前言
上一章节我们介绍了搭建Elasticsearch集群相关的知识。那么又该如何来操作Elasticsearch集群呢?在ES官网中提供了各种语言的客户端,我们在项目开发过程中有多种Elasticsearch版本和连接客户端可以选择,那么他们有什么区别?这一章节袁老师带领大家来学习Elasticsearch客户端相关的内容。

一. ES客户端介绍
在Elasticsearch官网中提供了各种语言的客户端:Elasticsearch Clients | Elastic。
|
| 优点 | 缺点 | 说明 |
| Java Low Level Rest Client | 与ES版本之间没有关系,适用于作为所有版本ES的客户端 | 低级别的REST客户端,通过HTTP与集群交互,用户需自己编组请求JSON串,及解析响应JSON串 | 不建议使用 |
| Java High Level Rest Client | 官方推出的,版本与ES同步更新 | 使用的版本需要保持和ES服务端的版本一致,否则会有版本问题 | 强烈推荐使用。基于Low Level Rest Client,它提供了更多的接口。注意:7.15版本之后将被弃用 |
| TransportClient | 启动速度快,轻量级,可创建极多连接,与应用程序解耦;推荐使用原生的,ES本身就很简单,灵活性很高 | JAR包版本需与ES集群版本一致,ES集群升级,客户端也跟着升级到相同版本 | 不建议使用。过时产品,7版本之后不再支持 |
| Elasticsearch Java API Client | 最新的ES客户端。Elasticsearch Java API Client通过API的方式来组装请求数据,避免直接编写JSON字符串 | 文档少 | 使用人较少 |
注意点击进入后,选择版本到6.2.4版本 ,因为我们之前按照的都是6.2.4版本讲解的。进入后可以通过官方文档了解和学习Java客户端相关的知识。
二. 搭建工程环境
1.创建一个Spring Initalizr类型的项目,项目名称设置为【es-client】。

2.创建项目时,勾选Lombok、Spring Boot DevTools和Spring Web依赖。
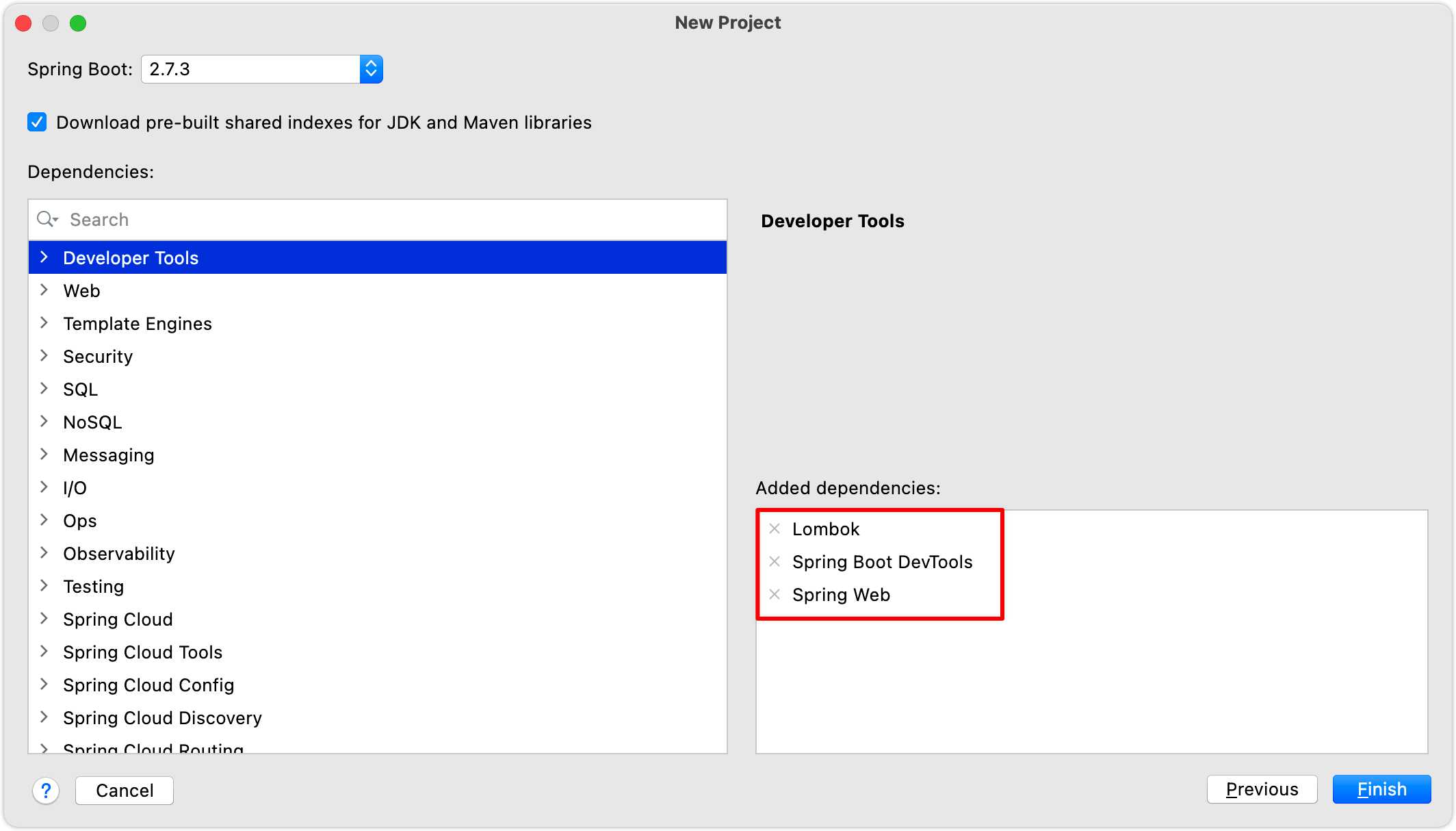
注意:这里我们直接导入了SpringBoot的启动器,方便后续讲解。
3.将resource目录下自动生成的application.properties文件修改成application.yml。
4.在项目的pom.xml文件中手动引入Elasticsearch的High-level-Rest-Client等相关的依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.6</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.yx</groupId>
<artifactId>es-client</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>es-client</name>
<description>es-client</description>
<properties>
<java.version>11</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.code.gson</groupId>
<artifactId>gson</artifactId>
<version>2.8.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Apache开源组织提供的用于操作Java Bean的工具包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-beanutils</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-beanutils</artifactId>
<version>1.9.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- ES高级Rest Client -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
<version>6.4.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId>
<version>6.4.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>三. 索引库及映射
创建索引库的同时,我们也会创建type及其映射关系,但是这些操作不建议使用Java客户端完成,原因如下:
- 索引库和映射往往是初始化时完成,不需要频繁操作,不如提前配置好。
- 官方提供的创建索引库及映射API非常繁琐,需要通过字符串拼接JSON结构。
因此,这些操作建议还是使用我们之前学习的Rest风格API去实现。
在项目的com.yx.pojo包下创建Product商品类,以这样一个商品数据为例来创建索引库。
package com.yx.pojo;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Product {
private Long id; // 主键
private String title; // 标题
private String category; // 分类
private String brand; // 品牌
private Double price; // 价格
private String images; // 图片地址
}分析一下数据结构:
| 属性 | 描述 |
| id | 可以认为是主键,将来判断数据是否重复的标识,不分词,可以使用keyword类型 |
| title | 搜索字段,需要分词,可以用text类型 |
| category | 商品分类,这个是整体,不分词,可以使用keyword类型 |
| brand | 品牌,与分类类似,不分词,可以使用keyword类型 |
| price | 价格,这个是double类型 |
| images | 图片,用来展示的字段,不搜索,index为false,不分词,可以使用keyword类型 |
使用Kibana控制台向集群中创建yx索引库并编写映射配置(如果之前创建过yx索引库则先删除)。
PUT /yx
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 3,
"number_of_replicas": 1
},
"mappings": {
"product": {
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"category": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"brand": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"price": {
"type": "double"
},
"images": {
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
}
}
}
}
}四. 索引数据操作
有了索引库之后,我们接下来看看如何对索引库中的数据进行增删改查操作。操作MySQL数据库:
1.获取数据库连接。
2.完成数据的增删改查操作。
3.释放资源。
1.初始化客户端
对索引库做任何操作,都需要通过RestHighLevelClient客户端来完成。
1.在项目的test测试文件夹下创建com.yx.es包,并在该包下创建一个ElasticsearchTests测试类。
2.然后在ElasticsearchTests类中编写RestHighLevelClient客户端的初始化方法init()和关闭方法close()。
package com.yx.es;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClientBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.io.IOException;
@SpringBootTest
public class ElasticsearchTests {
private RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient;
// JSON工具
private Gson gson = new Gson();
/** 初始化客户端 */
@Before
public void init() {
RestClientBuilder restClientBuilder = RestClient.builder(
new HttpHost("127.0.0.1", 9201, "http"),
new HttpHost("127.0.0.1", 9202, "http"),
new HttpHost("127.0.0.1", 9203, "http")
);
restHighLevelClient = new RestHighLevelClient(restClientBuilder);
}
/** 关闭客户端 */
@After
public void close() throws IOException {
// 关闭客户端
restHighLevelClient.close();
}
}2.新增文档
新增文档的实现是,先将数据封装到POJO对象中,然后通过restHighLevelClient对象来向索引库中新增数据。
2.1.新增文档实现
1.在ElasticsearchTests类中编写新增文档的insert()方法。
/** 新增文档 */
@Test
public void insert() throws IOException {
// 1.文档数据
Product product = new Product();
product.setId(1L);
product.setTitle("华为P60震撼发布");
product.setCategory("手机");
product.setBrand("华为");
product.setPrice(6999.99);
product.setImages("http://image.huawei.com/1.jpg");
// 2.将文档数据转换为JSON格式
String source = gson.toJson(product);
// 3.创建索引请求对象,访问哪个索引库、哪个type、指定文档ID
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("yx", "product", product.getId().toString());
request.source(source, XContentType.JSON);
// 4.发送请求
IndexResponse response = restHighLevelClient.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.err.println(response);
}2.运行insert()方法,输出结果见下:
IndexResponse[index=yx,type=product,id=1,version=2,result=updated,seqNo=1,primaryTerm=1,shards={"total":2,"successful":2,"failed":0}]3.运行insert()方法可能会报错,具体解决方案见下。
2.2.新增文档异常
1.如果导入Elasticsearch依赖时不指定其版本,可能导致找不到XContentType类。解决的方案就是在pom.xml文件中手动添加Elasticsearch对应版本的依赖,比如手动指定Elasticsearch的版本为6.4.3。如果没有这个问题,则忽略此步骤。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId>
<version>6.4.3</version>
</dependency>2.如果运行insert()方法提示java.lang.NullPointerException空指针异常,则可能的原因是@Test注解的包导入错误,注意导入的包是org.junit.Test而非org.junit.jupiter.api.Test。
3.查看文档
根据Rest风格,查看文档是根据文档id进行GET查询操作,难点是对结果的解析。
1.在ElasticsearchTests类中编写查看文档的select()方法。
/** 查看文档 */
@Test
public void select() throws IOException {
// 创建GET请求并指定id
GetRequest request = new GetRequest("yx", "product", "1");
// 查询,得到响应
GetResponse response = restHighLevelClient.get(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 获得响应结果数据
String source = response.getSourceAsString();
// 转化为JSON数据
Product product = gson.fromJson(source, Product.class);
System.err.println(product);
}2.运行select()方法,输出结果见下:
Product(id=1, title=华为P60震撼发布, category=手机, brand=华为, price=6999.99, images=http://image.huawei.com/1.jpg)4.修改文档
新增文档时,如果传递的id是已经存在的,则会完成修改文档操作,如果id不存在,则是新增文档操作。
1.在ElasticsearchTests类中编写修改文档的update()方法。
/** 修改文档 */
@Test
public void update() throws IOException {
// 1.文档数据
Product product = new Product();
product.setId(1L); // id存在则为修改操作
product.setTitle("华为P60直降1000");
product.setPrice(5999.99);
// 2.将文档数据转换为JSON格式
String source = gson.toJson(product);
// 3.创建索引请求对象,访问哪个索引库、哪个type、指定文档ID
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("yx", "product", product.getId().toString());
request.source(source, XContentType.JSON);
// 4.发送请求
IndexResponse response = restHighLevelClient.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.err.println(response);
}2.运行update()方法,输出结果见下:
IndexResponse[index=yx,type=product,id=1,version=2,result=updated,seqNo=1,primaryTerm=1,shards={"total":2,"successful":2,"failed":0}]5.删除文档
根据id删除文档。
1.在ElasticsearchTests类中编写删除文档的delete()方法。
/** 删除文档 */
@Test
public void delete() throws IOException {
// 准备删除的请求,参数为id
DeleteRequest request = new DeleteRequest("yx", "product", "1");
// 发起请求
DeleteResponse response = restHighLevelClient.delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.err.println(response);
}2.运行delete()方法,输出结果见下:
DeleteResponse[index=yx,type=product,id=1,version=3,result=deleted,shards=ShardInfo{total=2, successful=2, failures=[]}]
五. 结语
Elasticsearch客户端基础部分的内容袁老师就给大家介绍完了。回顾下这一章节我们学习的主要内容,介绍了ES客户端项目工程搭建、索引库及映射、索引数据操作,主要重点介绍了索引数据的增删改查操纵。关于ES客户端基础部分的内容就介绍到这里,下一章节袁老师带领大家学习Elasticsearch客户端高级操作部分的内容。
今天的内容就分享到这里吧。关注「袁庭新」,干货天天都不断!