当MySQL遇到慢查询(慢SQL)时,我们可以通过以下步骤进行排查和优化:
标题开启慢查询日志:
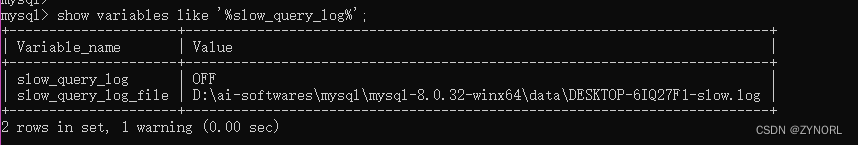
确保MySQL的慢查询日志已经开启。通过查看slow_query_log和slow_query_log_file变量来确认。
如果没有开启,可以在MySQL配置文件(如my.cnf(linux)或my.ini(windows))中设置这些变量,然后重启MySQL服务。
# 开启慢查询日志
slow_query_log = ON
# 设置慢查询的时间阈值,单位秒,查询耗时超过此值的SQL会被记录
long_query_time = 1
# 设置log位置
slow_query_log_file = D:/ai-softwares/mysql/mysql-8.0.32-winx64/data/DESKTOP-6IQ27F1-slow.log
# (可选)记录那些没有使用索引的查询
log_queries_not_using_indexes = 1
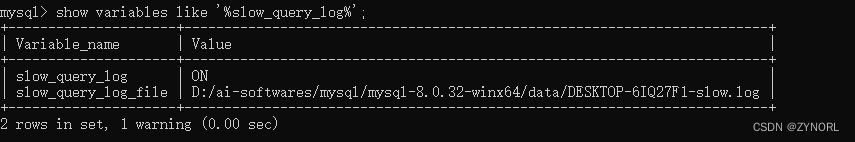
保存,重启后,可以看到:
查询几条数据后,查看慢日志文件内容:
D:\ai-softwares\mysql\mysql-8.0.32-winx64\bin\mysqld, Version: 8.0.32 (MySQL Community Server - GPL). started with:
TCP Port: 3306, Named Pipe: MySQL
Time Id Command Argument
# Time: 2024-04-05T06:33:16.321295Z
# User@Host: root[root] @ localhost [::1] Id: 8
# Query_time: 0.005313 Lock_time: 0.000010 Rows_sent: 100 Rows_examined: 100
use atguigudb1;
SET timestamp=1712298796;
select * from course;
# Time: 2024-04-05T06:33:39.469804Z
# User@Host: root[root] @ localhost [::1] Id: 8
# Query_time: 0.037054 Lock_time: 0.000037 Rows_sent: 25 Rows_examined: 25
use atguigudb;
SET timestamp=1712298819;
select * from countries;
# Time: 2024-04-05T06:44:06.818619Z
# User@Host: root[root] @ localhost [::1] Id: 8
# Query_time: 0.000289 Lock_time: 0.000004 Rows_sent: 25 Rows_examined: 25
SET timestamp=1712299446;
select * from countries;
# Time: 2024-04-05T06:44:42.748596Z
# User@Host: root[root] @ localhost [::1] Id: 8
# Query_time: 0.000215 Lock_time: 0.000003 Rows_sent: 25 Rows_examined: 25
SET timestamp=1712299482;
select * from countries;
# Time: 2024-04-05T06:44:52.762931Z
# User@Host: root[root] @ localhost [::1] Id: 8
# Query_time: 0.086578 Lock_time: 0.000010 Rows_sent: 19 Rows_examined: 19
SET timestamp=1712299492;
select * from jobs;
# Time: 2024-04-05T06:44:53.632521Z
# User@Host: root[root] @ localhost [::1] Id: 8
# Query_time: 0.000169 Lock_time: 0.000002 Rows_sent: 19 Rows_examined: 19
SET timestamp=1712299493;
select * from jobs;
# Time: 2024-04-05T06:44:54.245250Z
# User@Host: root[root] @ localhost [::1] Id: 8
# Query_time: 0.000166 Lock_time: 0.000001 Rows_sent: 19 Rows_examined: 19
SET timestamp=1712299494;
select * from jobs;
# Time: 2024-04-05T06:44:54.966701Z
# User@Host: root[root] @ localhost [::1] Id: 8
# Query_time: 0.000171 Lock_time: 0.000002 Rows_sent: 19 Rows_examined: 19
SET timestamp=1712299494;
select * from jobs;
# Time: 2024-04-05T06:44:55.613169Z
# User@Host: root[root] @ localhost [::1] Id: 8
# Query_time: 0.000160 Lock_time: 0.000002 Rows_sent: 19 Rows_examined: 19
SET timestamp=1712299495;
select * from jobs;
分析慢查询日志:
使用mysqldumpslow或其他慢查询日志分析工具来查看和分析慢查询日志中的条目。
查看MySQL安装目录的bin目录下,没有mysqldumpslow.exe文件,有一个mysqldumpslow.pl文件。
在目录该下,cmd运行命令:perl mysqldumpslow.pl --help查看命令帮助。
D:\ai-softwares\mysql\mysql-8.0.32-winx64\bin>perl mysqldumpslow.pl --help
Usage: mysqldumpslow [ OPTS... ] [ LOGS... ]
Parse and summarize the MySQL slow query log. Options are
--verbose verbose
--debug debug
--help write this text to standard output
-v verbose
-d debug
-s ORDER what to sort by (al, at, ar, c, l, r, t), 'at' is default
al: average lock time
ar: average rows sent
at: average query time
c: count
l: lock time
r: rows sent
t: query time
-r reverse the sort order (largest last instead of first)
-t NUM just show the top n queries
-a don't abstract all numbers to N and strings to 'S'
-n NUM abstract numbers with at least n digits within names
-g PATTERN grep: only consider stmts that include this string
-h HOSTNAME hostname of db server for *-slow.log filename (can be wildcard),
default is '*', i.e. match all
-i NAME name of server instance (if using mysql.server startup script)
-l don't subtract lock time from total time
比如分析时,指定-s c查询次数次数排序,不用-aN隐藏数字,执行下面命令,分析慢查询日志:
perl "D:\ai-softwares\mysql\mysql-8.0.32-winx64\bin\mysqldumpslow.pl" -s c -a "D:/ai-softwares/mysql/mysql-8.0.32-winx64/data/DESKTOP-6IQ27F1-slow.log"
分析结果如下:
D:\ai-softwares\mysql\mysql-8.0.32-winx64\bin>perl "D:\ai-softwares\mysql\mysql-8.0.32-winx64\bin\mysqldumpslow.pl" -s c -a "D:/ai-softwares/mysql/mysql-8.0.32-winx64/data/DESKTOP-6IQ27F1-slow.log"
Reading mysql slow query log from D:/ai-softwares/mysql/mysql-8.0.32-winx64/data/DESKTOP-6IQ27F1-slow.log
Count: 5 Time=0.02s (0s) Lock=0.00s (0s) Rows=19.0 (95), root[root]@localhost
select * from jobs
Count: 3 Time=0.01s (0s) Lock=0.00s (0s) Rows=25.0 (75), root[root]@localhost
select * from countries
Count: 1 Time=0.00s (0s) Lock=0.00s (0s) Rows=0.0 (0), 0users@0hosts
D:\ai-softwares\mysql\mysql-8.0.32-winx64\bin\mysqld, Version: 8.0.32 (MySQL Community Server - GPL). started with:
TCP Port: 3306, Named Pipe: MySQL
# Time: 2024-04-05T06:33:16.321295Z
# User@Host: root[root] @ localhost [::1] Id: 8
# Query_time: 0.005313 Lock_time: 0.000010 Rows_sent: 100 Rows_examined: 100
use atguigudb1;
SET timestamp=1712298796;
select * from course
可以看到,日志分析,可以通过命令定制化分析,并且对于每个select,有执行的个数、耗时、锁表的时间、查询的行数、用户与host信息:
Count: 3 Time=0.01s (0s) Lock=0.00s (0s) Rows=25.0 (75), root[root]@localhost
可以知道,相比于慢查询日志,它可以对其进行整合,比如将相同的查询SQL计数为count。
EXPLAIN命令:
对于日志中记录的慢查询,使用EXPLAIN命令来查看查询的执行计划。分析查询是否使用了合适的索引,以及是否存在全表扫描等低效操作。
explain select * from jobs;
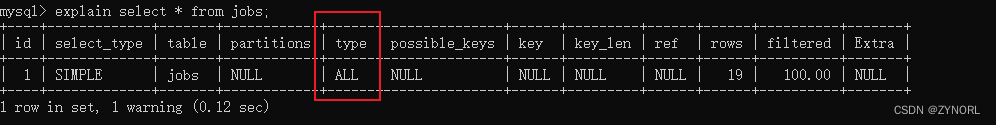
可以看到type=ALL,说明是全表扫描,没有进行索引。
优化查询
根据EXPLAIN的输出结果,优化查询语句,比如添加或修改索引。
避免在查询中使用*,而是指定需要的列。
减少JOIN操作的数量或复杂性,特别是在大数据集上。
考虑将计算密集型的操作移到应用层进行。







![练习14 Web [极客大挑战 2019]Upload](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/8cbc3da0411f4b15873e2fbdc27e2c3e.png)