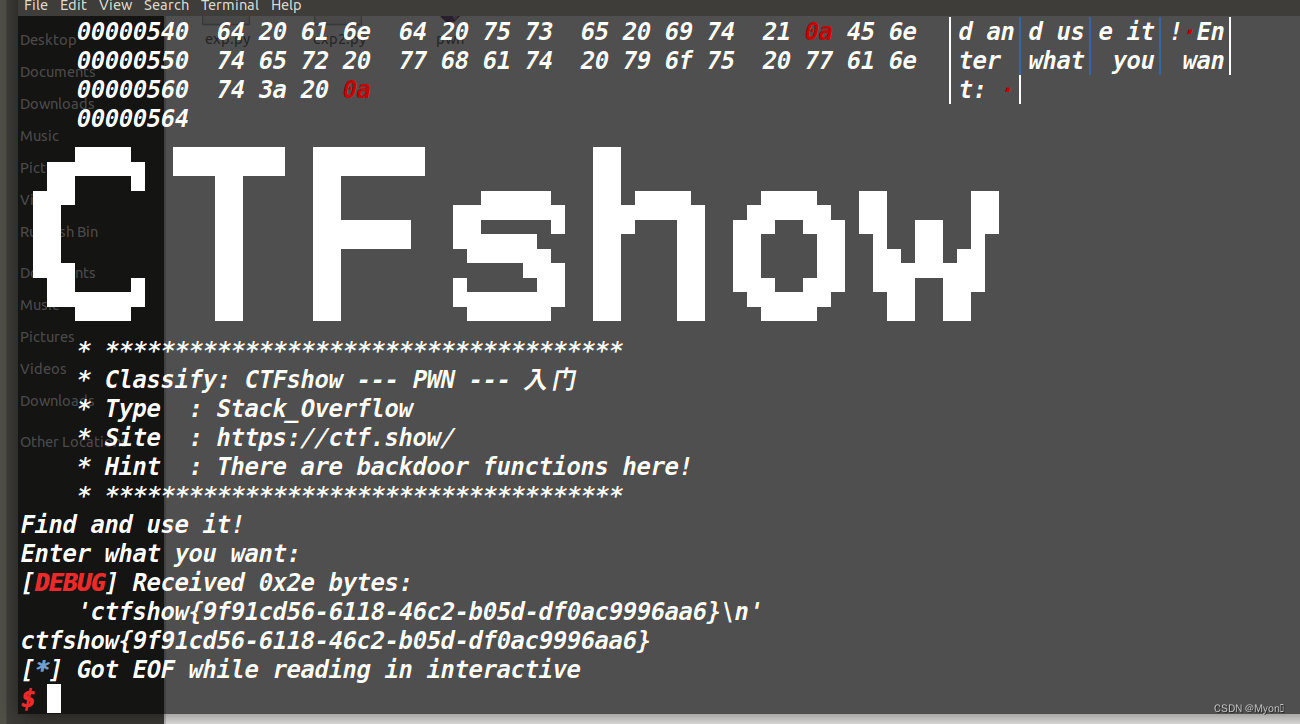
1. map() 的返回值是一个新的数组,新数组中的元素为 “原数组调用函数处理过后的值”
2. 简单使用:遍历整个数组,将大于4的元素乘以2
const array = [2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6]
console.log("array",array)
const map = array.map(x => {
if (x == 4) {
return x * 2
}
return x
})
console.log("map",map)
输出的结果为:等于4的元素乘以2
3. map()函数的参数详解
一般参数是一个回调函数
array.map((item,index,arr)=>{
//item是操作的当前元素
//index是操作元素的下表
//arr是需要被操作的元素
//具体需要哪些参数 就传入那个
})
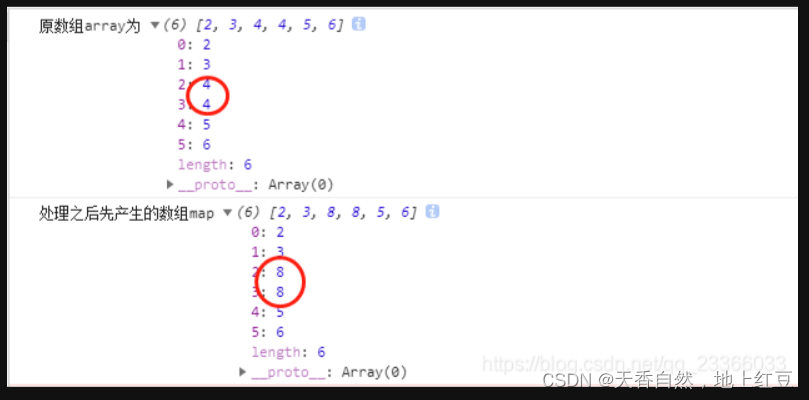
const array = [2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6]
console.log("原数组array为",array)
const map2=array.map((item,index,arr)=>{
console.log("操作的当前元素",item)
console.log("当前元素下标",index)
console.log("被操作的元素",arr)
//对元素乘以2
return item*2
})
console.log("处理之后先产生的数组map",map2)
输出的结果为:
4. 总结:map()方法经常拿来遍历数组,但是不改变原数组,但是会返回一个新的数组;
5.注意:有时候会出现这种现象,出现几个undefined
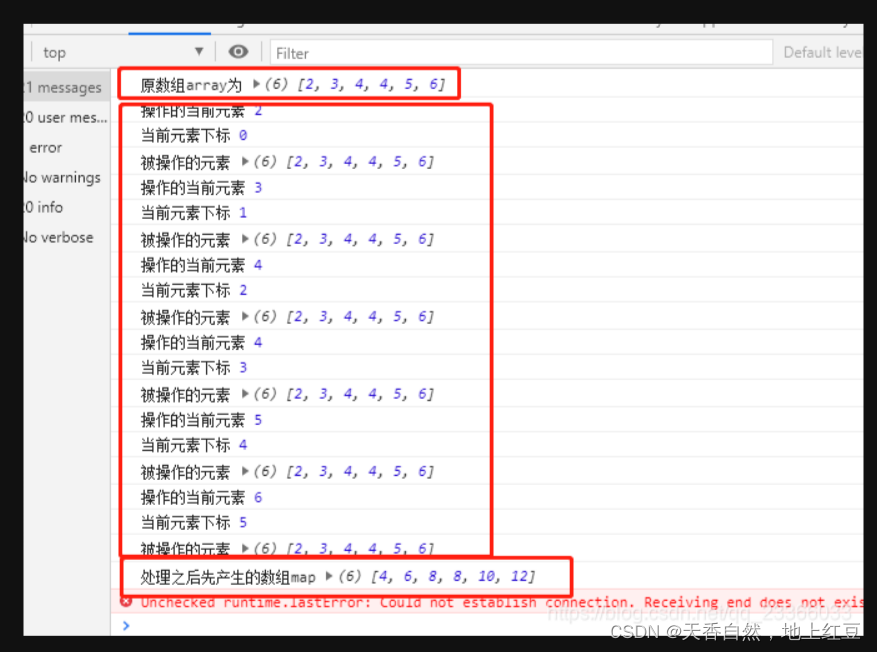
const array = [2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6]
console.log("原数组array为",array)
const map = array.map(x => {
if (x == 4) {
return x * 2
}
})
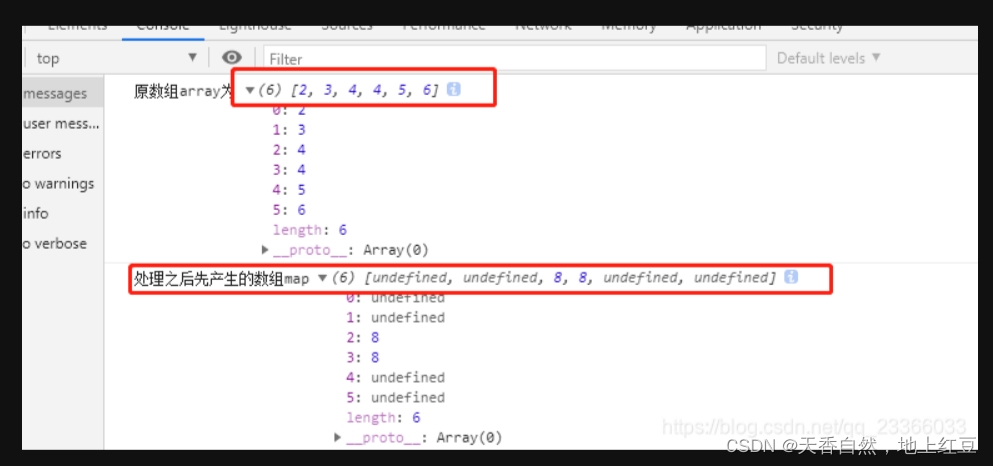
其实,map()方法是对每一项数组进行遍历,遍历一次,返回一个值,给新数组加上一个元素,这是就是满足x=4的元素,只有两个,所以其他项就返回了undefined。
6、map()方法是数组对象自带的方法,用于遍历数组中的每个元素,并对每个元素执行指定的函数,然后返回一个新的数组,包含所有函数的返回值。
在JavaScript中,map()方法是数组对象自带的方法,用于遍历数组中的每个元素,并对每个元素执行指定的函数,然后返回一个新的数组,包含所有函数的返回值。
map()方法的语法如下:
array.map(function(currentValue, index, arr), thisValue)在JavaScript中,map()方法是数组对象自带的方法,用于遍历数组中的每个元素,并对每个元素执行指定的函数,然后返回一个新的数组,包含所有函数的返回值。
map()方法的语法如下:
Copy code
array.map(function(currentValue, index, arr), thisValue)
其中,function(currentValue, index, arr)是一个回调函数,它可以接受三个参数:
currentValue: 当前正在处理的元素index: 当前正在处理的元素的索引arr: 调用map()方法的数组
另外,thisValue是可选的参数,用于设置回调函数中this的值。
下面是一个简单的例子,演示了如何使用map()方法:
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4];
const doubledNumbers = numbers.map(function(num) {
return num * 2;
});
console.log(doubledNumbers); // [2, 4, 6, 8]在该例子中,我们将数组numbers中的每个元素都乘以2,然后返回一个新的数组doubledNumbers。
希望可以帮到大家;