前情提要:因为数学水平原因,没法给出e的证明,因为我也是举例归类得出的结论,但是按理来说应该可以利用生成数函数证明
f题也是因为数学原因加上水平有限,我的理解可能有偏差。
目录
A. Contest Proposal:
题目大意:
思路解析:
代码实现:
B. Coin Games:
题目大意:
思路解析:
代码实现:
C. Permutation Counting:
题目大意:
思路解析:
代码实现:
D1. Reverse Card (Easy Version):
题目大意:
思路解析:
代码实现:
D2. Reverse Card (Hard Version):
题目大意:
思路解析:
代码实现:
E. Fenwick Tree:
题目大意:
思路解析:
代码实现:
F. Long Way to be Non-decreasing:
题目大意:
思路解析:
代码实现:
A. Contest Proposal:
题目大意:



思路解析:
现在求使得对于所有i中,ai<=bi,最少需要插入几个新的问题,这里一眼贪心即可。
代码实现:
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int t = f.nextInt();
while (t > 0) {
solve();
t--;
}
w.flush();
w.close();
}
static int mod = 998244353;
static long inf = (long) 1e18;
public static void solve() throws IOException {
int n = f.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[n];
int[] b= new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[i] = f.nextInt();
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
b[i] = f.nextInt();
}
int p = 0;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[p] <= b[i]){
p++;
}else {
ans++;
}
}
w.println(ans);
}
public static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int tmp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = tmp;
}
public static long qkm(long a, long b, long mod) {
long res = 1;
while (b > 0) {
if ((b & 1) == 1) res = res * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
public static class Pair {
long x, y;
int val;
public Pair(long ne, long val, int x) {
this.x = ne;
this.y = val;
this.val = x;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Pair pair = (Pair) o;
return x == pair.x && y == pair.y && val == pair.val;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(x, y, val);
}
}
public static class Node {
int x, y, val;
public Node(int x, int y, int val) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.val = val;
}
public Node(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
static PrintWriter w = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static Input f = new Input(System.in);
static class Input {
public BufferedReader reader;
public StringTokenizer tokenizer;
public Input(InputStream stream) {
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(stream), 32768);
tokenizer = null;
}
public String next() throws IOException {
while (tokenizer == null || !tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) {
tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(reader.readLine());
}
return tokenizer.nextToken();
}
public String nextLine() throws IOException {
String str = null;
str = reader.readLine();
return str;
}
public int nextInt() throws IOException {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public long nextLong() throws IOException {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
public Double nextDouble() throws IOException {
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
}
}B. Coin Games:
题目大意:



思路解析:
考虑所有可能的操作:
- ...UUU...->...DD......:U 的个数减少 3 。
- ...UUD...->...DU...:U 的数量减少 1 。
- ...DUU...->...UD...:U 的数量减少 1 。
- ...DUD... -> ...UU...:U 的数量增加 1
当U的个数为0时,当前棋手输,可以发现对于所有可能的操作,任意一种情况都会改变U的个数的奇偶性,那么可以得出结论,当初始情况U的个数为奇数时,Alice将赢得游戏。
代码实现:
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int t = f.nextInt();
while (t > 0) {
solve();
t--;
}
w.flush();
w.close();
}
static int mod = 998244353;
static long inf = (long) 1e18;
public static void solve() throws IOException {
int n = f.nextInt();
char[] s = f.next().toCharArray();
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (s[i] == 'U') cnt ^= 1;
}
if (cnt == 1) w.println("YES");
else w.println("NO");
}
public static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int tmp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = tmp;
}
public static long qkm(long a, long b, long mod) {
long res = 1;
while (b > 0) {
if ((b & 1) == 1) res = res * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
public static class Pair {
long x, y;
int val;
public Pair(long ne, long val, int x) {
this.x = ne;
this.y = val;
this.val = x;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Pair pair = (Pair) o;
return x == pair.x && y == pair.y && val == pair.val;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(x, y, val);
}
}
public static class Node {
int x, y, val;
public Node(int x, int y, int val) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.val = val;
}
public Node(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
static PrintWriter w = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static Input f = new Input(System.in);
static class Input {
public BufferedReader reader;
public StringTokenizer tokenizer;
public Input(InputStream stream) {
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(stream), 32768);
tokenizer = null;
}
public String next() throws IOException {
while (tokenizer == null || !tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) {
tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(reader.readLine());
}
return tokenizer.nextToken();
}
public String nextLine() throws IOException {
String str = null;
str = reader.readLine();
return str;
}
public int nextInt() throws IOException {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public long nextLong() throws IOException {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
public Double nextDouble() throws IOException {
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
}
}C. Permutation Counting:
题目大意:



思路解析:
这里可以发现能组成排列数的个数肯定与1-n中最少的那个数字相等。
假如 1的个数为3 2的个数为2 3的个数为3,那么肯定可以组成 1 2 3 1 2 3此时排列数为4,1 2 3两个2 3 1一个3 1 2一个,那么我们想剩下的1 和 3是否能再组成新的排列数,答案是可以的,
1 3 2 1 3 2 1 3此时 1 3 2 两个 3 2 1两个 2 1 3两个,此时已经最优了,
那么可以发现答案等于 min + (min-1)*(n-1)+ min(n-1,more+k),k可以提高min的大小
代码实现:
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int t = f.nextInt();
while (t > 0) {
solve();
t--;
}
w.flush();
w.close();
}
static int mod = 998244353;
static long inf = (long) 1e18;
public static void solve() throws IOException {
int n = f.nextInt(); long k = f.nextLong();
long[] a = new long[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[i] = f.nextLong();
}
int j = 1;
Arrays.sort(a);
long min = a[0];
while (true){
if (k < j) break;
if (j < n){
if ((a[j] - min) * j > k){
min += k / j;
k %= j;
break;
}else {
k -= (a[j] - min) * j;
min = a[j];
j++;
}
}else {
min += k / j;
k %= j;
break;
}
}
if (j == n){
long ans = min + (min - 1) * (n - 1) + k;
w.println(ans);
}else {
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = j; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] > min) cnt++;
}
long ans = min + (min - 1) * (n - 1) + Math.min(n - 1, cnt + k);
w.println(ans);
}
}
public static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int tmp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = tmp;
}
public static long qkm(long a, long b, long mod) {
long res = 1;
while (b > 0) {
if ((b & 1) == 1) res = res * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
public static class Pair {
long x, y;
int val;
public Pair(long ne, long val, int x) {
this.x = ne;
this.y = val;
this.val = x;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Pair pair = (Pair) o;
return x == pair.x && y == pair.y && val == pair.val;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(x, y, val);
}
}
public static class Node {
int x, y, val;
public Node(int x, int y, int val) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.val = val;
}
public Node(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
static PrintWriter w = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static Input f = new Input(System.in);
static class Input {
public BufferedReader reader;
public StringTokenizer tokenizer;
public Input(InputStream stream) {
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(stream), 32768);
tokenizer = null;
}
public String next() throws IOException {
while (tokenizer == null || !tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) {
tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(reader.readLine());
}
return tokenizer.nextToken();
}
public String nextLine() throws IOException {
String str = null;
str = reader.readLine();
return str;
}
public int nextInt() throws IOException {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public long nextLong() throws IOException {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
public Double nextDouble() throws IOException {
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
}
}D1. Reverse Card (Easy Version):
题目大意:



思路解析:
a+b是b*gcd(a,b)的倍数,如果gcd(a,b) == 1 ,那么就是 a+b 是b的倍数,那么可以推出a是b的倍数,与gcd(a,b)==1违背
a+b是b*gcd(a,b)的倍数 也可以等价于a+b是b的倍数 等价于 a是b的倍数,那么 a+b应该是b*b的倍数
令 a+b == b*b a+b == 2*b*b................... a == (b-1)*b
只要a和b有这样的关系就可以称为一个有序数对,那么利用这个关系也可以求解答案了 这里在求解时可以等价n中有多少个数是 (b-1)*b的倍数
代码实现:
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int t = f.nextInt();
while (t > 0) {
solve();
t--;
}
w.flush();
w.close();
}
static int mod = 998244353;
static long inf = (long) 1e18;
public static void solve() throws IOException {
int n = f.nextInt(); int m = f.nextInt();
long ans = n;
for (int i = 2; i <= m; i++) {
int t = i * (i - 1);
if (t > n) break;
ans += (n - t) / (i * i) + 1;
}
w.println(ans);
}
public static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int tmp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = tmp;
}
public static long qkm(long a, long b, long mod) {
long res = 1;
while (b > 0) {
if ((b & 1) == 1) res = res * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
public static class Pair {
long x, y;
int val;
public Pair(long ne, long val, int x) {
this.x = ne;
this.y = val;
this.val = x;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Pair pair = (Pair) o;
return x == pair.x && y == pair.y && val == pair.val;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(x, y, val);
}
}
public static class Node {
int x, y, val;
public Node(int x, int y, int val) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.val = val;
}
public Node(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
static PrintWriter w = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static Input f = new Input(System.in);
static class Input {
public BufferedReader reader;
public StringTokenizer tokenizer;
public Input(InputStream stream) {
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(stream), 32768);
tokenizer = null;
}
public String next() throws IOException {
while (tokenizer == null || !tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) {
tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(reader.readLine());
}
return tokenizer.nextToken();
}
public String nextLine() throws IOException {
String str = null;
str = reader.readLine();
return str;
}
public int nextInt() throws IOException {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public long nextLong() throws IOException {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
public Double nextDouble() throws IOException {
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
}
}D2. Reverse Card (Hard Version):
题目大意:



思路解析:
将 gcd(𝑎,𝑏) 表示为 d 。假设有 a=pd𝑎=𝑝𝑑 和 b=qd𝑏=𝑞𝑑 ,那么我们知道 gcd(p,q)=1
(a+b)∣(b⋅gcd(a,b))⟺(pd+qd)∣(qd2)⟺(p+q)∣(qd)
我们知道 gcd(p+q,q)=gcd(p,q)=1,所以是 (p+q)∣d(𝑝+𝑞)∣𝑑 。
我们还知道 p≥1,q≥1 ,所以 p<d=ap≤np ,从而 p2<n 。同样,我们可以证明 q2<m 。

这里有个很关键的地方就是打表,你利用100 1233这组数据就可以找到所有合法有序对(因为这组数据遍历时间并不复杂,并且又有几百的有效有序对,那么对于我们观察答案性质是很有效的)
那我们就可以得到很多对 a 和 b,此时再观察 a/gcd(a,b) ==p, b/gcd(a,b)==q,并且统计这样序关系出现次数,发现他们的出现次数刚好可以等价于 min(n/p,m/q)/(p+q), 那么得到这个式子后就可以进行求解,打表对于构造题和数学题这类题型是非常关键的。
代码实现:
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int t = f.nextInt();
while (t > 0) {
solve();
t--;
}
w.flush();
w.close();
}
static int mod = 998244353;
static long inf = (long) 1e18;
public static void solve() throws IOException {
int n = f.nextInt(); int m = f.nextInt();
long ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
if (j * (i + j) > n) break;
if (gcd(i, j) == 1){
ans += Math.min(m/i,n/j)/(i+j);
}
}
}
w.println(ans);
}
public static int gcd(int i, int j){
if(i == 0) return j;
if (j==0) return i;
return gcd(j, i % j);
}
public static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int tmp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = tmp;
}
static long pow(long a, long b){
long res = 1;
while (b > 0){
if ((b & 1) == 1) res = res * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>=1;
}
return res;
}
public static long qkm(long a, long b, long mod) {
long res = 1;
while (b > 0) {
if ((b & 1) == 1) res = res * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
public static class Pair {
long x, y;
int val;
public Pair(long ne, long val, int x) {
this.x = ne;
this.y = val;
this.val = x;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Pair pair = (Pair) o;
return x == pair.x && y == pair.y && val == pair.val;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(x, y, val);
}
}
public static class Node {
int x, y, val;
public Node(int x, int y, int val) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.val = val;
}
public Node(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
static PrintWriter w = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static Input f = new Input(System.in);
static class Input {
public BufferedReader reader;
public StringTokenizer tokenizer;
public Input(InputStream stream) {
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(stream), 32768);
tokenizer = null;
}
public String next() throws IOException {
while (tokenizer == null || !tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) {
tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(reader.readLine());
}
return tokenizer.nextToken();
}
public String nextLine() throws IOException {
String str = null;
str = reader.readLine();
return str;
}
public int nextInt() throws IOException {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public long nextLong() throws IOException {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
public Double nextDouble() throws IOException {
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
}
}E. Fenwick Tree:
题目大意:



思路解析:
给出官方题解
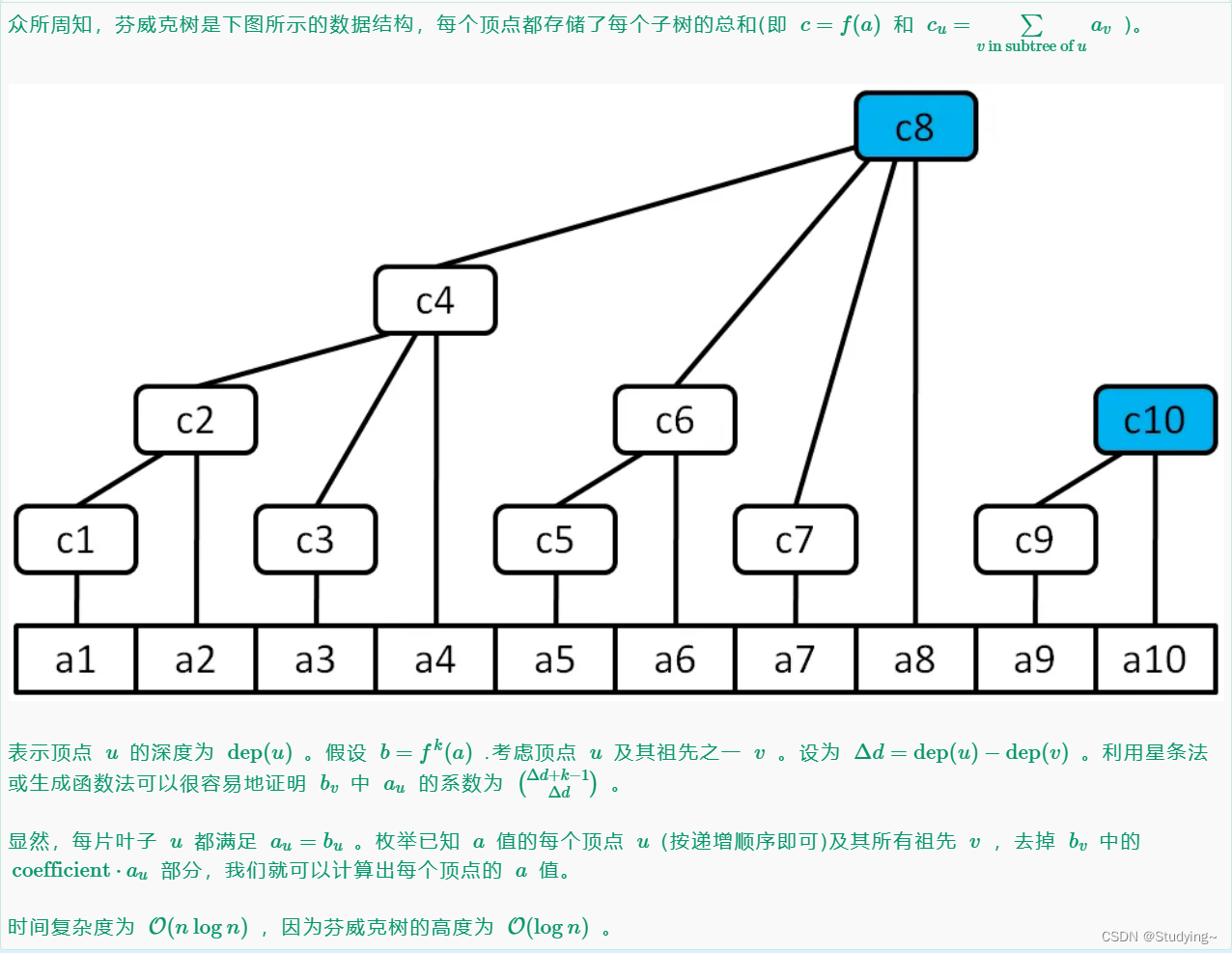
代码实现:
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static int N = (int) 1e6 + 100;
static long[] inv = new long[N];
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
inv[0] = inv[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < N; i++) {
inv[i] = (mod - mod /i ) * inv[mod % i] % mod;
}
int t = f.nextInt();
while (t > 0) {
solve();
t--;
}
w.flush();
w.close();
}
static int mod = 998244353;
static long inf = (long) 1e18;
public static void solve() throws IOException {
int n = f.nextInt(); int m = f.nextInt();
long[] a = new long[n+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
a[i] = f.nextInt();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
long mul = 1;
for (int j = i + lowbit(i), d=1; j <= n; j+=lowbit(j),++d) {
mul = mul * (d + m - 1) % mod * inv[d] % mod;
a[j] -= mul * a[i] % mod;
a[j] = (a[j] + mod) % mod;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
w.print(a[i] + " ");
}
w.println();
}
public static int lowbit(int x) {return x & -x;}
public static int gcd(int i, int j){
if(i == 0) return j;
if (j==0) return i;
return gcd(j, i % j);
}
public static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int tmp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = tmp;
}
static long pow(long a, long b){
long res = 1;
while (b > 0){
if ((b & 1) == 1) res = res * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>=1;
}
return res;
}
public static long qkm(long a, long b, long mod) {
long res = 1;
while (b > 0) {
if ((b & 1) == 1) res = res * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
public static class Pair {
long x, y;
int val;
public Pair(long ne, long val, int x) {
this.x = ne;
this.y = val;
this.val = x;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Pair pair = (Pair) o;
return x == pair.x && y == pair.y && val == pair.val;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(x, y, val);
}
}
public static class Node {
int x, y, val;
public Node(int x, int y, int val) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.val = val;
}
public Node(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
static PrintWriter w = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static Input f = new Input(System.in);
static class Input {
public BufferedReader reader;
public StringTokenizer tokenizer;
public Input(InputStream stream) {
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(stream), 32768);
tokenizer = null;
}
public String next() throws IOException {
while (tokenizer == null || !tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) {
tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(reader.readLine());
}
return tokenizer.nextToken();
}
public String nextLine() throws IOException {
String str = null;
str = reader.readLine();
return str;
}
public int nextInt() throws IOException {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public long nextLong() throws IOException {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
public Double nextDouble() throws IOException {
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
}
}F. Long Way to be Non-decreasing:
题目大意:



思路解析:

代码实现:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
namespace FastIO {
template <typename T> inline T read() { T x = 0, w = 0; char ch = getchar(); while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') w |= (ch == '-'), ch = getchar(); while ('0' <= ch && ch <= '9') x = x * 10 + (ch ^ '0'), ch = getchar(); return w ? -x : x; }
template <typename T> inline void write(T x) { if (!x) return; write<T>(x / 10), putchar(x % 10 ^ '0'); }
template <typename T> inline void print(T x) { if (x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x; else if (x == 0) putchar('0'); write<T>(x); }
template <typename T> inline void print(T x, char en) { if (x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x; else if (x == 0) putchar('0'); write<T>(x), putchar(en); }
}; using namespace FastIO;
#define MAXM 1000001
int dep[MAXM], id[MAXM], dfn[MAXM], to[MAXM], sz[MAXM], tot = 0;
std::vector<int> ch[MAXM];
void dfs(int u) {
sz[u] = 1, dfn[u] = ++tot;
for (int v : ch[u]) {
dep[v] = dep[u] + 1, id[v] = id[u];
dfs(v), sz[u] += sz[v];
}
}
inline bool inSub(int u, int v) /* v \in u ? */ { return dfn[u] <= dfn[v] && dfn[v] < dfn[u] + sz[u]; }
constexpr int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
inline int query(int u, int v) /* u -> v */ {
if (u == v) return 0;
if (id[u] != id[v]) return INF;
int res = INF;
if (inSub(v, u)) res = dep[u] - dep[v];
if (inSub(v, to[id[u]])) res = std::min(dep[u] - dep[v] + dep[to[id[u]]] + 1, res);
// printf("query(%d, %d) = %d\n", u, v, res);
return res;
}
#define MAXN 1000001
int a[MAXN], N, M;
bool check(int val) {
// printf("check %d\n", val);
int lst = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
while (lst <= M && query(a[i], lst) > val) ++lst;
if (lst > M) return false;
// printf("a[%d] = %d\n", i, lst);
}
return true;
}
namespace DSU {
int fa[MAXM];
void inis(int n) { for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) fa[i] = i; }
inline int find(int x) { return x == fa[x] ? x : fa[x] = find(fa[x]); }
inline bool merge(int x, int y) { if (find(x) == find(y)) return false; fa[fa[x]] = fa[y]; return true; }
}; using namespace DSU;
int main() {
int T = read<int>();
while (T--) {
N = read<int>(), M = read<int>(), inis(M);
for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) a[i] = read<int>();
for (int x = 1; x <= M; ++x) dep[x] = id[x] = dfn[x] = to[x] = sz[x] = 0, ch[x].clear();
tot = 0;
for (int i = 1, p; i <= M; ++i) {
p = read<int>();
if (merge(i, p)) ch[p].push_back(i); else to[i] = p;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= M; ++i) if (to[i] > 0) id[i] = i, dfs(i);
if (!check(M)) { puts("-1"); continue; }
int L = 0, R = M;
while (L < R) {
int mid = L + R >> 1;
if (check(mid)) R = mid; else L = mid + 1;
}
print<int>(R, '\n');
}
}