查询(排序、过滤、分页)
【0】准备
(1)Q查询
- 详细内容可见:Django模型层-CSDN博客
- Django 的
Q对象提供了一种在数据库查询中构造复杂查询的方法。当你想在单个查询中组合多个过滤条件,并且这些条件之间不仅仅是简单的AND关系时,Q对象就显得非常有用。 - 导入:
from django.db.models import Q - 简单示例:或与非
# 查找 name 字段为 'John' 或 age 字段大于 30 的对象
MyModel.objects.filter(Q(name='lily') | Q(age__gt=30))
# 查找 name 字段为 'John' 并且 age 字段大于 30 的对象
MyModel.objects.filter(Q(name='lily') & Q(age__gt=30))
# 查找 name 字段不是 'John' 的对象
MyModel.objects.filter(~Q(name='lily'))
(2)数据准备
- 模型表
from django.db import models
class Book(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=64, verbose_name="书名")
price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=6, decimal_places=2, verbose_name="价格")
publish_name = models.CharField(max_length=64, verbose_name="出版社名字")
# 数据信息
INSERT INTO `test04_book` (`id`, `name`, `price`, `publish_name`) VALUES (1, '三国演绎', 99.00, '东方出版社');
INSERT INTO `test04_book` (`id`, `name`, `price`, `publish_name`) VALUES (2, '新三国', 105.00, '东方出版社');
INSERT INTO `test04_book` (`id`, `name`, `price`, `publish_name`) VALUES (3, '小王子', 89.00, '西方出版社');
INSERT INTO `test04_book` (`id`, `name`, `price`, `publish_name`) VALUES (4, '新能源', 99.00, '南方出版社');
INSERT INTO `test04_book` (`id`, `name`, `price`, `publish_name`) VALUES (5, '永动机', 105.00, '东方出版社');
INSERT INTO `test04_book` (`id`, `name`, `price`, `publish_name`) VALUES (6, '黑火药', 99.00, '北方出版社');
INSERT INTO `test04_book` (`id`, `name`, `price`, `publish_name`) VALUES (7, '支付宝', 109.00, '东方出版社');
INSERT INTO `test04_book` (`id`, `name`, `price`, `publish_name`) VALUES (8, '云电脑', 101.00, '西方出版社');
- 序列化类
from rest_framework.serializers import ModelSerializer
from .models import Book
class BookModelSerializer(ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = Book
fields = '__all__'
- 视图函数和路由
# 视图层
from rest_framework.viewsets import ReadOnlyModelViewSet
from .serializer import BookModelSerializer
from .models import Book
class BookAPIView(ReadOnlyModelViewSet):
queryset = Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = BookModelSerializer
# 路由层
from django.urls import path, include
from .views import BookAPIView
from rest_framework.routers import SimpleRouter
router = SimpleRouter()
router.register(prefix='books', viewset=BookAPIView, basename='books')
urlpatterns = [
path('', include(router.urls))
]
【1】排序
(1)介绍
- 在
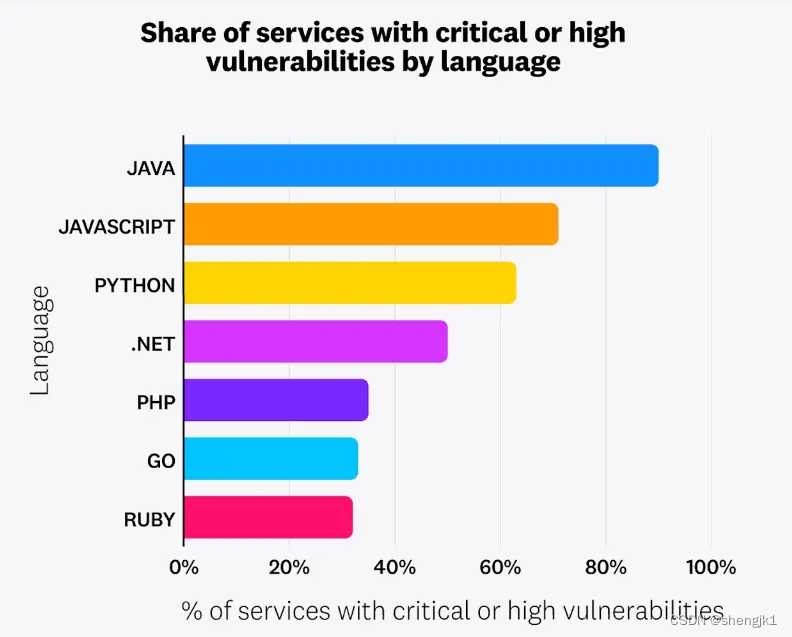
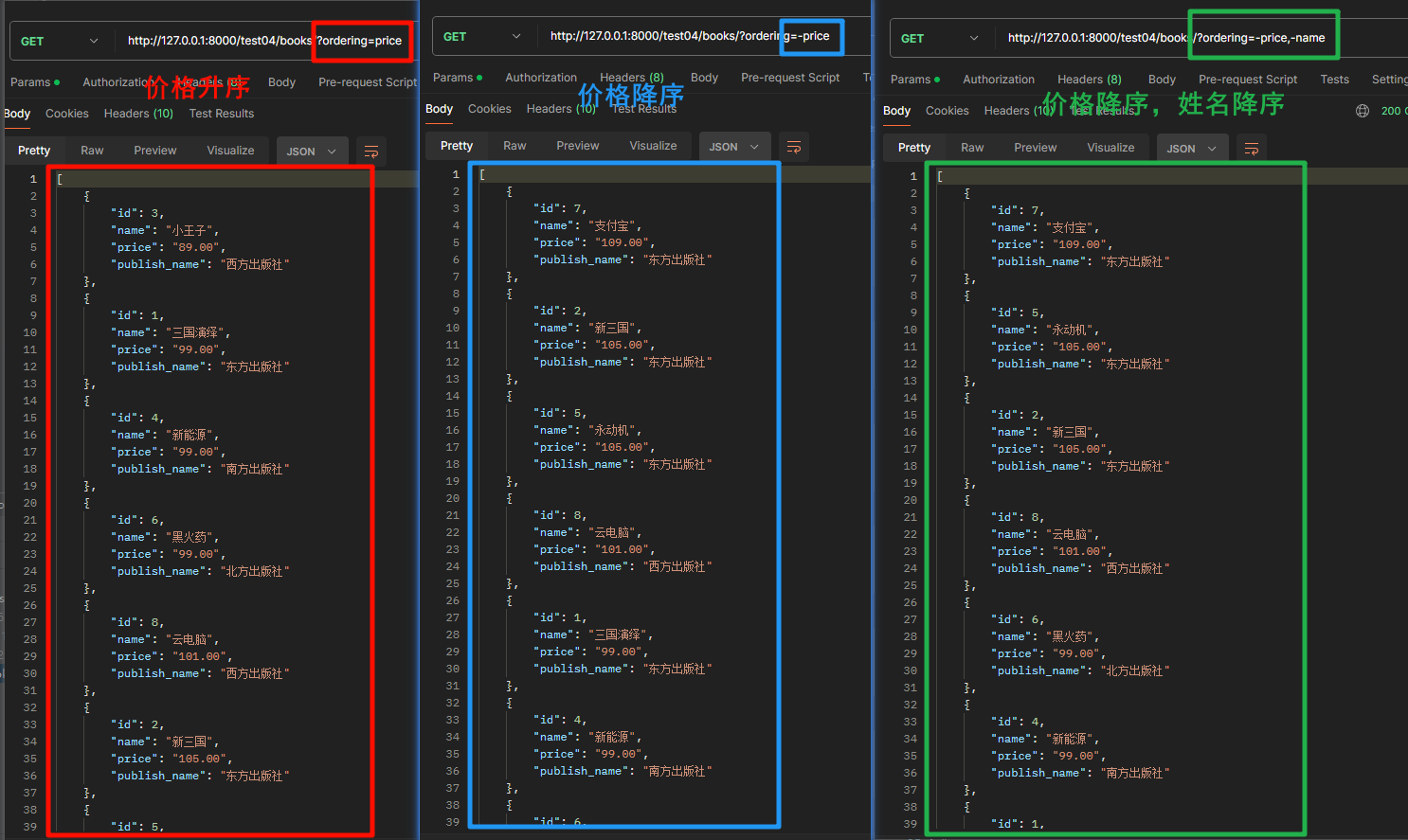
restful规范中,有提到查询地址中可以带条件,默认排序条件是pk - 即:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/test04/books/?ordering=price表示按照价格从低到高排序http://127.0.0.1:8000/test04/books/?ordering=-price表示按照价格从高到低排序http://127.0.0.1:8000/test04/books/?ordering=price,name表示价格从低到高,同价格的情况下,在名字以低到高排序
(2)简单使用
- 必须要是继承 GenericAPIView 的视图类
filter_backends=[排序类, ]:排序类的地址ordering_fields = ['子段1', '子段2'...]:这里的字段没有先后顺序,只是指定排序的字段可以有哪些
from rest_framework.filters import OrderingFilter, SearchFilter
class BookAPIView(ReadOnlyModelViewSet):
queryset = Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = BookModelSerializer
filter_backends = [OrderingFilter]
ordering_fields = ['price', 'name']
- 注意:如果有自定义的内容,需要重写父类的方法比如List,一定要使用self.filter_queryset(self.get_queryset()),而不是使用self.get_queryset(),因为后者将没有排序的功能
【2】过滤
- 如果提示
UnorderedObjectListWarning: Pagination may yield inconsistent results with an unordered object_list:- 可以在
queryset后面加上.order_by('id')默认以id排序
- 可以在
(1)内置:多字段(与的条件)模糊匹配
-
必须要是继承 GenericAPIView 的视图类
-
和排序一样需要,需要添加两个类属性,不过有个是一样的,即过滤和排序是可以同时使用的
-
filter_backends=[过滤类, ]:过滤类的地址,这里的先后顺序不影响结果,只不过一个是先过滤再排序,一个是先排序再过滤 -
search_fields= ['子段1', '子段2'...]:这里的字段也没有先后顺序,只是指定排序的字段可以有哪些 -
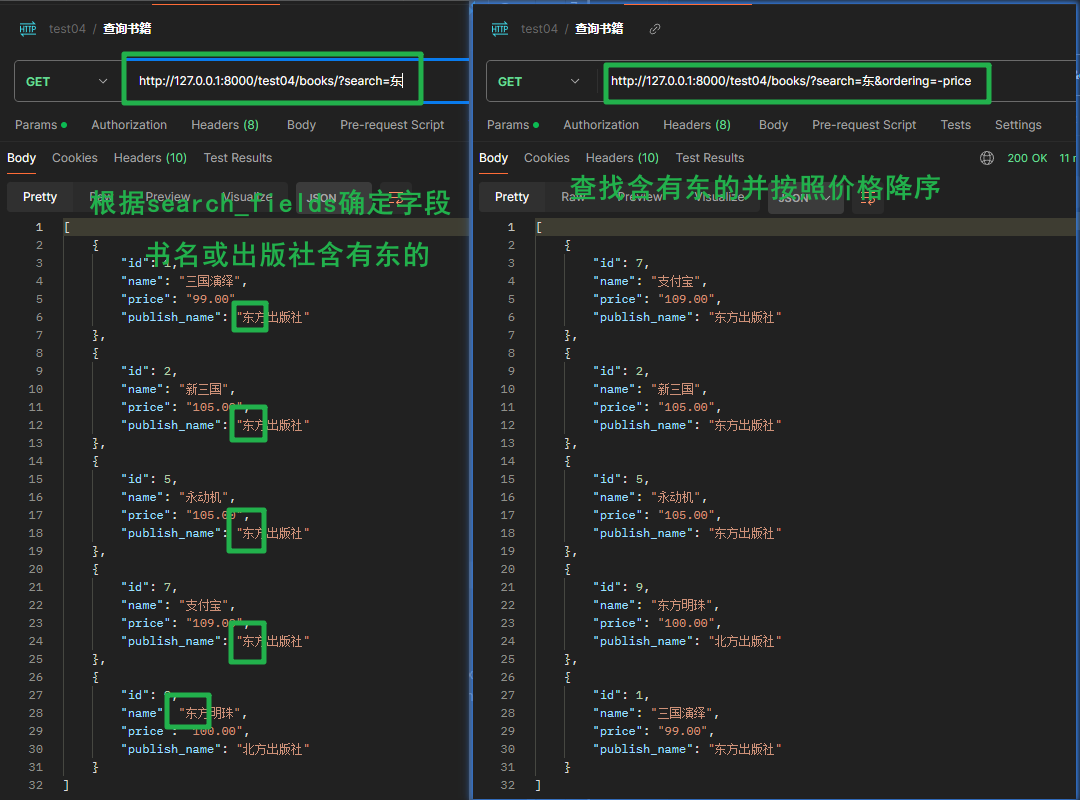
路由示例:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/test04/books/?search=东- 根据
search_fields的字段,模糊匹配含有东的
- 根据
from rest_framework.filters import OrderingFilter, SearchFilter
class BookAPIView(ReadOnlyModelViewSet):
queryset = Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = BookModelSerializer
filter_backends = [OrderingFilter, SearchFilter]
ordering_fields = ['price', 'name']
search_fields = ['name', 'publish_name']
(2)第三方过滤
-
导包:
pip install django-filterfrom django_filters.rest_framework import DjangoFilterBackend
-
类属性:
filter_backends=[过滤类, ]:过滤类的地址,这里的先后顺序不影响结果,只不过一个是先过滤再排序,一个是先排序再过滤filterset_fields= ['子段1', '子段2'...]:这里的字段也没有先后顺序,只是指定排序的字段可以有哪些
from django_filters.rest_framework import DjangoFilterBackend
class BookAPIView(ReadOnlyModelViewSet):
queryset = Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = BookModelSerializer
filter_backends = [DjangoFilterBackend]
filterset_fields = ['price', 'publish_name']
(3)自定义过滤类
-
自定义的难度虽然大,但是这确实使用最多的
- 需要写的类继承
BaseFilterBackend - 重写
filter_queryset方法 - 并返回过滤以后的
queryset对象
- 需要写的类继承
-
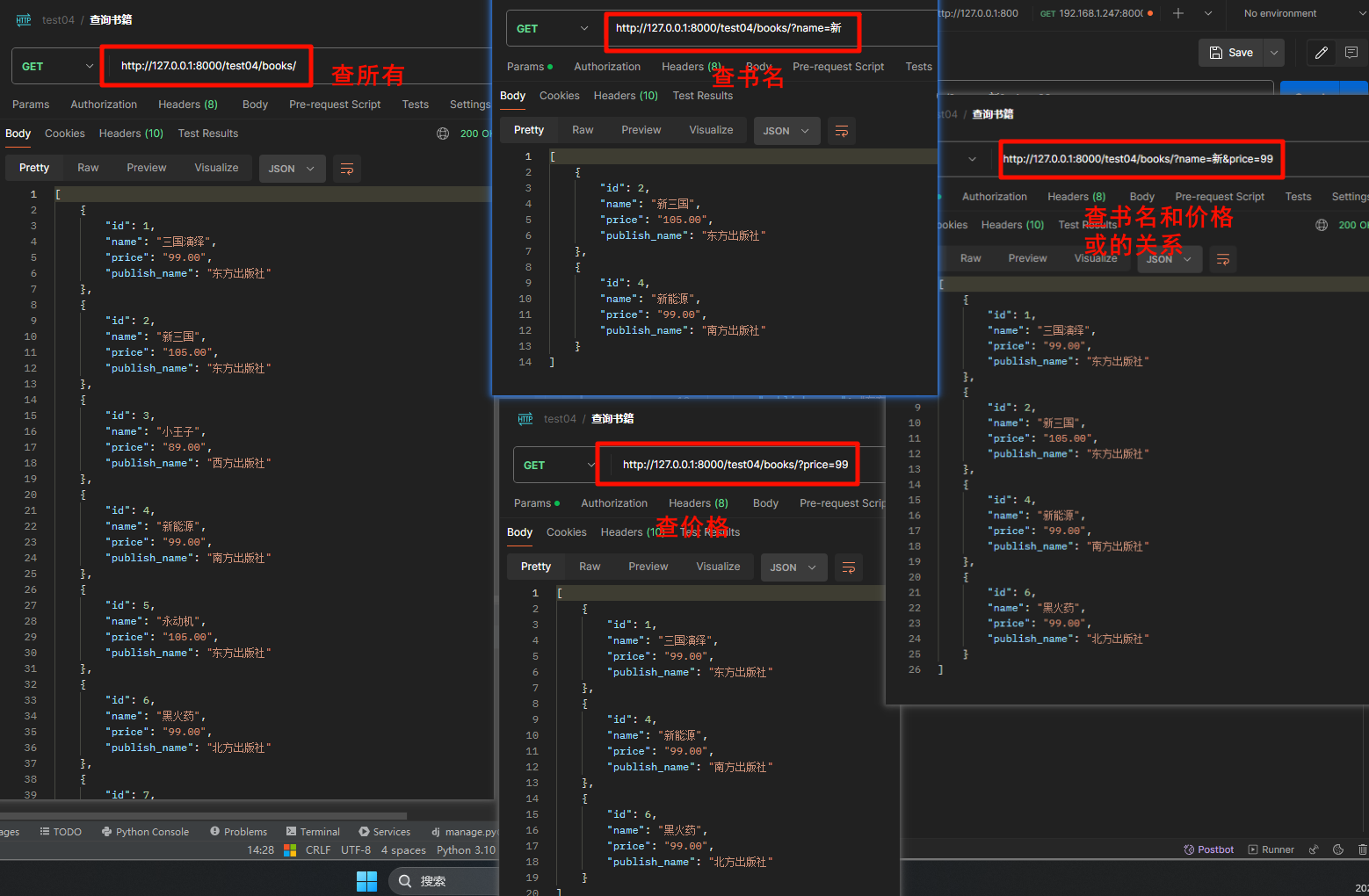
示例要求:
- 这里以价格或者书名进行过滤,可以两个同时给,可以不给,可以指定一个
- 书名模糊匹配,价格是指定价格
from rest_framework.filters import BaseFilterBackend
from django.db.models import Q
class CommonFilter(BaseFilterBackend):
def filter_queryset(self, request, queryset, view):
name = request.query_params.get('name')
price = request.query_params.get('price')
# 两个参数都有
if all([name, price]):
queryset = queryset.filter(Q(name__contains=name) | Q(price=price))
return queryset
# 只用价格
elif price:
queryset = queryset.filter(price=price)
return queryset
# 只用书名
elif name:
queryset = queryset.filter(name__contains=name)
return queryset
# 视图层
from .filter import CommonFilter
class BookAPIView(ReadOnlyModelViewSet):
queryset = Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = BookModelSerializer
filter_backends = [CommonFilter]
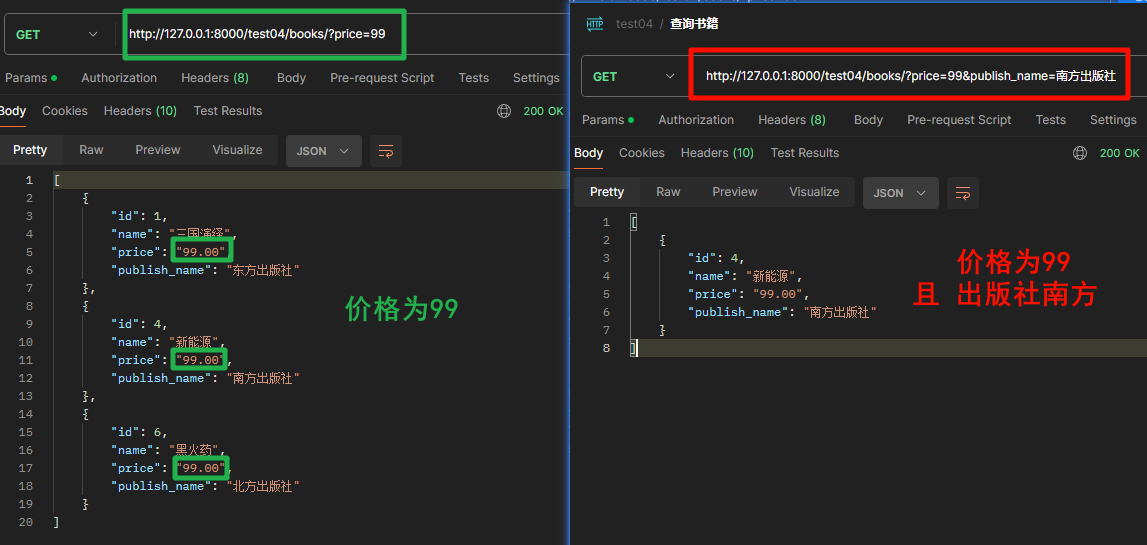
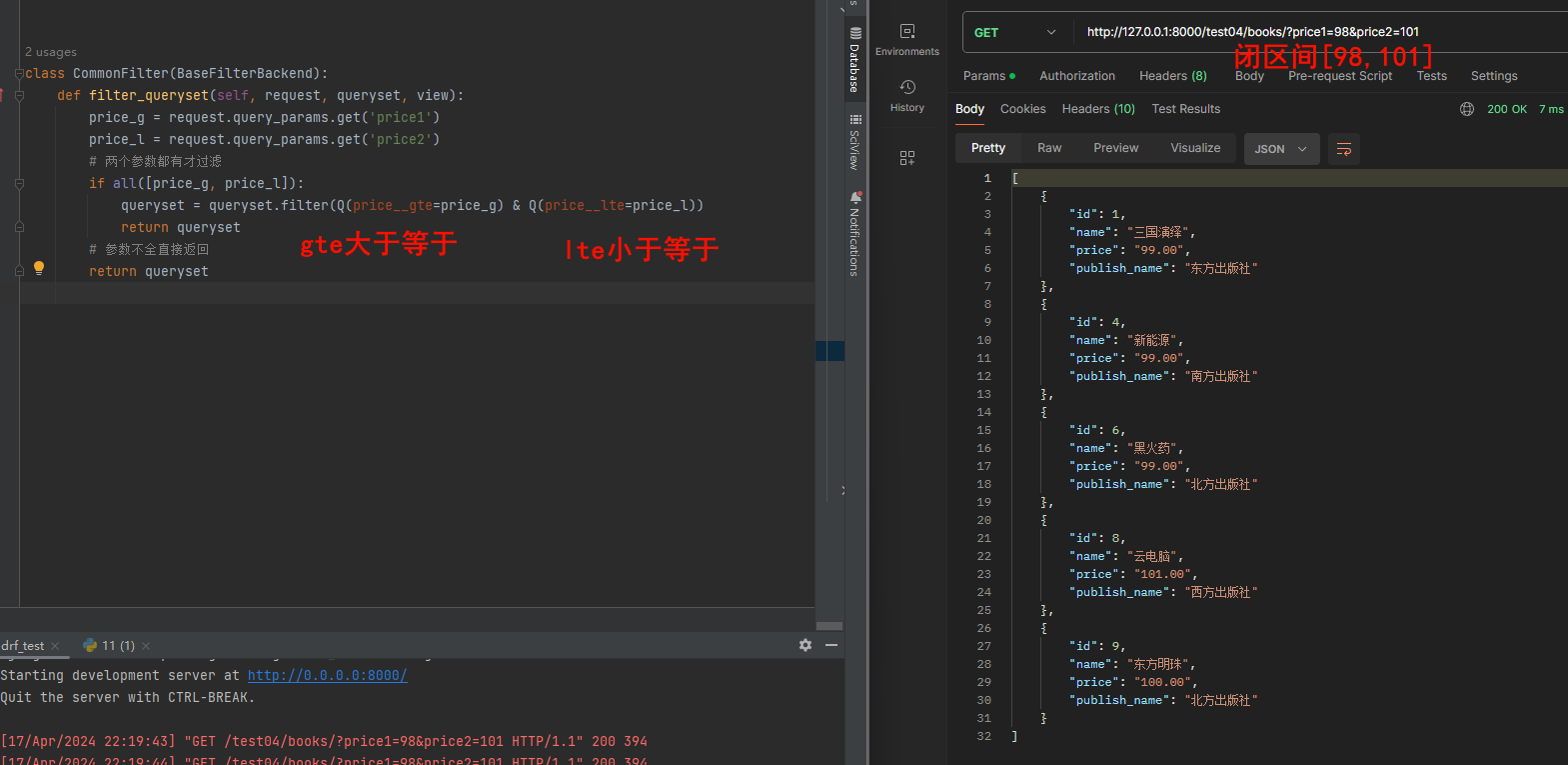
- 示例二:只按照价格过滤,但是价格是一个区间
class CommonFilter(BaseFilterBackend):
def filter_queryset(self, request, queryset, view):
price_g = request.query_params.get('price1')
price_l = request.query_params.get('price2')
# 两个参数都有才过滤
if all([price_g, price_l]):
queryset = queryset.filter(Q(price__gte=price_g) & Q(price__lte=price_l))
return queryset
# 参数不全直接返回
return queryset
【3】分页
pagination_class不是一个列表,所以只能
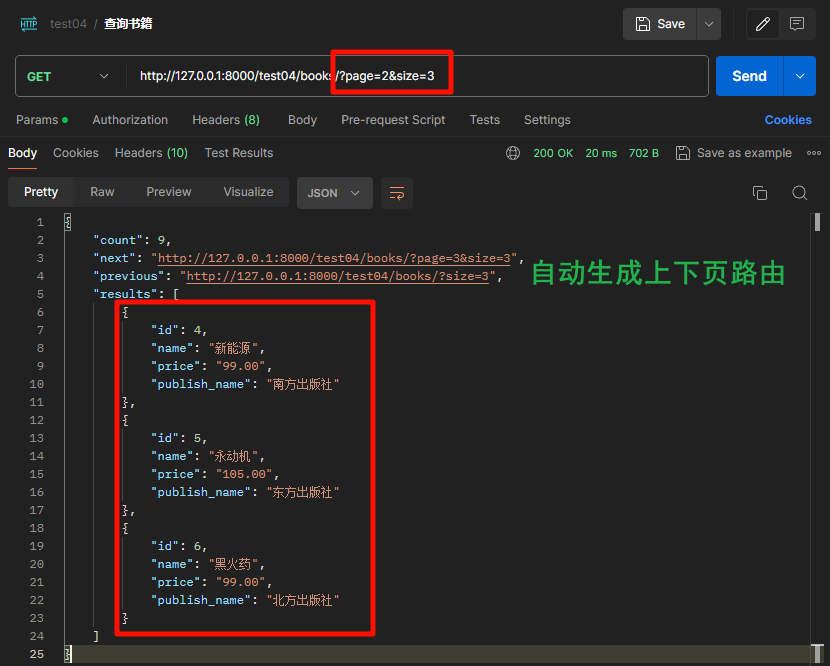
(1)基本分页
- 继承
PageNumberPagination指定类变量page_size = 2默认每页数量,可以指定size超过数量page_query_param = 'page'路由页码关键字page_size_query_param = 'size'路由每页数量关键字max_page_size = 10每页最多显示数量
from rest_framework.pagination import PageNumberPagination
class CommonPagination(PageNumberPagination):
page_size = 2 # 默认每页数量
page_query_param = 'page' # 路由页码关键字
page_size_query_param = 'size' # 路由每页数量关键字
max_page_size = 10 # 每页显示的最大条数
# 视图函数
from .pagination import CommonPagination
class BookAPIView(ReadOnlyModelViewSet):
queryset = Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = BookModelSerializer
pagination_class = CommonPagination
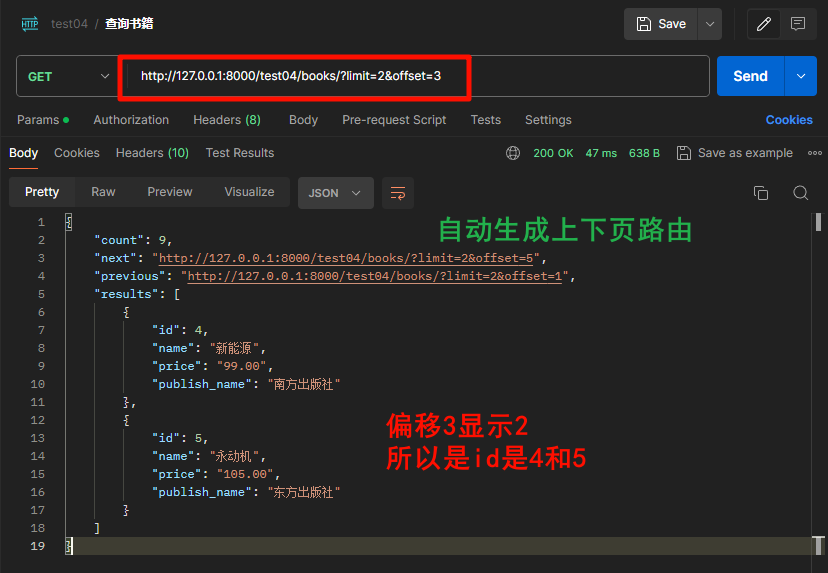
(2)偏移分页
- 继承
LimitOffsetPagination指定类变量default_limit= 2默认每页数量,可以指定limit超过数量limit_query_param = 'limit'路由每页数量关键字offset_query_param= 'offset'路由偏移量关键字max_limit = 10每页最多显示数量
from rest_framework.pagination import LimitOffsetPagination
class CommonPagination(LimitOffsetPagination):
default_limit = 2 # 默认每页数量
limit_query_param = 'limit' # 路由每页数量关键字
offset_query_param = 'offset' # 路由偏移量关键字
max_limit = 10 # 每页最多显示数量
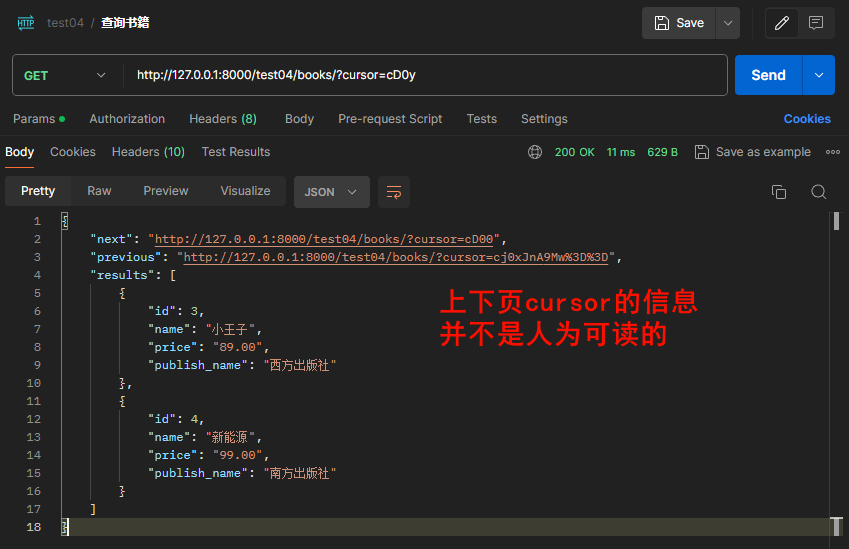
(3)游标分页
- 优势
- 性能优化:游标分页不需要跳过任何行,它只需要从上一页的最后一个项目开始。这意味着数据库只需要处理实际需要的数据,而不是像偏移分页那样需要处理OFFSET指定的所有数据。这种特性使得游标分页在处理大量数据时具有更高的效率。
- 数据一致性:即使有新的数据插入,也不会影响已经浏览过的页面。这是因为每一页的数据都是基于上一页的最后一个项目,而不是基于页数。这种特性确保了用户浏览的数据始终是最新的,避免了数据不一致的问题。
- 用户体验:游标分页允许用户连续浏览数据,提供了更好的用户体验。这是因为游标分页是根据当前查询结果的位置来动态生成分页结果,使得用户可以无缝地浏览数据库中大量的数据。
- 继承
PageNumberPagination指定类变量page_size= 2默认每页数量,可以指定size超过数量cursor_query_param = 'cursor'路由关键字ordering= 10排序字段,必须有- ordering= ‘-created’:created有这个字段的,按照倒叙来
from rest_framework.pagination import CursorPagination
class CommonPagination(CursorPagination):
cursor_query_param = 'cursor' # 路由关键字
page_size = 2 # 默认每页的数量
ordering = 'id' # 排序规则