1. 介绍
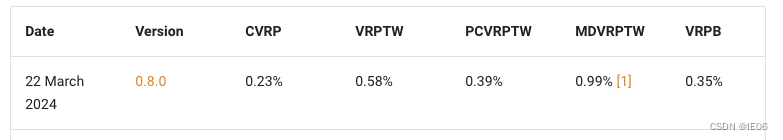
PyVRP使用HGS(hybrid genetic search)算法求解VRP类问题。在benchmark上的评测结果如下,看起来还不错:
2. 使用例子
2.1 CVRP
COORDS = [
(456, 320), # location 0 - the depot
(228, 0), # location 1
(912, 0), # location 2
(0, 80), # location 3
(114, 80), # location 4
(570, 160), # location 5
(798, 160), # location 6
(342, 240), # location 7
(684, 240), # location 8
(570, 400), # location 9
(912, 400), # location 10
(114, 480), # location 11
(228, 480), # location 12
(342, 560), # location 13
(684, 560), # location 14
(0, 640), # location 15
(798, 640), # location 16
]
DEMANDS = [0, 1, 1, 2, 4, 2, 4, 8, 8, 1, 2, 1, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8]
from pyvrp import Model
m = Model()
m.add_vehicle_type(4, capacity=15)
depot = m.add_depot(x=COORDS[0][0], y=COORDS[0][1])
clients = [
m.add_client(x=COORDS[idx][0], y=COORDS[idx][1], delivery=DEMANDS[idx])
for idx in range(1, len(COORDS))
]
locations = [depot] + clients
for frm in locations:
for to in locations:
distance = abs(frm.x - to.x) + abs(frm.y - to.y) # Manhattan
m.add_edge(frm, to, distance=distance)
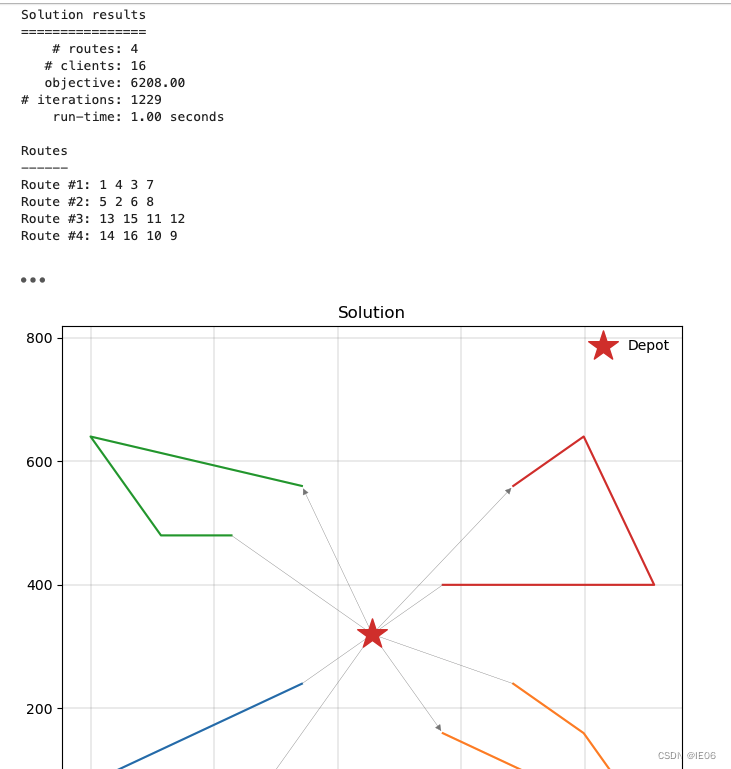
下面是求解和绘图:
from pyvrp.stop import MaxRuntime
from pyvrp.plotting import plot_solution
res = m.solve(stop=MaxRuntime(1), display=False)
print(res)
_, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 8))
plot_solution(res.best, m.data(), ax=ax)
2.2 VRPTW
X_COORD = [0,20,25,30,45]
TIME_WINDOWS = [(0, 1000),(100, 1002),(200, 1005),(180, 1008),(180, 1003),(90, 500),\
(95, 1000),(90, 400),(95, 1000),(90, 300), (90, 1600),(90, 150), \
(10, 500), (50, 100), (70, 800), (190, 1500), (100, 1005)]
SERVICE_TIME = [2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2]
DEMANDS = [1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1]
STATION = [1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 3, 4, 2, 4, 3, 1, 2]
#https://pyvrp.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api/pyvrp.html
from pyvrp.stop import MaxRuntime
from pyvrp.plotting import plot_solution
from pyvrp import Model
m = Model()
m.add_vehicle_type(20, capacity=4)
depot = m.add_depot(x=X_COORD[0],y=0,tw_early=0,tw_late=9999)
clients = [m.add_client(x=X_COORD[STATION[idx]], y=0,delivery=DEMANDS[idx],service_duration = 2, \
tw_early=TIME_WINDOWS[idx][0],tw_late=TIME_WINDOWS[idx][1],) for idx in range(len(DEMANDS))]
locations = [depot] + clients
for frm in locations:
for to in locations:
m.add_edge(frm, to, distance=abs(frm.x - to.x), duration=abs(frm.x - to.x))
res = m.solve(stop=MaxRuntime(2), display=False)
print(res)