obj->queue2);
non = &(obj->queue1);
}
while ((full->size) > 1)
{
QueuePush(non, QueueFront(full));
QueuePop(full);
}
int front = QueueFront(full);
QueuePop(full);
return front;
}
//返回栈顶元素
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
if (QueueEmpty(&(obj->queue1)))
{
return QueueBack(&(obj->queue2));
}
else
{
return QueueBack(&(obj->queue1));
}
}
//如果栈是空的,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
return (QueueEmpty(&(obj->queue1)) == 1 && QueueEmpty(&(obj->queue2)) == 1);
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
QueueDestroy(&(obj->queue1));
QueueDestroy(&(obj->queue2));
free(obj);
}三、括号匹配问题
3.1 题目
LeetCode原题链接:. - 力扣(LeetCode)
3.2 思路
栈先入后出特点恰好与本题括号排序特点一致,即左括号入栈,遇到右括号时将最近的栈顶左括号出栈,进行比较。
另外:遍历完所有括号后栈必须为空,也就是偶数个。
3.3 C语言题解
3.3.1 栈接口
typedef char STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a; //数组
int top; //栈顶元素
int capacity; //数据个数
}ST;
//栈初始化
void STInit(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = 0;
//top指向栈顶元素的下一个位置
pst->top = 0;
top指向栈顶元素的位置
//pst->top = -1;
}
//栈销毁
void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = pst->top = 0;
}
//入栈
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
//扩容
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = 0;
if (pst->capacity == 0)
{
newcapacity = 4;
}
else
{
newcapacity = pst->capacity * 2;
}
STDataType* temp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (temp == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
exit(1);
}
pst->a = temp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
//出栈
void STPop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst > 0);
pst->top--;
}
//返回栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst>0);
return pst->a[pst->top-1];
}
//判空
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == 0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
//栈的元素个数
int STSize(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}3.3.2 主函数
bool isValid(char* s) {
ST st;
STInit(&st);
//遍历数组
while(*s)
{
//左括号入栈
if(*s == '[' || *s == '(' || *s == '{')
{
STPush(&st,*s);
}
//右括号比较
else
{
//特殊情况判空
if(STEmpty(&st))
{
return false;
}
//取出最近的左括号比较
char top = STTop(&st);
STPop(&st);
if((top=='(' && *s != ')')
|| top=='[' && *s != ']'
|| top=='{' && *s != '}')
{
return false;
}
}
s++;
}
//判空
bool ret = STEmpty(&st);
return ret;
STDestroy(&st);
}