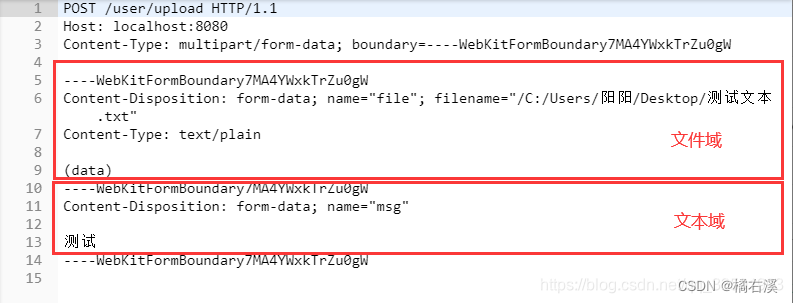
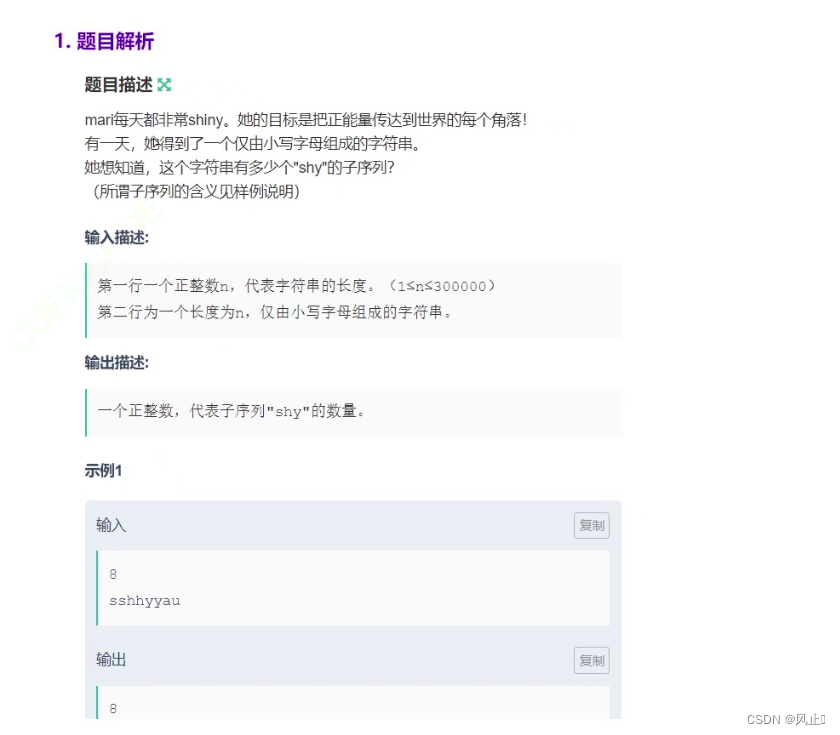
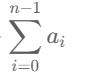'shy'的子序列的个数
这一题,我一开始就没什么思路,我就开始暴力枚举了,就是定义i,j(找i后面的),k(找j后面的),很显然这种方法超时了。所以我就想使用动态规划,但是空间又超了,我就很懵,到最后听老师讲空间优化(使用三个变量(滚动数组))进行优化才解决这道题
1.暴力枚举
定义: i 指针来找, 找到了s,后在定义 i + 1 位置为j 指针 找 h,找到定义k指针找y
public static void main1(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
// 注意 hasNext 和 hasNextLine 的区别
while (in.hasNextLine()) { // 注意 while 处理多个 case
in.nextLine();
String str = in.nextLine();
char[] chs = str.toCharArray();
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {
if (chs[i] == 's'){
for (int j = i + 1; j < chs.length; j++) {
if (chs[j] == 'h') {
for (int k = j + 1; k < chs.length; k++) {
if (chs[k] == 'y') {
count++;
}
}
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}2. 动态规划
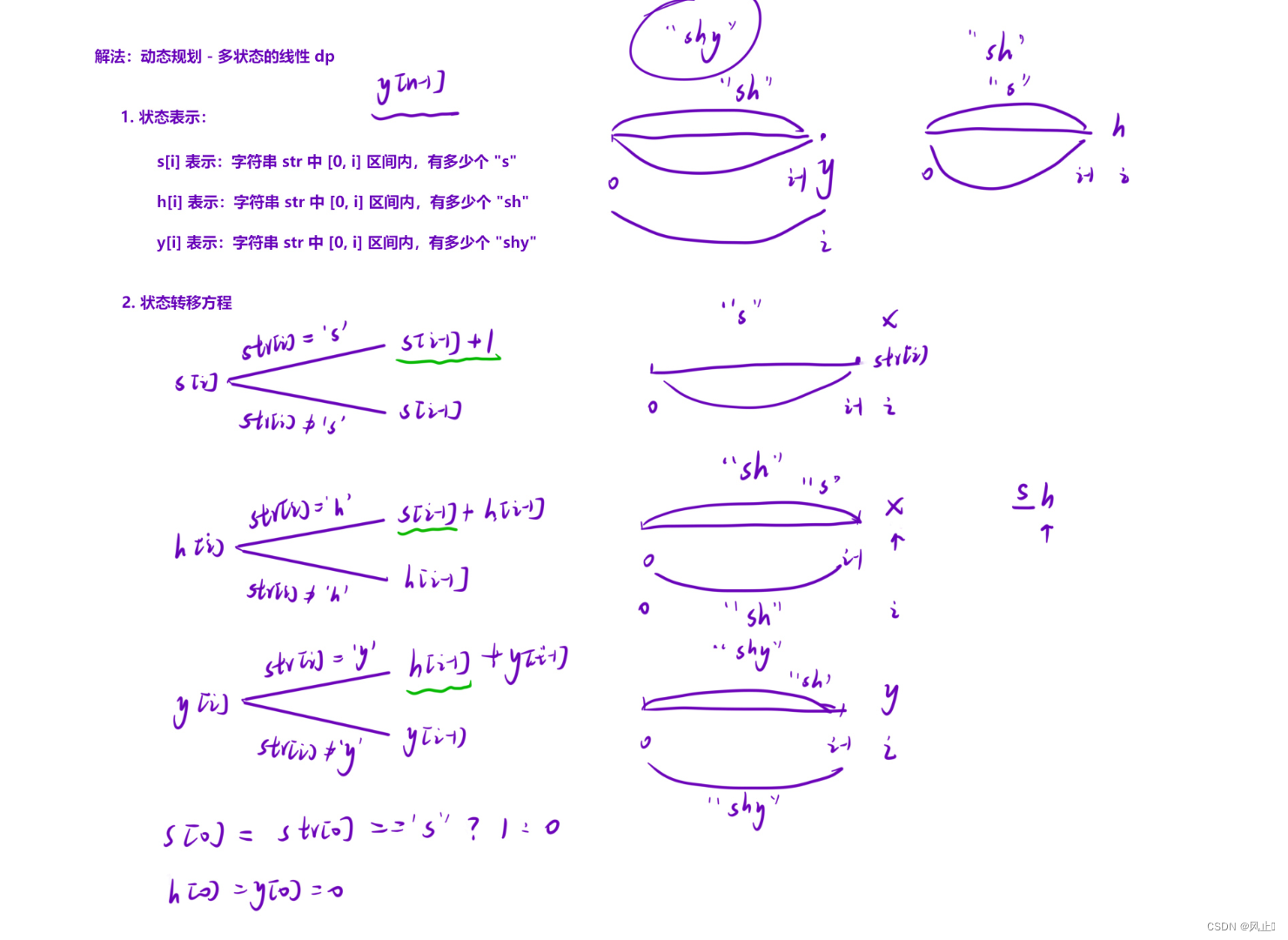
多状态dp表示 的状态表示
1. S[i] 以i位置为结尾的有多少个 'S'
2. H[i] 以i位置为结尾的有多少个 'SH'
3. Y[i] 以i位置为结尾的有多少个 'SHY'
状态转移方程: S[i] 1. i位置为'S' S[i] = S[i - 1] + 1
2. i位置不为'S' S[i] = S[i - 1]
状态转移方程: H[i] 1. i位置为'H' H[i] = H[i - 1] + S[i - 1] 因为sshh 第四个为h让本来有两个sh + s(h)s(h)的个数
2. i位置不为'H' H[i] = H[i - 1]
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
String str = " " + sc.next();
int[] s = new int[n + 1];
int[] h = new int[n + 1];
int[] y = new int[n + 1];
char[] chs = str.toCharArray();
for (int i = 1; i < chs.length; i++) {
if (chs[i] == 's'){
s[i] = s[i - 1] + 1;
h[i] = h[i - 1];
y[i] = y[i - 1];
}else if (chs[i] == 'h'){
h[i] = h[i - 1] + s[i - 1];
s[i] = s[i - 1];
y[i] = y[i - 1];
} else if (chs[i] == 'y') {
y[i] = y[i - 1] + h[i - 1];
s[i] = s[i - 1];
h[i] = h[i - 1];
}else {
s[i] = s[i - 1];
h[i] = h[i - 1];
y[i] = y[i - 1];
}
}
System.out.println(y[n]);
}3.空间优化
使用三个变量进行优化,因为只需要用到前面一个状态,其他状态都不需要,这样也不需要不处理,不为s位置设置为s[i] = s[i - 1],因为等于和不处理一样,这就像求斐波那契一样。
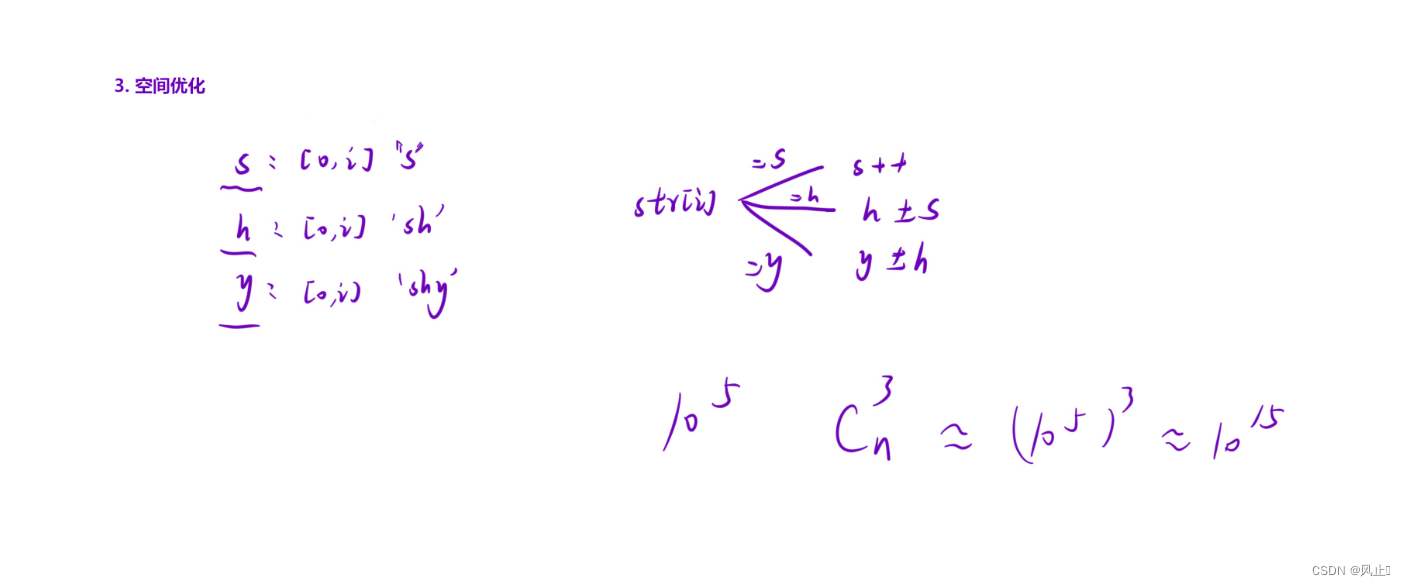
public static void main3(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
String str = " " + sc.next();
int s = 0, h = 0, y = 0;
char[] chs = str.toCharArray();
for (int i = 1; i < chs.length; i++) {
if (chs[i] == 's') {
s += 1;
} else if (chs[i] == 'h') {
h += s;
} else if (chs[i] == 'y') {
y += h;
}
}
}