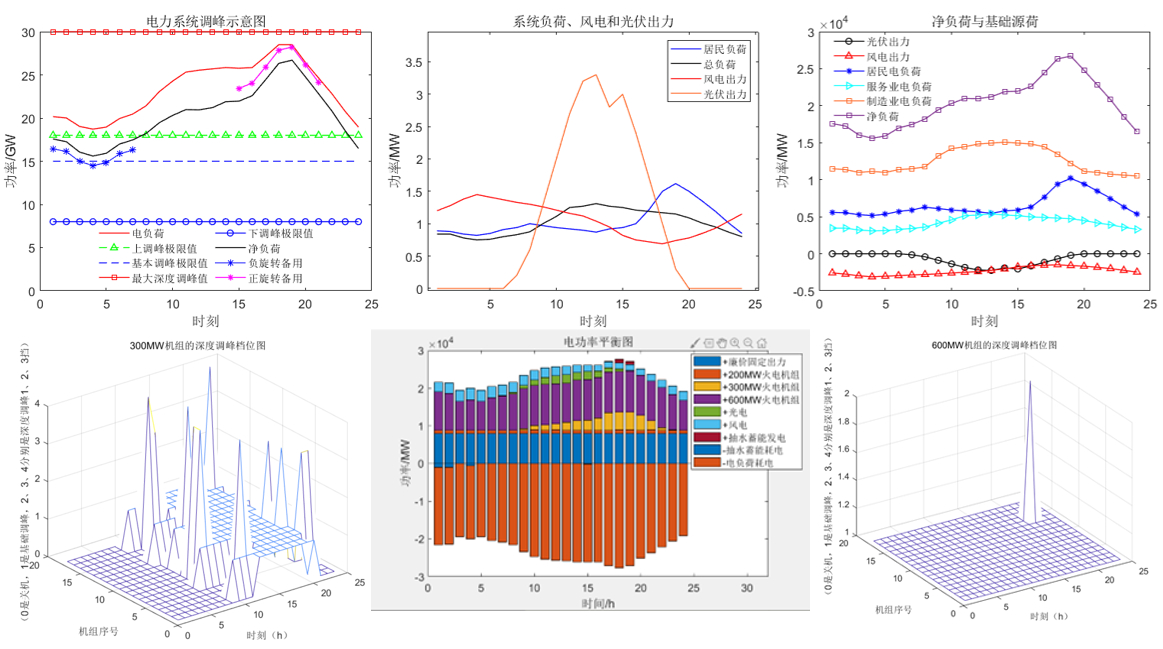
Bingbong的回文路径:
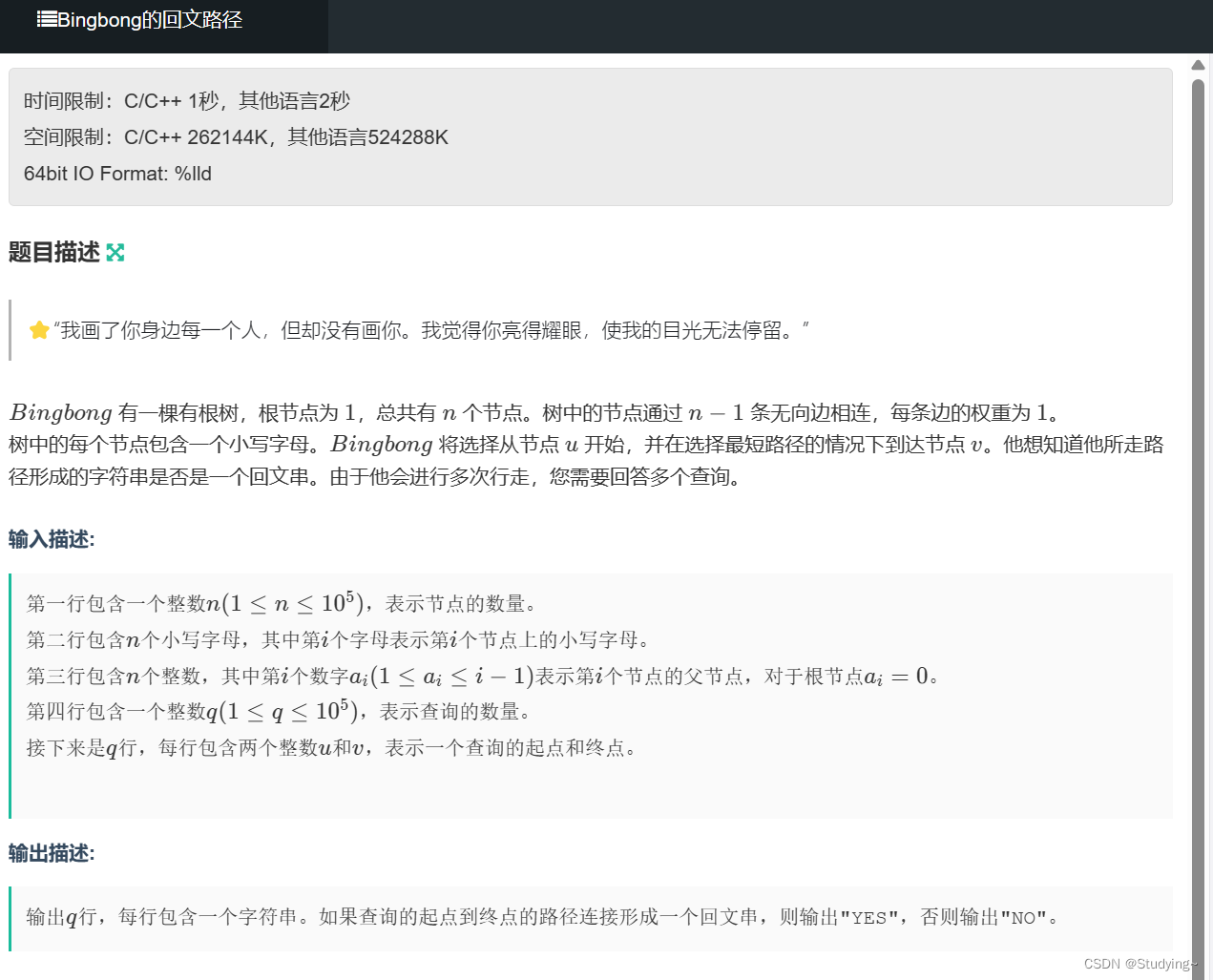
题目描述:
思路解析:
现在有一棵树,树上每个结点上都有一个小写字母,那么如果唯一确定了x和y两个结点,那么就唯一确定了一个字符串路径(最短路径)。 -现在给出q次查询,问x和y这个路径是否是回文字符串。
一看到回文字符串就可以应当想到字符串hash。但是怎么快速查询这个路径上字符串的hash值变成为了关键,可以发现,根节点到到任意结点的路径是确定的,并且是可以在一次dfs遍历中维护出来根据点到任意结点的字符串路径hash值的,那我们检查这个值有什么用。
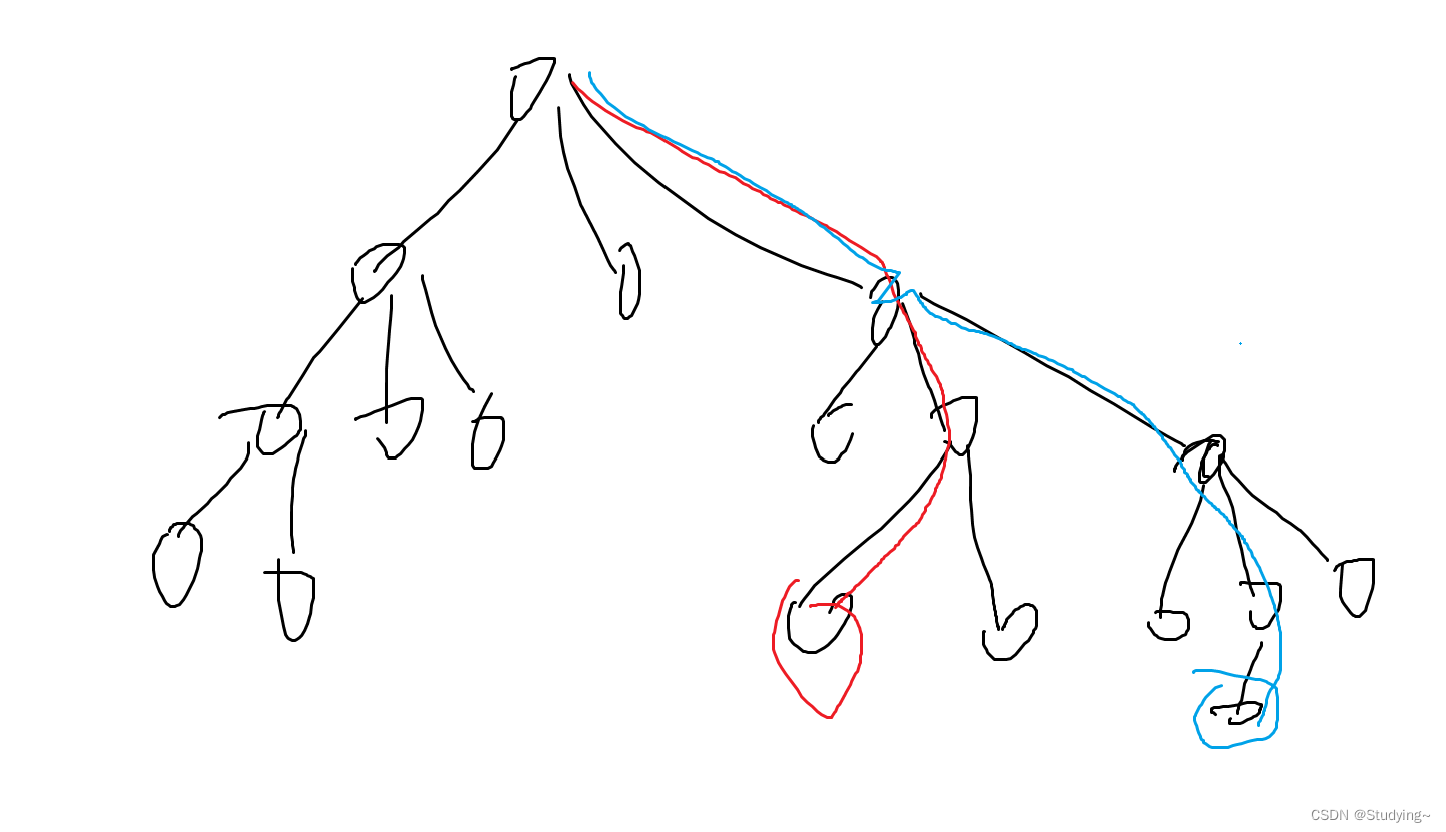
假设我们查询红色结点到蓝色结点,那么可以发现,我们只需要找到他们最小公共祖先就可以利用他们三个结点的hash值来维护任意结点之间的hash值了。那么这道题就可以做了
代码实现:
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static long[] pow = new long[100005];
static long[] inv = new long[100005];
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
s[i] = random.nextInt(10000);
}
pow[0] = 1;
inv[0] = 1;
long invb = qkm(base);
for (int i = 1; i < 100005; i++) {
pow[i] = pow[i - 1] * base % mod;
inv[i] = inv[i - 1] * invb % mod;
}
int t = 1;
while (t > 0) {
solve();
t--;
}
w.flush();
w.close();
}
static char[] str;
static int[] s = new int[26];
static int mod = (int) 1e9 + 9;
static int base = 131;
static Vector<Integer>[] g;
static int[] dep;
static int[][] st;
static long[] pre;
static long[] suf;
public static void solve() throws IOException {
int n = f.nextInt();
str = (" " + f.next()).toCharArray();
g = new Vector[n+1];
dep = new int[n+1];
st = new int[n+1][20];
pre = new long[n+1];
suf = new long[n+1];
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) {
g[i] = new Vector<>();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int x = f.nextInt();
g[x].add(i);
}
dfs(1, 0);
for (int j = 1; j < 20; j++) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
st[i][j] = st[st[i][j-1]][j-1];
}
}
int q = f.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) {
int x = f.nextInt(); int y = f.nextInt();
if (check(x,y)) w.println("YES");
else w.println("NO");
}
}
public static boolean check(int x, int y){
int fa = lca(x, y);
long a = (pre[x] - (pre[fa] * pow[dep[x] - dep[fa]] % mod)) % mod;
long b = (pre[y] - (pre[fa] * pow[dep[y] - dep[fa]] % mod)) % mod;
long c = (suf[x] - suf[fa]) * inv[dep[fa]] % mod;
long d = (suf[y] - suf[fa]) * inv[dep[fa]] % mod;
a = (a + mod) % mod;
b = (b + mod) % mod;
c = (c + mod) % mod;
d = (d + mod) % mod;
long A = (s[str[fa] - 'a'] * pow[dep[x] - dep[fa]] % mod + a + d * pow[dep[x] - dep[fa] + 1] % mod) % mod;
long B = (s[str[fa] - 'a'] * pow[dep[y] - dep[fa]] % mod + b + c * pow[dep[y] - dep[fa] + 1] % mod) % mod;
return A == B;
}
public static int lca(int x, int y){
if (dep[x] < dep[y]) {int tmp = x; x = y; y = tmp;}
for (int i = 19; i >= 0; i--) {
if (dep[st[x][i]] >= dep[y]){
x = st[x][i];
}
}
if (x == y) return x;
for (int i = 19; i >= 0; i--) {
if (st[x][i] != st[y][i]){
x = st[x][i]; y = st[y][i];
}
}
return st[x][0];
}
public static long qkm(long a){
long res = 1;
long b = mod - 2;
while (b > 0){
if ((b & 1) == 1) res = (res * a) % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
public static void dfs(int x, int fa){
dep[x] = dep[fa] + 1;
st[x][0] = fa;
pre[x] = (pre[fa] * base % mod+ s[str[x]-'a']) % mod;
suf[x] = (suf[fa] + s[str[x]-'a'] * pow[dep[fa]] % mod) % mod;
for (int i = 0; i < g[x].size(); i++) {
int y = g[x].get(i);
if (y == fa) continue;
dfs(y, x);
}
}
static PrintWriter w = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static Input f = new Input(System.in);
static class Input {
public BufferedReader reader;
public StringTokenizer tokenizer;
public Input(InputStream stream) {
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(stream), 32768);
tokenizer = null;
}
public String next() throws IOException {
while (tokenizer == null || !tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) {
tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(reader.readLine());
}
return tokenizer.nextToken();
}
public String nextLine() throws IOException {
String str = null;
str = reader.readLine();
return str;
}
public int nextInt() throws IOException {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public long nextLong() throws IOException {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
public Double nextDouble() throws IOException {
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
}
}