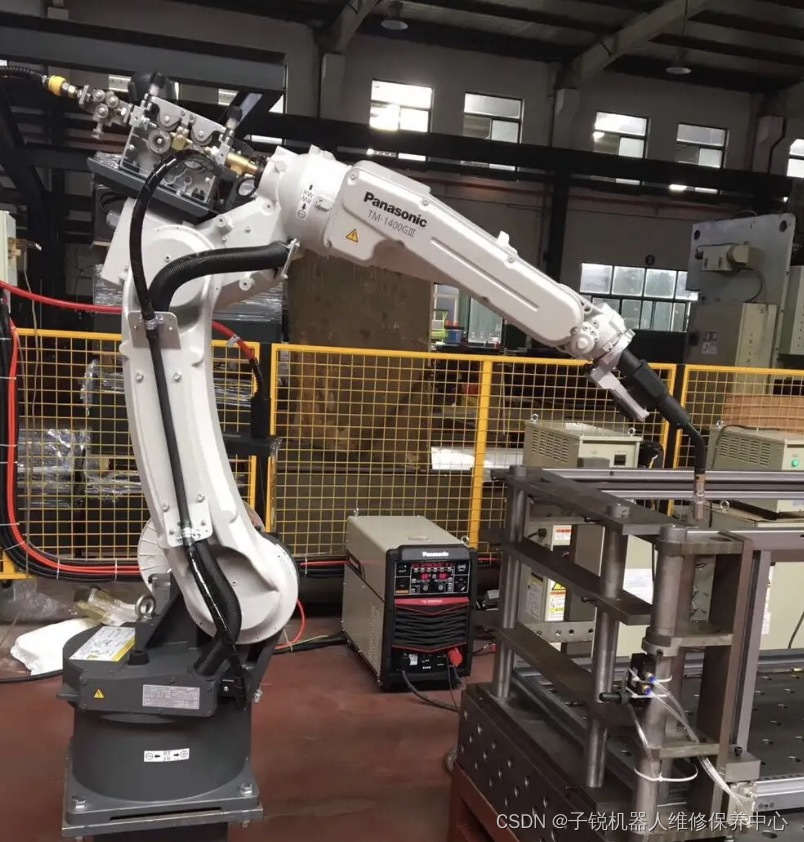
A–D部分见:霍金《时间简史 A Brief History of Time》书后索引(A–D)

图源:Wikipedia
INDEX
E
Earth: circumference, motion, shape
Eclipses
Eddington, Arthur
Einstein, Albert: biography, see also Relativity; Special relativity; Energy equation
Einstein-Rosen bridge
Elasticity
Electric charge
Electrical force
Electromagnetic field
Electromagnetic force
Electromagnetic waves
Electron
Electroweak unification theory
Elementary particles
Elements
Energy: black holes, conservation of, particles, see also Grand unification energy
Energy equation
Entropy
Eternal inflation
Ether
Euclid
European Centre for Nuclear Research (CERN)
Event
Event horizon
Evolution of the universe
Exclusion principle
Expanding universe
Expansion, critical rate of
F
Feynman, Richard
Field see Electromagnetic field; Magnetic field
‘First Cause’
Fitch, Val
Flamsteed, John
Forces
Frequency
Friedmann, Alexander
Friedmann models
G
Galaxies
Galilei, Galileo
Gamma rays
Gamow, George
Gell-Mann, Murray
General relativity
Geodesic
Geometry
GeV
Glashow, Sheldon
Gluon
Gold, Thomas
Godel, Kurt
Grand unification energy
Grand unified theory
Gravitational field
Gravitational force
Gravitational waves
Gravitons
Gravity: definition of, quantum effects, see also Quantum theory of gravity; Supergravity
Green, Mike
GUT see Grand unified theory
Guth, Alan
H
Halley, Edmond
Halliwell, Jonathan
Hartle, Jim
Heat
Heat conduction
Heisenberg, Werner see also Uncertainty principle
Heliocentric cosmology
Helium
Herschel, William
Hertog, Thomas
Heterotic string
Hewish, Antony
Hoyle, Fred
Hubble, Edwin
Hubble Space Telescope
Hulse, Russell
Human memory
Hydrogen
Hydrogen bomb
参考文献 Reference
Stephen Hawking, A Brief History of Time: from the Big Bang to Black Holes, Bantam Books, London, 2016.