InputReader线程主要负责读取输入数据,并把数据交给InputDispatcher线程。本文以多指触摸屏为例,梳理一下InputReader的流程。
InputReader线程主要完成以下工作:
- 处理已有的输入设备
- 处理新增或者移除的输入设备
- 对输入设备产生的输入数据进行处理
InputReader线程启动后,调用loopOnce方法
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\InputReader.cpp
void InputReader::loopOnce() {
//省略
size_t count = mEventHub->getEvents(timeoutMillis, mEventBuffer, EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE);//1
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
mReaderIsAliveCondition.broadcast();
if (count) {
processEventsLocked(mEventBuffer, count);//2
}
//省略
} // release lock
// Send out a message that the describes the changed input devices.
if (inputDevicesChanged) {
mPolicy->notifyInputDevicesChanged(inputDevices);
}
//省略
mQueuedListener->flush();//3
注释1处获取数据,注释2处理数据,注释3处将数据交给InputDispatcher线程。这个loopOnce方法会被循环调用。接下来分开分析InputReader线程需要完成的工作。
处理已有的输入设备
首先是调用EventHub的getEvents方法
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\EventHub.cpp
size_t EventHub::getEvents(int timeoutMillis, RawEvent* buffer, size_t bufferSize) {
RawEvent* event = buffer;
for (;;) {
//省略
if (mNeedToScanDevices) {//默认为true
mNeedToScanDevices = false;
scanDevicesLocked();//1
mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan = true;
}
while (mOpeningDevices != nullptr) {//2
Device* device = mOpeningDevices;
ALOGV("Reporting device opened: id=%d, name=%s\n", device->id, device->path.c_str());
mOpeningDevices = device->next;
event->when = now;
event->deviceId = device->id == mBuiltInKeyboardId ? 0 : device->id;
event->type = DEVICE_ADDED;
event += 1;
mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan = true;
if (--capacity == 0) {
break;
}
}
if (mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan) {//3
mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan = false;
event->when = now;
event->type = FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN;
event += 1;
if (--capacity == 0) {
break;
}
}
//省略
if (event != buffer || awoken) {//4
break;
}
//省略
}
}
注释1处,调用scanDevicesLocked来扫描已存在的输入设备。注释2处对已经打开的输入设备,构造event,event的type为DEVICE_ADDED表示增加设备。注释3处表示扫描完成,增加一个type为FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN的event。注释4处,此时event指向的地址不等于buffer,跳出循环,会回到InputReader的loopOnce方法,继续往下执行,调用processEventsLocked处理这些event。
先来看一下scanDevicesLocked方法
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\EventHub.cpp
void EventHub::scanDevicesLocked() {
status_t result = scanDirLocked(DEVICE_PATH);
//省略
}
继续调用scanDirLocked处理,DEVICE_PATH为“dev/input”
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\EventHub.cpp
status_t EventHub::scanDirLocked(const char* dirname) {
char devname[PATH_MAX];
char* filename;
DIR* dir;
struct dirent* de;
dir = opendir(dirname);//1
if (dir == nullptr) return -1;
strcpy(devname, dirname);
filename = devname + strlen(devname);
*filename++ = '/';
while ((de = readdir(dir))) {
if (de->d_name[0] == '.' &&
(de->d_name[1] == '\0' || (de->d_name[1] == '.' && de->d_name[2] == '\0')))
continue;
strcpy(filename, de->d_name);
openDeviceLocked(devname);//2
}
closedir(dir);
return 0;
}
注释1处打开dev/input这个目录,dev/input这个目录下代表的是一个个的输入设备,注释2处对目录下的每个设备,调用openDeviceLocked处理
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\EventHub.cpp
status_t EventHub::openDeviceLocked(const char* devicePath) {
int fd = open(devicePath, O_RDWR | O_CLOEXEC | O_NONBLOCK);//打开设备,得到fd
//省略
int32_t deviceId = mNextDeviceId++;
Device* device = new Device(fd, deviceId, devicePath, identifier);//新建Device对象
//省略
if (test_bit(ABS_MT_POSITION_X, device->absBitmask) &&
test_bit(ABS_MT_POSITION_Y, device->absBitmask)) {
// Some joysticks such as the PS3 controller report axes that conflict
// with the ABS_MT range. Try to confirm that the device really is
// a touch screen.
if (test_bit(BTN_TOUCH, device->keyBitmask) || !haveGamepadButtons) {
device->classes |= INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH | INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH_MT;//对于多指触摸
}
//省略
if (registerDeviceForEpollLocked(device) != OK) {//1
delete device;
return -1;
}
addDeviceLocked(device);//2
}
新建Device对象后,对于多指触摸,设置其classes 为INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH 和INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH_MT。注释1处将打开的设备添加进epoll中监听。注释2处将创建的Device对象添加到mDevices集合中并设置mOpeningDevices
registerDeviceForEpollLocked最终调用:
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\EventHub.cpp
status_t EventHub::registerFdForEpoll(int fd) {
// TODO(b/121395353) - consider adding EPOLLRDHUP
struct epoll_event eventItem = {};
eventItem.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLWAKEUP;
eventItem.data.fd = fd;
if (epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, &eventItem)) {
ALOGE("Could not add fd to epoll instance: %s", strerror(errno));
return -errno;
}
return OK;
}
addDeviceLocked:
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\EventHub.cpp
void EventHub::addDeviceLocked(Device* device) {
mDevices.add(device->id, device);
device->next = mOpeningDevices;
mOpeningDevices = device;
}
scanDevicesLocked就是扫描dev/input/这个目录并打开里面的设备节点,添加到epoll中监测(后续某个设备有输入数据时,epoll_wait会返回)。对于每个设备节点都会新建device,设置其classes,然后添加到mDevices集合中。
前面提到过,scanDevicesLocked执行完成后,就是构建event,然后getEvents方法返回,回到InputReader的loopOnce方法,继续执行processEventsLocked处理这些event
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\InputReader.cpp
void InputReader::processEventsLocked(const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {
for (const RawEvent* rawEvent = rawEvents; count;) {
int32_t type = rawEvent->type;
size_t batchSize = 1;
if (type < EventHubInterface::FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT) {//type 为DEVICE_ADDED或者FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN,不走这个分支
//省略
} else {
switch (rawEvent->type) {
case EventHubInterface::DEVICE_ADDED:
addDeviceLocked(rawEvent->when, rawEvent->deviceId);//1
break;
case EventHubInterface::DEVICE_REMOVED:
removeDeviceLocked(rawEvent->when, rawEvent->deviceId);
break;
case EventHubInterface::FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN:
handleConfigurationChangedLocked(rawEvent->when);
break;
default:
ALOG_ASSERT(false); // can't happen
break;
}
}
count -= batchSize;
rawEvent += batchSize;
}
}
对于type为DEVICE_ADDED的event,调用addDeviceLocked处理
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\InputReader.cpp
void InputReader::addDeviceLocked(nsecs_t when, int32_t eventHubId) {
if (mDevices.find(eventHubId) != mDevices.end()) {
ALOGW("Ignoring spurious device added event for eventHubId %d.", eventHubId);
return;
}
InputDeviceIdentifier identifier = mEventHub->getDeviceIdentifier(eventHubId);
std::shared_ptr<InputDevice> device = createDeviceLocked(eventHubId, identifier);
//省略
}
继续调用createDeviceLocked创建InputDevice对象
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\InputReader.cpp
std::shared_ptr<InputDevice> InputReader::createDeviceLocked(
int32_t eventHubId, const InputDeviceIdentifier& identifier) {
auto deviceIt = std::find_if(mDevices.begin(), mDevices.end(), [identifier](auto& devicePair) {
return devicePair.second->getDescriptor().size() && identifier.descriptor.size() &&
devicePair.second->getDescriptor() == identifier.descriptor;
});
std::shared_ptr<InputDevice> device;
if (deviceIt != mDevices.end()) {
device = deviceIt->second;
} else {
int32_t deviceId = (eventHubId < END_RESERVED_ID) ? eventHubId : nextInputDeviceIdLocked();
device = std::make_shared<InputDevice>(&mContext, deviceId, bumpGenerationLocked(),
identifier);//1
}
device->addEventHubDevice(eventHubId);//2
return device;
}
注释1处创建InputDevice,注释2处调用其addEventHubDevice方法
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\InputDevice.cpp
void InputDevice::addEventHubDevice(int32_t eventHubId, bool populateMappers) {
//省略
// Touchscreens and touchpad devices.
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH_MT) {
mappers.push_back(std::make_unique<MultiTouchInputMapper>(*contextPtr));//1
} else if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH) {
mappers.push_back(std::make_unique<SingleTouchInputMapper>(*contextPtr));
}
//省略
// insert the context into the devices set
mDevices.insert({eventHubId, std::make_pair(std::move(contextPtr), std::move(mappers))});//2
}
注释1处,对于多指触摸,设置其mapper为MultiTouchInputMapper,注释2处添加到mDevices集合中。
对于开机已存在的输入设备已经处理完了。主要是扫描并打开这些设备,添加到epoll中,监听这些设备有无事件发生,然后创建InputDevice,根据不同的设备设置其mapper。
处理新增或者移除的输入设备
在平时没有事件时,在EventHub方法中
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\EventHub.cpp
size_t EventHub::getEvents(int timeoutMillis, RawEvent* buffer, size_t bufferSize) {
if (event != buffer || awoken) {//没有事件这个不会返回,函数继续往下执行
break;
}
int pollResult = epoll_wait(mEpollFd, mPendingEventItems, EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS, timeoutMillis);
//省略
}
通过epoll_wait等待事件,而在Android11 InputManagerService启动流程分析 一文中提到,EventHub在初始化的时候,初始化inotify来监听dev/input目录,并使用epoll监听这个inotify。
假设现在有设备新增,则这个epoll_wait会返回,getEvents继续往下执行
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\EventHub.cpp
size_t EventHub::getEvents(int timeoutMillis, RawEvent* buffer, size_t bufferSize) {
int pollResult = epoll_wait(mEpollFd, mPendingEventItems, EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS, timeoutMillis);
if (pollResult < 0) {
} else {
// Some events occurred.
mPendingEventCount = size_t(pollResult);
}
}
设置了mPendingEventCount ,继续执行下一次循环
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\EventHub.cpp
size_t EventHub::getEvents(int timeoutMillis, RawEvent* buffer, size_t bufferSize) {
//省略
while (mPendingEventIndex < mPendingEventCount) {//这时候,这个条件满足
const struct epoll_event& eventItem = mPendingEventItems[mPendingEventIndex++];
if (eventItem.data.fd == mINotifyFd) {//有设备增加或删除
if (eventItem.events & EPOLLIN) {
mPendingINotify = true;//设置mPendingINotify 为ture
} else {
ALOGW("Received unexpected epoll event 0x%08x for INotify.", eventItem.events);
}
continue;//跳出循环
}
//省略
}
// readNotify() will modify the list of devices so this must be done after
// processing all other events to ensure that we read all remaining events
// before closing the devices.
if (mPendingINotify && mPendingEventIndex >= mPendingEventCount) {//满足条件
mPendingINotify = false;
readNotifyLocked();//1
deviceChanged = true;
}
}
有设备增加或删除时,调用注释1处的readNotifyLocked处理
status_t EventHub::readNotifyLocked() {
int res;
char event_buf[512];
int event_size;
int event_pos = 0;
struct inotify_event* event;
ALOGV("EventHub::readNotify nfd: %d\n", mINotifyFd);
res = read(mINotifyFd, event_buf, sizeof(event_buf));//读取数据
while (res >= (int)sizeof(*event)) {
event = (struct inotify_event*)(event_buf + event_pos);
if (event->len) {
if (event->wd == mInputWd) {
std::string filename = StringPrintf("%s/%s", DEVICE_PATH, event->name);
if (event->mask & IN_CREATE) {
openDeviceLocked(filename.c_str());//1
} else {
ALOGI("Removing device '%s' due to inotify event\n", filename.c_str());
closeDeviceByPathLocked(filename.c_str());
}
} else if (event->wd == mVideoWd) {
//省略
} else {
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("Unexpected inotify event, wd = %i", event->wd);
}
}
event_size = sizeof(*event) + event->len;
res -= event_size;
event_pos += event_size;
}
return 0;
}
注释1处也是调用openDeviceLocked来处理,openDeviceLocked前面分析过。
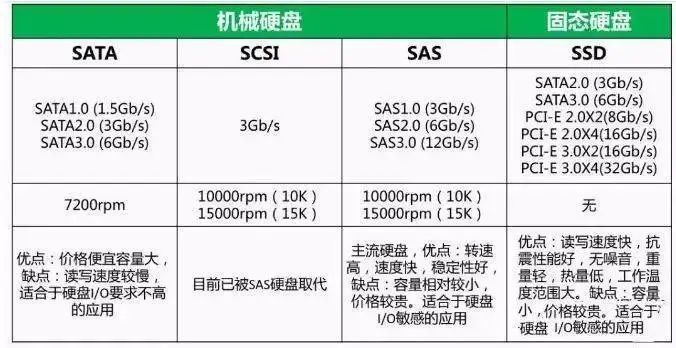
关于设备的处理,可以用一张图来总结

对输入设备产生的输入数据进行处理
和监听输入设备的添加一样,当有输入数据来的时候,getEvents方法中,epoll_wait会返回,设置mPendingEventCount的值,然后进入getEvents下次循环
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\EventHub.cpp
size_t EventHub::getEvents(int timeoutMillis, RawEvent* buffer, size_t bufferSize) {
//省略
for (;;) {
//省略
while (mPendingEventIndex < mPendingEventCount) {//前面设置了mPendingEventCount,满足条件
const struct epoll_event& eventItem = mPendingEventItems[mPendingEventIndex++];
//省略
Device* device = getDeviceByFdLocked(eventItem.data.fd);//根据产生事件设备的fd,找到device
//省略
// This must be an input event
if (eventItem.events & EPOLLIN) {
int32_t readSize = read(device->fd, readBuffer, sizeof(struct input_event) * capacity);//读取数据
//省略
int32_t deviceId = device->id == mBuiltInKeyboardId ? 0 : device->id;
size_t count = size_t(readSize) / sizeof(struct input_event);
for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) {
struct input_event& iev = readBuffer[i];
event->when = processEventTimestamp(iev);
event->deviceId = deviceId;
event->type = iev.type;
event->code = iev.code;
event->value = iev.value;
event += 1;
capacity -= 1;
}
if (capacity == 0) {
// The result buffer is full. Reset the pending event index
// so we will try to read the device again on the next iteration.
mPendingEventIndex -= 1;
break;
//省略
}
// Return now if we have collected any events or if we were explicitly awoken.
if (event != buffer || awoken) {//跳出循环
break;
}
}
}
对于设备产生的输入数据,也是构造RawEvent,只不过这些event的type为驱动上报的type,如:ABS_MT_POSITION_X 。
同样,跳出getEvents循环后,调用processEventsLocked来处理这些RawEvent
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\InputReader.cpp
void InputReader::processEventsLocked(const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {
for (const RawEvent* rawEvent = rawEvents; count;) {
int32_t type = rawEvent->type;
size_t batchSize = 1;
if (type < EventHubInterface::FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT) {//输入事件的type肯定远小于0x10000000,满足条件
int32_t deviceId = rawEvent->deviceId;
while (batchSize < count) {
if (rawEvent[batchSize].type >= EventHubInterface::FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT ||
rawEvent[batchSize].deviceId != deviceId) {
break;
}
batchSize += 1;
}
processEventsForDeviceLocked(deviceId, rawEvent, batchSize);//1
//省略
对于输入事件,继续调用注释1处的processEventsForDeviceLocked处理
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\InputReader.cpp
void InputReader::processEventsForDeviceLocked(int32_t eventHubId, const RawEvent* rawEvents,
size_t count) {
auto deviceIt = mDevices.find(eventHubId);//取出InputDevice
std::shared_ptr<InputDevice>& device = deviceIt->second;
if (device->isIgnored()) {//如果这个设备没有设置过mappers数组的话,就忽略这个设备
// ALOGD("Discarding event for ignored deviceId %d.", deviceId);
return;
}
device->process(rawEvents, count);//1
}
找到InputDevice之后,继续调用其process进行处理
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\InputDevice.cpp
void InputDevice::process(const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {
for (const RawEvent* rawEvent = rawEvents; count != 0; rawEvent++) {
if (mDropUntilNextSync) {
//省略
} else {
//省略
}
} else if (rawEvent->type == EV_SYN && rawEvent->code == SYN_DROPPED) {
//省略
} else {
for_each_mapper_in_subdevice(rawEvent->deviceId, [rawEvent](InputMapper& mapper) {
mapper.process(rawEvent);
});
}
--count;
}
}
找出InputDevice对应的mapper(之前在处理输入设备的时候,设置过mappers集合),调用这些mapper的process方法。对于多指触摸屏,mapper为MultiTouchInputMapper
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\mapper\MultiTouchInputMapper.cpp
void MultiTouchInputMapper::process(const RawEvent* rawEvent) {
TouchInputMapper::process(rawEvent);//1,处理type为EV_SYN,code为SYN_REPORT的事件
mMultiTouchMotionAccumulator.process(rawEvent);
}
EV_SYN同步事件是在一个event结束时驱动上报的。比如下面的触摸协议:
EV_ABS ABS_MT_SLOT 00000000
EV_ABS ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID 00000016
EV_KEY BTN_TOUCH DOWN
EV_KEY BTN_TOOL_FINGER DOWN
EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_X 0000011a
EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_Y 00000475
EV_ABS ABS_MT_TOUCH_MAJOR 00000003
EV_SYN SYN_REPORT 00000000
对于其它类型的数据,调用mMultiTouchMotionAccumulator的process处理,先来看一下这个方法
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\mapper\MultiTouchInputMapper.cpp
void MultiTouchMotionAccumulator::process(const RawEvent* rawEvent) {
if (rawEvent->type == EV_ABS) {//处理type为EV_ABS的数据
bool newSlot = false;
if (mUsingSlotsProtocol) {//这个值一般为true
if (rawEvent->code == ABS_MT_SLOT) {
mCurrentSlot = rawEvent->value;
newSlot = true;
}
} else if (mCurrentSlot < 0) {
mCurrentSlot = 0;
}
if (mCurrentSlot < 0 || size_t(mCurrentSlot) >= mSlotCount) {
//省略
} else {
Slot* slot = &mSlots[mCurrentSlot];
switch (rawEvent->code) {
case ABS_MT_POSITION_X:
slot->mInUse = true;
slot->mAbsMTPositionX = rawEvent->value;
break;
case ABS_MT_POSITION_Y:
slot->mInUse = true;
slot->mAbsMTPositionY = rawEvent->value;
break;
case ABS_MT_TOUCH_MAJOR:
slot->mInUse = true;
slot->mAbsMTTouchMajor = rawEvent->value;
break;
case ABS_MT_TOUCH_MINOR:
slot->mInUse = true;
slot->mAbsMTTouchMinor = rawEvent->value;
slot->mHaveAbsMTTouchMinor = true;
break;
case ABS_MT_WIDTH_MAJOR:
slot->mInUse = true;
slot->mAbsMTWidthMajor = rawEvent->value;
break;
case ABS_MT_WIDTH_MINOR:
slot->mInUse = true;
slot->mAbsMTWidthMinor = rawEvent->value;
slot->mHaveAbsMTWidthMinor = true;
break;
case ABS_MT_ORIENTATION:
slot->mInUse = true;
slot->mAbsMTOrientation = rawEvent->value;
break;
case ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID:
if (mUsingSlotsProtocol && rawEvent->value < 0) {
// The slot is no longer in use but it retains its previous contents,
// which may be reused for subsequent touches.
slot->mInUse = false;
} else {
slot->mInUse = true;
slot->mAbsMTTrackingId = rawEvent->value;
}
break;
case ABS_MT_PRESSURE:
slot->mInUse = true;
slot->mAbsMTPressure = rawEvent->value;
break;
case ABS_MT_DISTANCE:
slot->mInUse = true;
slot->mAbsMTDistance = rawEvent->value;
break;
case ABS_MT_TOOL_TYPE:
slot->mInUse = true;
slot->mAbsMTToolType = rawEvent->value;
slot->mHaveAbsMTToolType = true;
break;
}
}
} else if (rawEvent->type == EV_SYN && rawEvent->code == SYN_MT_REPORT) {//code一般为
// MultiTouch Sync: The driver has returned all data for *one* of the pointers.
mCurrentSlot += 1;
}
}
可以看出该方法,就是处理type为EV_ABS的数据,填充slot。对于code为ABS_MT_SLOT,则认为是一个新手指,新建slot。经过这个方法的处理,数据都放入mSlots里面了。
最后上报的是EV_SYN同步事件,回到MultiTouchInputMapper的process方法,对于同步事件,调用TouchInputMapper的process处理
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\mapper\TouchInputMapper.cpp
void TouchInputMapper::process(const RawEvent* rawEvent) {
//省略
if (rawEvent->type == EV_SYN && rawEvent->code == SYN_REPORT) {
sync(rawEvent->when);
}
}
继续调用sync处理
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\mapper\TouchInputMapper.cpp
void TouchInputMapper::sync(nsecs_t when) {
const RawState* last =
mRawStatesPending.empty() ? &mCurrentRawState : &mRawStatesPending.back();
// Push a new state.
mRawStatesPending.emplace_back();//往mRawStatesPending的尾部插入一个空的RawState
RawState* next = &mRawStatesPending.back();//将next指向mRawStatesPending的最后一个
next->clear();
next->when = when;
//省略
// Sync touch
syncTouch(when, next);//1
// Assign pointer ids.
if (!mHavePointerIds) {
assignPointerIds(last, next);
}
processRawTouches(false /*timeout*/);//2
}
注释1处填充next(next为RawState对象),即填充mRawStatesPending,注释2处开始处理数据。先来看一下syncTouch方法
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\mapper\MultiTouchInputMapper.cpp
void MultiTouchInputMapper::syncTouch(nsecs_t when, RawState* outState) {
size_t inCount = mMultiTouchMotionAccumulator.getSlotCount();
size_t outCount = 0;
BitSet32 newPointerIdBits;
mHavePointerIds = true;
for (size_t inIndex = 0; inIndex < inCount; inIndex++) {
const MultiTouchMotionAccumulator::Slot* inSlot =
mMultiTouchMotionAccumulator.getSlot(inIndex);//遍历取出Slot
if (!inSlot->isInUse()) {
continue;
}
//省略
/*根据slot的数据,开始填充RawState*/
RawPointerData::Pointer& outPointer = outState->rawPointerData.pointers[outCount];
outPointer.x = inSlot->getX();
outPointer.y = inSlot->getY();
outPointer.pressure = inSlot->getPressure();
outPointer.touchMajor = inSlot->getTouchMajor();
outPointer.touchMinor = inSlot->getTouchMinor();
outPointer.toolMajor = inSlot->getToolMajor();
outPointer.toolMinor = inSlot->getToolMinor();
outPointer.orientation = inSlot->getOrientation();
outPointer.distance = inSlot->getDistance();
outPointer.tiltX = 0;
outPointer.tiltY = 0;
outPointer.toolType = inSlot->getToolType();
//省略
/*开始处理id和index*/
// Assign pointer id using tracking id if available.
if (mHavePointerIds) {
int32_t trackingId = inSlot->getTrackingId();
int32_t id = -1;
if (trackingId >= 0) {
for (BitSet32 idBits(mPointerIdBits); !idBits.isEmpty();) {
uint32_t n = idBits.clearFirstMarkedBit();
if (mPointerTrackingIdMap[n] == trackingId) {
id = n;
}
}
if (id < 0 && !mPointerIdBits.isFull()) {
id = mPointerIdBits.markFirstUnmarkedBit();
mPointerTrackingIdMap[id] = trackingId;
}
}
if (id < 0) {
mHavePointerIds = false;
outState->rawPointerData.clearIdBits();
newPointerIdBits.clear();
} else {
outPointer.id = id;
outState->rawPointerData.idToIndex[id] = outCount;
outState->rawPointerData.markIdBit(id, isHovering);
newPointerIdBits.markBit(id);
}
}
outCount += 1;
}
outState->rawPointerData.pointerCount = outCount;
mPointerIdBits = newPointerIdBits;
mMultiTouchMotionAccumulator.finishSync();
}
在syncTouch方法中,除了填充RawState,还有对id和index的处理,可以看出id和index不一定相等。在多指的开发中注意,只有id才能代表一个手指,需要根据id,从idToIndex中得到index,从而找到对应的触摸信息。
继续回到sync方法,syncTouch处理完成后,调用processRawTouches继续处理数据
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\mapper\TouchInputMapper.cpp
void TouchInputMapper::processRawTouches(bool timeout) {
//省略
const size_t N = mRawStatesPending.size();//前面已经填充过mRawStatesPending了,这里取出来
size_t count;
for (count = 0; count < N; count++) {
const RawState& next = mRawStatesPending[count];//遍历取出RawState
//省略
mCurrentRawState.copyFrom(next);//将数据拷贝到mCurrentRawState中
if (mCurrentRawState.when < mLastRawState.when) {
mCurrentRawState.when = mLastRawState.when;
}
cookAndDispatch(mCurrentRawState.when);//1
}
if (count != 0) {
mRawStatesPending.erase(mRawStatesPending.begin(), mRawStatesPending.begin() + count);//处理完之后要擦除
}
//省略
}
注释1处调用cookAndDispatch方法来处理以及分发数据
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\mapper\TouchInputMapper.cpp
void TouchInputMapper::cookAndDispatch(nsecs_t when) {
mCurrentCookedState.clear();
//省略
cookPointerData();//1
if (mDeviceMode == DEVICE_MODE_POINTER) {
//省略
}else{
if (!mCurrentMotionAborted) {
dispatchButtonRelease(when, policyFlags);
dispatchHoverExit(when, policyFlags);
dispatchTouches(when, policyFlags);//2
dispatchHoverEnterAndMove(when, policyFlags);
dispatchButtonPress(when, policyFlags);
}
}
//省略
// Copy current touch to last touch in preparation for the next cycle.
mLastRawState.copyFrom(mCurrentRawState);//将这次的数据拷贝到mLastRawState
mLastCookedState.copyFrom(mCurrentCookedState);//拷贝数据
}
注释1处cookPointerData方法比较长,主要是对数据进行加工,加工后的数据放入mCurrentCookedState中。为什么要进行加工呢?因为当前的数据,比如X,Y坐标还是针对触摸屏的,我们要加工成显示屏上对应的坐标
注释2处开始分发数据了,主要是根据不同的情况调用dispatchMotion,分发AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_MOVE,AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_UP和 AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_DOWN 的 action
接着直接来看下dispatchMotion
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\reader\mapper\TouchInputMapper.cpp
void TouchInputMapper::dispatchMotion(nsecs_t when, uint32_t policyFlags, uint32_t source,
int32_t action, int32_t actionButton, int32_t flags,
int32_t metaState, int32_t buttonState, int32_t edgeFlags,
const PointerProperties* properties,
const PointerCoords* coords, const uint32_t* idToIndex,
BitSet32 idBits, int32_t changedId, float xPrecision,
float yPrecision, nsecs_t downTime) {
PointerCoords pointerCoords[MAX_POINTERS];
PointerProperties pointerProperties[MAX_POINTERS];
uint32_t pointerCount = 0;
while (!idBits.isEmpty()) {
uint32_t id = idBits.clearFirstMarkedBit();
uint32_t index = idToIndex[id];
pointerProperties[pointerCount].copyFrom(properties[index]);
pointerCoords[pointerCount].copyFrom(coords[index]);//拷贝,coords包含了坐标信息等数据
if (changedId >= 0 && id == uint32_t(changedId)) {
action |= pointerCount << AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_INDEX_SHIFT;
}
pointerCount += 1;
}
ALOG_ASSERT(pointerCount != 0);
if (changedId >= 0 && pointerCount == 1) {
/*可以看出,如果是第一根手指,这里做了处理,变成AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN和AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_UP*/
if (action == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_DOWN) {
action = AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN;
} else if (action == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_UP) {
action = AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_UP;
} else {
// Can't happen.
ALOG_ASSERT(false);
}
}
//省略
NotifyMotionArgs args(getContext()->getNextId(), when, deviceId, source, displayId, policyFlags,
action, actionButton, flags, metaState, buttonState,
MotionClassification::NONE, edgeFlags, pointerCount, pointerProperties,
pointerCoords, xPrecision, yPrecision, xCursorPosition, yCursorPosition,
downTime, std::move(frames));//1
getListener()->notifyMotion(&args);//2
}
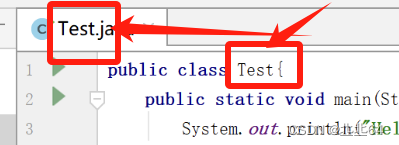
注释1处又将数据构造成了一个NotifyMotionArgs 对象。注释2处这个getListener()返回的是什么呢?返回的是一个QueuedInputListener对象。具体参考这张简易的类图

调用QueuedInputListener的notifyMotion方法
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\InputListener.cpp
void QueuedInputListener::notifyMotion(const NotifyMotionArgs* args) {
traceEvent(__func__, args->id);
mArgsQueue.push_back(new NotifyMotionArgs(*args));
}
这里只是将数据放入了队列。在InputReader线程中,最后会调用flush方法,来处理这个队列
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\InputListener.cpp
void QueuedInputListener::flush() {
size_t count = mArgsQueue.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) {
NotifyArgs* args = mArgsQueue[i];
args->notify(mInnerListener);//1
delete args;
}
mArgsQueue.clear();
}
遍历队列,注释1处调用NotifyMotionArgs的notify方法,注意传入的参数为mInnerListener,mInnerListener指向的是一个InputClassifier对象(看上图)
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\InputListener.cpp
void NotifyMotionArgs::notify(const sp<InputListenerInterface>& listener) const {
listener->notifyMotion(this);
}
直接调用InputClassifier的notifyMotion方法
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\InputClassifier.cpp
void InputClassifier::notifyMotion(const NotifyMotionArgs* args) {
std::scoped_lock lock(mLock);
//省略
NotifyMotionArgs newArgs(*args);
newArgs.classification = mMotionClassifier->classify(newArgs);
mListener->notifyMotion(&newArgs);//mListener是InputDispatcher
}
调用InputDispatcher的notifyMotion方法
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\dispatcher\InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::notifyMotion(const NotifyMotionArgs* args) {
//省略
mPolicy->interceptMotionBeforeQueueing(args->displayId, args->eventTime, /*byref*/ policyFlags);//1
bool needWake;
{ // acquire lock
mLock.lock();
if (shouldSendMotionToInputFilterLocked(args)) {//可以设置拦截器直接处理
//省略
}
// Just enqueue a new motion event.
MotionEntry* newEntry =
new MotionEntry(args->id, args->eventTime, args->deviceId, args->source,
args->displayId, policyFlags, args->action, args->actionButton,
args->flags, args->metaState, args->buttonState,
args->classification, args->edgeFlags, args->xPrecision,
args->yPrecision, args->xCursorPosition, args->yCursorPosition,
args->downTime, args->pointerCount, args->pointerProperties,
args->pointerCoords, 0, 0);//2
needWake = enqueueInboundEventLocked(newEntry);//3
mLock.unlock();
} // release lock
if (needWake) {
mLooper->wake();//4
}
}
注释1处通过JNI调用到Java层的interceptMotionBeforeQueueingNonInteractive方法,注释2处又将数据封装成了MotionEntry对象,注释3处入“iq”队列,注释4处虽然这个是在InputDispatcher中,但实际上还是在InputReader线程中调用的,所以需要唤醒InputDispatcher线程。
//frameworks\native\services\inputflinger\dispatcher\InputDispatcher.cpp
bool InputDispatcher::enqueueInboundEventLocked(EventEntry* entry) {
bool needWake = mInboundQueue.empty();
mInboundQueue.push_back(entry);//放入iq队列
traceInboundQueueLengthLocked();//这就是为什么可以在trace中看到iq的原因
//省略
return needWake;
}
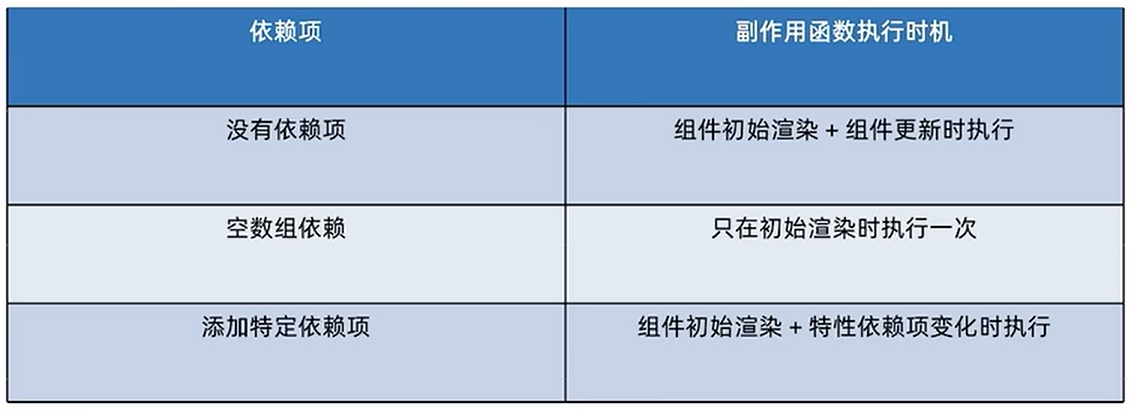
到这里,InputReader的工作就完成了,接下来就是InputDispatcher线程的处理了。对于多指触摸,总结下InputReader处理数据的流程