目录
导入与设置
加载 CIFAR10 数据集
定义超参数
初始化 RandAugment 对象
创建 TensorFlow 数据集对象
可视化使用 RandAugment 增强的数据集
可视化使用 simple_aug 增强的数据集
定义模型构建实用功能
使用 RandAugment 训练模型
用 simple_aug 训练模型
加载 CIFAR-10-C 数据集并评估性能
政安晨的个人主页:政安晨
欢迎 👍点赞✍评论⭐收藏
收录专栏: TensorFlow与Keras机器学习实战
希望政安晨的博客能够对您有所裨益,如有不足之处,欢迎在评论区提出指正!
本文目标:用于训练图像分类模型的 RandAugment,具有更强的鲁棒性。
数据增强是一种非常有用的技术,有助于提高卷积神经网络(CNN)的平移不变性。RandAugment 是一种用于视觉数据的随机数据增强程序,在 RandAugment 中提出:RandAugment: Practical automated data augmentation with a reduced search space》一书中提出的。它由色彩抖动、高斯模糊、饱和度等强增强变换和随机作物等更传统的增强变换组成。
这些参数可根据给定的数据集和网络结构进行调整。
最近,它已成为 "噪声学生训练 "和 "一致性训练的无监督数据增强 "等工作的关键组成部分。它也是 EfficientNets 取得成功的关键。
pip install keras-cv导入与设置
import os
os.environ["KERAS_BACKEND"] = "tensorflow"
import keras
import keras_cv
from keras import ops
from keras import layers
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
tfds.disable_progress_bar()
keras.utils.set_random_seed(42)加载 CIFAR10 数据集
在本例中,我们将使用 CIFAR10 数据集。
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = keras.datasets.cifar10.load_data()
print(f"Total training examples: {len(x_train)}")
print(f"Total test examples: {len(x_test)}")演绎展示:
Total training examples: 50000
Total test examples: 10000定义超参数
AUTO = tf.data.AUTOTUNE
BATCH_SIZE = 128
EPOCHS = 1
IMAGE_SIZE = 72初始化 RandAugment 对象
现在,我们将使用 RandAugment 作者建议的参数,从 imgaug.augmenters 模块中初始化一个 RandAugment 对象。
rand_augment = keras_cv.layers.RandAugment(
value_range=(0, 255), augmentations_per_image=3, magnitude=0.8
)创建 TensorFlow 数据集对象
train_ds_rand = (
tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_train, y_train))
.shuffle(BATCH_SIZE * 100)
.batch(BATCH_SIZE)
.map(
lambda x, y: (tf.image.resize(x, (IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE)), y),
num_parallel_calls=AUTO,
)
.map(
lambda x, y: (rand_augment(tf.cast(x, tf.uint8)), y),
num_parallel_calls=AUTO,
)
.prefetch(AUTO)
)
test_ds = (
tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_test, y_test))
.batch(BATCH_SIZE)
.map(
lambda x, y: (tf.image.resize(x, (IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE)), y),
num_parallel_calls=AUTO,
)
.prefetch(AUTO)
)为了便于比较,我们还可以定义一个简单的增强管道,其中包括随机翻转、随机旋转和随机缩放。
simple_aug = keras.Sequential(
[
layers.Resizing(IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE),
layers.RandomFlip("horizontal"),
layers.RandomRotation(factor=0.02),
layers.RandomZoom(height_factor=0.2, width_factor=0.2),
]
)
# Now, map the augmentation pipeline to our training dataset
train_ds_simple = (
tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_train, y_train))
.shuffle(BATCH_SIZE * 100)
.batch(BATCH_SIZE)
.map(lambda x, y: (simple_aug(x), y), num_parallel_calls=AUTO)
.prefetch(AUTO)
)可视化使用 RandAugment 增强的数据集
sample_images, _ = next(iter(train_ds_rand))
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
for i, image in enumerate(sample_images[:9]):
ax = plt.subplot(3, 3, i + 1)
plt.imshow(image.numpy().astype("int"))
plt.axis("off")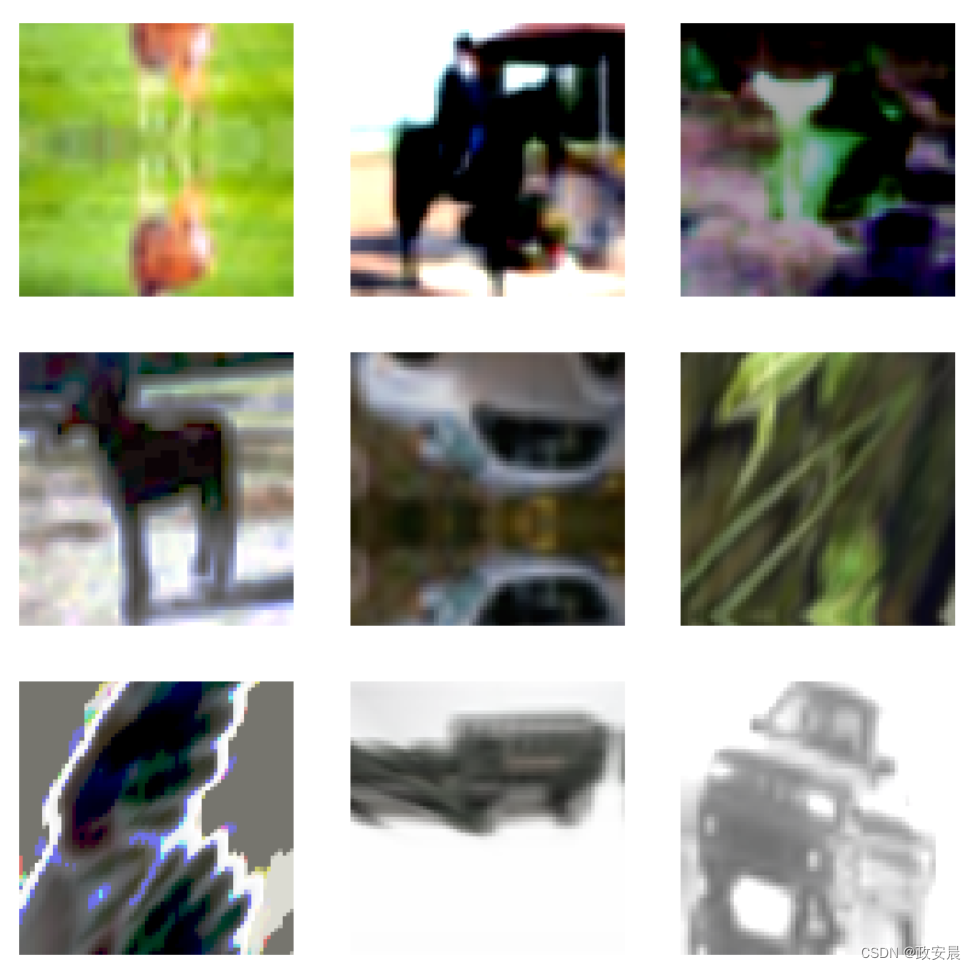
建议您多运行几次上述代码块,以了解不同的变化。
可视化使用 simple_aug 增强的数据集
sample_images, _ = next(iter(train_ds_simple))
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
for i, image in enumerate(sample_images[:9]):
ax = plt.subplot(3, 3, i + 1)
plt.imshow(image.numpy().astype("int"))
plt.axis("off")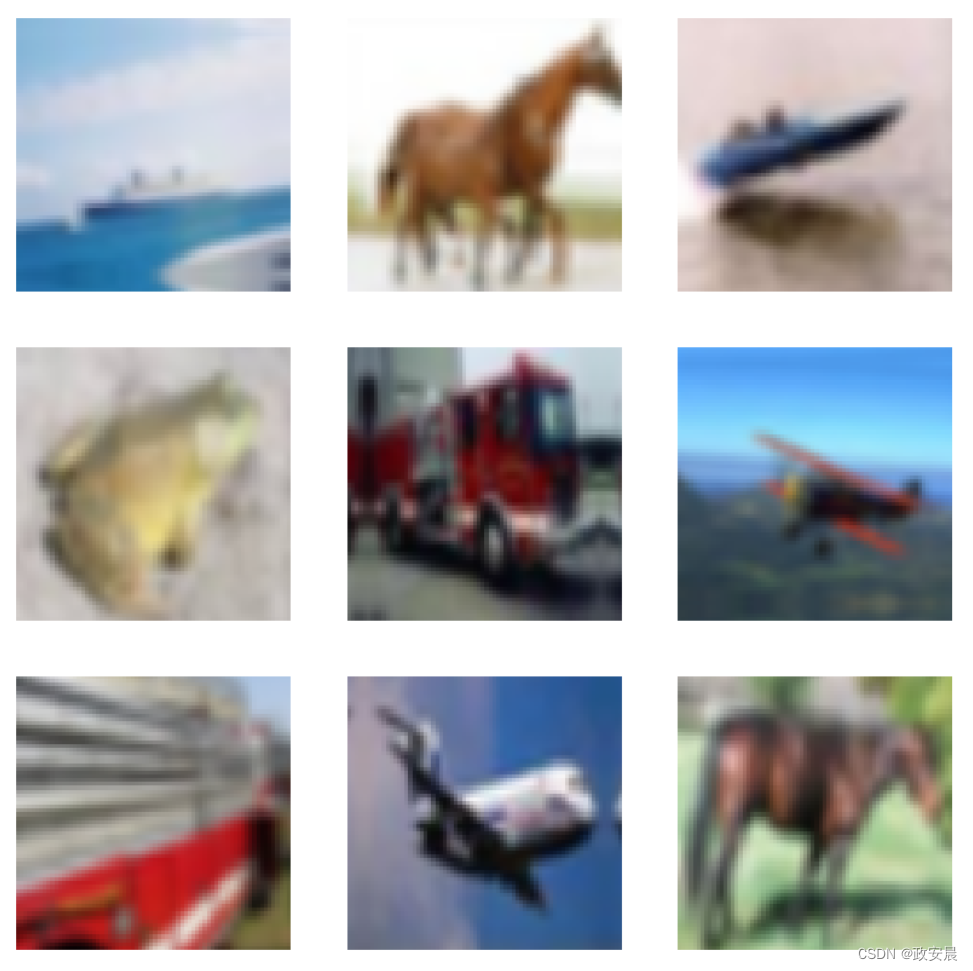
定义模型构建实用功能
现在,我们定义一个基于 ResNet50V2 架构的 CNN 模型。此外,请注意该网络内部已经有一个重缩放层。这样,我们就无需对数据集进行任何单独的预处理,特别是在部署时非常有用。
def get_training_model():
resnet50_v2 = keras.applications.ResNet50V2(
weights=None,
include_top=True,
input_shape=(IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, 3),
classes=10,
)
model = keras.Sequential(
[
layers.Input((IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, 3)),
layers.Rescaling(scale=1.0 / 127.5, offset=-1),
resnet50_v2,
]
)
return model
get_training_model().summary()演绎展示:
Model: "sequential_1"┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━┓ ┃ Layer (type) ┃ Output Shape ┃ Param # ┃ ┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━┩ │ rescaling (Rescaling) │ (None, 72, 72, 3) │ 0 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼───────────────────────────┼────────────┤ │ resnet50v2 (Functional) │ (None, 10) │ 23,585,290 │ └─────────────────────────────────┴───────────────────────────┴────────────┘Total params: 23,585,290 (89.97 MB)Trainable params: 23,539,850 (89.80 MB)Non-trainable params: 45,440 (177.50 KB)
我们将在两个不同版本的数据集上对该网络进行训练:
一个使用 RandAugment 增强。
另一个使用 simple_aug 增强。
众所周知,RandAugment 可以增强模型对常见扰动和损坏的鲁棒性,因此我们还将在 CIFAR-10-C 数据集上评估我们的模型,该数据集是 Hendrycks 等人在《神经网络对常见损坏和扰动的鲁棒性基准测试》(Benchmarking Neural Network Robustness to Common Corruptions and Perturbations)一文中提出的。
在本示例中,我们将使用以下配置:cifar10_corrupted/saturate_5。该配置下的图像如下。

为了提高可重复性,我们将浅层网络的初始随机权重序列化。
initial_model = get_training_model()
initial_model.save_weights("initial.weights.h5")使用 RandAugment 训练模型
rand_aug_model = get_training_model()
rand_aug_model.load_weights("initial.weights.h5")
rand_aug_model.compile(
loss="sparse_categorical_crossentropy", optimizer="adam", metrics=["accuracy"]
)
rand_aug_model.fit(train_ds_rand, validation_data=test_ds, epochs=EPOCHS)
_, test_acc = rand_aug_model.evaluate(test_ds)
print("Test accuracy: {:.2f}%".format(test_acc * 100))演绎展示:
391/391 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 1146s 3s/step - accuracy: 0.1677 - loss: 2.3232 - val_accuracy: 0.2818 - val_loss: 1.9966
79/79 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 39s 489ms/step - accuracy: 0.2803 - loss: 2.0073
Test accuracy: 28.18%用 simple_aug 训练模型
simple_aug_model = get_training_model()
simple_aug_model.load_weights("initial.weights.h5")
simple_aug_model.compile(
loss="sparse_categorical_crossentropy", optimizer="adam", metrics=["accuracy"]
)
simple_aug_model.fit(train_ds_simple, validation_data=test_ds, epochs=EPOCHS)
_, test_acc = simple_aug_model.evaluate(test_ds)
print("Test accuracy: {:.2f}%".format(test_acc * 100))演绎展示:
391/391 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 1132s 3s/step - accuracy: 0.3673 - loss: 1.7929 - val_accuracy: 0.4789 - val_loss: 1.4296
79/79 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 39s 494ms/step - accuracy: 0.4762 - loss: 1.4368
Test accuracy: 47.89%加载 CIFAR-10-C 数据集并评估性能
# Load and prepare the CIFAR-10-C dataset
# (If it's not already downloaded, it takes ~10 minutes of time to download)
cifar_10_c = tfds.load("cifar10_corrupted/saturate_5", split="test", as_supervised=True)
cifar_10_c = cifar_10_c.batch(BATCH_SIZE).map(
lambda x, y: (tf.image.resize(x, (IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE)), y),
num_parallel_calls=AUTO,
)
# Evaluate `rand_aug_model`
_, test_acc = rand_aug_model.evaluate(cifar_10_c, verbose=0)
print(
"Accuracy with RandAugment on CIFAR-10-C (saturate_5): {:.2f}%".format(
test_acc * 100
)
)
# Evaluate `simple_aug_model`
_, test_acc = simple_aug_model.evaluate(cifar_10_c, verbose=0)
print(
"Accuracy with simple_aug on CIFAR-10-C (saturate_5): {:.2f}%".format(
test_acc * 100
)
)演绎展示:
Downloading and preparing dataset 2.72 GiB (download: 2.72 GiB, generated: Unknown size, total: 2.72 GiB) to /home/sachinprasad/tensorflow_datasets/cifar10_corrupted/saturate_5/1.0.0...
Dataset cifar10_corrupted downloaded and prepared to /home/sachinprasad/tensorflow_datasets/cifar10_corrupted/saturate_5/1.0.0. Subsequent calls will reuse this data.
Accuracy with RandAugment on CIFAR-10-C (saturate_5): 30.36%
Accuracy with simple_aug on CIFAR-10-C (saturate_5): 37.18%在本例中,我们只对模型进行了单次训练。
在 CIFAR-10-C 数据集上,与使用 simple_aug 训练的模型(例如,64.80%)相比,使用 RandAugment 的模型表现更好,准确率更高(例如,在一次实验中为 76.64%)。RandAugment 还有助于稳定训练。
您可能会注意到,虽然使用 RandAugment 增加了训练时间,但我们在 CIFAR-10-C 数据集上的表现却要好得多。您可以在运行相同的 CIFAR-10-C 数据集时,尝试使用其他损坏和扰动设置,看看 RandAugment 是否有帮助。
您还可以尝试使用 RandAugment 对象中不同的 n 和 m 值。