1.OOP面向对象编程 vs. GP泛型编程
- OOP将data和method放在一起,目的是通过封装、继承、多态提高软件的可维护性和可扩展性
- GP将data和method分开,可以将任何容器与任何算法结合使用,只要容器满足塞饭所需的迭代器类型
2.算法与仿函数的区别
bool strLonger(const string &s1, const string &s2)
{
return s1.size() < s2.size();
}
// 算法
cout << "max of zoo and hello:" << max(string("zoo"), string("hello")) << endl;
// 仿函数
cout << "max of zoo and hello:" << max(string("zoo"), string("hello"), strLonger) << endl;
3.泛化、特化、偏特化
- 泛化:支持广泛的数据类型和情况,而不是针对特定类型
- 特化:为特定类型或一组类型提供特定的实现
#include <iostream>
// General template
template <typename T>
void print(T arg) {
std::cout << "General print: " << arg << std::endl;
}
// Specialization for const char*
template <>
void print<const char*>(const char* arg) {
std::cout << "Specialized print for const char*: " << arg << std::endl;
}
int main() {
print(123); // Uses general template
print("Hello, world"); // Uses specialized template
}
- 偏特化:针对特定类型组合提供优化的行为或特殊实现。完全特化需要指定模板的所有参数,偏特化只需指定部分参数,或对参数施加某些约束。
- 第一种偏特化处理第二个模板参数为
int的情况。 - 第二种偏特化处理两个模板参数相同的情况。
- 第一种偏特化处理第二个模板参数为
#include <iostream>
// 基本模板
template <typename T, typename U>
class MyClass {
public:
void print() {
std::cout << "Base template\\n";
}
};
// 偏特化:特化第二个类型为 int 的情况
template <typename T>
class MyClass<T, int> {
public:
void print() {
std::cout << "Partially specialized template for T and int\\n";
}
};
// 偏特化:特化两个类型都为相同类型的情况
template <typename T>
class MyClass<T, T> {
public:
void print() {
std::cout << "Partially specialized template for T, T\\n";
}
};
int main() {
MyClass<double, double> myClass1; // 会匹配 MyClass<T, T>
MyClass<double, int> myClass2; // 会匹配 MyClass<T, int>
MyClass<double, char> myClass3; // 会匹配基本模板 MyClass<T, U>
myClass1.print(); // 输出: Partially specialized template for T, T
myClass2.print(); // 输出: Partially specialized template for T and int
myClass3.print(); // 输出: Base template
}
4.分配器allocates
分配器(allocators)是用来管理内存分配和回收的对象。
- 在 VC6 中,
operator new()通常通过调用malloc()实现,malloc()函数不仅会开辟用户请求的内存外,还会引入额外的内存开销:
void* operator new(size_t size) {
void* p = malloc(size);
if (p == 0) // 如果malloc失败,则抛出std::bad_alloc异常
throw std::bad_alloc();
return p;
}
- 例如:当我们需要分配512个整型数据时
int *p = allocator<int>().allocate(512,(int *)0);
allocator<int>().deallocate(p,512);
- 在 VC6 / BC++ / G++中,
allocator类都是使用operator new来分配内存,并使用operator delete来释放内存。其中,operator new()通常通过调用malloc()实现开辟内存,operator delete()通常通过调用free()实现回收内存:
// VC6 STL中容器对allocator的使用
template<class _Ty, class _A=allocator<_Ty>> // 调用allocator类
class vector
{ ...
};
template <typename T>
class allocator {
public:
typedef size_t size_type; // size_t是一个无符合整型数据类型
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type; // 表示同一个数组中任意两个元素之间的差异
typedef T* pointer;
typedef T value_type;
pointer allocate(size_type n, const void* hint = 0) {
return (pointer) (::operator new(n * sizeof(value_type)));
}
void deallocate(pointer p, size_type n) {
::operator delete(p);
}
}
- 在GCC2.9中
// VC6 STL中容器对allocator的使用
template<class T, class Alloc = alloc> // 调用allocator类
class vector
{ ...
};

①内存池:由一系列内存块组成,每块预分配一定数量的内存。
②自由列表:每个固定大小的内存块都有自己的自由列表。
③大小分类:根据内存请求的大小被分类到不同的自由列表。
-
GCC4.9所附的标准库,其中**__pool_alloc就是GCC2.9中的alloc**
// 使用方法 vector<string, __gnn_cxx::__pool_alloc<string>> vec;
5.容器的分类
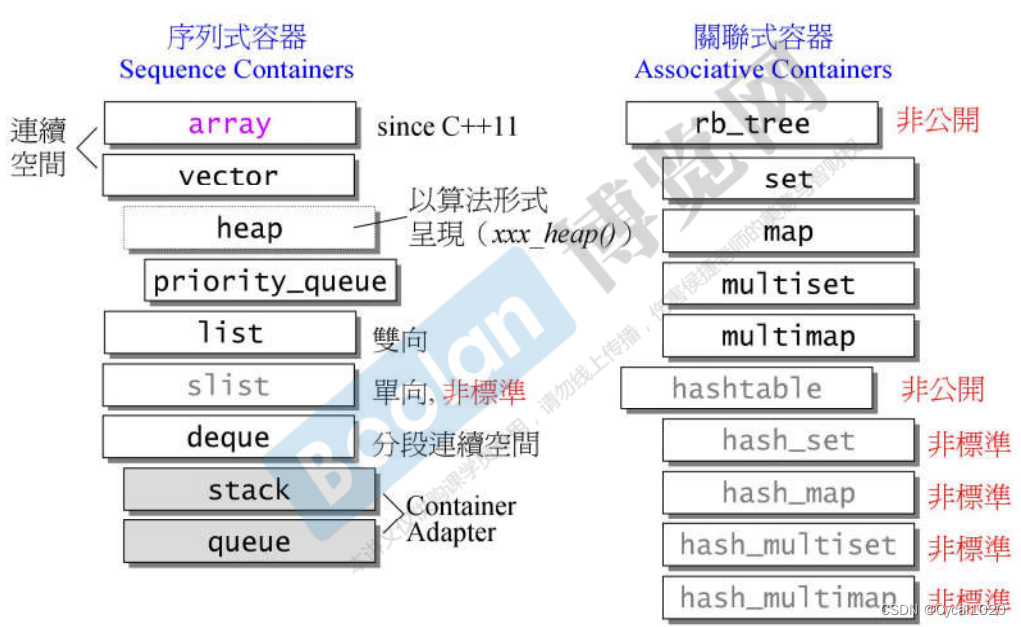
6.容器list
G2.9版本:
template <class T, class Alloc = alloc>
class list{
protected:
typeof __list_node<T> list_node; // 1号代码块
public:
typeof list_node* link_type;
typeof __list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator; // 2号代码块
protected:
link_type node;
}
// 1号代码块
template <class T>
struct __list_node {
void* prev;
void* next;
T data;
};
// 2号代码块
template <class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator{
typedef bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category; // (1)
typedef T value_type; // (2)
typedef Ptr pointer; // (3)
typedef Ref reference; // (4)
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type; // (5)
typedef __list_node<T> list_node;
typedef list_node* list_type;
typedef __list_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr> self;
link_type node;
reference operator*() const{ return (*node).data; } // 返回引用
pointer operator->() const{ return &(operator *());} // 返回指针。获得该对象的内存地址,即一个指向该对象的指针
self& operator++() // i++
{ node = (link_type) ((*node).next); return *this; // 返回自身的引用}
// (*node).next是一个 __list_node<T>* 类型的值,加上(list_type)是显式类型转换
// (*node).next 等价于 node->next 等价于 (&(*node))->next;
// node只是一个迭代器的指针,不是迭代器本身
// self&表示返回迭代器的引用
self operator++(int) // ++i
{ self tmp = *this; ++*this; return tmp;}
};
- 前缀递增 (
operator++()) 将迭代器向前移动到下一个元素 - 后缀递增 (
operator++(int)) 返回迭代器的一个临时副本(在递增前的状态),然后再递增迭代器。 - 内置
->操作符 用于直接从指针访问对象成员。 - 重载的
operator->()提供了一种方式,通过迭代器对象模拟原生指针的行为,允许通过迭代器间接访问对象成员。 (*node).next等价于node->next等价于(&(*node))->next
G4.9版本:
template<typename _Tp, typename _Alloc=std::allocator<_Tp>>
class list:protected_List_base<_Tp,_Alloc>
{
public:typedef _List_iterator<_Tp> iterator;
}
template<typename _Tp, typename _Alloc = std::allocator<_Tp>>- 这是一个类模板,接受两个模板参数。
_Tp表示列表中要存储的数据类型。_Alloc是分配器类型,用于控制链表中元素的内存分配。这个参数有一个默认值,即std::allocator<_Tp>,这是 C++ 标准库提供的一种通用内存分配器。
: protected _List_base<_Tp, _Alloc>list类从_List_base类继承而来,使用保护(protected)继承。这意味着_List_base中的公共和保护成员在list类中将变为保护成员。_List_base是一个实现链表基础功能的类
template<typename _Tp>
struct _List_iterator
{
typedef _Tp* pointer;
typedef _Tp& reference;
...
};
// 自身类型的指针使得可以从任何一个节点开始
// 沿着链表向前或向后移动,这对于双向遍历和双向操作非常重要。
struct _List_node_base
{
_List_node_base* _M_next;
_List_node_base* _M_prev;
};
template<typename _Tp>
struct _List_node:public _List_node_base
{
_Tp _M_data;
};
7.Iterator必须提供5中associated types
算法提问:
template<typename T>
incline void
algorithm(T first, T last) // 迭代器
{
...
T::iterator_category
T::value_type
T::pointer
T::reference
T::difference_type
...
};
迭代器回答:
template <class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator{
typedef bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category; // (1)
typedef T value_type; // (2)
typedef Ptr pointer; // (3)
typedef Ref reference; // (4)
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type; // (5)
...
};
8. iterator_traits 类型萃取
但当我们向算法中传入的是指针,而不是迭代器时,就需要用到traits。也就是说,iterator_traits 为所有类型的迭代器(包括原生指针)提供统一的方式来访问迭代器的属性,是在 <iterator> 头文件中定义的。
作用:
std::iterator_traits 模板用于提取迭代器相关的类型信息。
举例:
#include<iostream>
#include<iterator>
#include<vector>
template<typename Iterator>
void print_vector(Iterator first, Iterator last)
{
// using关键字用来定义类型的别名
// typename关键字告诉编译器这是一个依赖于模版参数Iterator的类型,而不是变量
using ValueType = typename iterator_traits<Iterator>::value_type;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v = {1,2,3,4,5};
print_vector(v.begin(), v.end());
}
// 当Iterator是一个类时
template<class Iterator>
struct iterator_traits
{
typedef typename Iterator::value_type value_type;
};
// 两种偏特化情况
// 当Iterator是一个普通指针时
// 如int*,那么T为int,得到value_type就被定义为“int”
template<class T>
struct iterator_traits<T*>
{
typedef T value_type;
};
// 当Iterator是一个常量指针(指针的指向可以修改,指针指向的值不能修改)
template<class T>
struct iterator_traits<const T*>
{
typedef T value_type;
};
- Iterator若是int*,ValueType 就是 int
- Iterator若是const int*,ValueType 还是 int
- 因为如果 ValueType 是 const int,后续再使用ValueType创建其他容器时,就会受到限制。因为标准库中的容器(如 std::vector)不能存储常量类型的元素,它们需要能被赋值和移动。
完整的iterator_traits:
template<class Iterator>
struct iterator_traits
{
typedef typename Iterator::iterator_category iterator_category;
typedef typename Iterator::value_type value_type;
typedef typename Iterator::pointer iterator_category;
typedef typename Iterator::reference reference;
typedef typename Iterator::difference_type difference_type;
};
template<class T>
struct iterator_traits<T*>
{
typedef random_access_iterator_tag iterator_category;
typedef T value_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
typedef T* pointer;
typedef T& reference;
};
template<class T>
struct iterator_traits<const T*>
{
typedef random_access_iterator_tag iterator_category;
typedef T value_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
typedef const T* pointer;
typedef const T& reference;
};
9.容器vector
定义:
template <class T, class Alloc = std::allocator<T>>
class vector
{
public:
typedef T value_type;
typedef T* pointer;
typedef &T reference;
typedef size_t size_type;
protected:
iterator **start**;
iterator **finish**;
iterator **end_of_range**;
Allocator alloc;
public:
iterator begin() { return **start**;}
iterator end() { return **finish**;}
size_type size const { return size_type(end() - start());}
size_type capacity() const
{ return size_type(**end_of_storage** - begin());}
bool empty() const { return begin() == end();}
reference operator[](size_type n}
{return *(begin()+n);
referebce front() {return *begin();}
reference back() {return *(end()-1);}
};
push_back操作源码:
template <class T, class Alloc=std::allocator<T>>
void push_back(const T& value)
{
if(finish == end_of_storage) // 原始空间不足
{
size_type old_size = size();
// old_size == 0:当前vector中没有任何元素,新分配的存储空间至少有一个元素的容量
// old_size != 0:分配新的容量将是当前大小的两倍, 称为指数增长
size_type new_capacity = old_size == 0 ? 1 : 2 * old_size;
iterator new_start = alloc.allocator(new_capacity);
iterator new_finsih = new_start;
try{
// 将原数据移动到新空间
for(iterator old_iter = start; old_iter != finish; )
{
alloc.construct(new_finish++, *old_iter);
alloc.destroy(old_iter++);
}
// 添加新元素
alloc.construct(new_finish++, value);
}catch(...){
// 如果构造失败,释放已分配的内存
for(iterator it=new_start; it!=new_finish; ++it)
{
alloc.destory(it);
}
alloc.deallocate(new_start, new_capacity);
throw; // 重新抛出当前异常
}
// 释放旧空间
if (start) {
alloc.deallocate(start, end_of_storage - start);
}
// 更新指针
start = new_start;
finish = new_finish;
end_of_storage = start + new_capacity;
}
else
{
alloc.construct(finish++, value); // 有足够空间,直接构造新元素
}
}
vector的迭代器iterator:
template <class T, class Alloc = alloc>
class vector
{
public:
typedef T value_type;
typedef T* iterator;
};
// 调用方法
vectot<int> v;
vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();
10.容器deque
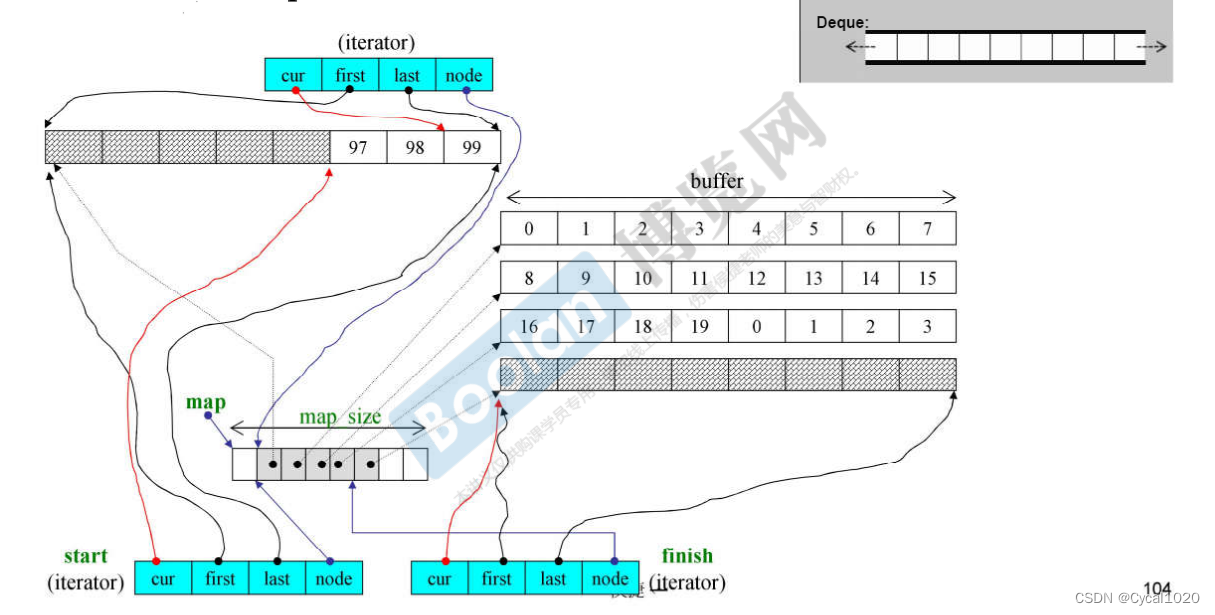
// BufSize是指缓冲区buffer的长度
template<class T,class Alloc = alloc, size_t BufSize=0>
class deque
{
public:
typedef T value_type;
typedef size_t size_type;
typedef __deque_iterator<T,T&,T*,BufSiz> iterator;
protected:
typedef T** map_pointer; // 指向指针数组的指针
protected:
iterator start;
iterator finish;
map_point map; // 指向指针数组的指针,每一个都指向一个缓冲区
size_type map_size;
public:
iterator begin() {return start;}
iterator end() {return finish;}
size_type size() {return finish - start;}
...
};
deque的迭代器iterator:
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr, size_t BufSize>
struct __deque_iterator
{
typedef random_access_iterator_tag iterator_category;
typedef T value_type;
typedef Ref reference; // T&
typedef Ptr pointer; // T*
typedef size_t size_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
typedef T** map_pointer;
typedef __deque_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr,BufSiz> self;
T* **cur**;
T* **first**;
T* **last**;
map_point **node**;
};