接着上文,[muduo网络库]——muduo库三大核心组件之Channel类(剖析muduo网络库核心部分、设计思想),本章我们来学习muduo网络库中第二大核心组件Poller/EpollPoller类。
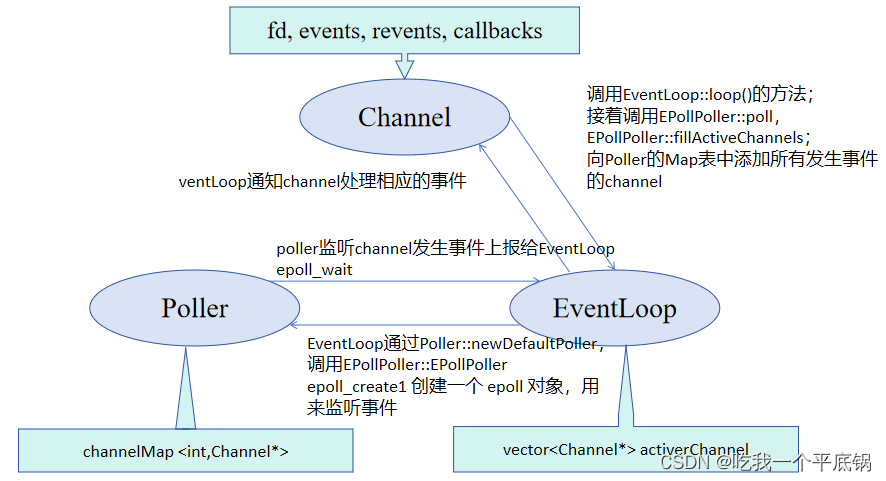
先回顾一下三大核心组件之间的关系。
 接着我们进入正题。
接着我们进入正题。
Poller/EpollPoller
Poller负责监听文件描述符事件是否触发以及返回发生事件的文件描述符以及具体事件。在 muduo 中,使用抽象基类 Poller ,并由EpollPoller和PollPoller派生基类中继承实现 epoll 和 poll ,但是在我自己重构的muduo库中,仅支持epoll,以后会将poll补充进去。
重要成员变量
int epollfd_;
EventList events_;
using ChannelMap = std::unordered_map<int,Channel*>;
ChannelMap channels_;
EventLoop *ownerLoop_;
epollfd_是epollfd_(::epoll_create1(EPOLL_CLOEXEC))返回的epoll句柄。events_为using EventList = std::vector<epoll_event>;中的元素,它为调用epoll_wait返回的事件集合。channels_为std::unordered_map<int, Channel*>类型,它主要负责记录 fd —> Channel的映射,也保管所有注册在这个Poller上的Channel。ownerLoop_:就是所属的EventLoop对象
重要成员函数
首先EPollPoller重写了基类Poller的抽象方法
TimeStamp poll(int timeoutMs, ChannelList* activeChannels) override;
void updateChannel(Channel* channel) override;
void removeChannel(Channel* channel) override;
需要强调的一点: 在EPollPoller重写的抽象方法,首先派生类要继承基类,基类定义为虚函数,且如果派生类在虚函数声明时使用了override描述符,那么该函数必须重载其基类中的同名函数,否则代码将无法通过编译,所以在Poller中,我们可以看出:
virtual TimeStamp poll(int timeoutMs, ChannelList *activeChannel) = 0;
virtual void updateChannel(Channel* channel) = 0;
virtual void removeChannel(Channel* channel) = 0;
其中poll为重中之重
TimeStamp EPollPoller::poll(int timeoutMs, ChannelList* activeChannels)
{
//实际上因为运行起来poll很多,使用LOG_DEBUG更合理,但是学习阶段使用LOG_INFO即可
LOG_INFO("func=%s => fd total count:%lu \n",__FUNCTION__, channels_.size());
int numEvents= ::epoll_wait(epollfd_, &*events_.begin(),static_cast<int>(events_.size()),timeoutMs);
int saveErrno = errno; //记录最开始poll里面的错误值
TimeStamp now(TimeStamp::now());
if(numEvents>0)
{
LOG_INFO("%d eventS happened \n",numEvents);
fillActiveChannels(numEvents,activeChannels);
if(numEvents == events_.size())
{
events_.resize(events_.size() * 2);
//说明当前发生的事件可能多于vector能存放的 ,需要扩容,等待下一轮处理
}
}
else if (numEvents == 0)
{
LOG_DEBUG("%s timeout! \n",__FUNCTION__);
}
else
{
if(saveErrno != EINTR) //不是外部中断引起的
{
errno = saveErrno;
LOG_ERROR("EPollPoller::poll() errno!");
}
}
return now;
}
- 通过epoll_wait将发生事件的channel通过activeChannels告知给EventLoop
TimeStamp EPollPoller::poll(int timeoutMs, ChannelList* activeChannels)
在这个函数中,实际上就是调用了epoll_wait得到了事件发生的集合,然后调用fillActiveChannels
- 将发生的事件装入
activeChannels
void EPollPoller::fillActiveChannels(int numEvents, ChannelList *activeChannels) const
{
for(int i=0; i<numEvents; ++i)
{
Channel *channel = static_cast<Channel*>(events_[i].data.ptr);
channel->set_revents(events_[i].events);
//EventLoop就拿到了他的poller给他返回的所有发生事件的channel列表了
activeChannels->push_back(channel);
}
}
activeChannels 是 ChannelList = std::vector<Channel*>;类型,将监听到该fd发生的事件写进这个Channel中的revents成员变量中。这样获取到了发生事件的集合,然后把这个Channel装进activeChannels中,当外界调用完poll之后就能拿到事件监听器的监听结果,在EventLoop中就可以对它进行处理。
- 更新
channel通道epoll_ctl add/mod/del
void EPollPoller::updateChannel(Channel* channel)
{
const int index = channel->index();
LOG_INFO("func=%s => fd=%d events=%d index=%d\n",__FUNCTION__, channel->fd(),channel->events(), index);
if(index == kNew || index ==kDeleted)//如果是完全没在或者曾经在epoll队列中的,就添加到epoll队列中
{
if(index == kNew)
{
int fd = channel->fd();
channels_[fd] = channel;//将新添加的fd和channel添加到channels_中
}
channel->set_index(kAdded);
update(EPOLL_CTL_ADD,channel);
}
else //channel 已经在poller上注册过了
{
int fd = channel->fd();
if (channel->isNoneEvent()) //没有到关注的事件
{
update(EPOLL_CTL_DEL,channel);
channel->set_index(kDeleted);
}
else
{
update(EPOLL_CTL_MOD,channel);
}
}
}
在这个函数中,通过判断 index 来决定对channel的修改 mod/add/del,index在channel类中,对其初始化为-1,在这里对应:
const int kNew = -1; //表示一个channel还没有被添加进epoll里面 channel中index_初始化为-1
const int kAdded = 1; //表示一个channel已经添加进epoll里面
const int kDeleted = 2; //表示一个channel已经从epoll里面删除
归根到底,在updateChannel进一步调用了update,然后调用了epoll_ctl,实现了更新channel。同时在removeChannel以及updateChannel中也更改channels_删除/添加,也就是改了Map表。
- 删除Channel
void EPollPoller::removeChannel(Channel* channel)
{
int fd = channel->fd();
channels_.erase(fd);
LOG_INFO("func=%s => fd=%d \n",__FUNCTION__, fd);
int index = channel->index();
if (index == kAdded)
{
update(EPOLL_CTL_DEL,channel);
}
channel->set_index(kNew);
}
- 在
Poller还存在一个newDefaultPoller函数
static Poller* newDefaultPoller(EventLoop *loop);
通过单独创建一个 DefaultPoller.cc 的文件去实现。在EventLoop中,会调用poller_(Poller::newDefaultPoller(this)),而此函数源码如下:
Poller* Poller::newDefaultPoller(EventLoop *loop)
{
if(::getenv("MODUO_USE_POLL"))
{
return nullptr; //生成poll的实例
}
else
{
return new EPollPoller(loop); //生成epoll的实例
}
}
可以看出,本质是还是调用了EPollPoller。需要强调的一点: muduo库在这里选择了poll还是epoll,这里因为我没有实现poll,所以只能选择EPollPoller。
好了,梳理到这里,我们可以看出经过Poller/EpollPoller, EventLoop就会获得它的poller给他返回的所有发生事件的channel列表了。
实际上,流程是这样的 channel update remove => EventLoop updateChannel removeChannel =>Poller updateChannel removeChannel 在讲到EventLoop时还会在梳理一下。
思考一下,为什么要单独创建一个DefaultPoller.cc文件呢?
我们来回忆一下,newDefaultPoller函数是在poller.h文件中的,如果我们在poller.cc去实现它,从它的实现上可以看出,我们是需要包含 "EPollPoller.h" PollPoller.h等头文件的,但是Poller是一个基类,我们使用EPollPoller派生类去实现它,又在基类中去包含派生类的头文件,这样的设计是非常不好的,所以我们会采用一个单独的文件去实现newDefaultPoller函数。
代码地址:https://github.com/Cheeron955/mymuduo/tree/master