目录
104. 二叉树的最大深度
题目描述:
输入输出描述:
思路和想法:
111. 二叉树的最小深度
题目描述:
输入输出描述:
思路和想法:
222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
题目描述:
输入输出描述:
思路和想法:
104. 二叉树的最大深度
题目描述:
给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
输入输出描述:
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:3示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2]
输出:2提示:
- 树中节点的数量在 [0, 104] 区间内。
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
思路和想法:
①确认递归函数的参数以及返回值,只需将节点放入即可,返回深度,返回值为int类型
②确定终止条件即为,如果为空节点,就返回0
③先求左子树的深度,再求右子树的深度,最后取最大值再加一,就是目前二叉树的最大深度。
class Solution {
public:
int getdepth(TreeNode* cur){
if(cur == NULL) return 0;
int leftdepth = getdepth(cur->left);
int rightdepth = getdepth(cur->right);
int maxdepth = 1 + max(leftdepth, rightdepth);
return maxdepth;
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return getdepth(root);
}
};111. 二叉树的最小深度
题目描述:
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
输入输出描述:
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
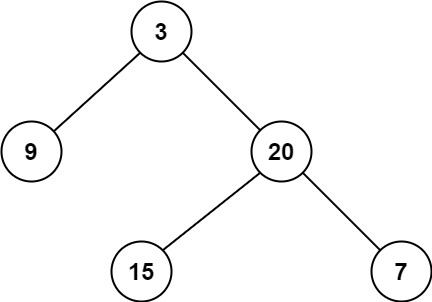
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:2示例 2:
输入:root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
输出:5提示:
- 树中节点数的范围在 [0, 105] 内
- -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
思路和想法:
判断左右孩子是否为空,空了就停止,这里进行左右子树的持续遍历判断。
class Solution {
public:
int getdepth(TreeNode* cur){
if(cur == NULL) return 0;
int leftdepth = getdepth(cur->left);
int rightdepth = getdepth(cur->right);
if(cur->left == NULL && cur->right != NULL){
return 1+ rightdepth;
}
if(cur->left != NULL && cur->right == NULL){
return 1+ leftdepth;
}
int result = 1 + min(leftdepth, rightdepth);
return result;
}
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return getdepth(root);
}
};222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
题目描述:
给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点 root ,求出该树的节点个数。
完全二叉树 的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
输入输出描述:
示例 1:
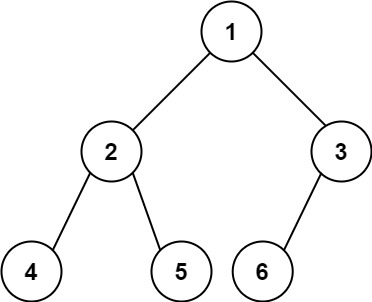
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
输出:6示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:0示例 3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:1提示:
- 树中节点的数目范围是[0, 5 * 104]
- 0 <= Node.val <= 5 * 104
- 题目数据保证输入的树是 完全二叉树
思路和想法:
(1)普通二叉树
求左子树的节点个数,再求右子树的节点个数,最终求和再加1,即为二叉树的节点个数。
class Solution {
private:
int getNodesNum(TreeNode* cur) {
if (cur == NULL) return 0;
int leftNum = getNodesNum(cur->left); // 左
int rightNum = getNodesNum(cur->right); // 右
int treeNum = leftNum + rightNum + 1; // 中
return treeNum;
}
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
return getNodesNum(root);
}
};(2)完全二叉树
完全二叉树只有两种情况,情况一:就是满二叉树,情况二:最后一层叶子节点没有满。
在二叉树为完全二叉树的情况下,只需要一直左孩子和右孩子递归,判断子树是否为满二叉树,之后采用满二叉树求节点个数的公式。
以这种方式,利用完全二叉树的特点,节省了遍历次数。
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) return 0;
TreeNode* left = root->left;
TreeNode* right = root->right;
int leftdepth = 0;
int rightdepth = 0;
while(left){
left = left->left;
leftdepth++;
}
while(right){
right = right->right;
rightdepth++;
}
if(leftdepth == rightdepth){
return (2 << leftdepth) - 1;
}
return countNodes(root->left) + countNodes(root->right) + 1;
}
};