课程简介:
Linux内核开发入门是一门旨在帮助学习者从最基本的知识开始学习Linux内核开发的入门课程。该课程旨在为对Linux内核开发感兴趣的初学者提供一个扎实的基础,让他们能够理解和参与到Linux内核的开发过程中。
课程特点:
1. 入门级别:该课程专注于为初学者提供Linux内核开发的入门知识。无论你是否具有编程或操作系统的背景,该课程都将从最基本的概念和技术开始,逐步引导学习者深入了解Linux内核开发的核心原理。
2. 系统化学习:课程内容经过系统化的安排,涵盖了Linux内核的基础知识、内核模块编程、设备驱动程序开发等关键主题。学习者将逐步了解Linux内核的结构、功能和工作原理,并学习如何编写和调试内核模块和设备驱动程序。
3. 实践导向:该课程强调实践,通过丰富的实例和编程练习,帮助学习者将理论知识应用到实际的Linux内核开发中。学习者将有机会编写简单的内核模块和设备驱动程序,并通过实际的测试和调试来加深对Linux内核开发的理解。
4. 配套资源:为了帮助学习者更好地掌握课程内容,该课程提供了丰富的配套资源,包括教学文档、示例代码、实验指导和参考资料等。学习者可以根据自己的学习进度和需求,灵活地利用这些资源进行学习和实践。
无论你是计算机科学专业的学生、软件工程师还是对Linux内核开发感兴趣的爱好者,Linux内核开发入门课程都将为你提供一个扎实的学习平台,帮助你掌握Linux内核开发的基础知识,为进一步深入研究和应用Linux内核打下坚实的基础。
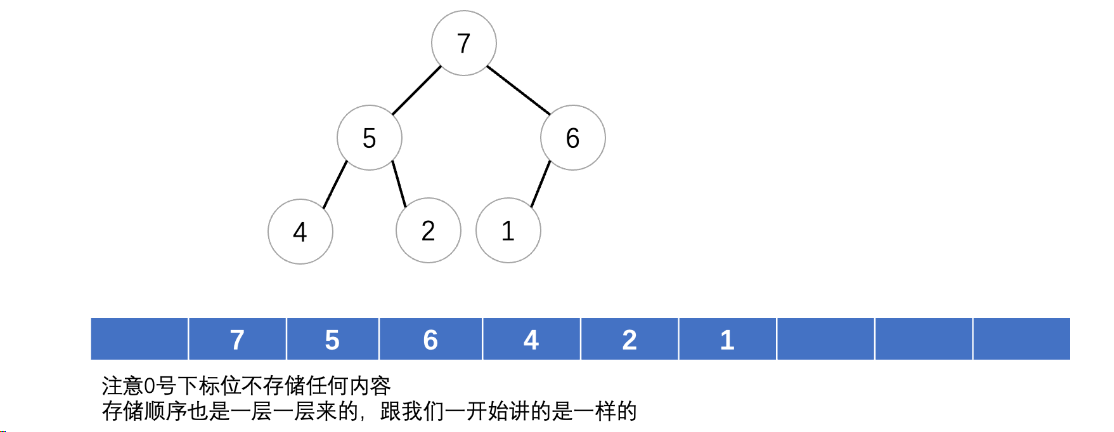
这一讲,主要分享内核中的重点数据结构,并且以脑图的形式进行整理,后面如果有其他内核数据结构,会一同整理到这里。主要介绍内核中使用的4大数据结构:链表,队列,映射,二叉树。
以下是脑图主要内容。
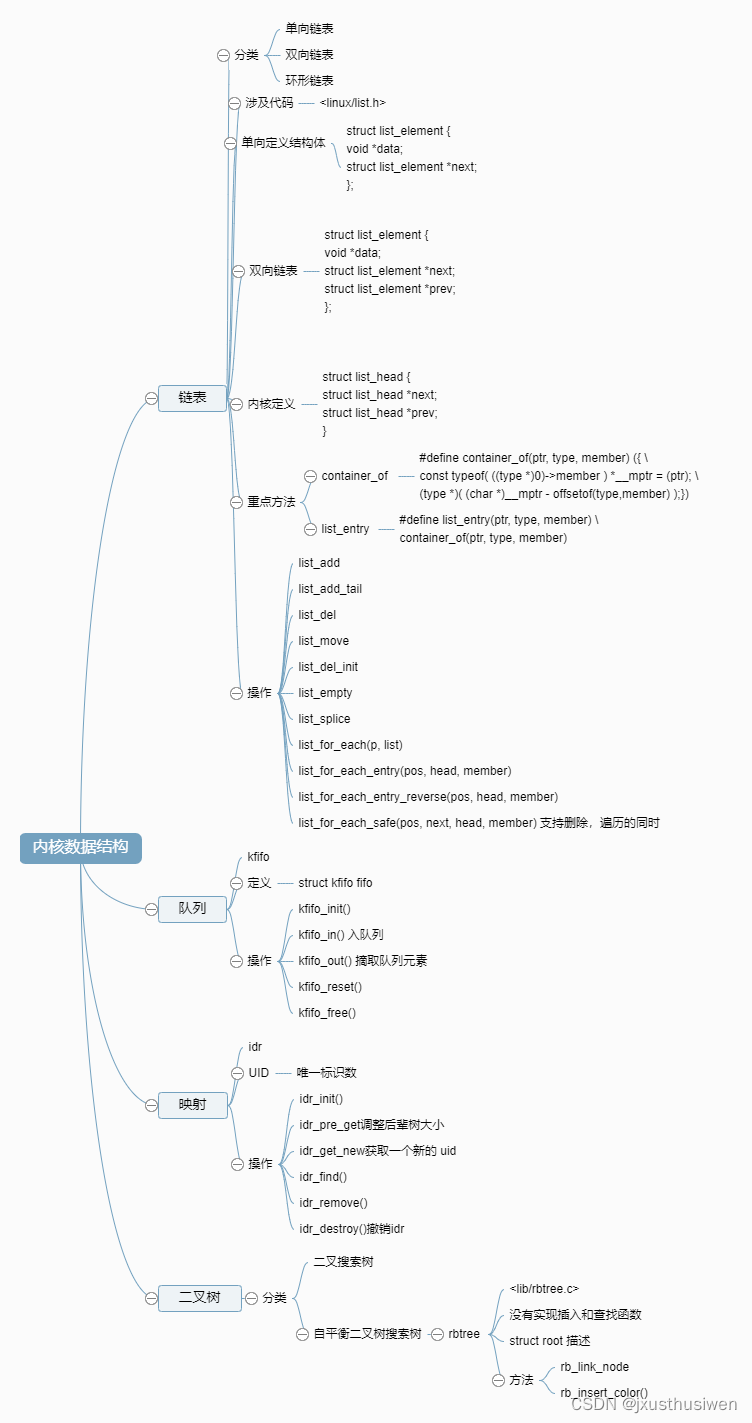
需要脑图文件的可以私信或者评论留言,可以免费同步给你。文章后再贴下 list.h kfifo.h 相关文件定义
LXR linux/include/linux/klist.h
1/*
2 * klist.h - Some generic list helpers, extending struct list_head a bit.
3 *
4 * Implementations are found in lib/klist.c
5 *
6 *
7 * Copyright (C) 2005 Patrick Mochel
8 *
9 * This file is rleased under the GPL v2.
10 */
11
12#ifndef _LINUX_KLIST_H
13#define _LINUX_KLIST_H
14
15#include <linux/spinlock.h>
16#include <linux/completion.h>
17#include <linux/kref.h>
18#include <linux/list.h>
19
20struct klist_node;
21struct klist {
22 spinlock_t k_lock;
23 struct list_head k_list;
24 void (*get)(struct klist_node *);
25 void (*put)(struct klist_node *);
26};
27
28
29extern void klist_init(struct klist * k, void (*get)(struct klist_node *),
30 void (*put)(struct klist_node *));
31
32struct klist_node {
33 struct klist * n_klist;
34 struct list_head n_node;
35 struct kref n_ref;
36 struct completion n_removed;
37};
38
39extern void klist_add_tail(struct klist_node * n, struct klist * k);
40extern void klist_add_head(struct klist_node * n, struct klist * k);
41
42extern void klist_del(struct klist_node * n);
43extern void klist_remove(struct klist_node * n);
44
45extern int klist_node_attached(struct klist_node * n);
46
47
48struct klist_iter {
49 struct klist * i_klist;
50 struct list_head * i_head;
51 struct klist_node * i_cur;
52};
53
54
55extern void klist_iter_init(struct klist * k, struct klist_iter * i);
56extern void klist_iter_init_node(struct klist * k, struct klist_iter * i,
57 struct klist_node * n);
58extern void klist_iter_exit(struct klist_iter * i);
59extern struct klist_node * klist_next(struct klist_iter * i);
60
61#endif
62
The original LXR software by the LXR community, this experimental version by lxr@linux.no.
LXR linux/include/linux/kfifo.h
1/*
2 * A simple kernel FIFO implementation.
3 *
4 * Copyright (C) 2004 Stelian Pop <stelian@popies.net>
5 *
6 * This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
7 * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
8 * the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
9 * (at your option) any later version.
10 *
11 * This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
12 * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
13 * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
14 * GNU General Public License for more details.
15 *
16 * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
17 * along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software
18 * Foundation, Inc., 675 Mass Ave, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA.
19 *
20 */
21#ifndef _LINUX_KFIFO_H
22#define _LINUX_KFIFO_H
23
24#ifdef __KERNEL__
25
26#include <linux/kernel.h>
27#include <linux/spinlock.h>
28
29struct kfifo {
30 unsigned char *buffer; /* the buffer holding the data */
31 unsigned int size; /* the size of the allocated buffer */
32 unsigned int in; /* data is added at offset (in % size) */
33 unsigned int out; /* data is extracted from off. (out % size) */
34 spinlock_t *lock; /* protects concurrent modifications */
35};
36
37extern struct kfifo *kfifo_init(unsigned char *buffer, unsigned int size,
38 gfp_t gfp_mask, spinlock_t *lock);
39extern struct kfifo *kfifo_alloc(unsigned int size, gfp_t gfp_mask,
40 spinlock_t *lock);
41extern void kfifo_free(struct kfifo *fifo);
42extern unsigned int __kfifo_put(struct kfifo *fifo,
43 unsigned char *buffer, unsigned int len);
44extern unsigned int __kfifo_get(struct kfifo *fifo,
45 unsigned char *buffer, unsigned int len);
46
47/**
48 * __kfifo_reset - removes the entire FIFO contents, no locking version
49 * @fifo: the fifo to be emptied.
50 */
51static inline void __kfifo_reset(struct kfifo *fifo)
52{
53 fifo->in = fifo->out = 0;
54}
55
56/**
57 * kfifo_reset - removes the entire FIFO contents
58 * @fifo: the fifo to be emptied.
59 */
60static inline void kfifo_reset(struct kfifo *fifo)
61{
62 unsigned long flags;
63
64 spin_lock_irqsave(fifo->lock, flags);
65
66 __kfifo_reset(fifo);
67
68 spin_unlock_irqrestore(fifo->lock, flags);
69}
70
71/**
72 * kfifo_put - puts some data into the FIFO
73 * @fifo: the fifo to be used.
74 * @buffer: the data to be added.
75 * @len: the length of the data to be added.
76 *
77 * This function copies at most 'len' bytes from the 'buffer' into
78 * the FIFO depending on the free space, and returns the number of
79 * bytes copied.
80 */
81static inline unsigned int kfifo_put(struct kfifo *fifo,
82 unsigned char *buffer, unsigned int len)
83{
84 unsigned long flags;
85 unsigned int ret;
86
87 spin_lock_irqsave(fifo->lock, flags);
88
89 ret = __kfifo_put(fifo, buffer, len);
90
91 spin_unlock_irqrestore(fifo->lock, flags);
92
93 return ret;
94}
95
96/**
97 * kfifo_get - gets some data from the FIFO
98 * @fifo: the fifo to be used.
99 * @buffer: where the data must be copied.
100 * @len: the size of the destination buffer.
101 *
102 * This function copies at most 'len' bytes from the FIFO into the
103 * 'buffer' and returns the number of copied bytes.
104 */
105static inline unsigned int kfifo_get(struct kfifo *fifo,
106 unsigned char *buffer, unsigned int len)
107{
108 unsigned long flags;
109 unsigned int ret;
110
111 spin_lock_irqsave(fifo->lock, flags);
112
113 ret = __kfifo_get(fifo, buffer, len);
114
115 /*
116 * optimization: if the FIFO is empty, set the indices to 0
117 * so we don't wrap the next time
118 */
119 if (fifo->in == fifo->out)
120 fifo->in = fifo->out = 0;
121
122 spin_unlock_irqrestore(fifo->lock, flags);
123
124 return ret;
125}
126
127/**
128 * __kfifo_len - returns the number of bytes available in the FIFO, no locking version
129 * @fifo: the fifo to be used.
130 */
131static inline unsigned int __kfifo_len(struct kfifo *fifo)
132{
133 return fifo->in - fifo->out;
134}
135
136/**
137 * kfifo_len - returns the number of bytes available in the FIFO
138 * @fifo: the fifo to be used.
139 */
140static inline unsigned int kfifo_len(struct kfifo *fifo)
141{
142 unsigned long flags;
143 unsigned int ret;
144
145 spin_lock_irqsave(fifo->lock, flags);
146
147 ret = __kfifo_len(fifo);
148
149 spin_unlock_irqrestore(fifo->lock, flags);
150
151 return ret;
152}
153
154#else
155#warning "don't include kernel headers in userspace"
156#endif /* __KERNEL__ */
157#endif
158