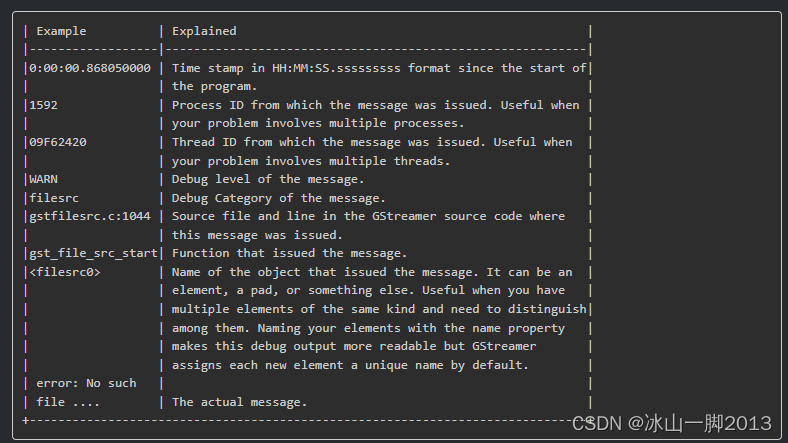
一、旋转矩阵(右手坐标系)
绕x轴旋转
旋转矩阵:右边矩阵是点云的原始坐标,左边的是旋转矩阵
可视化:绕x轴旋转90度
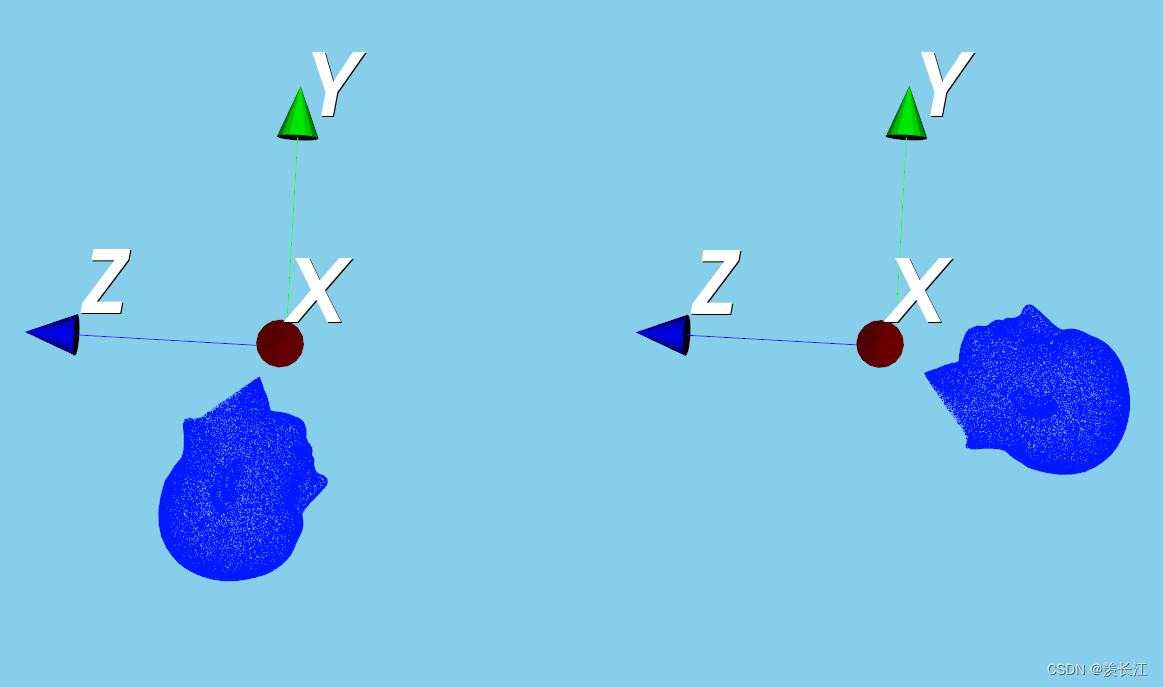
代码:
import vtk
import numpy as np
import math
def pointPolydataCreate(pointCloud):
points = vtk.vtkPoints()
cells = vtk.vtkCellArray()
i = 0
for point in pointCloud:
points.InsertPoint(i, point[0], point[1], point[2])
cells.InsertNextCell(1)
cells.InsertCellPoint(i)
i += 1
PolyData = vtk.vtkPolyData()
PolyData.SetPoints(points)
PolyData.SetVerts(cells)
mapper = vtk.vtkPolyDataMapper()
mapper.SetInputData(PolyData)
actor = vtk.vtkActor()
actor.SetMapper(mapper)
actor.GetProperty().SetColor(0.0, 0.1, 1.0)
return actor
def visiualize(pointCloud, pointCloud2):
colors = vtk.vtkNamedColors()
actor1 = pointPolydataCreate(pointCloud)
actor2 = pointPolydataCreate(pointCloud2)
Axes = vtk.vtkAxesActor()
# 可视化
renderer1 = vtk.vtkRenderer()
renderer1.SetViewport(0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 1)
renderer1.AddActor(actor1)
renderer1.AddActor(Axes)
renderer1.SetBackground(colors.GetColor3d('skyblue'))
renderer2 = vtk.vtkRenderer()
renderer2.SetViewport(0.5, 0.0, 1.0, 1)
renderer2.AddActor(actor2)
renderer2.AddActor(Axes)
renderer2.SetBackground(colors.GetColor3d('skyblue'))
renderWindow = vtk.vtkRenderWindow()
renderWindow.AddRenderer(renderer1)
renderWindow.AddRenderer(renderer2)
renderWindow.SetSize(1040, 880)
renderWindow.Render()
renderWindow.SetWindowName('PointCloud')
renderWindowInteractor = vtk.vtkRenderWindowInteractor()
renderWindowInteractor.SetRenderWindow(renderWindow)
renderWindowInteractor.Initialize()
renderWindowInteractor.Start()
pointCloud = np.loadtxt("C:/Users/A/Desktop/pointCloudData/model.txt") #读取点云数据
angel_x = 90 # 旋转角度
radian = angel_x * np.pi / 180 # 旋转弧度
Rotation_Matrix_1 = [ # 绕x轴三维旋转矩阵
[1, 0, 0],
[0, math.cos(radian), -math.sin(radian)],
[0, math.sin(radian), math.cos(radian)]]
Rotation_Matrix_1 = np.array(Rotation_Matrix_1)
p = np.dot(Rotation_Matrix_1, pointCloud.T) # 计算
p = p.T
visiualize(pointCloud, p)绕y轴旋转
旋转矩阵:
可视化:绕y轴旋转180度
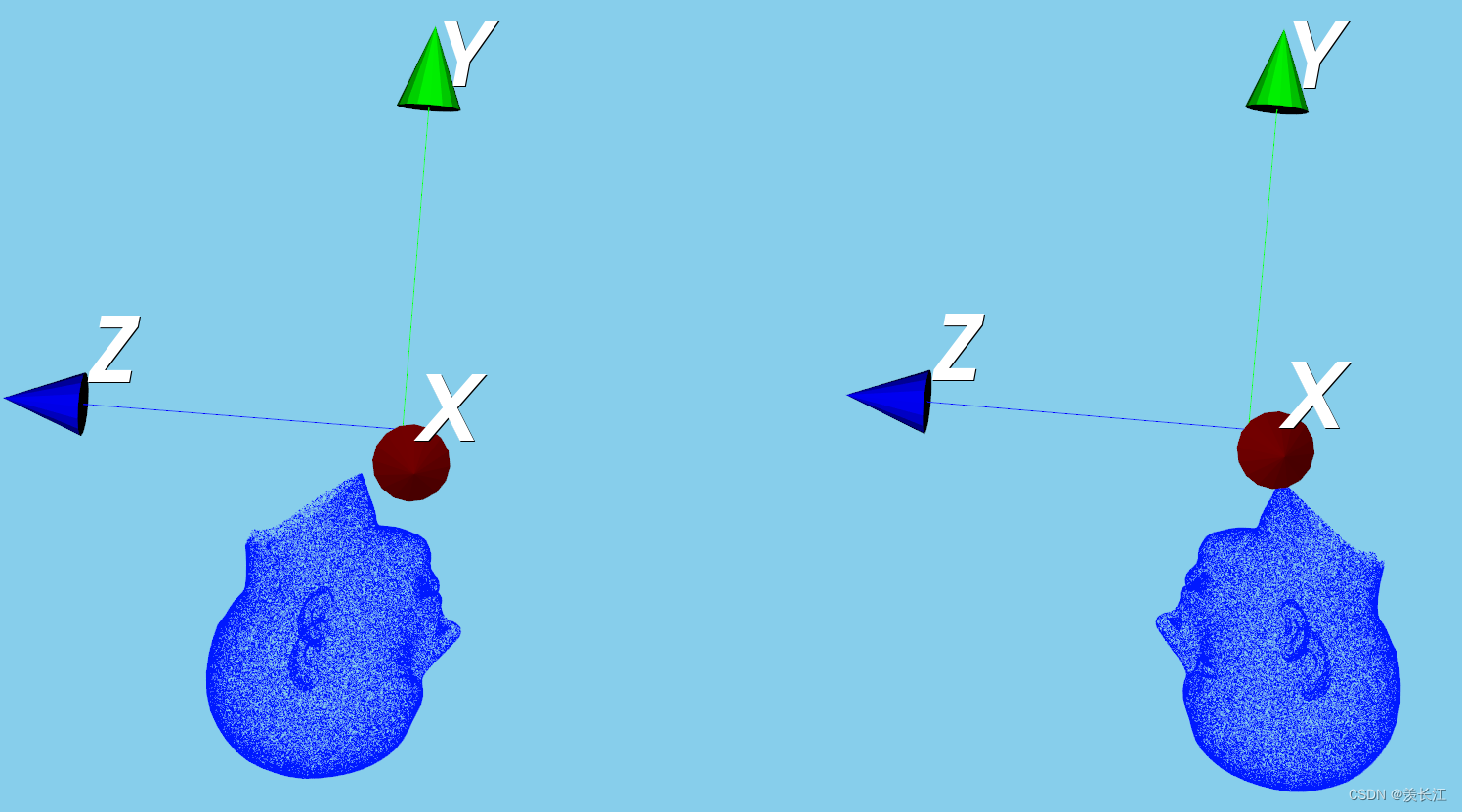
代码:
angel_y = 180 # 旋转角度
radian = angel_y * np.pi / 180 # 旋转弧度
Rotation_Matrix_2 = [ # 绕y轴三维旋转矩阵
[math.cos(radian), 0, math.sin(radian)],
[0, 1, 0],
[-math.sin(radian), 0, math.cos(radian)]]
Rotation_Matrix_1 = np.array(Rotation_Matrix_1)
p = np.dot(Rotation_Matrix_1, pointCloud.T) # 计算
p = p.T
visiualize(pointCloud, p)绕z轴旋转
旋转矩阵:
可视化:绕z轴旋转90度
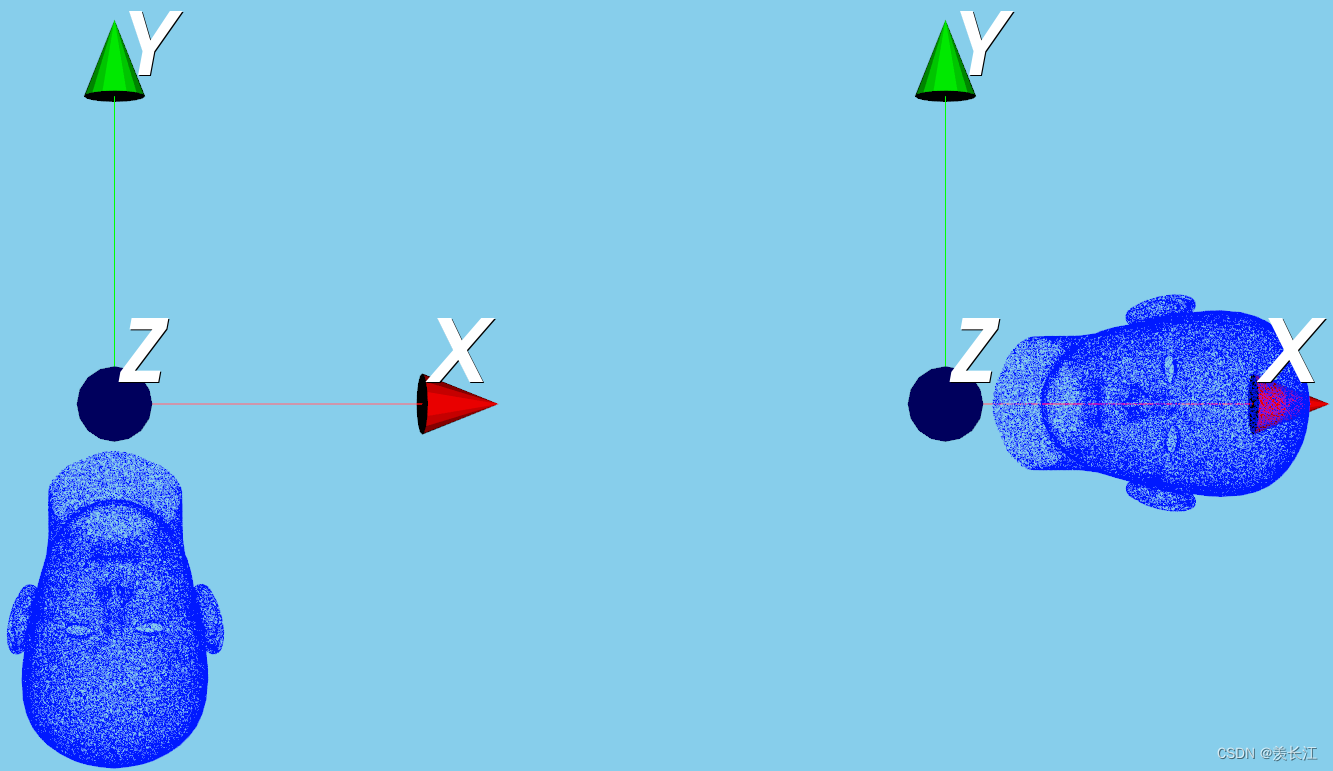
代码:
angel_z = 90 # 旋转角度
radian = angel_z * np.pi / 180 # 旋转弧度
Rotation_Matrix_1 = [ # 绕z轴三维旋转矩阵
[math.cos(radian), -math.sin(radian), 0],
[math.sin(radian), math.cos(radian), 0],
[0, 0, 1]]
Rotation_Matrix_1 = np.array(Rotation_Matrix_1)
p = np.dot(Rotation_Matrix_1, pointCloud.T) # 计算
p = p.T
visiualize(pointCloud, p)线绕z轴旋转,再绕x轴旋转:
旋转矩阵: 线绕哪个轴转,xyz矩阵就和哪和轴的旋转矩阵先计算
可视化:先绕z轴旋转90度,再绕x轴旋转90度
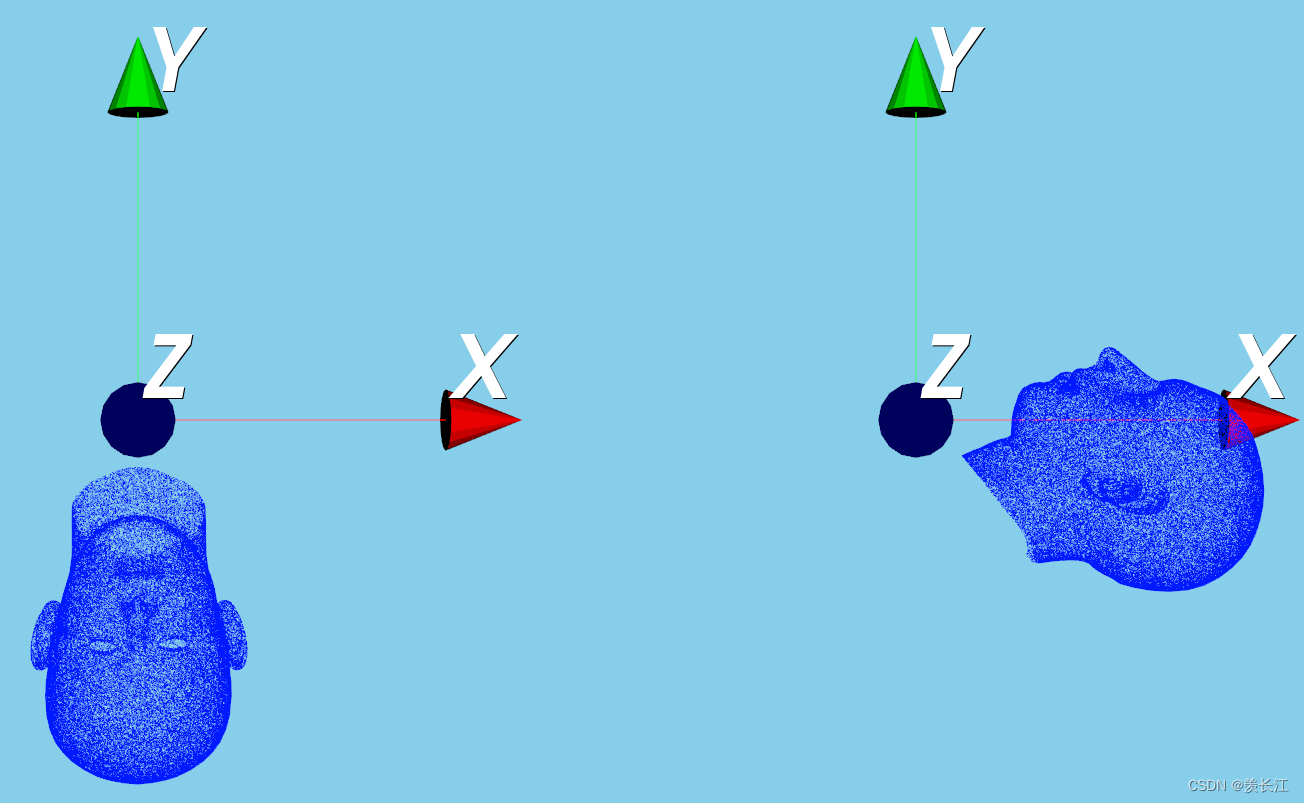
代码:
angel_z = 90 # 旋转角度
radian = angel_z * np.pi / 180 # 旋转弧度
Rotation_Matrix_z = [ # 绕z轴三维旋转矩阵
[math.cos(radian), -math.sin(radian), 0],
[math.sin(radian), math.cos(radian), 0],
[0, 0, 1]]
angel_x = 90 # 旋转角度
radian = angel_x * np.pi / 180 # 旋转弧度
Rotation_Matrix_x = [ # 绕x轴三维旋转矩阵
[1, 0, 0],
[0, math.cos(radian), -math.sin(radian)],
[0, math.sin(radian), math.cos(radian)]]
Rotation_Matrix_z = np.array(Rotation_Matrix_z)
Rotation_Matrix_x = np.array(Rotation_Matrix_x)
p = np.dot(Rotation_Matrix_z, pointCloud.T) # 计算
p = np.dot(Rotation_Matrix_x, p) # 计算
p = p.T
visiualize(pointCloud, p)二、缩放矩阵
缩放矩阵:
计算过程:三个k是xyz对应的缩放系数
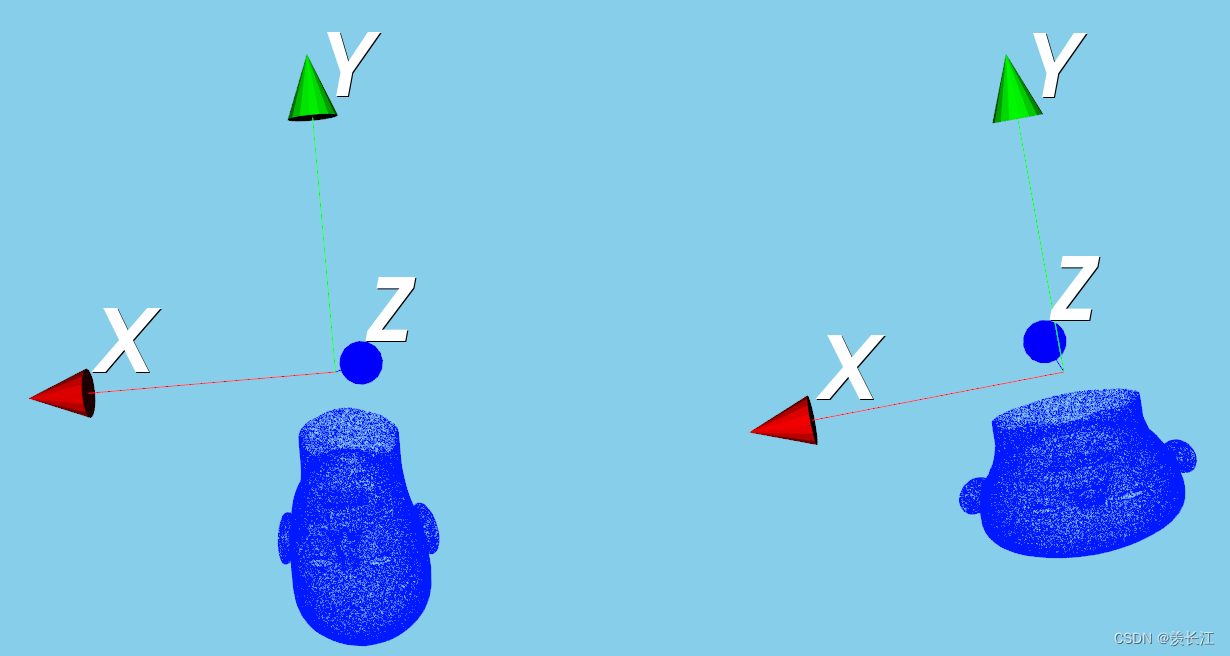
x坐标变为原来的1.5倍,y变为0.7倍,z不变
可视化:
三、镜像矩阵
3D镜像矩阵:
向量n是垂直于镜像平面的单位向量
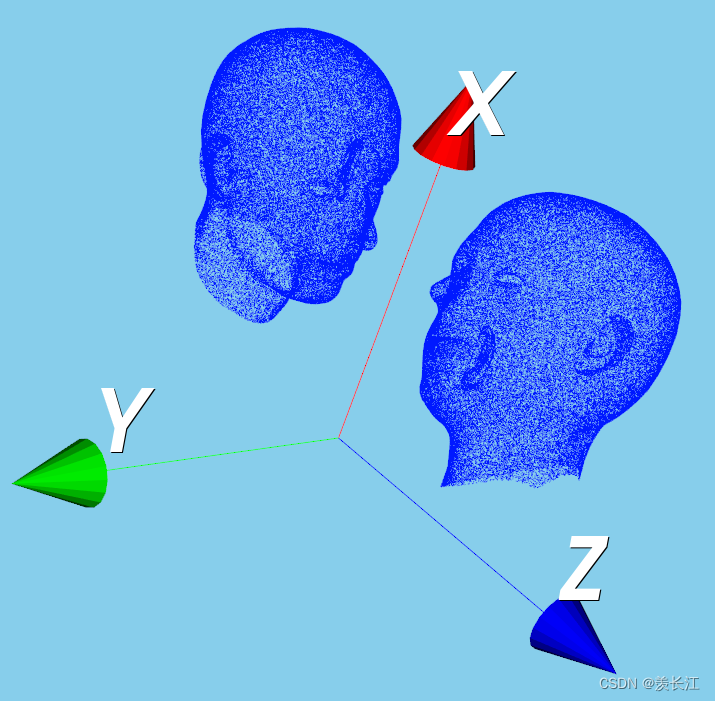
三维点云对xz平面的镜像:
①首先,确定一个垂直于xz平面的单位向量 n=[0, 1, 0]
②将该单位向量带入上述3D镜像矩阵
可视化:
代码:
import vtk
import numpy as np
import math
def pointPolydataCreate(pointCloud):
points = vtk.vtkPoints()
cells = vtk.vtkCellArray()
i = 0
for point in pointCloud:
points.InsertPoint(i, point[0], point[1], point[2])
cells.InsertNextCell(1)
cells.InsertCellPoint(i)
i += 1
PolyData = vtk.vtkPolyData()
PolyData.SetPoints(points)
PolyData.SetVerts(cells)
mapper = vtk.vtkPolyDataMapper()
mapper.SetInputData(PolyData)
actor = vtk.vtkActor()
actor.SetMapper(mapper)
actor.GetProperty().SetColor(0.0, 0.1, 1.0)
return actor
def visiualize(pointCloud, pointCloud2):
colors = vtk.vtkNamedColors()
actor1 = pointPolydataCreate(pointCloud)
actor2 = pointPolydataCreate(pointCloud2)
Axes = vtk.vtkAxesActor()
# 可视化
renderer1 = vtk.vtkRenderer()
renderer1.SetViewport(0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 1)
renderer1.AddActor(actor1)
renderer1.AddActor(Axes)
renderer1.SetBackground(colors.GetColor3d('skyblue'))
renderer2 = vtk.vtkRenderer()
renderer2.SetViewport(0.5, 0.0, 1.0, 1)
renderer2.AddActor(actor1)
renderer2.AddActor(actor2)
renderer2.AddActor(Axes)
renderer2.SetBackground(colors.GetColor3d('skyblue'))
renderWindow = vtk.vtkRenderWindow()
renderWindow.AddRenderer(renderer1)
renderWindow.AddRenderer(renderer2)
renderWindow.SetSize(1040, 880)
renderWindow.Render()
renderWindow.SetWindowName('PointCloud')
renderWindowInteractor = vtk.vtkRenderWindowInteractor()
renderWindowInteractor.SetRenderWindow(renderWindow)
renderWindowInteractor.Initialize()
renderWindowInteractor.Start()
pointCloud = np.loadtxt("C:/Users/A/Desktop/pointCloudData/model.txt") #读取点云数据
nx = 0
ny = 0
nz = 1
n = [nx, ny, nz] # 垂直xy平面的单位向量
# 镜像矩阵
Mirror_Matrix = [
[1-2*nx**2, -2*nx*ny, -2*nx*nz],
[-2*nx*ny, 1-2*ny**2, -2*ny*nz],
[-2*nx*nz, -2*ny*nz, 1-2*nz**2]]
Mirror_Matrix = np.array(Mirror_Matrix)
p = np.dot(Mirror_Matrix, pointCloud.T) # 计算
p = p.T
visiualize(pointCloud, p)四、错切矩阵
沿xy平面错切(z不变)
矩阵 计算过程
沿xz平面错切(y不变)
矩阵 计算过程
沿yz平面错切(x不变)
矩阵 计算过程
可视化:沿yz平面错切

代码:
pointCloud = np.loadtxt("C:/Users/A/Desktop/pointCloudData/model.txt") #读取点云数据
s = 0.3
t = 0.3
# 沿yz平面错切矩阵
Shear_Matrix = [
[1, 0, 0],
[s, 1, 0],
[t, 0, 1]]
Shear_Matrix = np.array(Shear_Matrix)
p = np.dot(Shear_Matrix, pointCloud.T) # 计算
p = p.T
visiualize(pointCloud, p)五、正交投影
正交投影矩阵(投影到三维空间任意平面):
向量n是垂直于投影平面的单位向量
可视化:点云在xy平面上的正交投影
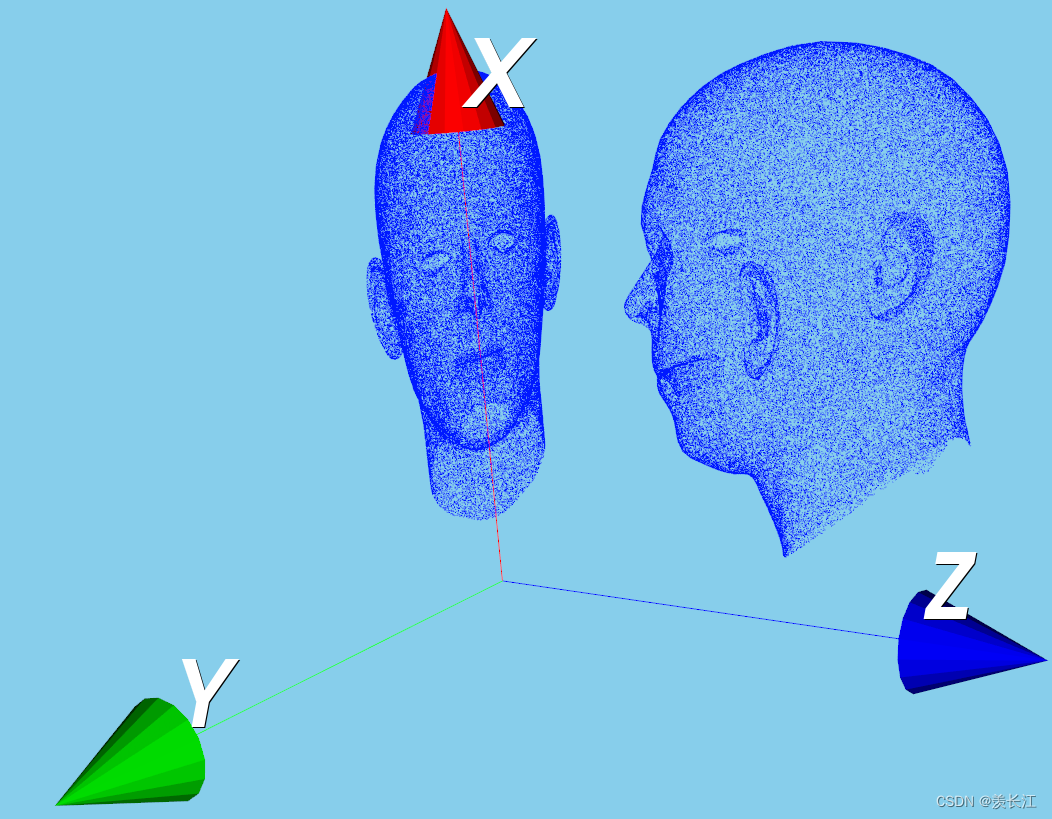
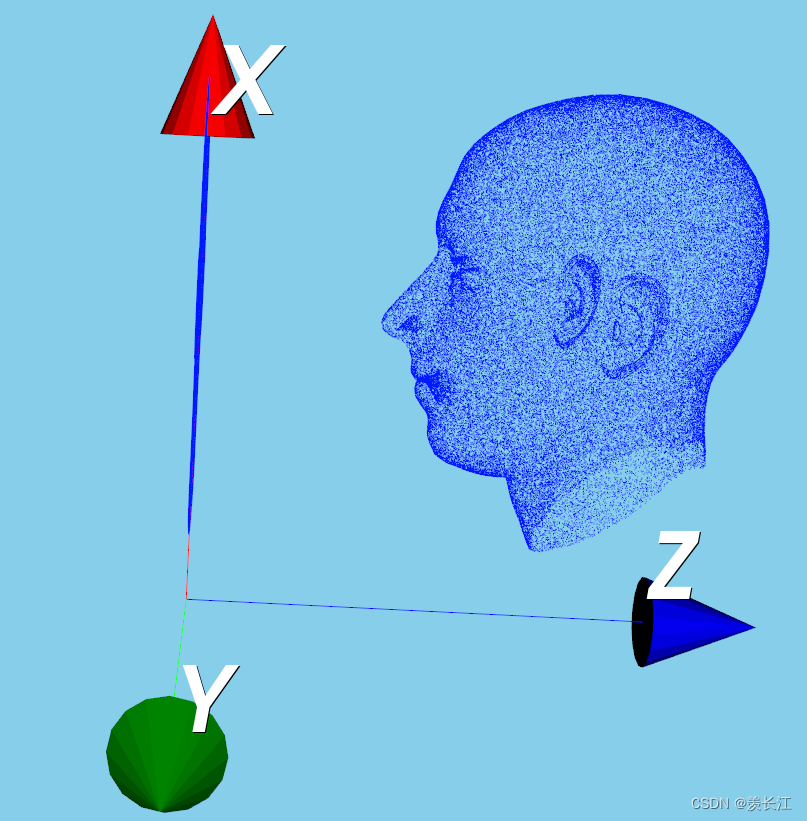
六、平移矩阵
平移矩阵需要利用齐次矩阵(4*4矩阵),下面是一个平移矩阵
最右边一列是xyz的位移量
计算过程:
线性变换+平移:
增加的平移对原来的线性变换没影响,可以将前面介绍的变换矩阵和平移结合
例如:沿xy平面错切+平移