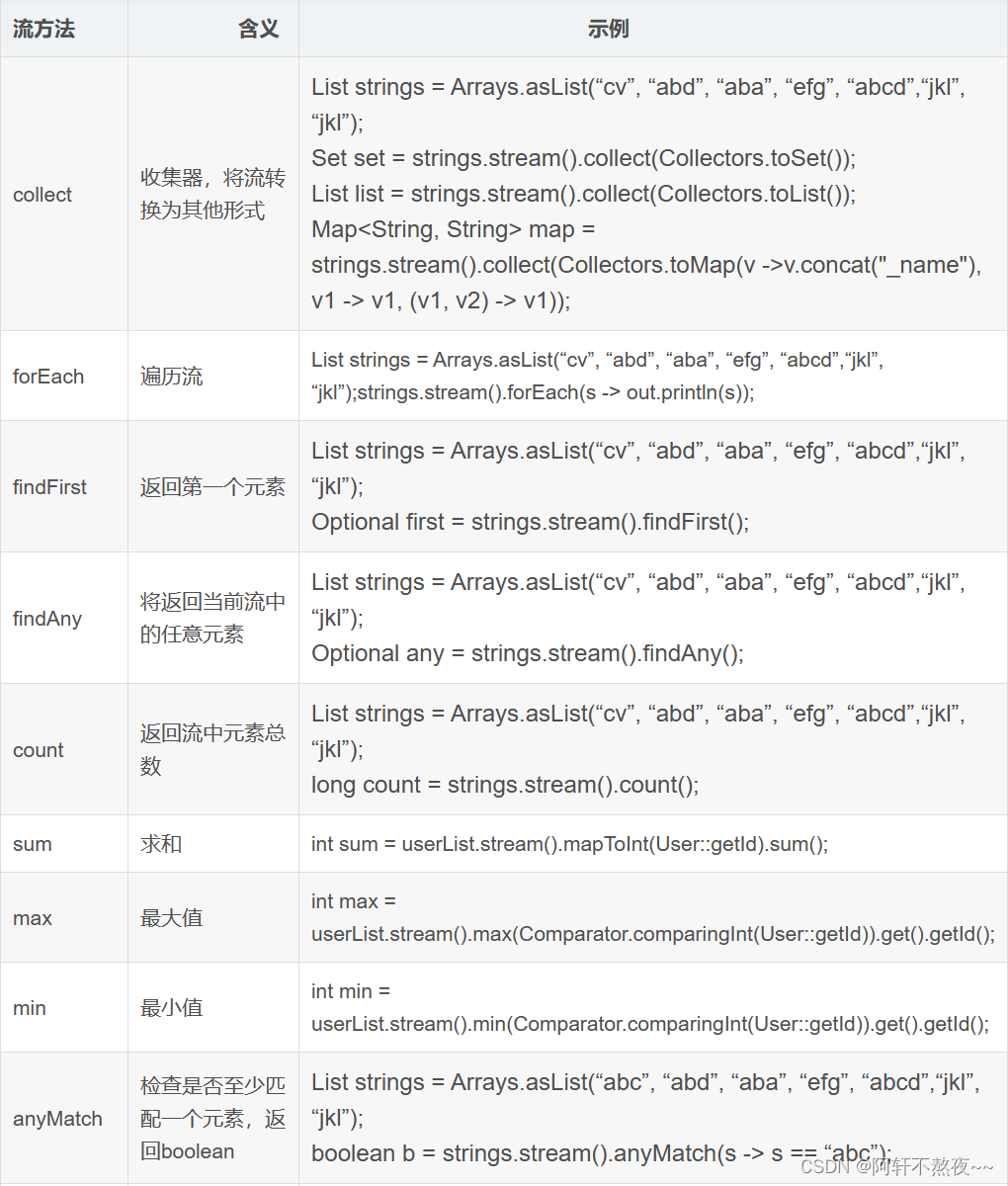
语义分割任务中VOC数据集的制作,任务中只有一种标签:gas
文章目录
- 1、由黑白图像识别为txt标签
- 2、txt转json
- 3、数据集转VOC格式
1、由黑白图像识别为txt标签
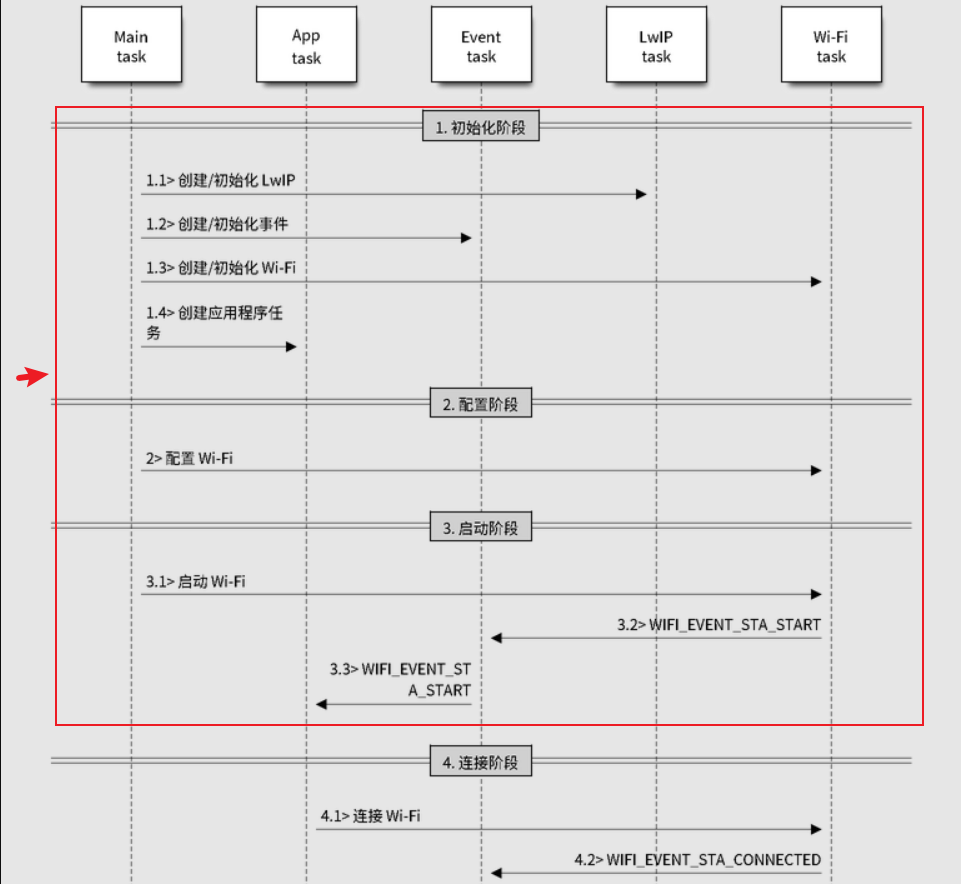
由于使用CycleGAN网络进行风格迁移学习,生成了大量伪标签图像,因此需要自动提取出标签,标签格式为YOLOv8训练所需要的语义分割的标签格式
例如:提取出下图中白色的区域的标签信息

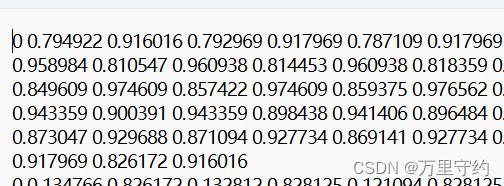
txt标签:
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
'''
该段代码读取文件夹中的二值图像,输出白色区域的标注信息
格式为YOLOv8图像分割的txt格式
'''
def process_images(input_folder, output_folder):
# 如果输出文件夹不存在,则创建它
if not os.path.exists(output_folder):
os.makedirs(output_folder)
# 列出输入文件夹中的所有图像文件
image_files = [f for f in os.listdir(input_folder) if f.endswith(('.png', '.jpg', '.jpeg', '.bmp'))]
total_images = len(image_files)
print(f"在文件夹'{input_folder}'中找到了 {total_images} 张图像。")
# 处理每张图像
for idx, filename in enumerate(image_files, 1):
print(f"正在处理图像 {idx} / {total_images} : {filename}")
# 加载图像
image_path = os.path.join(input_folder, filename)
image = cv2.imread(image_path, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
# 检查图像是否正确加载
if image is None:
print(f"图像 {filename} 未能正确加载。")
continue
# 对图像进行阈值处理以获得二值图像
_, binary_image = cv2.threshold(image, 128, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# 寻找轮廓
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(binary_image, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# 初始化一个列表来存储轮廓坐标
contour_coordinates = []
# 获取图像的尺寸以进行归一化
height, width = image.shape
# 遍历轮廓以提取归一化坐标
for contour in contours:
# 初始化一个列表来存储单个轮廓的坐标
coords = ['0'] # 开头的数字0(没有小数点)
for point in contour:
# 归一化x和y坐标并添加到列表中
x_normalized = point[0][0] / width
y_normalized = point[0][1] / height
coords.extend([f"{x_normalized:.6f}", f"{y_normalized:.6f}"])
# 将单个轮廓的坐标添加到主列表中
contour_coordinates.append(' '.join(coords))
# 定义输出文本文件的路径
output_file_path = os.path.join(output_folder, os.path.splitext(filename)[0] + '.txt')
# 将坐标写入文本文件
with open(output_file_path, 'w') as file:
file.write('\n'.join(contour_coordinates))
# 输入和输出文件夹路径(请替换为实际路径)
input_folder_path = 'D:\Desktop\\test0326' # 替换为实际的输入图片文件夹
output_folder_path = 'D:\Desktop\\test0326' # 替换为实际的输出txt标签文件夹
# 调用函数以处理图像
process_images(input_folder_path, output_folder_path)
2、txt转json
由txt文件转换为labelme标注的json格式,本人的labelme版本为5.3.1,json文件内涵图像数据,具体格式为:
json_data = {
"version": "5.3.1",
"flags": {},
"shapes": [],
"imagePath": img_filename,
"imageData": encoded_string,
"imageHeight": height,
"imageWidth": width
}
代码如下:
import os
import json
import base64
from PIL import Image
import io
# 文件夹路径
label_folder = 'D:\\Desktop\\Unet\\dataset\\500txt' # txt标签文件夹
image_folder = 'D:\\Desktop\\Unet\\dataset\\500images' # 图像文件夹
output_folder = 'D:\\Desktop\\Unet\\dataset\\500jsons' # json标签输出的文件夹
# 确保输出文件夹存在
os.makedirs(output_folder, exist_ok=True)
# 遍历文件夹中的所有 txt 文件
for filename in os.listdir(label_folder):
if filename.endswith('.txt'):
# 构造完整的文件路径
txt_path = os.path.join(label_folder, filename)
# 构造对应的图像文件路径
img_filename = filename.replace('.txt', '.jpg')
img_path = os.path.join(image_folder, img_filename)
# 读取图像尺寸并转换为 base64
with Image.open(img_path) as img:
width, height = img.size
buffered = io.BytesIO()
img.save(buffered, format="JPEG")
encoded_string = base64.b64encode(buffered.getvalue()).decode('utf-8')
# 初始化 JSON 数据结构
json_data = {
"version": "5.3.1",
"flags": {},
"shapes": [],
"imagePath": img_filename,
"imageData": encoded_string,
"imageHeight": height,
"imageWidth": width
}
# 读取 txt 文件并解析多边形坐标
with open(txt_path, 'r') as file:
for line in file:
parts = line.strip().split()
label_index = parts[0] # 假设第一部分是类别索引
if len(parts) < 3 or len(parts) % 2 == 0:
print(f"Unexpected format in {filename}")
continue
# 将相对坐标转换为实际坐标(像素值)
label = 'gas' if label_index == '0' else 'unknown'
points = [(float(parts[i]) * width, float(parts[i + 1]) * height) for i in range(1, len(parts), 2)]
shape_data = {
"label": label,
"points": points,
"group_id": None,
"description": "",
"shape_type": "polygon",
"flags": {}
}
json_data["shapes"].append(shape_data)
# 输出 JSON 文件
output_path = os.path.join(output_folder, filename.replace('.txt', '.json'))
with open(output_path, 'w') as jsonfile:
json.dump(json_data, jsonfile, indent=2)
print(f"文件 {output_path} 已转换完成!")
print("Conversion to JSON completed.")
3、数据集转VOC格式
准备好原图和json格式的标签后,转换为VOC所需的语义分割数据集
还需要准备一个labels.txt文件,里面写上所有的类别,格式如下:
__ignore__
_background_
gas
由于我的任务中只有gas这一类,所以只需要写gas,如果是多类,则依次往下添加即可,“ignore”和“background”这两行不要动,准备好labels.txt文件后还需要将路径填到下方转换代码中注明的位置:
from __future__ import print_function
import argparse
import glob
import os
import os.path as osp
import sys
import imgviz
import numpy as np
import labelme
def main(args):
if osp.exists(args.output_dir):
print("Output directory already exists:", args.output_dir)
sys.exit(1)
os.makedirs(args.output_dir)
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "JPEGImages"))
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "SegmentationClassnpy"))
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "SegmentationClass"))
if not args.noviz:
os.makedirs(
osp.join(args.output_dir, "SegmentationClassVisualization")
)
print("Creating dataset:", args.output_dir)
class_names = []
class_name_to_id = {}
for i, line in enumerate(open(args.labels).readlines()):
class_id = i - 1 # starts with -1
class_name = line.strip()
class_name_to_id[class_name] = class_id
if class_id == -1:
assert class_name == "__ignore__"
continue
elif class_id == 0:
assert class_name == "_background_"
class_names.append(class_name)
class_names = tuple(class_names)
print("class_names:", class_names)
out_class_names_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "class_names.txt")
with open(out_class_names_file, "w") as f:
f.writelines("\n".join(class_names))
print("Saved class_names:", out_class_names_file)
for filename in glob.glob(osp.join(args.input_dir, "*.json")):
print("Generating dataset from:", filename)
label_file = labelme.LabelFile(filename=filename)
base = osp.splitext(osp.basename(filename))[0]
out_img_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "JPEGImages", base + ".jpg")
out_lbl_file = osp.join(
args.output_dir, "SegmentationClassnpy", base + ".npy"
)
out_png_file = osp.join(
args.output_dir, "SegmentationClass", base + ".png"
)
if not args.noviz:
out_viz_file = osp.join(
args.output_dir,
"SegmentationClassVisualization",
base + ".jpg",
)
with open(out_img_file, "wb") as f:
f.write(label_file.imageData)
img = labelme.utils.img_data_to_arr(label_file.imageData)
lbl, _ = labelme.utils.shapes_to_label(
img_shape=img.shape,
shapes=label_file.shapes,
label_name_to_value=class_name_to_id,
)
labelme.utils.lblsave(out_png_file, lbl)
np.save(out_lbl_file, lbl)
if not args.noviz:
viz = imgviz.label2rgb(
label=lbl,
# img=imgviz.rgb2gray(img),
# img=img,
font_size=15,
label_names=class_names,
loc="rb",
)
imgviz.io.imsave(out_viz_file, viz)
def get_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--input_dir", default="D:\Desktop\\Unet\dataset\\500jsons", type=str, ## 在这里输入json标签文件夹
help="input annotated directory")
parser.add_argument("--output_dir", default="D:\Desktop\\Unet\dataset\VOC500images\\", type=str, ## 在这里输入图片文件夹
help="output dataset directory")
parser.add_argument("--labels", default="D:\Desktop\\Unet\\dataset\\labels.txt", type=str, ## 输入labels.txt文件所在的路径
help="labels file")
parser.add_argument("--noviz", help="no visualization", action="store_true")
args = parser.parse_args()
return args
if __name__ == "__main__":
args = get_args()
main(args)