目录
设置
简介
动机
结构
全局Token创建
模块
窗口
级别
模型
建立模型
预训练权重的理智检查
微调 GCViT 模型
配置
数据加载器
花卉数据集
为花卉数据集重建模型
训练
政安晨的个人主页:政安晨
欢迎 👍点赞✍评论⭐收藏
收录专栏: TensorFlow与Keras机器学习实战
希望政安晨的博客能够对您有所裨益,如有不足之处,欢迎在评论区提出指正!
本文目标:用于图像分类的全局上下文视觉变换器的实现和微调。
设置
!pip install --upgrade keras_cv tensorflow
!pip install --upgrade kerasimport keras
from keras_cv.layers import DropPath
from keras import ops
from keras import layers
import tensorflow as tf # only for dataloader
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds # for flower dataset
from skimage.data import chelsea
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np简介
在本文中,我们将利用多后端 Keras 3.0 来实现 A Hatamizadeh 等人在 ICML 2023 上发表的 GCViT:Global Context Vision Transformer 论文,并利用官方 ImageNet 预训练的权重在 Flower 数据集上对模型进行微调,以完成图像分类任务。
本文的一大亮点是与多个后端兼容:TensorFlow、PyTorch 和 JAX,展示了多后端 Keras 的真正潜力。
动机
注:在本文这部分中,我们将了解 GCViT 的背景,并尝试理解提出它的原因。
近年来,变换器在自然语言处理(NLP)任务中占据了主导地位,其自我注意机制可同时捕捉长程和短程信息。
顺应这一趋势,Vision Transformer(ViT)提出在一个类似于原始 Transformer 编码器的巨大架构中利用图像补丁作为标记。
尽管卷积神经网络(CNN)在计算机视觉领域一直占据主导地位,但基于 ViT 的模型已在各种计算机视觉任务中显示出 SOTA 或具有竞争力的性能。

然而,由于自注意的计算复杂度为二次方[O(n^2)],且缺乏多尺度信息,因此很难将 ViT 视为计算视觉任务(如分割和物体检测)的通用架构,因为它需要在像素级进行密集预测。
Swin Transformer 曾试图通过提出多分辨率/分层架构来解决 ViT 的问题,在这种架构中,自注意力是在局部窗口中计算的,而跨窗口连接(如窗口移动)则用于对不同区域之间的交互进行建模。但局部窗口的感受野有限,无法捕捉长距离信息,而窗口移动等跨窗口连接方案只能覆盖每个窗口附近的小范围邻域。此外,它还缺乏归纳偏差,而归纳偏差鼓励一定的翻译不变性,这对于通用视觉建模,尤其是物体检测和语义分割等密集预测任务来说,仍然是可取的。



针对上述局限性,我们提出了全局语境(GC)ViT 网络。
结构
让我们快速浏览一下我们的关键组件:
1. 干/补丁嵌入层(Stem/PatchEmbed):干/补丁层在网络开始时处理图像。对于该网络,它创建补丁/标记,并将其转换为嵌入。
2.层(Level):它是重复性的构建模块,使用不同的模块提取特征。
3.全局令牌生成/特征提取:它利用 Deepthwise-CNN、SqueezeAndExcitation(Squeeze-Excitation)、CNN 和 MaxPooling 生成全局标记/片段。因此,它基本上就是一个特征提取器。
4.块:它是一个重复性模块,用于关注特征并将其投射到某个维度。
1.局部-MSA:局部多头自我关注。
2.Global-MSA:全局多头自我注意。
3.MLP:将向量投射到另一维度的线性层。
5.Downsample/ReduceSize:它与全局令牌生成模块非常相似,但它使用 CNN 而不是 MaxPooling 进行降采样,并增加了层归一化模块。
6.头部:它是负责分类任务的模块。
1.池化:它将 N x 2D 特征转换为 N x 1D 特征。
2.分类器:它处理 N x 1D 个特征,从而对类别做出判断。
为了便于理解,我对架构图做了注释、

单元模块
注:本模块用于构建本文中的其他模块。大多数模块都是从其他作品中借用的,或者是旧作的修改版。
1.挤压和激发(SqueezeAndExcitation):挤压-激发(SE)又称瓶颈模块,是一种通道关注。它由 AvgPooling、Dense/FullyConnected(FC)/Linear、GELU 和 Sigmoid 模块组成。

2.Fused-MBConv: 这与 EfficientNetV2 中使用的方法类似。它使用 Depthwise-Conv、GELU、SqueezeAndExcitation 和 Conv 来提取具有重邻关系的特征。需要注意的是,这个模块没有声明新的模块,我们只是直接应用了相应的模块。

3.ReduceSize:这是一个基于 CNN 的降采样模块,其中包括提取特征的 Fused-MBConv 模块、同时降低空间维度和增加通道维度的 Strided Conv 模块,以及对特征进行归一化处理的 LayerNormalization 模块。
在本文/图中,该模块被称为下采样模块。值得一提的是,SwniTransformer 使用了 PatchMerging 模块,而不是 ReduceSize 来减少空间维度和增加通道维度,后者使用的是全连接/密集/线性模块。根据 GCViT 的论文,使用 ReduceSize 的目的之一是通过 CNN 模块增加感应偏置。

4.MLP:这是我们自己的多层感知器模块。这是一个前馈/全连接/线性模块,只需将输入投射到一个任意维度。
class SqueezeAndExcitation(layers.Layer):
"""Squeeze and excitation block.
Args:
output_dim: output features dimension, if `None` use same dim as input.
expansion: expansion ratio.
"""
def __init__(self, output_dim=None, expansion=0.25, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.expansion = expansion
self.output_dim = output_dim
def build(self, input_shape):
inp = input_shape[-1]
self.output_dim = self.output_dim or inp
self.avg_pool = layers.GlobalAvgPool2D(keepdims=True, name="avg_pool")
self.fc = [
layers.Dense(int(inp * self.expansion), use_bias=False, name="fc_0"),
layers.Activation("gelu", name="fc_1"),
layers.Dense(self.output_dim, use_bias=False, name="fc_2"),
layers.Activation("sigmoid", name="fc_3"),
]
super().build(input_shape)
def call(self, inputs, **kwargs):
x = self.avg_pool(inputs)
for layer in self.fc:
x = layer(x)
return x * inputs
class ReduceSize(layers.Layer):
"""Down-sampling block.
Args:
keepdims: if False spatial dim is reduced and channel dim is increased
"""
def __init__(self, keepdims=False, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.keepdims = keepdims
def build(self, input_shape):
embed_dim = input_shape[-1]
dim_out = embed_dim if self.keepdims else 2 * embed_dim
self.pad1 = layers.ZeroPadding2D(1, name="pad1")
self.pad2 = layers.ZeroPadding2D(1, name="pad2")
self.conv = [
layers.DepthwiseConv2D(
kernel_size=3, strides=1, padding="valid", use_bias=False, name="conv_0"
),
layers.Activation("gelu", name="conv_1"),
SqueezeAndExcitation(name="conv_2"),
layers.Conv2D(
embed_dim,
kernel_size=1,
strides=1,
padding="valid",
use_bias=False,
name="conv_3",
),
]
self.reduction = layers.Conv2D(
dim_out,
kernel_size=3,
strides=2,
padding="valid",
use_bias=False,
name="reduction",
)
self.norm1 = layers.LayerNormalization(
-1, 1e-05, name="norm1"
) # eps like PyTorch
self.norm2 = layers.LayerNormalization(-1, 1e-05, name="norm2")
def call(self, inputs, **kwargs):
x = self.norm1(inputs)
xr = self.pad1(x)
for layer in self.conv:
xr = layer(xr)
x = x + xr
x = self.pad2(x)
x = self.reduction(x)
x = self.norm2(x)
return x
class MLP(layers.Layer):
"""Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) block.
Args:
hidden_features: hidden features dimension.
out_features: output features dimension.
activation: activation function.
dropout: dropout rate.
"""
def __init__(
self,
hidden_features=None,
out_features=None,
activation="gelu",
dropout=0.0,
**kwargs,
):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.hidden_features = hidden_features
self.out_features = out_features
self.activation = activation
self.dropout = dropout
def build(self, input_shape):
self.in_features = input_shape[-1]
self.hidden_features = self.hidden_features or self.in_features
self.out_features = self.out_features or self.in_features
self.fc1 = layers.Dense(self.hidden_features, name="fc1")
self.act = layers.Activation(self.activation, name="act")
self.fc2 = layers.Dense(self.out_features, name="fc2")
self.drop1 = layers.Dropout(self.dropout, name="drop1")
self.drop2 = layers.Dropout(self.dropout, name="drop2")
def call(self, inputs, **kwargs):
x = self.fc1(inputs)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.drop1(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.drop2(x)
return xStem
注释在代码中,该模块被称为 PatchEmbed,但在纸面上,它被称为 Stem。
在模型中,我们首先使用了 patch_embed 模块。让我们试着理解一下这个模块。
从调用方法中我们可以看到:
1.该模块首先对输入进行填充。
2.然后使用卷积提取带有嵌入的补丁。
3.最后,使用 ReduceSize 模块先用卷积提取特征,但既不降低空间维度,也不增加空间维度。
4.值得注意的一点是,与 ViT 或 SwinTransformer 不同,GCViT 会创建重叠的补丁。
我们可以从代码 Conv2D(self.embed_dim, kernel_size=3, strides=2, name='proj') 中发现这一点。如果我们想要不重叠的补丁,就应该使用相同的 kernel_size 和 strides。
5.该模块将输入的空间维度减少了 4 倍。
摘要:图像 → 填充 → 卷积 → (特征提取 + 下采样)
class PatchEmbed(layers.Layer):
"""Patch embedding block.
Args:
embed_dim: feature size dimension.
"""
def __init__(self, embed_dim, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
def build(self, input_shape):
self.pad = layers.ZeroPadding2D(1, name="pad")
self.proj = layers.Conv2D(self.embed_dim, 3, 2, name="proj")
self.conv_down = ReduceSize(keepdims=True, name="conv_down")
def call(self, inputs, **kwargs):
x = self.pad(inputs)
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.conv_down(x)
return x
全局Token创建
注释它是两个 CNN 模块之一,用于模拟感应偏差。
从上面的单元格中我们可以看到,在这一层中,我们首先使用了 to_q_global/Global Token Gen./FeatureExtraction。
让我们来了解一下它是如何工作的:
× 此模块是 FeatureExtract 模块的系列,根据论文,我们需要重复此模块 K 次,其中 K = log2(H/h),H = feature_map_height,W = feature_map_width。
× 特征提取:这一层与 ReduceSize 模块非常相似,但它使用 MaxPooling 模块来减少维度,不增加特征维度(channelie),也不使用 LayerNormalizaton。该模块被反复用于 Generate Token Gen. 模块,为全局上下文关注生成全局标记。
×从图中需要注意的一点是,全局标记在整个图像中共享,这意味着我们只使用一个全局窗口来处理图像中的所有局部标记。这使得计算非常高效。
×对于输入形状为(B、H、W、C)的特征图,我们将得到输出形状(B、H、W、C)。如果我们将这些全局标记复制到图像中的 M 个局部窗口,其中 M = (H x W)/(h x w) = num_window,那么输出形状为:(B * M, h, w, C)"。
摘要:该模块用于调整图像大小以适应窗口。

class FeatureExtraction(layers.Layer):
"""Feature extraction block.
Args:
keepdims: bool argument for maintaining the resolution.
"""
def __init__(self, keepdims=False, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.keepdims = keepdims
def build(self, input_shape):
embed_dim = input_shape[-1]
self.pad1 = layers.ZeroPadding2D(1, name="pad1")
self.pad2 = layers.ZeroPadding2D(1, name="pad2")
self.conv = [
layers.DepthwiseConv2D(3, 1, use_bias=False, name="conv_0"),
layers.Activation("gelu", name="conv_1"),
SqueezeAndExcitation(name="conv_2"),
layers.Conv2D(embed_dim, 1, 1, use_bias=False, name="conv_3"),
]
if not self.keepdims:
self.pool = layers.MaxPool2D(3, 2, name="pool")
super().build(input_shape)
def call(self, inputs, **kwargs):
x = inputs
xr = self.pad1(x)
for layer in self.conv:
xr = layer(xr)
x = x + xr
if not self.keepdims:
x = self.pool(self.pad2(x))
return x
class GlobalQueryGenerator(layers.Layer):
"""Global query generator.
Args:
keepdims: to keep the dimension of FeatureExtraction layer.
For instance, repeating log(56/7) = 3 blocks, with input
window dimension 56 and output window dimension 7 at down-sampling
ratio 2. Please check Fig.5 of GC ViT paper for details.
"""
def __init__(self, keepdims=False, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.keepdims = keepdims
def build(self, input_shape):
self.to_q_global = [
FeatureExtraction(keepdims, name=f"to_q_global_{i}")
for i, keepdims in enumerate(self.keepdims)
]
super().build(input_shape)
def call(self, inputs, **kwargs):
x = inputs
for layer in self.to_q_global:
x = layer(x)
return x注意事项
这是本文的核心要点。
从调用方法中我们可以看到: WindowAttention 模块会根据 global_query 参数应用本地和全局窗口注意力。
1.首先,它将输入特征转换成查询、键、值,用于局部关注;将键、值转换成键、值,用于全局关注。对于全局关注,它将从全局令牌 Gen 中获取全局查询。qkv = tf.reshape(qkv, [B_, N, self.qkv_size, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads])
2.在发送查询、键和值以引起注意之前,全局令牌要经过一个重要的过程。q_global = tf.repeat(q_global,repeats=B_//B,axis=0),这里 B_//B 表示图像中的窗口数。
3.然后根据 global_query 参数,简单地应用局部窗口自注意或全局窗口注意。代码中值得注意的一点是,我们使用注意力掩码添加了相对位置嵌入,而不是补丁嵌入。 attn = attn + relative_position_bias[tf.newaxis,

4.现在,让我们思考一下,试着理解一下这里发生了什么。
请看下图。从左图我们可以看到,在本地注意力模式下,查询是本地的,而且仅限于本地窗口(红色方框),因此我们无法获取远程信息。而在右图中,由于是全局查询,我们现在不再局限于本地窗口(蓝色方框),我们可以获取远距离信息。

5. 在 ViT 中,我们将(注意力)图像图元与图像图元进行比较,在 SwinTransformer 中,我们将窗口图元与窗口图元进行比较,但在 GCViT 中,我们将图像图元与窗口图元进行比较。
但现在您可能会问,即使图像图元的尺寸比窗口图元的尺寸大,又如何比较(关注)图像图元和窗口图元呢?
从上图可以看出,图像图元的形状是(1, 8, 8, 3),而窗口图元的形状是(1, 4, 4, 3))。是的,你说得对,我们无法直接比较它们,因此我们使用全局令牌生成/特征提取 CNN 模块调整了图像令牌的大小,以适应窗口令牌。
下表应该能给您一个清晰的比较:

class WindowAttention(layers.Layer):
"""Local window attention.
This implementation was proposed by
[Liu et al., 2021](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.14030) in SwinTransformer.
Args:
window_size: window size.
num_heads: number of attention head.
global_query: if the input contains global_query
qkv_bias: bool argument for query, key, value learnable bias.
qk_scale: bool argument to scaling query, key.
attention_dropout: attention dropout rate.
projection_dropout: output dropout rate.
"""
def __init__(
self,
window_size,
num_heads,
global_query,
qkv_bias=True,
qk_scale=None,
attention_dropout=0.0,
projection_dropout=0.0,
**kwargs,
):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
window_size = (window_size, window_size)
self.window_size = window_size
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.global_query = global_query
self.qkv_bias = qkv_bias
self.qk_scale = qk_scale
self.attention_dropout = attention_dropout
self.projection_dropout = projection_dropout
def build(self, input_shape):
embed_dim = input_shape[0][-1]
head_dim = embed_dim // self.num_heads
self.scale = self.qk_scale or head_dim**-0.5
self.qkv_size = 3 - int(self.global_query)
self.qkv = layers.Dense(
embed_dim * self.qkv_size, use_bias=self.qkv_bias, name="qkv"
)
self.relative_position_bias_table = self.add_weight(
name="relative_position_bias_table",
shape=[
(2 * self.window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * self.window_size[1] - 1),
self.num_heads,
],
initializer=keras.initializers.TruncatedNormal(stddev=0.02),
trainable=True,
dtype=self.dtype,
)
self.attn_drop = layers.Dropout(self.attention_dropout, name="attn_drop")
self.proj = layers.Dense(embed_dim, name="proj")
self.proj_drop = layers.Dropout(self.projection_dropout, name="proj_drop")
self.softmax = layers.Activation("softmax", name="softmax")
super().build(input_shape)
def get_relative_position_index(self):
coords_h = ops.arange(self.window_size[0])
coords_w = ops.arange(self.window_size[1])
coords = ops.stack(ops.meshgrid(coords_h, coords_w, indexing="ij"), axis=0)
coords_flatten = ops.reshape(coords, [2, -1])
relative_coords = coords_flatten[:, :, None] - coords_flatten[:, None, :]
relative_coords = ops.transpose(relative_coords, axes=[1, 2, 0])
relative_coords_xx = relative_coords[:, :, 0] + self.window_size[0] - 1
relative_coords_yy = relative_coords[:, :, 1] + self.window_size[1] - 1
relative_coords_xx = relative_coords_xx * (2 * self.window_size[1] - 1)
relative_position_index = relative_coords_xx + relative_coords_yy
return relative_position_index
def call(self, inputs, **kwargs):
if self.global_query:
inputs, q_global = inputs
B = ops.shape(q_global)[0] # B, N, C
else:
inputs = inputs[0]
B_, N, C = ops.shape(inputs) # B*num_window, num_tokens, channels
qkv = self.qkv(inputs)
qkv = ops.reshape(
qkv, [B_, N, self.qkv_size, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads]
)
qkv = ops.transpose(qkv, [2, 0, 3, 1, 4])
if self.global_query:
k, v = ops.split(
qkv, indices_or_sections=2, axis=0
) # for unknown shame num=None will throw error
q_global = ops.repeat(
q_global, repeats=B_ // B, axis=0
) # num_windows = B_//B => q_global same for all windows in a img
q = ops.reshape(q_global, [B_, N, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads])
q = ops.transpose(q, axes=[0, 2, 1, 3])
else:
q, k, v = ops.split(qkv, indices_or_sections=3, axis=0)
q = ops.squeeze(q, axis=0)
k = ops.squeeze(k, axis=0)
v = ops.squeeze(v, axis=0)
q = q * self.scale
attn = q @ ops.transpose(k, axes=[0, 1, 3, 2])
relative_position_bias = ops.take(
self.relative_position_bias_table,
ops.reshape(self.get_relative_position_index(), [-1]),
)
relative_position_bias = ops.reshape(
relative_position_bias,
[
self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1],
self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1],
-1,
],
)
relative_position_bias = ops.transpose(relative_position_bias, axes=[2, 0, 1])
attn = attn + relative_position_bias[None,]
attn = self.softmax(attn)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
x = ops.transpose((attn @ v), axes=[0, 2, 1, 3])
x = ops.reshape(x, [B_, N, C])
x = self.proj_drop(self.proj(x))
return x模块
备注:该模块没有任何卷积模块。
在本级别中,我们使用的第二个模块是块。让我们来了解一下它是如何工作的。
从调用方法中我们可以看到:
1.Block 模块只接受用于局部关注的 feature_maps,或者接受用于全局关注的附加全局查询。
2. 在发送用于关注的特征图之前,该模块会将批量特征图转换为批量窗口,因为我们将应用窗口关注。
3. 然后,我们将批量发送批量窗口以供关注。
4. 应用注意力后,我们将批量窗口还原为批量特征图。
5. 在将注意力发送到应用特征输出之前,该模块会在残差连接中应用随机深度正则化。
此外,在应用随机深度正则化之前,它还会使用可训练参数对输入进行重新缩放。
需要注意的是,随机深度模块并没有在本文的图中显示。

窗口
在图块模块中,我们在应用注意力前后创建了窗口。下面的模块将特征图(B、H、W、C)转换为堆叠窗口(B x H/h x W/w、h、w、C)→(num_windows_batch、window_size、window_size、channel) * 该模块使用重塑和转置(reshape & transpose)从图像中创建这些窗口,而不是对它们进行迭代。
class Block(layers.Layer):
"""GCViT block.
Args:
window_size: window size.
num_heads: number of attention head.
global_query: apply global window attention
mlp_ratio: MLP ratio.
qkv_bias: bool argument for query, key, value learnable bias.
qk_scale: bool argument to scaling query, key.
drop: dropout rate.
attention_dropout: attention dropout rate.
path_drop: drop path rate.
activation: activation function.
layer_scale: layer scaling coefficient.
"""
def __init__(
self,
window_size,
num_heads,
global_query,
mlp_ratio=4.0,
qkv_bias=True,
qk_scale=None,
dropout=0.0,
attention_dropout=0.0,
path_drop=0.0,
activation="gelu",
layer_scale=None,
**kwargs,
):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.window_size = window_size
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.global_query = global_query
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio
self.qkv_bias = qkv_bias
self.qk_scale = qk_scale
self.dropout = dropout
self.attention_dropout = attention_dropout
self.path_drop = path_drop
self.activation = activation
self.layer_scale = layer_scale
def build(self, input_shape):
B, H, W, C = input_shape[0]
self.norm1 = layers.LayerNormalization(-1, 1e-05, name="norm1")
self.attn = WindowAttention(
window_size=self.window_size,
num_heads=self.num_heads,
global_query=self.global_query,
qkv_bias=self.qkv_bias,
qk_scale=self.qk_scale,
attention_dropout=self.attention_dropout,
projection_dropout=self.dropout,
name="attn",
)
self.drop_path1 = DropPath(self.path_drop)
self.drop_path2 = DropPath(self.path_drop)
self.norm2 = layers.LayerNormalization(-1, 1e-05, name="norm2")
self.mlp = MLP(
hidden_features=int(C * self.mlp_ratio),
dropout=self.dropout,
activation=self.activation,
name="mlp",
)
if self.layer_scale is not None:
self.gamma1 = self.add_weight(
name="gamma1",
shape=[C],
initializer=keras.initializers.Constant(self.layer_scale),
trainable=True,
dtype=self.dtype,
)
self.gamma2 = self.add_weight(
name="gamma2",
shape=[C],
initializer=keras.initializers.Constant(self.layer_scale),
trainable=True,
dtype=self.dtype,
)
else:
self.gamma1 = 1.0
self.gamma2 = 1.0
self.num_windows = int(H // self.window_size) * int(W // self.window_size)
super().build(input_shape)
def call(self, inputs, **kwargs):
if self.global_query:
inputs, q_global = inputs
else:
inputs = inputs[0]
B, H, W, C = ops.shape(inputs)
x = self.norm1(inputs)
# create windows and concat them in batch axis
x = self.window_partition(x, self.window_size) # (B_, win_h, win_w, C)
# flatten patch
x = ops.reshape(x, [-1, self.window_size * self.window_size, C])
# attention
if self.global_query:
x = self.attn([x, q_global])
else:
x = self.attn([x])
# reverse window partition
x = self.window_reverse(x, self.window_size, H, W, C)
# FFN
x = inputs + self.drop_path1(x * self.gamma1)
x = x + self.drop_path2(self.gamma2 * self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))
return x
def window_partition(self, x, window_size):
"""
Args:
x: (B, H, W, C)
window_size: window size
Returns:
local window features (num_windows*B, window_size, window_size, C)
"""
B, H, W, C = ops.shape(x)
x = ops.reshape(
x,
[
-1,
H // window_size,
window_size,
W // window_size,
window_size,
C,
],
)
x = ops.transpose(x, axes=[0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5])
windows = ops.reshape(x, [-1, window_size, window_size, C])
return windows
def window_reverse(self, windows, window_size, H, W, C):
"""
Args:
windows: local window features (num_windows*B, window_size, window_size, C)
window_size: Window size
H: Height of image
W: Width of image
C: Channel of image
Returns:
x: (B, H, W, C)
"""
x = ops.reshape(
windows,
[
-1,
H // window_size,
W // window_size,
window_size,
window_size,
C,
],
)
x = ops.transpose(x, axes=[0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5])
x = ops.reshape(x, [-1, H, W, C])
return x级别
注:该模块包含变压器模块和 CNN 模块。
在模型中,我们使用的第二个模块是 Level。让我们试着理解一下这个模块。从调用方法中我们可以看到:
1.首先,它创建了带有一系列特征提取模块的 global_token。稍后我们会看到,FeatureExtraction 只是一个基于 CNN 的简单模块。
2. 然后,它使用一系列的 Block 模块,根据深度级别应用局部或全局窗口注意力。
3. 最后,它使用 ReduceSize 缩减上下文特征的维度。
摘要: feature_map → global_token → local/lobal window attention → dowsample

class Level(layers.Layer):
"""GCViT level.
Args:
depth: number of layers in each stage.
num_heads: number of heads in each stage.
window_size: window size in each stage.
keepdims: dims to keep in FeatureExtraction.
downsample: bool argument for down-sampling.
mlp_ratio: MLP ratio.
qkv_bias: bool argument for query, key, value learnable bias.
qk_scale: bool argument to scaling query, key.
drop: dropout rate.
attention_dropout: attention dropout rate.
path_drop: drop path rate.
layer_scale: layer scaling coefficient.
"""
def __init__(
self,
depth,
num_heads,
window_size,
keepdims,
downsample=True,
mlp_ratio=4.0,
qkv_bias=True,
qk_scale=None,
dropout=0.0,
attention_dropout=0.0,
path_drop=0.0,
layer_scale=None,
**kwargs,
):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.depth = depth
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.window_size = window_size
self.keepdims = keepdims
self.downsample = downsample
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio
self.qkv_bias = qkv_bias
self.qk_scale = qk_scale
self.dropout = dropout
self.attention_dropout = attention_dropout
self.path_drop = path_drop
self.layer_scale = layer_scale
def build(self, input_shape):
path_drop = (
[self.path_drop] * self.depth
if not isinstance(self.path_drop, list)
else self.path_drop
)
self.blocks = [
Block(
window_size=self.window_size,
num_heads=self.num_heads,
global_query=bool(i % 2),
mlp_ratio=self.mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=self.qkv_bias,
qk_scale=self.qk_scale,
dropout=self.dropout,
attention_dropout=self.attention_dropout,
path_drop=path_drop[i],
layer_scale=self.layer_scale,
name=f"blocks_{i}",
)
for i in range(self.depth)
]
self.down = ReduceSize(keepdims=False, name="downsample")
self.q_global_gen = GlobalQueryGenerator(self.keepdims, name="q_global_gen")
super().build(input_shape)
def call(self, inputs, **kwargs):
x = inputs
q_global = self.q_global_gen(x) # shape: (B, win_size, win_size, C)
for i, blk in enumerate(self.blocks):
if i % 2:
x = blk([x, q_global]) # shape: (B, H, W, C)
else:
x = blk([x]) # shape: (B, H, W, C)
if self.downsample:
x = self.down(x) # shape: (B, H//2, W//2, 2*C)
return x模型
让我们直接跳转到模型。从调用方法中我们可以看到:
1.它从图像中创建补丁嵌入。这一层不会对这些嵌入式进行扁平化处理,这意味着该模块的输出将是(batch, height/window_size, width/window_size, embed_dim),而不是(batch, height x width/window_size^2, embed_dim)。
2. 将这些嵌入信息传递给一系列 Level 模块,我们称之为 Level,其中包括:
× 生成全局标记
× 应用局部和全局注意力
× 最后应用降采样。
3.因此,经过 n 层后的输出形状为:(batch, width/window_size x 2^{n-1}, width/window_size x 2^{n-1}, embed_dim x 2^{n-1})。
在最后一层,本文不使用降采样和增加通道。
4.使用 LayerNormalization 模块对上述层的输出进行归一化处理。
5.在头部,使用池化模块将二维特征转换为一维特征。该模块之后的输出形状为(batch, embed_dim x 2^{n-1})。
最后,池化后的特征被发送到 Dense/Linear 模块进行分类。
总和:图像 → (补丁 + 嵌入) → 剔除 → (注意 + 特征提取) → 归一化 → 汇集 → 分类
class GCViT(keras.Model):
"""GCViT model.
Args:
window_size: window size in each stage.
embed_dim: feature size dimension.
depths: number of layers in each stage.
num_heads: number of heads in each stage.
drop_rate: dropout rate.
mlp_ratio: MLP ratio.
qkv_bias: bool argument for query, key, value learnable bias.
qk_scale: bool argument to scaling query, key.
attention_dropout: attention dropout rate.
path_drop: drop path rate.
layer_scale: layer scaling coefficient.
num_classes: number of classes.
head_activation: activation function for head.
"""
def __init__(
self,
window_size,
embed_dim,
depths,
num_heads,
drop_rate=0.0,
mlp_ratio=3.0,
qkv_bias=True,
qk_scale=None,
attention_dropout=0.0,
path_drop=0.1,
layer_scale=None,
num_classes=1000,
head_activation="softmax",
**kwargs,
):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.window_size = window_size
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.depths = depths
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.drop_rate = drop_rate
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio
self.qkv_bias = qkv_bias
self.qk_scale = qk_scale
self.attention_dropout = attention_dropout
self.path_drop = path_drop
self.layer_scale = layer_scale
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.head_activation = head_activation
self.patch_embed = PatchEmbed(embed_dim=embed_dim, name="patch_embed")
self.pos_drop = layers.Dropout(drop_rate, name="pos_drop")
path_drops = np.linspace(0.0, path_drop, sum(depths))
keepdims = [(0, 0, 0), (0, 0), (1,), (1,)]
self.levels = []
for i in range(len(depths)):
path_drop = path_drops[sum(depths[:i]) : sum(depths[: i + 1])].tolist()
level = Level(
depth=depths[i],
num_heads=num_heads[i],
window_size=window_size[i],
keepdims=keepdims[i],
downsample=(i < len(depths) - 1),
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
qk_scale=qk_scale,
dropout=drop_rate,
attention_dropout=attention_dropout,
path_drop=path_drop,
layer_scale=layer_scale,
name=f"levels_{i}",
)
self.levels.append(level)
self.norm = layers.LayerNormalization(axis=-1, epsilon=1e-05, name="norm")
self.pool = layers.GlobalAvgPool2D(name="pool")
self.head = layers.Dense(num_classes, name="head", activation=head_activation)
def build(self, input_shape):
super().build(input_shape)
self.built = True
def call(self, inputs, **kwargs):
x = self.patch_embed(inputs) # shape: (B, H, W, C)
x = self.pos_drop(x)
for level in self.levels:
x = level(x) # shape: (B, H_, W_, C_)
x = self.norm(x)
x = self.pool(x) # shape: (B, C__)
x = self.head(x)
return x
def build_graph(self, input_shape=(224, 224, 3)):
"""
ref: https://www.kaggle.com/code/ipythonx/tf-hybrid-efficientnet-swin-transformer-gradcam
"""
x = keras.Input(shape=input_shape)
return keras.Model(inputs=[x], outputs=self.call(x), name=self.name)
def summary(self, input_shape=(224, 224, 3)):
return self.build_graph(input_shape).summary()建立模型
让我们用上面介绍的所有模块建立一个完整的模型。
我们将按照论文中提到的配置建立 GCViT-XXTiny 模型。
此外,我们还将加载移植的官方预训练权重,并尝试进行一些预测。
# Model Configs
config = {
"window_size": (7, 7, 14, 7),
"embed_dim": 64,
"depths": (2, 2, 6, 2),
"num_heads": (2, 4, 8, 16),
"mlp_ratio": 3.0,
"path_drop": 0.2,
}
ckpt_link = (
"https://github.com/awsaf49/gcvit-tf/releases/download/v1.1.6/gcvitxxtiny.keras"
)
# Build Model
model = GCViT(**config)
inp = ops.array(np.random.uniform(size=(1, 224, 224, 3)))
out = model(inp)
# Load Weights
ckpt_path = keras.utils.get_file(ckpt_link.split("/")[-1], ckpt_link)
model.load_weights(ckpt_path)
# Summary
model.summary((224, 224, 3))执行:
Downloading data from https://github.com/awsaf49/gcvit-tf/releases/download/v1.1.6/gcvitxxtiny.keras
48767519/48767519 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 0us/step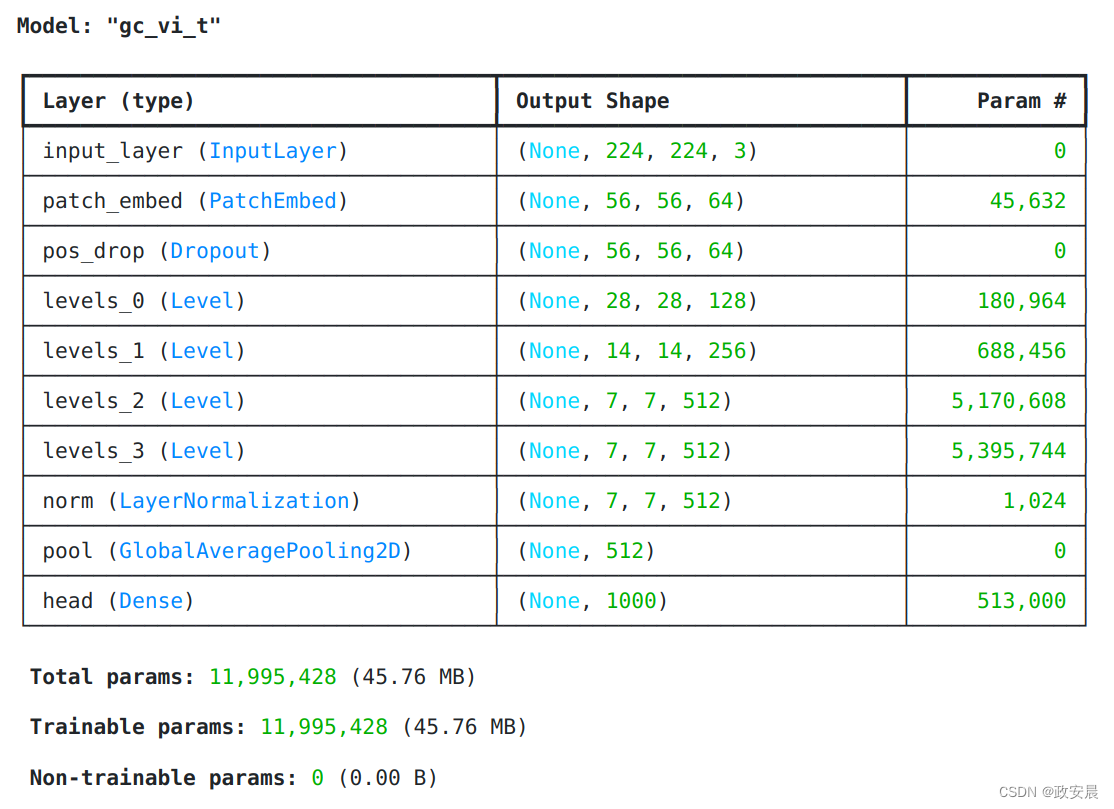
预训练权重的理智检查
img = keras.applications.imagenet_utils.preprocess_input(
chelsea(), mode="torch"
) # Chelsea the cat
img = ops.image.resize(img, (224, 224))[None,] # resize & create batch
pred = model(img)
pred_dec = keras.applications.imagenet_utils.decode_predictions(pred)[0]
print("\n# Image:")
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
plt.imshow(chelsea())
plt.show()
print()
print("# Prediction (Top 5):")
for i in range(5):
print("{:<12} : {:0.2f}".format(pred_dec[i][1], pred_dec[i][2]))执行:
Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/imagenet_class_index.json
35363/35363 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 0us/step微调 GCViT 模型
在接下来的单元中,我们将在包含 104 个类别的花朵数据集上对 GCViT 模型进行微调。
配置
# Model
IMAGE_SIZE = (224, 224)
# Hyper Params
BATCH_SIZE = 32
EPOCHS = 5
# Dataset
CLASSES = [
"dandelion",
"daisy",
"tulips",
"sunflowers",
"roses",
] # don't change the order
# Other constants
MEAN = 255 * np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], dtype="float32") # imagenet mean
STD = 255 * np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225], dtype="float32") # imagenet std
AUTO = tf.data.AUTOTUNE数据加载器
def make_dataset(dataset: tf.data.Dataset, train: bool, image_size: int = IMAGE_SIZE):
def preprocess(image, label):
# for training, do augmentation
if train:
if tf.random.uniform(shape=[]) > 0.5:
image = tf.image.flip_left_right(image)
image = tf.image.resize(image, size=image_size, method="bicubic")
image = (image - MEAN) / STD # normalization
return image, label
if train:
dataset = dataset.shuffle(BATCH_SIZE * 10)
return dataset.map(preprocess, AUTO).batch(BATCH_SIZE).prefetch(AUTO)花卉数据集
train_dataset, val_dataset = tfds.load(
"tf_flowers",
split=["train[:90%]", "train[90%:]"],
as_supervised=True,
try_gcs=False, # gcs_path is necessary for tpu,
)
train_dataset = make_dataset(train_dataset, True)
val_dataset = make_dataset(val_dataset, False)Downloading and preparing dataset 218.21 MiB (download: 218.21 MiB, generated: 221.83 MiB, total: 440.05 MiB) to /root/tensorflow_datasets/tf_flowers/3.0.1...
Dl Completed...: 0%| | 0/5 [00:00<?, ? file/s]
Dataset tf_flowers downloaded and prepared to /root/tensorflow_datasets/tf_flowers/3.0.1. Subsequent calls will reuse this data.为花卉数据集重建模型
# Re-Build Model
model = GCViT(**config, num_classes=104)
inp = ops.array(np.random.uniform(size=(1, 224, 224, 3)))
out = model(inp)
# Load Weights
ckpt_path = keras.utils.get_file(ckpt_link.split("/")[-1], ckpt_link)
model.load_weights(ckpt_path, skip_mismatch=True)
model.compile(
loss="sparse_categorical_crossentropy", optimizer="adam", metrics=["accuracy"]
)演绎展示:
/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/keras/src/saving/saving_lib.py:269: UserWarning: A total of 1 objects could not be loaded. Example error message for object <Dense name=head, built=True>:
Layer 'head' expected 2 variables, but received 0 variables during loading. Expected: ['kernel', 'bias']
List of objects that could not be loaded:
[<Dense name=head, built=True>]
warnings.warn(msg)训练
Epoch 1/5
104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 153s 581ms/step - accuracy: 0.5140 - loss: 1.4615 - val_accuracy: 0.8828 - val_loss: 0.3485
Epoch 2/5
104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 7s 69ms/step - accuracy: 0.8775 - loss: 0.3437 - val_accuracy: 0.8828 - val_loss: 0.3508
Epoch 3/5
104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 7s 68ms/step - accuracy: 0.8937 - loss: 0.2918 - val_accuracy: 0.9019 - val_loss: 0.2953
Epoch 4/5
104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 7s 68ms/step - accuracy: 0.9232 - loss: 0.2397 - val_accuracy: 0.9183 - val_loss: 0.2212
Epoch 5/5
104/104 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 7s 68ms/step - accuracy: 0.9456 - loss: 0.1645 - val_accuracy: 0.9210 - val_loss: 0.2897



![[lesson30]操作符重载的概念](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f8736f7b66334007acb45df57a2098c0.png#pic_center)

![[Java EE] 计算机工作原理与操作系统简明概要](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/990f97548d1d40689b9e5729d1ea75bd.png)