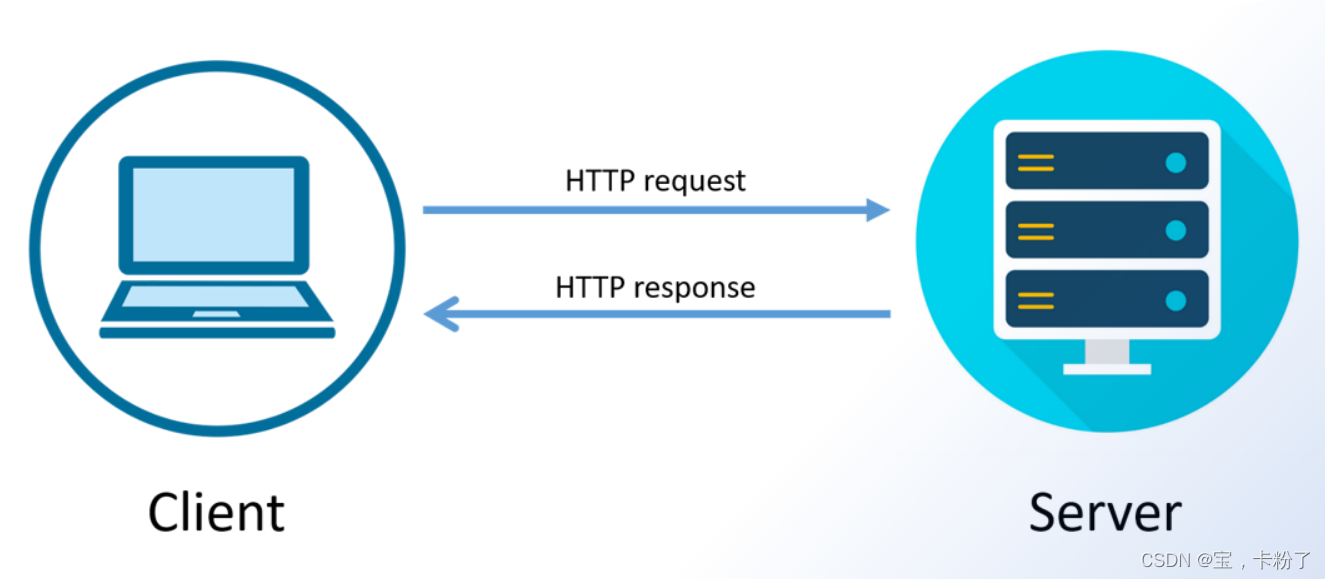
Web 访问过程:
HTTP请求报文(请求行、请求头、请求体)以及响应报文:
http://t.csdnimg.cn/GtEJw![]() http://t.csdnimg.cn/GtEJw
http://t.csdnimg.cn/GtEJw
补充:
Apache HTTPD服务器的安装与配置
安装:
[root@webserver ~]# yum -y install httpd
[root@webserver ~]# systemctl enable --now httpd
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service →/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service.
[root@webserver ~]# echo test for apache httpd > /var/www/html/index.html
[root@webserver ~]# cat /var/www/html/index.html
test for apache httpd
[root@webserver ~]# curl 127.0.0.1
test for apache httpd
[root@webserver ~]# curl -I 127.0.0.1
HTTP/1.1 200 OK //状态码为 200 说明服务端
//为客户端的访问提供了响应代码为200的
响应
Date: Sun, 21 Apr 2024 08:49:55 GMT
Server: Apache/2.4.37 (Red Hat Enterprise Linux)
Last-Modified: Sun, 21 Apr 2024 08:49:23 GMT
ETag: "16-6169765c97f13"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
Content-Length: 22
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8配置:
[root@webserver ~]# grep -v '#' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf | grep -v '^$'
ServerRoot "/etc/httpd" # 使用相对路径引入文件到主配置文件时,相对路径+此处的路径
来形成一个从/开始的绝对路径
Listen 80 # 监听TCP 80端口,可以使用Ip地址:端口的当时修改
# 可以配置多个Listen监听多个不同的端口,但是重复的
Listen配置将导致HTTPD无法启动
Include conf.modules.d/*.conf
# 所有/etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/目录下.conf结尾的文件都
# 导入到/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
User apache # 程序用户为apache
Group apache # 程序组账号为apache
ServerAdmin root@localhost # 服务器管理员邮箱
<Directory />
# <Directory>块设置指定目录以及所有后代目录的配置指令。
# <Directory>块中的常见指令包括以下几种:
# Allow0verride None:对于按目录的配置设置,将不会查阅
# .htaccess 文件。将其设置为任何其他设置都将导致
# 性能损失以及可能的安全后果。
# Require A11 Denied:httpd 将拒绝提供此目录的内容,
# 当客户端请求时,将返回HTTP/1.1403 Forbidden错误。
# Require A11 Granted:允许访问此目录。对普通内容树之
# 外的目录设置此选项可能会产生安全影响。
# 0ptions[[+|-]0PTIONS]...:为某个目录开启(或关闭)
# 特定选项。例如,如果请求了某个目录并且该目录中不存在
# index.htm1文件,则Indexes 选项将显示一个目录列表。
AllowOverride none
Require all denied
</Directory>
DocumentRoot "/var/www/html" #此设置确定 httpd 将搜索请求文件的位置。重要的一点是,
# 此处指定的目录可以由httpd(常规权限和 SELinux)读取
# ,并且对应的 <Directory>块已声明为允许访问。
<Directory "/var/www">
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
<Directory "/var/www/html">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
<IfModule dir_module> # 仅当加载指定扩展模块时,此块才会应用其内容。在此情况下,
# 会加载dir_module,因此DirectoryIndex 指令可用于
# 指定在请求目录时应使用的文件。
DirectoryIndex index.html
</IfModule>
<Files ".ht*"> # 类似于Directory,
Require all denied
</Files>
ErrorLog "logs/error_log" # 错误日志
LogLevel warn
<IfModule log_config_module> # 指定了几种日志格式,分别是combined、common、
combinedio;默认场景下均使用combined这种日志格式
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\""
combined
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b" common
<IfModule logio_module>
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{UserAgent}i\" %I %O" combinedio
</IfModule>
CustomLog "logs/access_log" combined
</IfModule>
<IfModule alias_module>
ScriptAlias /cgi-bin/ "/var/www/cgi-bin/"
</IfModule>
<Directory "/var/www/cgi-bin">
AllowOverride None
Options None
Require all granted
</Directory>
<IfModule mime_module>
TypesConfig /etc/mime.types
AddType application/x-compress .Z
AddType application/x-gzip .gz .tgz
AddType text/html .shtml
AddOutputFilter INCLUDES .shtml
</IfModule>
AddDefaultCharset UTF-8 # 此设置向 text/plain和 text/htm1 资源的
# Content-Type 报头中添加 charset 部分。
# 可以使用 AddDefaultCharset 0ff将其禁用
<IfModule mime_magic_module>
MIMEMagicFile conf/magic
</IfModule>
EnableSendfile on # 启用 EnableSendfile 以提高文件传输的性能和效率。
IncludeOptional conf.d/*.conf # 所有/etc/httpd/conf.d/目录下.conf结尾的文件都
# 导入到/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
修改首页:
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
修改 Listen 80 一行 为 Listen 8080
修改 DocumentRoot “/var/www/html“一行为 DocumentRoot "/home/www“
修改<Directory “/var/www/html”> 一行为 <Directory "/home/www">
修改 <IfModule dir_module> 块 内 DirectoryIndex index.html 一行为 DirectoryIndex home.html打开目录权限 :
chmod 755 /home/www
chmod 644 /home/www/home.html
重启:
systemctl restart httpd
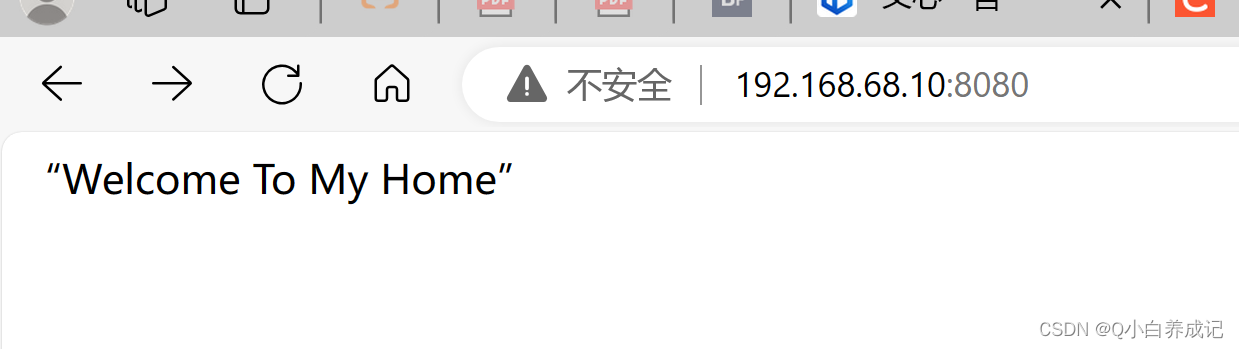
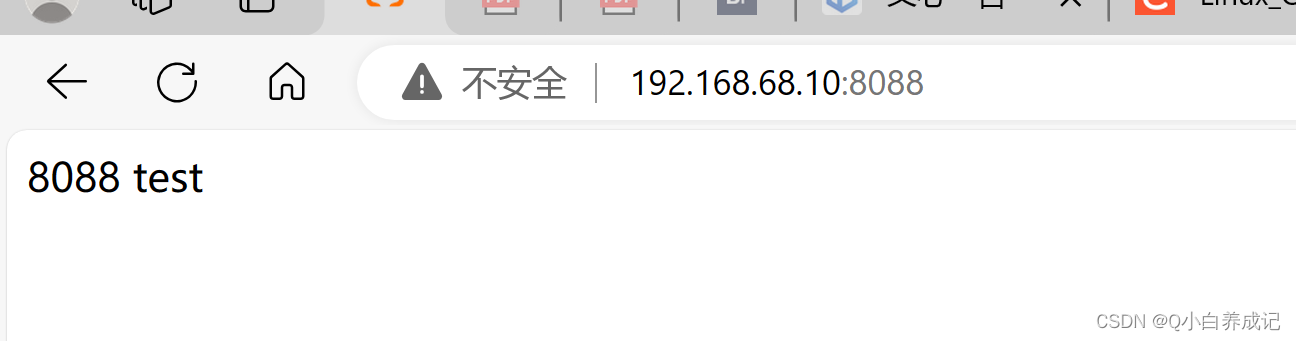
配置基于端口的虚拟主机
创建目录、文件,并赋予权限755
mkdir /home/www/8088
mkdir /home/www/8089
# 8088 对应的页面
echo "8088 test" >> /home/www/8088/index.html
# 8089 对应的页面
echo "8089 test" >> /home/www/8089/index.html
chmod 755 /home/www/8088
chmod 755 /home/www/8089
修改配置
恢复原来的主配置文件为默认,所有的虚拟主机配置,保存在专门的文件中
cp /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf.bac /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf[root@nfs-server conf]# touch /etc/httpd/conf.d/myvhost.conf
[root@nfs-server conf]# cat /etc/httpd/conf.d/myvhost.conf
# match a ServerName or ServerAlias in any <VirtualHost> block.
Listen 8088
<VirtualHost *:8088>
DocumentRoot "/home/www/8088"
ServerName localhost
ErrorLog "/var/log/httpd/host8088-error_log"
CustomLog "/var/log/httpd/host8088-access_log" combined
</VirtualHost>
<Directory "/home/www/8088">
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
Listen 8089
<VirtualHost *:8089>
DocumentRoot "/home/www/8089"
ServerName localhost
ErrorLog "/var/log/httpd/host8089-error_log"
CustomLog "/var/log/httpd/host8089-access_log" combined
</VirtualHost>
<Directory "/home/www/8089">
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
重启验证
[root@nfs-server conf]# systemctl restart httpd

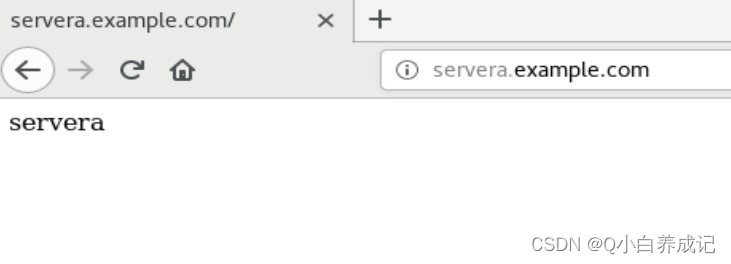
基于主机名的虚拟主机配置
创建目录、文件,并赋予权限755
[root@nfs-server conf]# mkdir -p /vhost/server{a,b}
[root@nfs-server conf]# echo servera > /vhost/servera/index.html
[root@nfs-server conf]# echo serverb > /vhost/serverb/index.html
[root@nfs-server conf]# chmod 755 /vhost/servera
[root@nfs-server conf]# chmod 755 /vhost/serverb
配置主机名解析记录
[root@nfs-server conf]# echo '192.168.68.10 servera.example.com servera' >>/etc/hosts
[root@nfs-server conf]# echo '192.168.68.10 serverb.example.com serverb' >>/etc/hosts
修改配置文件
ServerName localhost[root@nfs-server conf]# cat /etc/httpd/conf.d/mhost.conf
<VirtualHost *:80>
DocumentRoot "/vhost/servera"
ServerName servera.example.com
ServerAlias servera
ErrorLog "/var/log/httpd/servera-error_log"
CustomLog "/var/log/httpd/servera-access_log" combined
</VirtualHost>
<Directory "/vhost/servera">
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
<VirtualHost *:80>
DocumentRoot "/vhost/serverb"
ServerName serverb.example.com
ErrorLog "/var/log/httpd/serverb-error_log"
CustomLog "/var/log/httpd/serverb-access_log" combined
</VirtualHost>
<Directory "/vhost/serverb">
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
重启测试
systemctl restart httpd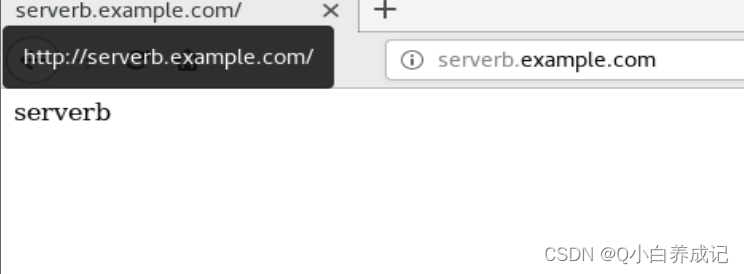
动态内容和CGI
常见支持动态内容解析的 Web 架构通常包括以下组件:
1. Web 服务器:负责接收客户端的请求并返回响应,通常使用 Apache、Nginx 等流行的 Web 服务 器。
2. 应用服务器:负责处理动态内容生成的逻辑,执行程序代码,并生成最终的 HTML 页面或其他格 式的响应。常见的应用服务器包括: PHP:PHP 是一种广泛使用的服务器端脚本语言,通常与 Apache 或 Nginx 搭配使用,通过 解释 PHP 脚本来生成动态内容。 Python:Python 也是一种常用的服务器端脚本语言,常用的 Web 框架如 Django、Flask 等 可以用来处理动态内容。 Node.js:Node.js 是基于 JavaScript 的服务器端运行环境,可以用于构建高性能的动态内容 应用程序。 Java:Java 可以通过 Java Servlet、JSP 等技术来处理动态内容生成。
3. 数据库:用于存储和管理动态内容所需的数据,常见的数据库包括: MySQL:MySQL 是一种流行的关系型数据库管理系统,常用于存储和管理网站的数据。 PostgreSQL:PostgreSQL 是另一种开源的关系型数据库管理系统,具有更强大的功能和扩 展性。 MongoDB:MongoDB 是一种非关系型数据库,适用于存储和处理非结构化或半结构化的数 据。
处理过程:
1. 用户发送 HTTP 请求: 用户在浏览器中输入 URL 或者点击链接,向 Web 服务器发送 HTTP 请 求。
2. Apache 接收请求: Apache Web 服务器接收到用户的 HTTP 请求。
3. 请求路由: Apache 根据请求的 URL 路径和配置的虚拟主机配置,将请求路由到相应的网站根目 录或者指定的目录。
4. 处理静态资源: 如果请求的是静态资源(如 HTML、CSS、JavaScript、图片等),Apache 直接 从文件系统中读取并返回给客户端。
5. 动态内容请求: 如果请求的是动态内容(如 PHP 脚本),Apache 将请求转发给 PHP 解释器。
6. PHP 解释器处理请求: PHP 解释器接收到请求后,会执行相应的 PHP 脚本,根据脚本中的逻辑 生成动态的 HTML 内容。
7. 与数据库交互: 如果 PHP 脚本需要从数据库中读取或者写入数据,它会通过 MySQL(或 MariaDB)客户端库与 MySQL 数据库服务器建立连接,并执行相应的 SQL 查询或者操作。
8. 生成响应: PHP 脚本执行完毕后,将生成的 HTML 内容以及其他资源(如图片、CSS、JavaScript 等)返回给 Apache。
9. Apache 返回响应: Apache 将 PHP 脚本生成的 HTML 内容以及其他资源打包成 HTTP 响应,并 发送给客户端浏览器。
10. 浏览器渲染页面: 客户端浏览器接收到 HTTP 响应后,根据 HTML 内容解析和渲染页面,呈现给 用户。
安装并启动所有的程序
[root@webserver ~]# yum -y install httpd php php-fpm mariadb-server
[root@webserver ~]# systemctl start php-fpm mariadb httpd
[root@webserver ~]# systemctl enable php-fpm mariadb httpd
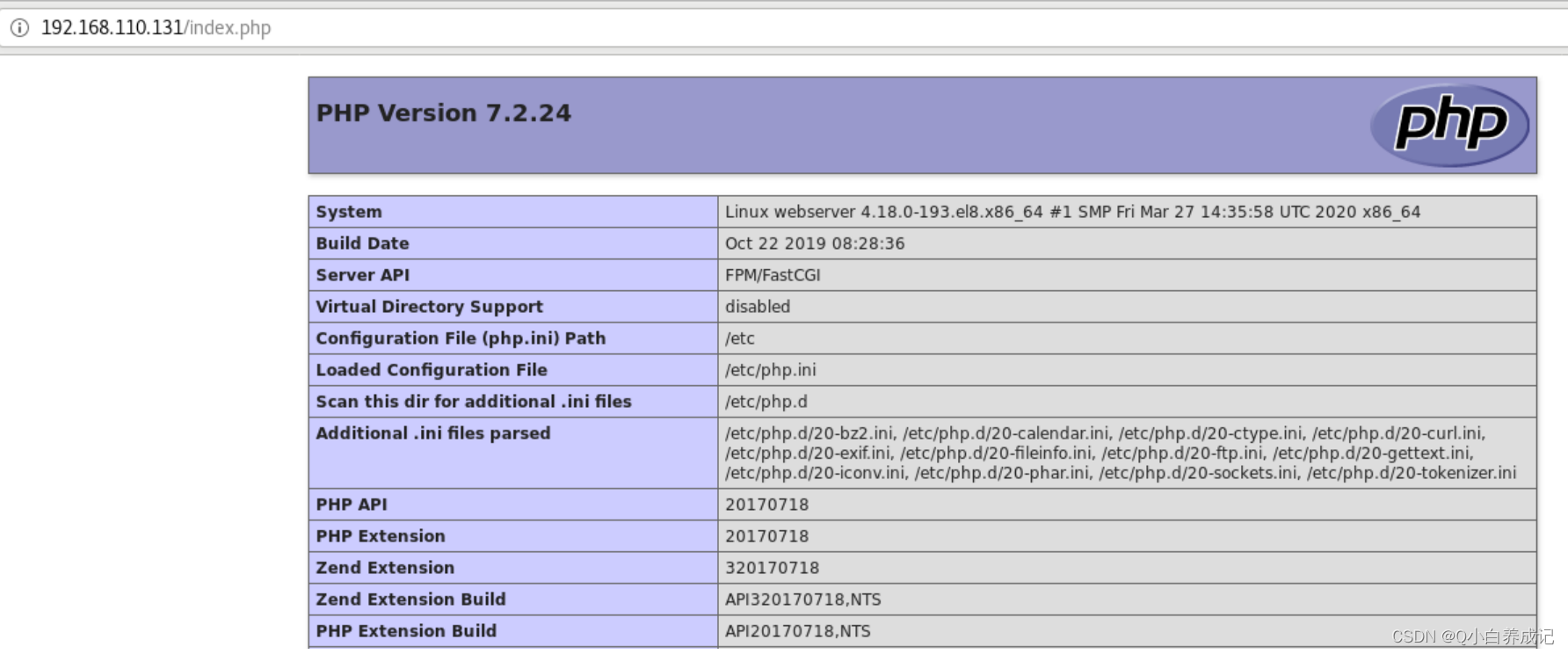
调试web服务器可以传递PHP脚本的运行结果给客户端
# 编写一个测试文件,在默认的主页目录下
[root@webserver ~]# vim /var/www/html/index.php
<?php
phpinfo();
?>