上一节课,我们学了线性表 单向存储结构(也就是单链表),这个是企业常用的技术,且是后面各种的基本,一定要牢牢掌握,如果没有掌握,下面的课程会云里雾里。
一 ,循环链表
1、什么是循环链表
— 概念上:
1、任何数据元素都有一个前驱和一个后继
2、所有的数据元素的关系构成一个逻辑的环
— 实现上:
1、循环链表是一种特殊的单链表
2、尾结点的指针域保存了首结点的地址
2、循环链表的逻辑构成
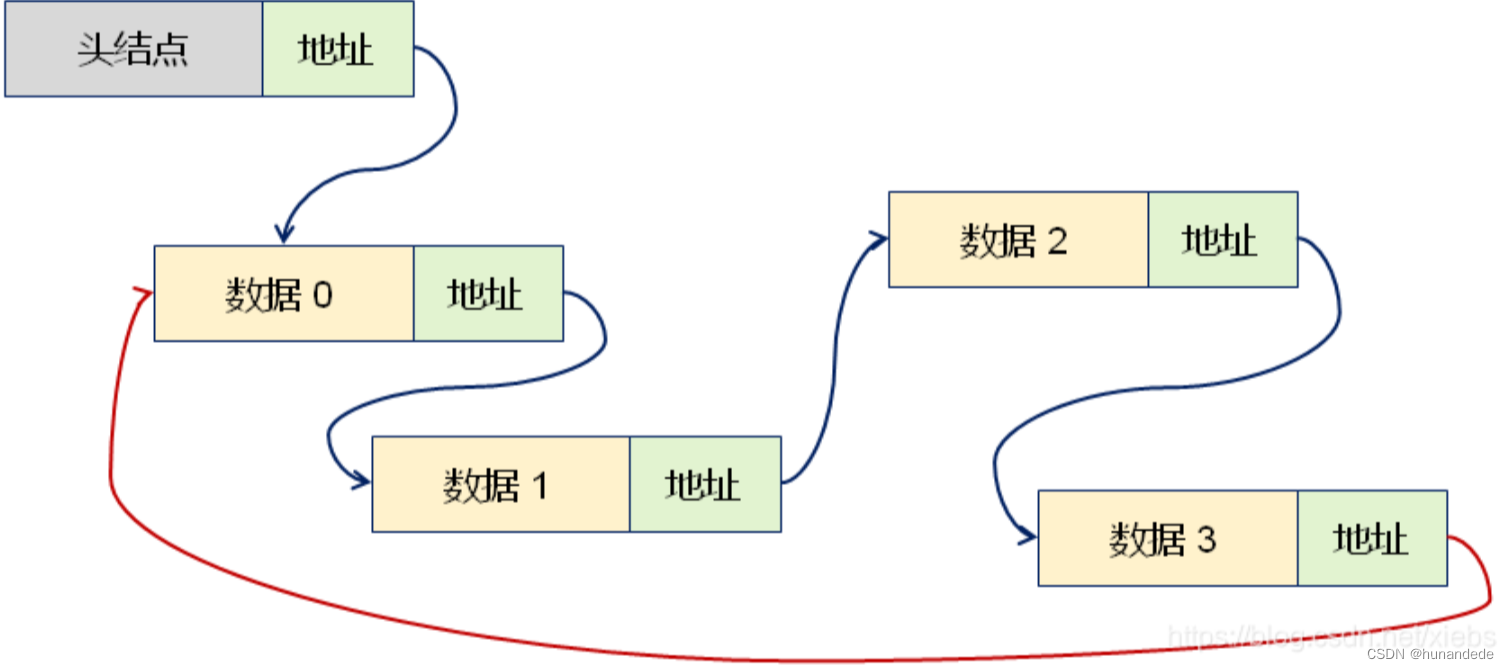
二 循环链表的插入示意图
头插法第一次插入

头插法非第一次插入
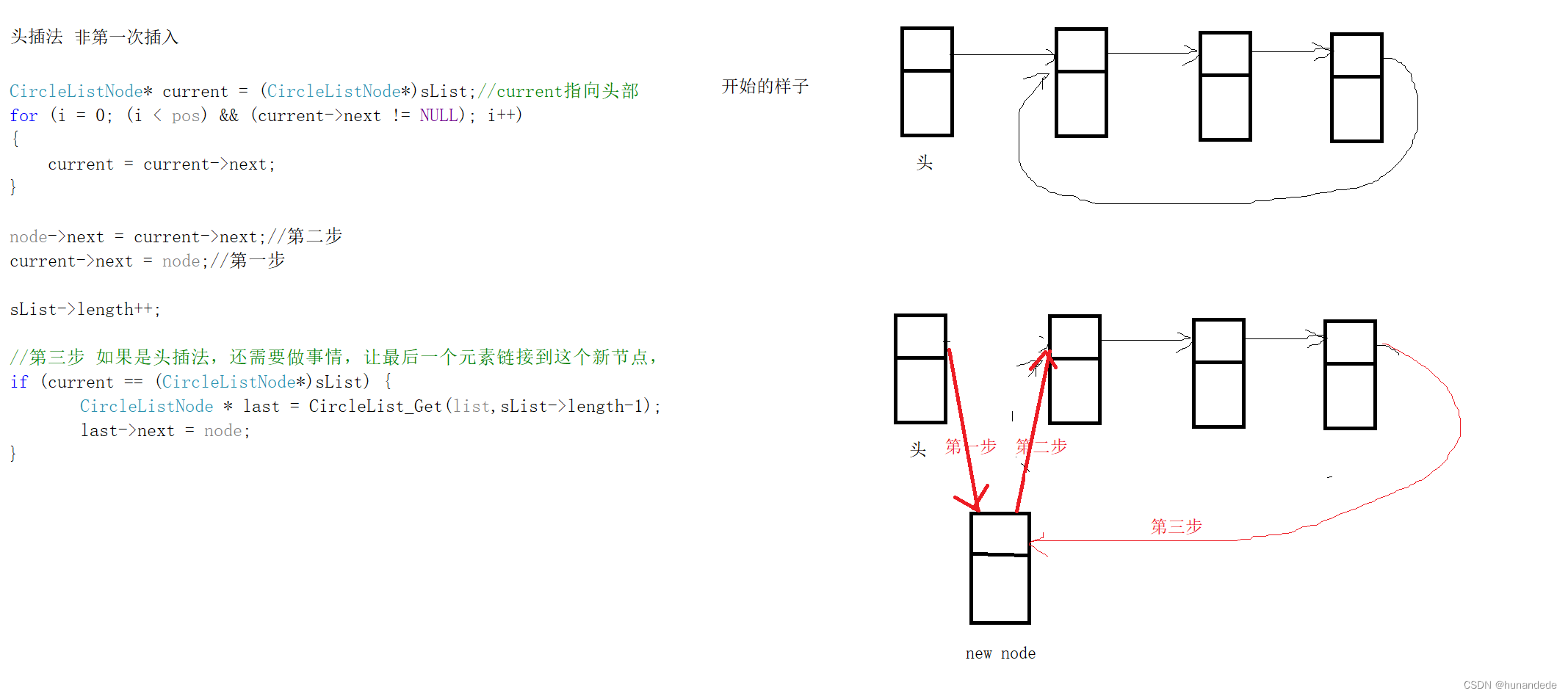
删除非第一个元素

删除第一个元素
三 代码实现
.h实现
#ifndef _003CIRCLELIST_H_
#define _003CIRCLELIST_H_
typedef void CircleList; //要返回给上层的list 的首地址为 void *,为了阅读起名为CircleList
typedef struct _tag_CircleListNode //list 中的节点
{
struct _tag_CircleListNode* next;
}CircleListNode;
//创建循环链表
CircleList* CircleList_Create();
//销毁循环链表
void CircleList_Destroy(CircleList* list);
//清空循环列表
void CircleList_Clear(CircleList* list);
//循环列表中目前存在的元素个数
int CircleList_Length(CircleList* list);
//给循环列表中插入元素,node为要插入的元素的值,pos为位置
int CircleList_Insert(CircleList* list, CircleListNode* node, int pos);
//从循环列表中的pos 位置获得具体的值
CircleListNode* CircleList_Get(CircleList* list, int pos);
//从循环列表中删除pos位置的数据
CircleListNode* CircleList_Delete(CircleList* list, int pos);
//从循环列表中删除 数据 为node 的点
CircleListNode* CircleList_DeleteNode(CircleList* list, CircleListNode* node);
CircleListNode* CircleList_Reset(CircleList* list);
CircleListNode* CircleList_Current(CircleList* list);
CircleListNode* CircleList_Next(CircleList* list);
#endif
底层实现
#include "003CircleList.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include <string.h>
typedef struct _tag_CircleList{
CircleListNode header;
CircleListNode* slider; //多了一个游标
int length;
} TCircleList;
CircleList* CircleList_Create(){
TCircleList* ret = (TCircleList*)malloc(sizeof(TCircleList));
if (ret == NULL) {
printf("CircleList_Create func malloc error\n");
return ret;
}
memset(ret,0,sizeof(TCircleList));
ret->length = 0;
ret->header.next = NULL;
ret->slider = NULL;
return ret;
}
void CircleList_Destroy(CircleList* list) // O(1)
{
free(list);
}
void CircleList_Clear(CircleList* list){
TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;
if (sList != NULL)
{
sList->length = 0;
sList->header.next = NULL;
sList->slider = NULL;
}
}
int CircleList_Length(CircleList* list){
TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;
int ret = -1;
if (sList != NULL){
ret = sList->length;
}
return ret;
}
int CircleList_Insert(CircleList* list, CircleListNode* node, int pos) // O(n)
{
TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;
int ret = (sList != NULL) && (pos >= 0) && (node != NULL);
int i = 0;
if (ret){
CircleListNode* current = (CircleListNode*)sList;//current指向头部
for (i = 0; (i < pos) && (current->next != NULL); i++)
{
current = current->next;
}
//假设我们要插入的是pos =3,头结点不算,下来从0,1,2,3,4,5,6开始计算
//循环完成后,current刚好是在 pos=2的位置,
//要变成的是 2 node 3 ,也就是说node->next要是3
node->next = current->next;
//current的->next,现在也是2,指向新的节点node
current->next = node;
if (sList->length == 0){
//如果是第一次插入将slider的指向node
sList->slider = node;
}
sList->length++;
//如果是头插法,还需要做事情,让最后一个元素链接到这个新节点,
if (current == (CircleListNode*)sList) {
CircleListNode * last = CircleList_Get(list,sList->length-1);
last->next = node;
}
//此处要理解,需结合图来看,后续会将 头插法,尾插法,中间插入法的三种图示画一下,方便理解
}
return ret;
}
CircleListNode* CircleList_Get(CircleList* list, int pos) // O(n)
{
TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;
CircleListNode* ret = NULL;
int i = 0;
if ((sList != NULL) && (pos >= 0)){
CircleListNode* current = (CircleListNode*)sList;
for (i = 0; i < pos; i++)
{
current = current->next;
}
ret = current->next;
}
return ret;
}
CircleListNode* CircleList_Delete(CircleList* list, int pos) // O(n)
{
TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;
CircleListNode* ret = NULL;
int i = 0;
if ((sList != NULL) && (pos >= 0)){
CircleListNode* current = (CircleListNode*)sList;
CircleListNode* first = sList->header.next;
CircleListNode* last = (CircleListNode*)CircleList_Get(sList, sList->length - 1);
for (i = 0; i < pos; i++){
current = current->next;
}
ret = current->next;
current->next = ret->next;
sList->length--;
//如果删除的第一个结点。要额外处理
if (first == ret){
//让头结点的next要重新指向,指向的内容是保存在 被删除的节点的next中的。
sList->header.next = ret->next;
//让最后一个节点的next也要重新指向,指向的内容是保存在 被删除的节点的next中的。
last->next = ret->next;
}
//如果删除的元素刚好是 游标指向的元素,则将游标往下移动
if (sList->slider == ret){
sList->slider = ret->next;
}
//如果list只有一个元素,删除后,就没有元素了,那么就需要将
if (sList->length == 0){
sList->header.next = NULL;
sList->slider = NULL;
}
}
return ret;
}
CircleListNode* CircleList_DeleteNode(CircleList* list, CircleListNode* node) // O(n)
{
TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;
CircleListNode* ret = NULL;
int i = 0;
if (sList != NULL){
CircleListNode* current = (CircleListNode*)sList;
for (i = 0; i < sList->length; i++){
if (current->next == node){
ret = current->next;
break;
}
current = current->next;
}
if (ret != NULL){
CircleList_Delete(sList, i);
}
}
return ret;
}
CircleListNode* CircleList_Reset(CircleList* list) // O(1)
{
TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;
CircleListNode* ret = NULL;
if (sList != NULL){
sList->slider = sList->header.next;
ret = sList->slider;
}
return ret;
}
CircleListNode* CircleList_Current(CircleList* list) // O(1)
{
TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;
CircleListNode* ret = NULL;
if (sList != NULL){
ret = sList->slider;
}
return ret;
}
CircleListNode* CircleList_Next(CircleList* list) // O(1)
{
TCircleList* sList = (TCircleList*)list;
CircleListNode* ret = NULL;
if ((sList != NULL) && (sList->slider != NULL)){
ret = sList->slider;
sList->slider = ret->next;
}
return ret;
}测试代码
#include "iostream"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
extern "C" {
#include "003CircleList.h"
}
using namespace std;
struct Value
{
CircleListNode header;
int v;
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int i = 0;
CircleList* list = CircleList_Create();
struct Value v1;
struct Value v2;
struct Value v3;
struct Value v4;
struct Value v5;
struct Value v6;
struct Value v7;
struct Value v8;
v1.v = 1;
v2.v = 2;
v3.v = 3;
v4.v = 4;
v5.v = 5;
v6.v = 6;
v7.v = 7;
v8.v = 8;
CircleList_Insert(list, (CircleListNode*)&v1, CircleList_Length(list));
CircleList_Insert(list, (CircleListNode*)&v2, CircleList_Length(list));
CircleList_Insert(list, (CircleListNode*)&v3, CircleList_Length(list));
CircleList_Insert(list, (CircleListNode*)&v4, CircleList_Length(list));
for (i = 0; i < CircleList_Length(list); i++)
{
struct Value* pv = (struct Value*)CircleList_Get(list, i);
printf("%d\n", pv->v);
}
//注意这里,这时候list除了头结点外,只有4个元素,1,2,3,4,对应0,1,2,3
//代码中插入的pos =5,相当于在1和2中间插入一个5.
CircleList_Insert(list, (CircleListNode*)&v5, 5);
//因此如下的循环后,打印出来的是 1,5,2,3,4
for (i = 0; i < CircleList_Length(list); i++)
{
struct Value* pv = (struct Value*)CircleList_Get(list, i);
printf("%d\n", pv->v);
}
CircleList_Delete(list, 0);//删除第一个元素,将1删除了
//再次打印是 5 2 3 4 5 2 3 4
for (i = 0; i < 2 * CircleList_Length(list); i++)
{
struct Value* pv = (struct Value*)CircleList_Get(list, i);
printf("%d\n", pv->v);
}
printf("\n");
while (CircleList_Length(list) > 0){
struct Value* pv = (struct Value*)CircleList_Delete(list, 0);
printf("%d\n", pv->v);
}
printf("aaaaaa\n");
CircleList_Insert(list, (CircleListNode*)&v1, 0);
CircleList_Insert(list, (CircleListNode*)&v2, 0);
CircleList_Insert(list, (CircleListNode*)&v3, 0);
CircleList_Insert(list, (CircleListNode*)&v4, 0);
CircleList_Insert(list, (CircleListNode*)&v5, 0);
CircleList_Insert(list, (CircleListNode*)&v6, 0);
CircleList_Insert(list, (CircleListNode*)&v7, 0);
CircleList_Insert(list, (CircleListNode*)&v8, 0);
//注意,这里是用的头插法,因此是8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,但是第一个插入的是1,因此游标指向1,又因为是循环的,因此下一个是8,结果是1,8,7,6,5,4,3,2
for (i = 0; i < CircleList_Length(list); i++){
struct Value* pv = (struct Value*)CircleList_Next(list);
printf("%d\n", pv->v);
}
printf("bbbbbbbbbb\n");
//游标reset 是指向的第一个元素
CircleList_Reset(list);
//1,2,3 将3剔除队列的游戏,游标reset后,指向的是8,因此123,将3剔除队列的有些结果为 6,3,8,4,7,1,5,2
while (CircleList_Length(list) > 0){
struct Value* pv = NULL;
for (i = 1; i < 3; i++){
CircleList_Next(list);
}
printf("ccc\n");//游标reset之后,指向数字8,往后移动了2次,就是指向6
pv = (struct Value*)CircleList_Current(list);
printf("%d\n", pv->v);
CircleList_DeleteNode(list, (CircleListNode*)pv);
}
CircleList_Destroy(list);
return 0;
}





![春秋云境:CVE-2022-32991[漏洞复现]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/c4773e1bdfc849a79441e95bad7b7a61.png)

