文章目录
- 最小生成树的概念
- Prim算法
- 邻接表
- 邻接矩阵
- 验证Prim
- Kruskal算法
- 邻接表
- 邻接矩阵
- 验证Kruskal
- 源代码
- 邻接表
- 邻接矩阵
最小生成树的概念
最小生成树(Minimum Spanning Tree) : 在加权连通图(连通网)的所有生成树中, 各边权值之和最小的生成树, 称为最小生成树.
- 该定义是在无向连通图的基础上的.
- 最小生成树可能不唯一, 但是其权值之和是唯一的.
- 对于n个顶点的图, 其生成树中必定有n-1条边.
例如:
下图代表6个城市间的交通网, 边上的权值表示公路的造价. 现在要用公路把6个城市连接起来, 也即修5条公路使得公路的总造价最少.

有如下两种方案:
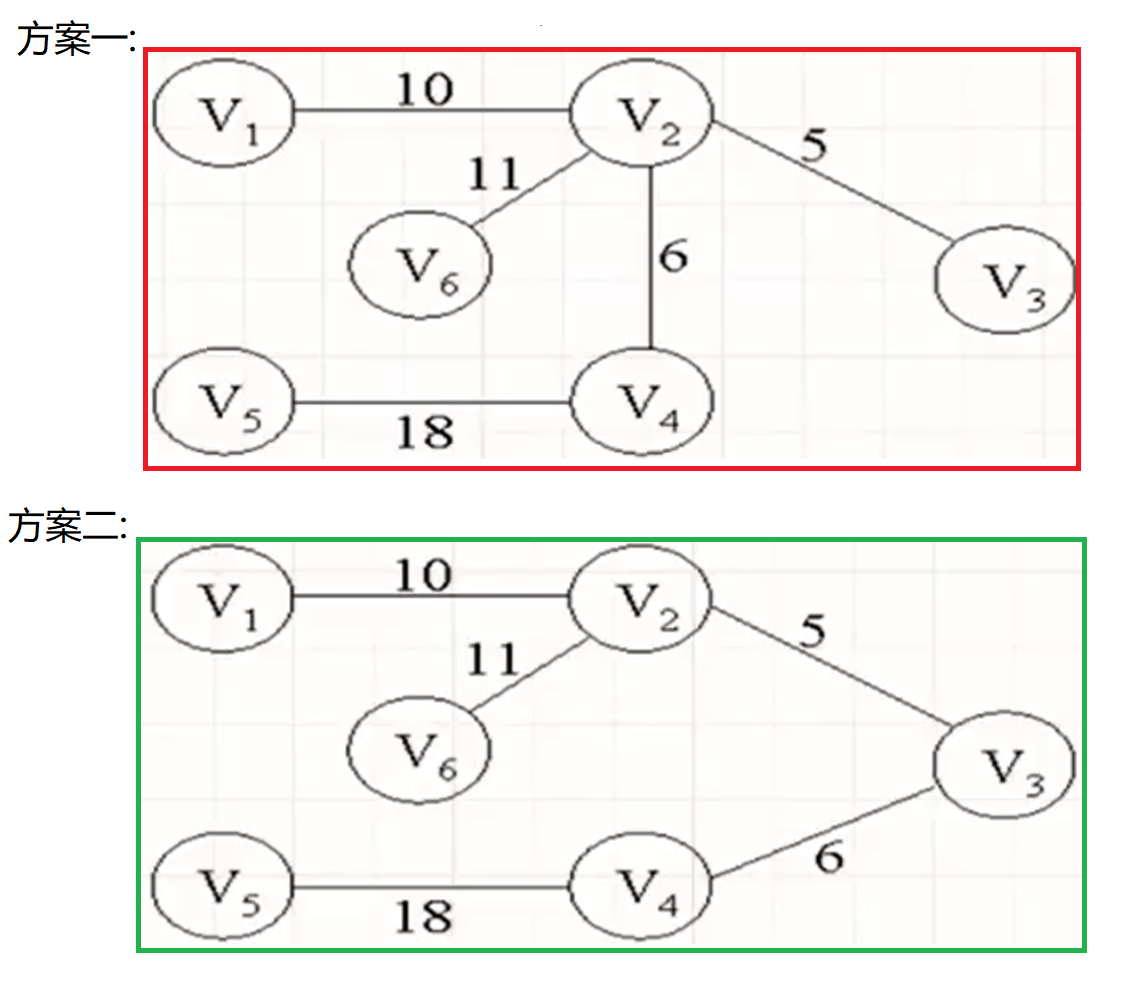
我们可以发现如果图中有较小相等的权值边, 最小生成树可能不唯一, 但是最小生成树上的权值之和是相等的. 上面两种方案的权值之和都是50, 但因为(v2 , v4)和(v3 , v4)这两条边的权值相等, 所以在选边的时候, 方案一选择了(v2 , v4)边, 方案二选择了(v3 , v4)边, 所以造成最小生成树可能不唯一.
MST性质 : 假设G=(V,E)是一个加权连通图, U是顶点集V的一个非空子集. 若(u,v)是一条具有最小权值的边, 其中u∈U, v∈V-U, 则必定存在一棵包含(u,v)的最小生成树.
Prim算法
思路(局部贪心): 设G=(V,E)是一个连通的带权图, 其中V是顶点的集合, E是边的集合, TE为最小生成树的边的集合. 则Prim算法通过以下步骤得到最小生成树:
- 最小生成树T的初始状态为U={u0}(u0∈V), TE={ }, 此时图中只有一个起始顶点, 边集为空.
- 在所有u∈U, v∈V-U的边中找一条代价最小的边(u,v); 把边(u,v)添加到生成树的边集TE, 同时v并入到生成树的顶点集U中.
- 重复执行步骤2, 直到U=V为止. 此时, TE中必有n-1条边, 且T=(U,TE)为G的最小生成树.
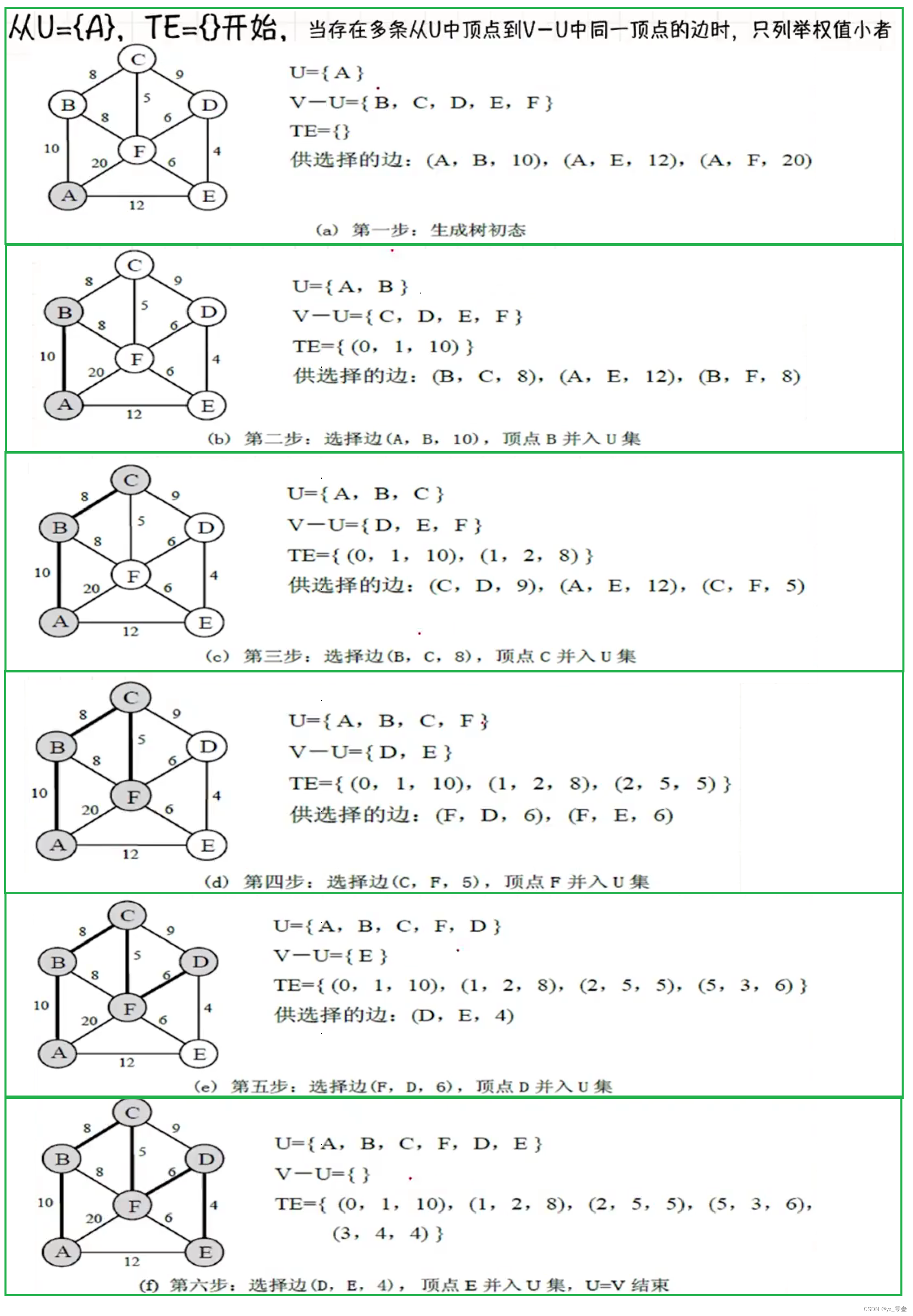
要实现Prim算法需要解决两个问题: 一. 如何选出从U集合中顶点到V集合中顶点权值最小的相连边, 二. 如何区分U集合中的顶点与V集合中的顶点.
- 对于问题一可以使用优先级队列(小根堆)来选出从集合U到集合V之间权值最小的相连边, 每当有顶点加入到集合U时, 就将该加入集合U的顶点与集合V顶点相连的边加入到优先级队列(小根堆)中.
因为需要将相连的边压入到堆中, 所以将压入到堆中的边类型定义为:
struct UndirectedEdge
{
int _srci;
int _dsti;
W _weight; // 边的权值
UndirectedEdge(int srci, int dsti, const W& weight)
:_srci(srci)
, _dsti(dsti)
, _weight(weight)
{}
bool operator>(const UndirectedEdge& ue) const
{
return this->_weight > ue._weight;
}
bool operator<(const UndirectedEdge& ue) const
{
return this->_weight < ue._weight;
}
};
- 而对于问题二可以使用位图或者vector来区分集合U与集合V, 因为我们知道顶点对应的下标. 例如顶点v对应的下标为vi, 如果vi在集合U则对应的位图BitMap[vi]或者vector[vi]为true, 否则为false.
邻接表
namespace AdjacentList
{
template<typename W>
struct Edge
{
int _dsti;
W _weight;
struct Edge<W>* _next;
Edge(int dsti, const W& weight)
:_dsti(dsti)
, _weight(weight)
, _next(nullptr)
{}
};
template<typename V, typename W, bool Directed = false>
class Graph
{
using Edge = Edge<W>;
private:
std::vector<V> _vertexSet; // 顶点的集合
std::map<V, int> _vertexIndex; // 顶点映射下标
std::vector<Edge*> _table; // 出度边表
}
}

邻接矩阵
namespace AdjacentMatrix
{
template<typename V, typename W, W W_MAX, bool Directed = false>
class Graph
{
private:
std::vector<V> _vertexSet;
std::map<V, int> _vertexIndex;
std::vector<std::vector<W>> _matrix;
}
}

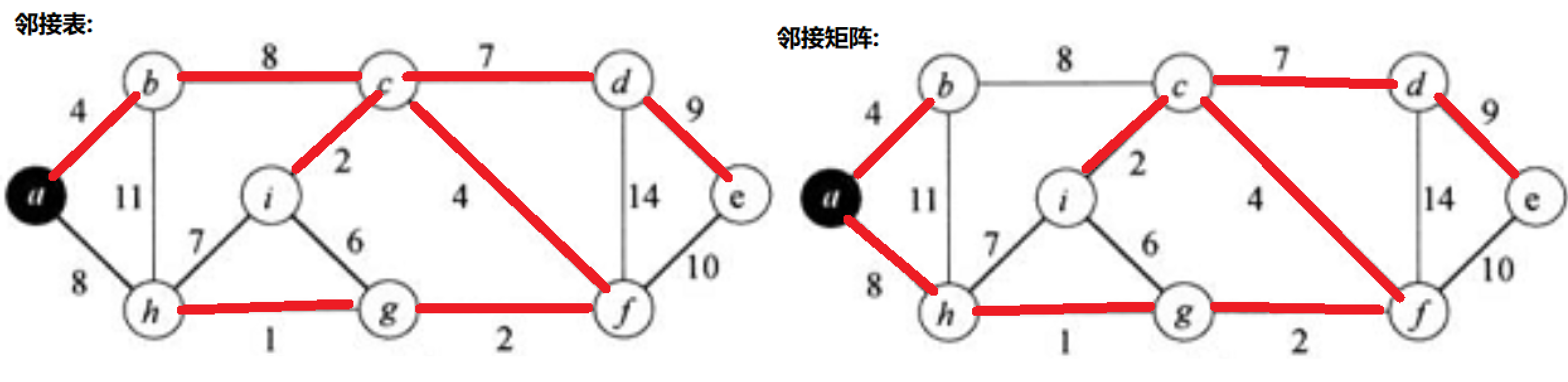
验证Prim
Kruskal算法
思路(全局贪心): 每次从剩下的边中选择具有最小权值且不会产生环路的边加入到生成树的边集中.
- 首先将G中的n个顶点看成是独立的n个连通分量, 这时的状态是有n个顶点而无边的森林, 可以记作为T={V,{}}.
- 然后再E中选择代价最小的边, 如果该边依附两个不同的连通分量, 那么将这条边加入到T中, 否则舍去这条边而选择下一条代价最小的边.
- 以此类推, 直到T中所有顶点都在同一个连通分量中为止, 此时就得到图G的一棵最小生成树.
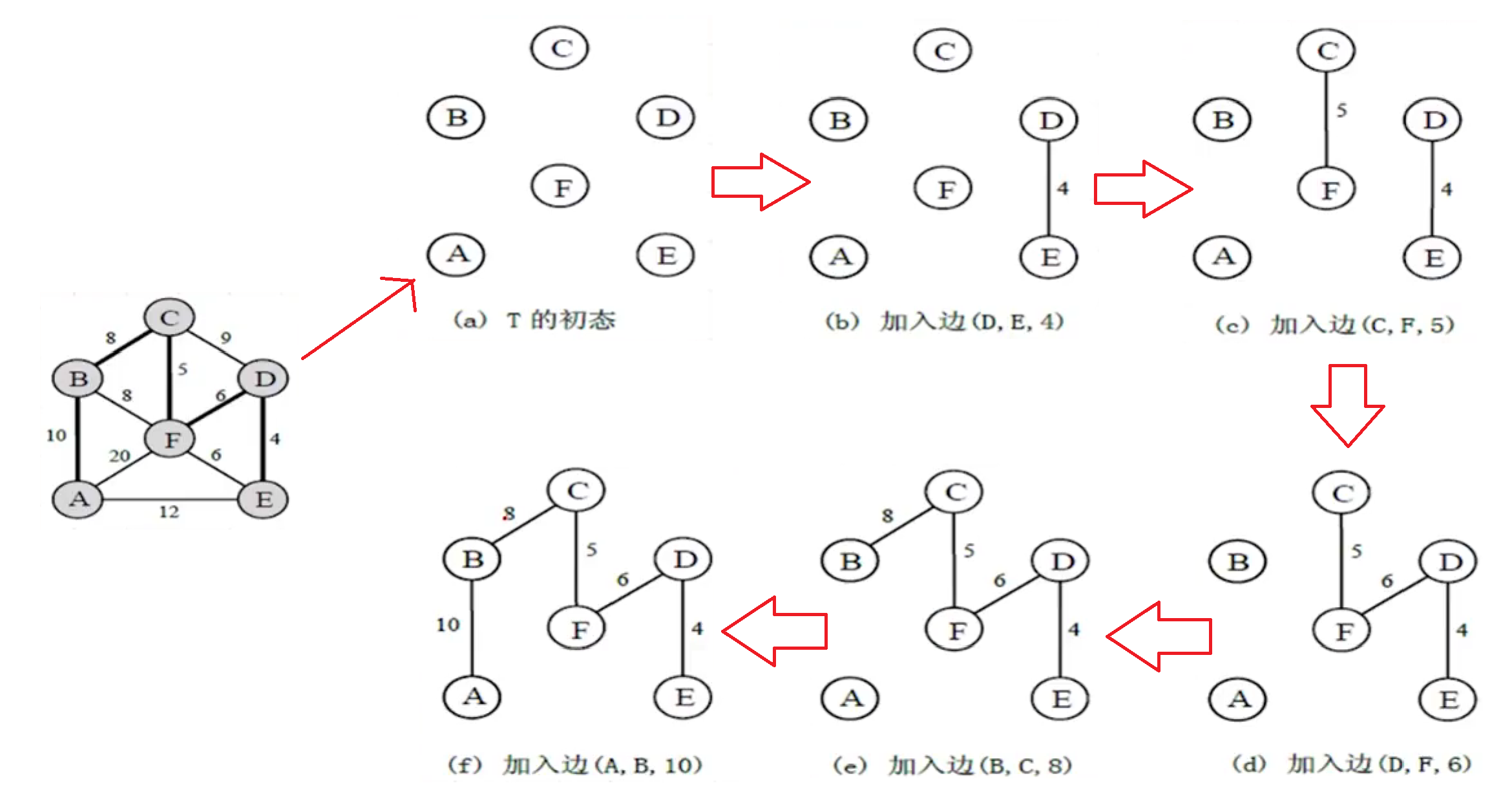
想要实现Kruskal算法就必须解决掉两个问题:一. 如何选出最小权值的边?二. 如何判断选出的边会不会构成环?
- 对于第一个问题可以使用堆,建立小根堆将所有的边压入堆中,堆顶即为权值最小的边。
- 而对于第二个问题需要用到并查集(森林),只有选出边的两个顶点不在同一个集合中才能加入到minTree中,加入minTree之后将这两个顶点合并到一个集合中。
邻接表
在无向图中, 一条边会在邻接表中存储两次, 对于(u,v)这条边, (u,v)与(v,u)这两条意义相同的边都会存储到邻接表中, 所以我们该如何将这两条边中的一条压入堆中呢?
- 我们需要用到unordered_set来标记某条边对应的边, 如果(u,v)入堆则(v,u)插入到unordered_set中.
- 在遍历(即将边压入小根堆)图中的边时, 如果先遇到(u,v)这条边 (没有在unordered_set中) 则将这条边压入小根堆中, 然后将边(v,u)插入到unordered_set中, 如果之后遇到边(v,u)时则先去unordered_set中查找是否有边(v,u), 有则不压入到堆中, 没有则压入堆中.
插入到unordered_set中边的定义:
// 记录已经入堆的边
struct Entry
{
int _srci;
int _dsti;
Entry() = default;
Entry(int srci,int dsti)
:_srci(srci)
,_dsti(dsti)
{}
// 运算符重载以便哈希
bool operator==(const Entry& e) const
{
return _srci == e._srci && _dsti == e._dsti;
}
bool operator!=(const Entry& e) const
{
return _srci != e._srci && _dsti != e._dsti;
}
};
// 仿函数
struct hashFunc
{
int operator()(const Entry& e) const
{
return e._srci + e._dsti + (e._srci * e._dsti);
}
};

邻接矩阵
在无向图中, 一条边会在邻接矩阵中存储两次, 对于(u,v)这条边, (u,v)与(v,u)这两条意义相同的边都会存储到邻接矩阵中, 所以我们该如何将这两条边中的一条压入堆中呢?
因为无向图的邻接矩阵是对称的, 所以在遍历的时候可以只遍历上三角或者下三角来避免两条意义相同的边都压入小根堆中.

验证Kruskal


源代码
邻接表
namespace AdjacentList
{
template<typename W>
struct Edge
{
int _dsti;
W _weight;
struct Edge<W>* _next;
Edge(int dsti, const W& weight)
:_dsti(dsti)
, _weight(weight)
, _next(nullptr)
{}
};
template<typename V, typename W, bool Directed = false>
class Graph
{
using Edge = Edge<W>;
private:
std::vector<V> _vertexSet; // 顶点的集合
std::map<V, int> _vertexIndex; // 顶点映射下标
std::vector<Edge*> _table; // 出度边表
public:
typedef Graph<V, W, Directed> Self;
Graph() = default;
Graph(const V* a, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
AddVertex(a[i]);
}
}
int GetVertexIndex(const V& v)
{
typename std::map<V, int>::iterator pos = _vertexIndex.find(v);
if (pos != _vertexIndex.end())
{
return pos->second;
}
else
{
return -1;
}
}
bool AddVertex(const V& v)
{
if (GetVertexIndex(v) != -1)
return false;
_vertexSet.push_back(v);
_vertexIndex.insert(std::make_pair(v, _vertexSet.size() - 1));
_table.push_back(nullptr);
return true;
}
bool _AddEdge(int srci, int dsti, const W& weight)
{
Edge* edge = new Edge(dsti, weight);
// 头插
edge->_next = _table[srci];
_table[srci] = edge;
// 无向图
if (!Directed)
{
edge = new Edge(srci, weight);
edge->_next = _table[dsti];
_table[dsti] = edge;
}
return true;
}
bool AddEdge(const V& src, const V& dst, const W& weight)
{
int srci = GetVertexIndex(src);
int dsti = GetVertexIndex(dst);
// 顶点不在图中,添加边失败
if (srci == -1 || dsti == -1)
return false;
//Edge* edge = new Edge(dsti, weight);
头插
//edge->_next = _table[srci];
//_table[srci] = edge;
无向图
//if (!Directed)
//{
// edge = new Edge(srci, weight);
// edge->_next = _table[dsti];
// _table[dsti] = edge;
//}
return _AddEdge(srci, dsti, weight);
}
struct UndirectedEdge
{
int _srci;
int _dsti;
W _weight; // 边的权值
UndirectedEdge(int srci, int dsti, const W& weight)
:_srci(srci)
, _dsti(dsti)
, _weight(weight)
{}
bool operator>(const UndirectedEdge& ue) const
{
return this->_weight > ue._weight;
}
bool operator<(const UndirectedEdge& ue) const
{
return this->_weight < ue._weight;
}
};
// 记录已经入堆的边
struct Entry
{
int _srci;
int _dsti;
Entry() = default;
Entry(int srci,int dsti)
:_srci(srci)
,_dsti(dsti)
{}
// 运算符重载以便哈希
bool operator==(const Entry& e) const
{
return _srci == e._srci && _dsti == e._dsti;
}
bool operator!=(const Entry& e) const
{
return _srci != e._srci && _dsti != e._dsti;
}
};
// 仿函数
struct hashFunc
{
int operator()(const Entry& e) const
{
return e._srci + e._dsti + (e._srci * e._dsti);
}
};
pair<W, bool> Prim(Self& minTree, const V& src)
{
// 起始源点
int srci = GetVertexIndex(src);
if (srci == -1) // 只有起始源点在图中才能开始
{
return make_pair(W(), false);
}
// 这里可以判断该图是否为无向图并且为连通图
// 因为只有连通图才能产生最小生成树
// ...
// 顶点的个数
int n = static_cast<int>(_vertexSet.size());
// 生成零图
minTree._vertexSet = _vertexSet;
minTree._vertexIndex = _vertexIndex;
minTree._table.resize(n, nullptr);
// 小根堆
priority_queue<UndirectedEdge, vector<UndirectedEdge>, greater<UndirectedEdge>> q;
vector<bool> XY(n, false);
XY[srci] = true;
// 将与src相连的边入堆
Edge* curr = _table[srci];
while (curr != nullptr)
{
q.push(UndirectedEdge(srci, curr->_dsti, curr->_weight));
curr = curr->_next;
}
// 记录添加到minTree中边的权值和
W result = W();
// 记录添加到minTree中边个数
int edgeCount = 0;
// 选边
while (!q.empty())
{
UndirectedEdge top = q.top();
q.pop();
if (XY[top._srci] && !XY[top._dsti])
{
std::cout << _vertexSet[top._srci] << "<--->" << _vertexSet[top._dsti] << std::endl;
minTree._AddEdge(top._srci, top._dsti, top._weight);
XY[top._dsti] = true;
result += top._weight;
edgeCount++;
// 再将与dst相连的顶点对应的边入堆
Edge* curr = _table[top._dsti];
while (curr != nullptr)
{
q.push(UndirectedEdge(top._dsti, curr->_dsti, curr->_weight));
curr = curr->_next;
}
}
if (edgeCount == static_cast<int>(_vertexSet.size()) - 1)
{
return make_pair(result, true);
}
}
return make_pair(W(), false);
}
// 获取两个相连顶点之间边的权值
const W& GetEdgeWeight(const V& src, const V& dst)
{
int srci = GetVertexIndex(src);
int dsti = GetVertexIndex(dst);
if (srci == -1 || dsti == -1)
{
return W(); // 可以选择抛异常
}
Edge* curr = _table[srci];
while (curr != nullptr)
{
if (curr->_dsti == dsti)
{
return curr->_weight;
}
curr = curr->_next;
}
return W();
}
pair<W, bool> Kruskal(Self& minTree)
{
// 这里可以判断该图是否为无向图并且为连通图
// 因为只有连通图才能产生最小生成树
// 顶点的个数
int n = static_cast<int>(_vertexSet.size());
// 生成零图
minTree._vertexSet = _vertexSet;
minTree._vertexIndex = _vertexIndex;
minTree._table.resize(n, nullptr);
// 将所有的无向边压入小根堆中
priority_queue<UndirectedEdge, vector<UndirectedEdge>, greater<UndirectedEdge>> q;
// 因为要遍历的图为无向图,所有可能会造成同一条边入小根堆两次
// 所以需要用Entry来记录已经入堆的边,只有没有入堆的边才能入堆
// 例如a-b边先入堆,则在unordered_set插入Entry(b,a),所以下次遍历到b-a边就不会入堆了
std::unordered_set<Entry,hashFunc> entrys;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
Edge* curr = _table[i];
while (curr != nullptr)
{
if (entrys.find(Entry(i, curr->_dsti)) == entrys.end())
{
q.push(UndirectedEdge(i, curr->_dsti, curr->_weight));
entrys.insert(Entry(curr->_dsti, i));
}
curr = curr->_next;
}
}
// 创建n个单元素集合的并查集
UnionFindSet ufs(n);
// 记录添加到minTree中边的权值和
W result = W();
// 记录添加到minTree中边个数
int edgeCount = 0;
// 全局贪心,不断选出不构成环并且权值最小的边
while (!q.empty())
{
UndirectedEdge top = q.top();
q.pop();
// 两个顶点不在一个集合,说明选出的边不会构成环
if (!ufs.IsInSet(top._srci, top._dsti))
{
std::cout << _vertexSet[top._srci] << "<--->" << _vertexSet[top._dsti] << " : "<<GetEdgeWeight(_vertexSet[top._srci],_vertexSet[top._dsti])<<std::endl;
// 将选出的边加入minTree中
minTree._AddEdge(top._srci, top._dsti, top._weight);
// 将两个顶点合并到一个集合
ufs.Union(top._srci, top._dsti);
// 更新权值
result += top._weight;
// 更新边数
edgeCount++;
}
if (edgeCount == static_cast<int>(_vertexSet.size()) - 1)
{
return make_pair(result, true);
}
}
return make_pair(W(), false);
}
};
void TestGraph()
{
const char* str = "abcdefghi";
AdjacentList::Graph<char, int> g(str, strlen(str));
g.AddEdge('a', 'b', 4);
g.AddEdge('a', 'h', 8);
g.AddEdge('b', 'c', 8);
g.AddEdge('b', 'h', 11);
g.AddEdge('c', 'd', 7);
g.AddEdge('c', 'i', 2);
g.AddEdge('c', 'f', 4);
g.AddEdge('d', 'e', 9);
g.AddEdge('d', 'f', 14);
g.AddEdge('e', 'f', 10);
g.AddEdge('f', 'g', 2);
g.AddEdge('g', 'h', 1);
g.AddEdge('g', 'i', 6);
g.AddEdge('h', 'i', 7);
AdjacentList::Graph<char, int>::Self minTree;
//std::cout << g.Prim(minTree, 'a').first << std::endl;
std::cout << g.Kruskal(minTree).first << std::endl;
}
}
邻接矩阵
namespace AdjacentMatrix
{
template<typename V, typename W, W W_MAX, bool Directed = false>
class Graph
{
private:
std::vector<V> _vertexSet;
std::map<V, int> _vertexIndex;
std::vector<std::vector<W>> _matrix;
public:
typedef Graph<V, W, W_MAX, Directed> Self;
Graph() = default;
Graph(const V *a,int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
AddVertex(a[i]);
}
}
int GetVertexIndex(const V& v)
{
typename std::map<V, int>::iterator pos = _vertexIndex.find(v);
if (pos != _vertexIndex.end())
{
return pos->second;
}
else
{
return -1;
}
}
bool AddVertex(const V& v)
{
// 顶点存在不需要继续增加
if (GetVertexIndex(v) != -1)
return false;
_vertexSet.push_back(v);
_vertexIndex.insert(std::make_pair(v, _vertexSet.size() - 1));
// 先在原有的行上一列
for (int i = 0; i < _matrix.size(); i++)
{
_matrix[i].push_back(W_MAX);
}
// 增加一行
_matrix.push_back(std::vector<W>(_vertexSet.size(), W_MAX));
return true;
}
bool AddEdge(const V& src, const V& dst, const W& weight)
{
int srci = GetVertexIndex(src);
int dsti = GetVertexIndex(dst);
// 顶点不在图中,添加边失败
if (srci == -1 || dsti == -1)
return false;
//_matrix[srci][dsti] = weight;
如果为无向图,则需要再添加一条dst->src的边
//if (!Directed)
//{
// _matrix[dsti][srci] = weight;
//}
//return true;
return _AddEdge(srci, dsti, weight);
}
bool _AddEdge(int srci,int dsti,const W& weight)
{
// 顶点不在图中,添加边失败
if (srci == -1 || dsti == -1)
return false;
_matrix[srci][dsti] = weight;
// 如果为无向图,则需要再添加一条dst->src的边
if (!Directed)
{
_matrix[dsti][srci] = weight;
}
return true;
}
struct UndirectedEdge
{
int _srci;
int _dsti;
W _weight;
UndirectedEdge(int srci,int dsti,const W &weight)
:_srci(srci)
,_dsti(dsti)
,_weight(weight)
{}
bool operator>(const UndirectedEdge& ue) const
{
return this->_weight > ue._weight;
}
bool operator<(const UndirectedEdge& ue) const
{
return this->_weight < ue._weight;
}
};
pair<W,bool> Prim(Self& minTree,const V& src)
{
int srci = GetVertexIndex(src);
if (srci == -1)
return make_pair(W(), false);
// 生成零图
minTree._vertexSet = _vertexSet;
minTree._vertexIndex = _vertexIndex;
minTree._matrix.resize(_vertexSet.size(), vector<W>(_vertexSet.size(), W_MAX));
// 每次选出集合X到Y的最小边,所以建小堆
priority_queue<UndirectedEdge, vector<UndirectedEdge>, greater<UndirectedEdge>> q;
vector<bool> XY(_vertexSet.size(), false);
XY[srci] = true;
// 先把与src发出的边压入小根堆中
for (int i = 0; i < _vertexSet.size(); i++)
{
if (_matrix[srci][i] != W_MAX)
{
q.push( UndirectedEdge(srci, i, _matrix[srci][i]) );
}
}
// 记录添加到minTree中边的权值和
W result = W();
// 记录添加到minTree中边个数
int edgeCount = 0;
while (!q.empty())
{
UndirectedEdge front = q.top();
q.pop();
// 只有srci在X集合中,dsti在Y集合中的边才能选出
if (XY[front._srci] && !XY[front._dsti])
{
std::cout << _vertexSet[front._srci] << "<--->" << _vertexSet[front._dsti] << std::endl;
// 将符合的边加入到minTree中
minTree._AddEdge(front._srci, front._dsti, front._weight);
XY[front._dsti] = true;
result += front._weight;
edgeCount++;
// 将从Y集合到X集合的顶点发出的边压入小根堆中
for (int i = 0; i < _vertexSet.size(); i++)
{
// 只有边存在,并且一个顶点在X集合,一个顶点在Y集合才能压入
if (_matrix[front._dsti][i] && !XY[i])
{
q.push(UndirectedEdge(front._dsti, i, _matrix[front._dsti][i]));
}
}
}
// 当选出的边为_vertexSet.size() - 1时,说明选边完成
if (edgeCount == static_cast<int>(_vertexSet.size()) - 1)
{
return make_pair(result, true);
}
}
return make_pair(W(), false);
}
pair<W, bool> Kruskal(Self& minTree)
{
// 生成零图
minTree._vertexSet = _vertexSet;
minTree._vertexIndex = _vertexIndex;
minTree._matrix.resize(_vertexSet.size(), vector<W>(_vertexSet.size(), W_MAX));
// 将所有的无向边压入小根堆中
priority_queue<UndirectedEdge, vector<UndirectedEdge>, greater<UndirectedEdge>> q;
int n = static_cast<int>(_vertexSet.size());
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (i < j && _matrix[i][j] != W_MAX)
{
q.push(UndirectedEdge(i, j, _matrix[i][j]));
}
}
}
// 创建n个单元素集合的并查集
UnionFindSet ufs(n);
// 记录添加到minTree中边的权值和
W result = W();
// 记录添加到minTree中边个数
int edgeCount = 0;
// 每次选出不构成环的权值最小边
while (!q.empty())
{
UndirectedEdge front = q.top();
q.pop();
// 只有两个顶点不在一个集合才能选出
if (!ufs.IsInSet(front._srci, front._dsti))
{
std::cout << _vertexSet[front._srci] << "<--->" << _vertexSet[front._dsti] <<" : "<<_matrix[front._srci][front._dsti]<< std::endl;
minTree._AddEdge(front._srci, front._dsti, front._weight);
// 选出边之后,将这条边的两个顶点合并到一个集合
ufs.Union(front._srci, front._dsti);
result += front._weight;
edgeCount++;
}
// 当选出的边为_vertexSet.size() - 1时,说明选边完成
if (edgeCount == static_cast<int>(_vertexSet.size()) - 1)
{
return make_pair(result, true);
}
}
return make_pair(W(), false);
}
};
void TestGraph()
{
const char* str = "abcdefghi";
AdjacentMatrix::Graph<char,int,INT_MAX> g(str, strlen(str));
g.AddEdge('a', 'b', 4);
g.AddEdge('a', 'h', 8);
g.AddEdge('b', 'c', 8);
g.AddEdge('b', 'h', 11);
g.AddEdge('c', 'd', 7);
g.AddEdge('c', 'i', 2);
g.AddEdge('c', 'f', 4);
g.AddEdge('d', 'e', 9);
g.AddEdge('d', 'f', 14);
g.AddEdge('e', 'f', 10);
g.AddEdge('f', 'g', 2);
g.AddEdge('g', 'h', 1);
g.AddEdge('g', 'i', 6);
g.AddEdge('h', 'i', 7);
AdjacentMatrix::Graph<char, int, INT_MAX>::Self minTree;
// 以a为起始源点
//std::cout << g.Prim(minTree,'a').first << std::endl;
std::cout << g.Kruskal(minTree).first << std::endl;
}
}