C++ String 用法详解
C++中的 std::string 是一个非常强大且灵活的类,用于处理字符串。std::string 类是C++标准库中的一部分,它提供了丰富的成员函数来执行各种字符串操作,如连接、比较、查找、替换等。在本篇博客中,我们将深入探索 std::string 的用法,并通过一些示例代码展示如何在实际编程中使用它。
一、string 基本概念
1.本质:
string 是 C++ 风格的字符串,而 string 本质上是一个类
string 和 char* 区别:
- char* 是一个指针
- string 是一个类,类内部封装了char*,管理这个字符串,是一个char*型的容器。
2.特点:
string 类内部封装了很多成员方法 例如:查找 find,拷贝 copy,删除 delete 替换 replace,插入insert string 管理 char*所分配的内存,不用担心复制越界和取值越界等,由类内部进行负责
3.引入头文件
首先,你需要包含 <string> 头文件来使用 std::string。
#include <string>
4.命名空间
为了简化代码,我们通常使用 std 命名空间,这样就可以直接写 string 而不是 std::string。
using namespace std;
二、string 构造函数
1.构造函数原型:
string();创建一个空的字符串例如: string str;string(const char* s);使用字符串s初始化;string(const string& str);使用一个string对象初始化另一个string对象;string(int n, char c);使用n个字符c初始化;
2.示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void test1() {
// 创建空字符串,调用默认构造函数
string s1;
cout << "s1: " << s1 << endl;
const char* cstr = "hello world";
// 用c_string构造字符串
string s2(cstr);
cout << "s2: " << s2 << endl;
// 用字符串构造字符串,调用拷贝构造函数
string s3(s2);
cout << "s3: " << s3 << endl;
// 用指定长度和字符构造字符串
string s4(10, 'x');
cout << "s4: " << s4 << endl;
}
int main() {
test1();
return 0;
}
三、string 赋值操作
1.功能描述:
- 给string字符串进行赋值。
2.赋值的函数原型:
string& operator=(const char* s);char*类型字符串赋值给当前的字符串;string& operator=(const string &s);把字符串s赋给当前的字符串;string& operator=(char c);字符赋值给当前的字符串;string& assign(const char *s);把字符串s赋给当前的字符串;string& assign(const char *s, int n);把字符串s的前n个字符赋给当前的字符串;string& assign(const string &s);把字符串s赋给当前字符串;string& assign(int n, char c);用n个字符c赋给当前字符串;
3.示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void test1() {
string str1;
str1 = "hello world";
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
string str2;
str2 = str1;
cout << "str2 = " << str2 << endl;
string str3;
str3 = 'a';
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
string str4;
str4.assign("hello c++");
cout << "str4 = " << str4 << endl;
string str5;
str5.assign("hello c++",5);
cout << "str5 = " << str5 << endl;
string str6;
str6.assign(str5);
cout << "str6 = " << str6 << endl;
string str7;
str7.assign(5, 'x');
cout << "str7 = " << str7 << endl;
}
int main() {
test1();
return 0;
}
// str1 = hello world
// str2 = hello world
// str3 = a
// str4 = hello c++
// str5 = hello
// str6 = hello
// str7 = xxxxx
四、string 字符串拼接
1.功能描述:
- 在字符串末尾拼接字符串
2.函数原型:
string& operator+=(const char* str);重载+=操作符;string& operator+=(const char c);重载+=操作符;string& operator+=(const string& str);重载+=操作符;string& append(const char *s);把字符串s连接到当前字符串结尾;string& append(const char *s, int n);把字符串s的前n个字符连接到当前字符串结尾;string& append(const string &s);同operator+=(const string& str);string& append(const string &s, int pos, int n);字符串s中从pos开始的n个字符连接到字符串结尾;
3.示例
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
//字符串拼接
void test1()
{
string str1 = "我";
str1 += "爱玩游戏";
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
str1 += ':';
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
string str2 = "LOL DNF";
str1 += str2;
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
string str3 = "I";
str3.append(" love ");
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
str3.append("game abcde", 4);
//str3.append(str2);
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
str3.append(str2, 4, 3); // 从下标4位置开始 ,截取3个字符,拼接到字符串末尾
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
}
int main() {
test1();
return 0;
}
// str1 = 我爱玩游戏
// str1 = 我爱玩游戏:
// str1 = 我爱玩游戏:LOL DNF
// str3 = I love
// str3 = I love game
// str3 = I love gameDNF
五、string 查找和替换
1.功能描述:
- 查找:查找指定字符串是否存在
- 替换:在指定的位置替换字符串
2.函数原型:
int find(const string& str, int pos = 0) const;查找 str 第一次出现位置,从 pos 开始查找,没有找到返回 -1,否则返回出现位置;int find(const char* s, int pos = 0) const;查找 s 第一次出现位置,从 pos 开始查找;int find(const char* s, int pos, int n) const;从 pos 位置查找 s 的前 n 个字符第一次位置;int find(const char c, int pos = 0) const;查找字符 c 第一次出现位置;int rfind(const string& str, int pos = npos) const;查找 str 最后一次位置,从 pos 开始查找;int rfind(const char* s, int pos = npos) const;查找 s 最后一次出现位置,从 pos 开始查找;int rfind(const char* s, int pos, int n) const;从 pos 查找 s 的前 n 个字符最后一次位置;int rfind(const char c, int pos = 0) const;查找字符 c 最后一次出现位置;string& replace(int pos, int n, const string& str);替换从 pos 开始 n 个字符为字符串 str;string& replace(int pos, int n,const char* s);替换从 pos 开始的 n 个字符为字符串 s;
3.示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
inline void print_pos(int pos) {
if (pos == string::npos) {
cout << "未找到" << endl;
} else {
cout << "pos: " << pos << endl;
}
}
void test1() {
// 定义一个字符串str1
string str1 = "abcdefgdefgde";
// 使用find函数查找"de"在str1中第一次出现的位置
int pos = str1.find("de");
print_pos(pos);
// 使用rfind函数查找"de"在str1中最后一次出现的位置
pos = str1.rfind("de");
print_pos(pos);
// 使用find函数从索引6开始查找"de"在str1中第一次出现的位置
pos = str1.find("de", 6);
print_pos(pos);
// 使用rfind函数从索引6开始查找"de"在str1中最后一次出现的位置
pos = str1.rfind("de", 6);
print_pos(pos);
// 使用find函数从索引1开始,查找长度为2的子串"de"在str1中第一次出现的位置
pos = str1.find("de", 1, 2);
print_pos(pos);
// 使用rfind函数从索引10开始,查找长度为2的子串"de"在str1中最后一次出现的位置
pos = str1.rfind("de", 10, 2);
print_pos(pos);
// 定义一个字符ch
const char ch = 'e';
// 使用find函数查找字符ch在str1中第一次出现的位置
pos = str1.find(ch);
print_pos(pos);
// 使用rfind函数查找字符ch在str1中最后一次出现的位置
pos = str1.rfind(ch);
print_pos(pos);
// 使用find函数从索引6开始查找字符ch在str1中第一次出现的位置
pos = str1.find(ch, 6);
print_pos(pos);
// 使用rfind函数从索引6开始查找字符ch在str1中最后一次出现的位置
pos = str1.rfind(ch, 6);
print_pos(pos);
// 定义一个字符串str2
string str2 = "de";
// 使用find函数查找str2在str1中第一次出现的位置
pos = str1.find(str2);
print_pos(pos);
// 使用rfind函数查找str2在str1中最后一次出现的位置
pos = str1.rfind(str2);
print_pos(pos);
// 使用find函数从索引6开始查找str2在str1中第一次出现的位置
pos = str1.find(str2, 6);
print_pos(pos);
// 使用rfind函数从索引6开始查找str2在str1中最后一次出现的位置
pos = str1.rfind(str2, 6);
print_pos(pos);
}
void test2() {
string str1 = "abcdefgdefgde";
// 将str1中从索引1开始的5个字符替换为"123456"
str1.replace(1, 5, "123456");
cout << str1 << endl;
str1 = "abcdefgdefgde";
string str2 = "123";
// 将str1中从索引1开始的3个字符替换为str2
str1.replace(1, 3, str2);
cout << str1 << endl;
str1 = "abcdefgdefgde";
// 将str1中从索引1开始的5个字符替换为"123456",只替换前3个字符
str1.replace(1, 5, "123456", 3);
cout << str1 << endl;
}
int main() {
test1();
test2();
return 0;
}
// pos: 3
// pos: 11
// pos: 7
// pos: 3
// pos: 3
// pos: 7
// pos: 4
// pos: 12
// pos: 8
// pos: 4
// pos: 3
// pos: 11
// pos: 7
// pos: 3
// a123456gdefgde
// a123efgdefgde
// a123gdefgde
4.总结:
- find查找是从左往后,rfind从右往左;
- find找到字符串后返回查找的第一个字符位置,找不到返回-1;
- replace在替换时,要指定从哪个位置起,多少个字符,替换成什么样的字符串;
六、string 字符串比较
1.功能描述:
- 字符串之间的比较
2.比较方式:
- 字符串比较是按字符的ASCII码进行对比
- = 返回 0
-
返回 1
- < 返回 -1
3.函数原型:
int compare(const string &s) const;与字符串s比较int compare(const char *s) const;与字符串s比较
4.示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void test1() {
std::string s1 = "hello";
std::string s2 = "world";
std::string s3 = "hello";
int ret = s1.compare(s2);
int ret2 = s1.compare(s3);
if (ret == 0) {
cout << "s1 and s2 are equal" << endl;
} else if (ret < 0) {
cout << "s1 is less than s2" << endl;
} else {
cout << "s1 is greater than s2" << endl;
}
if (ret2 == 0) {
cout << "s1 and s3 are equal" << endl;
} else if (ret2 < 0) {
cout << "s1 is less than s3" << endl;
} else {
cout << "s1 is greater than s3" << endl;
}
}
int main() {
test1();
return 0;
}
// s1 is less than s2
// s1 and s3 are equal
5.总结:
字符串对比主要是用于比较两个字符串是否相等,判断谁大谁小的意义并不是很大
七、string 字符存取
string 中单个字符存取方式有两种
1.函数原型:
char& operator[](int n);通过[]方式取字符char& at(int n);通过at方法获取字符
2.示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void test1() {
string str = "hello world";
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++) {
cout << str[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++) {
cout << str.at(i) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//字符修改
str[0] = 'x';
cout << str << endl;
str.at(1) = 'x';
cout << str << endl;
}
int main() {
test1();
return 0;
}
// h e l l o w o r l d
// h e l l o w o r l d
// xello world
// xxllo world

3.总结:
string字符串中单个字符存取有两种方式,利用 [ ] 或 at
八、string 插入和删除
1.功能描述:
- 对string字符串进行插入和删除字符操作
2.函数原型:
string& insert(int pos, const char* s);插入字符串string& insert(int pos, const string& str);插入字符串string& insert(int pos, int n, char c);在指定位置插入n个字符cstring& erase(int pos, int n = npos);删除从Pos开始的n个字符
3.示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
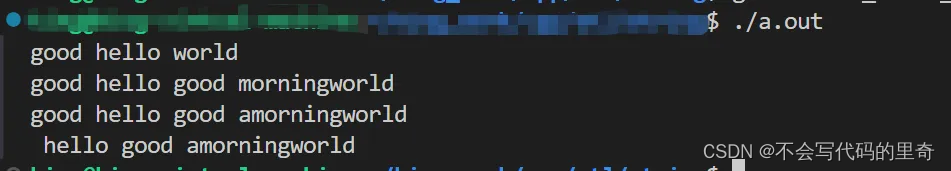
void test() {
string s1 = "hello world";
s1.insert(0, "good ");
cout << s1 << endl;
string s2 = "good morning";
s1.insert(s1.find("world"), s2);
cout << s1 << endl;
char c = 'a';
s1.insert(s1.find("morning"), 1, c);
cout << s1 << endl;
s1.erase(s1.find("good"), 4);
cout << s1 << endl;
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
// good hello world
// good hello good morningworld
// good hello good amorningworld
// hello good amorningworld
4.总结:
插入和删除的起始下标都是从0开始
九、string 子串
1.功能描述:
- 从字符串中获取想要的子串
2.函数原型:
string substr(int pos = 0, int n = npos) const;返回由pos开始的n个字符组成的字符串
3.示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void test1() {
string s = "hello world";
string sub = s.substr(6);
cout << sub << endl;
sub = s.substr(0, 5);
cout << sub << endl;
string email = "hello@sina.com";
int pos = email.find("@");
string username = email.substr(0, pos);
cout << "username: " << username << endl;
}
int main() {
test1();
return 0;
}
// world
// hello
// username: hello
4.总结:
灵活的运用求子串功能,可以在实际开发中获取有效的信息
十、string 求字符串长度 (length 或 size)
1.功能描述:
可以使用 length 或 size 方法来获取字符串的长度。
2.函数原型:
size_type length() const noexcept;返回 string类型的字符串长度,不包括终止符,单位字节size_type size() const noexcept;返回 string类型的字符串长度,不包括终止符,单位字节
3.示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void test1() {
string s = "hello world";
cout << s.length() << endl;
cout << s.size() << endl;
}
int main() {
test1();
return 0;
}
// 11
// 11
十一、字符串到数值的转换
C++标准库提供了多种将字符串转换为数值类型的方法,如std::stoi、std::stof、std::stod等。
1.整数转换
std::string s = "123";
int i = std::stoi(s); // 将字符串s转换为整数i
2.浮点数转换
std::string s = "3.14";
float f = std::stof(s); // 将字符串s转换为浮点数f
3.双精度浮点数转换
std::string s = "2.71828";
double d = std::stod(s); // 将字符串s转换为双精度
4.将其他类型转换为字符串
int num = 123456;
std::string s1 = std::to_string(num); // 将int类型转换为字符串
需要注意的是,如果字符串不能转换为有效的数字,上述函数会抛出异常。
5.转换为C风格的字符串
可以使用 c_str 方法将 std::string 转换为C风格的字符串。
const char* cstr = s1.c_str();
十二、总结
std::string 类提供了丰富的功能和灵活的操作,使得在C++中处理字符串变得简单而高效。通过深入了解和熟练掌握 std::string 的基本用法和高级特性,你可以更加有效地处理字符串相关的任务,编写出更加高效和可维护的代码。随着C++标准的不断演进,我们可以期待 std::string 类会添加更多有用的功能和性能优化。希望这篇博客能帮助你更好地理解和使用 C++ 中的 std::string 类!
参考链接:cppreference string