Leetcode 39. 组合总和
讲解前:
这道题其实在掌握了之前的组合问题之后再看并不是那么难,其关键就在于我们这道题中没有一个特定需要的组合大小,并且列表中的元素是可以重复使用的,那么比如说给的例子中的
输入: candidates = [2,3,5]
target = 8输出: [[2,2,2,2],[2,3,3],[3,5]]
这种情况如果画图的话就这样的
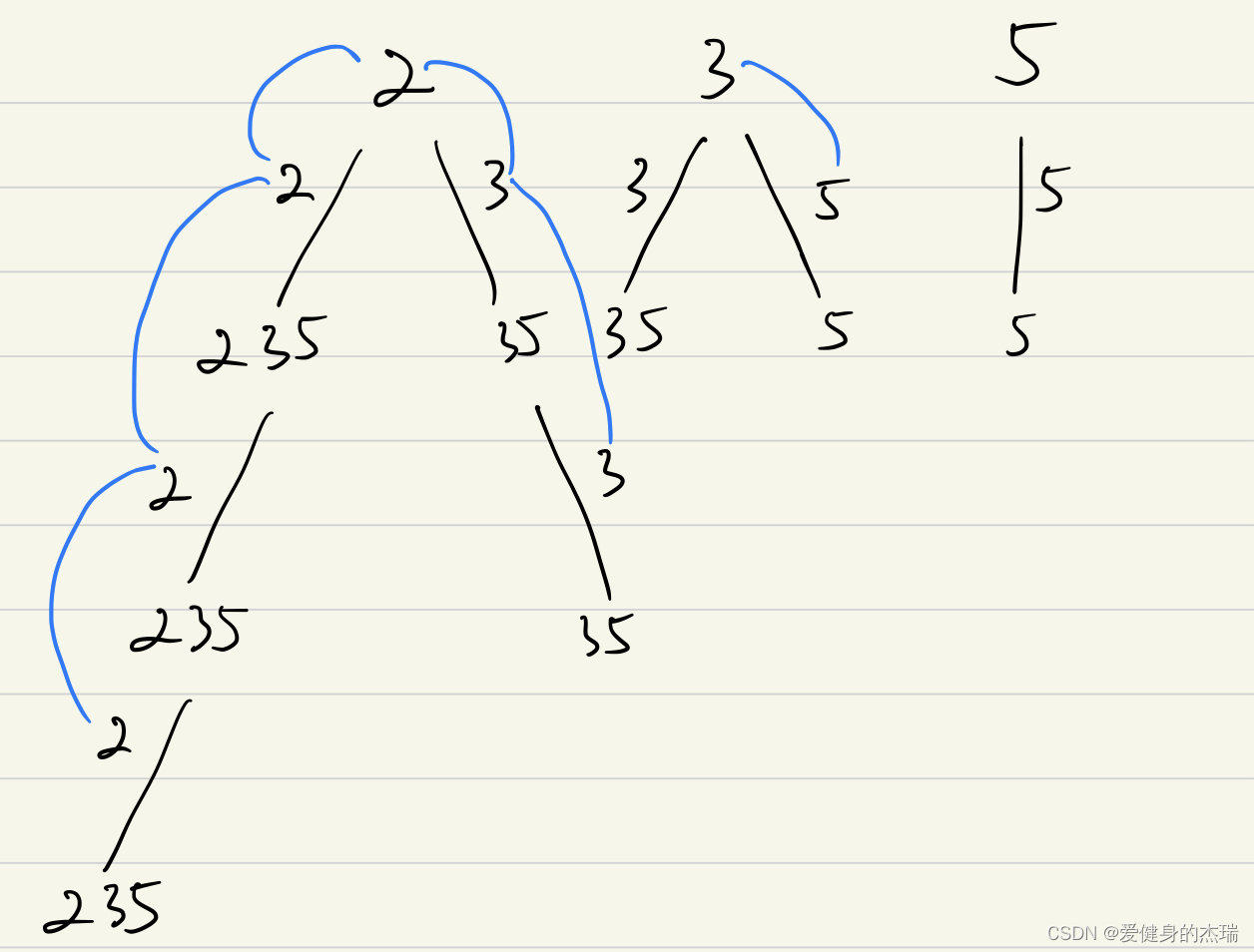
如图中所示的,我们发现每一层递归中,可选择的元素是包括当前元素在内的列表中的元素,这个设定和之前的组合问题相比较的区别在于我们可以包括自身的元素在内,这样以来,每一次选择的时候就给了我们重复利用一个数字的可能,所以startindex其实就是每一层for循环中我们遍历的数字,for循环的范围就是startindex到end of list
class Solution:
def combinationSum(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
path = []
def backtracking(candidates, res, path, sum_, start_index):
# base case
if sum_ > target:
return
elif sum_ == target:
res.append(path[:])
return
# recursive case
# every time we at a num, the next num to add to the list can be any number
# that's left from here including here
for i in range(start_index, len(candidates)):
sum_ = sum_ + candidates[i]
path.append(candidates[i])
start_index = i
backtracking(candidates, res, path, sum_, start_index)
sum_ = sum_ - candidates[i]
path.pop()
backtracking(candidates, res, path, 0, 0)
return res 讲解后:
卡哥的思路和我的一样,但是当我以为这道题其实因为控制递归的是target一个因素而不是还有规定的组合大小的时候,我以为没有剪枝操作了,但是后来发现卡哥还是给了一个剪枝的可能,也就是在我们还没有进行递归之前,就检查是否当前的sum已经超过了target,这样就不进入递归了,这样的话可以减少横向的for 循环中的递归次数,对于每一个list中的数字,如果加上会大于target,就直接continue跳过这次循环,再看下一个
这里其实如果我们能提前给candidate数组排个序的话,甚至可以把continue改成break,因为剩余的数字都不用检查了,因为全部都还是会大于target
class Solution:
def combinationSum(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
path = []
def backtracking(candidates, res, path, sum_, start_index):
# base case
if sum_ > target:
return
elif sum_ == target:
res.append(path[:])
return
# recursive case
# every time we at a num, the next num to add to the list can be any number
# that's left from here including here
for i in range(start_index, len(candidates)):
# 剪枝操作,如果知道sum会大于target,直接跳过进入递归的代码
if sum_ + candidates[i] > target:
continue
sum_ = sum_ + candidates[i]
path.append(candidates[i])
start_index = i
backtracking(candidates, res, path, sum_, start_index)
sum_ = sum_ - candidates[i]
path.pop()
backtracking(candidates, res, path, 0, 0)
return res Leetcode 40. 组合总和
讲解前:
一开始我只是想的是如果答案不能有重复的数字出现,那每次添加到res之前检查一下path是否在res中已经存在过不就好了,但后来我发现这样也不行,因为重复的组合并不一定代表顺序也是重复的,然后我发现可能我们只要把candidate排序,按照从大到小,这样就算有重复的组合,也会有一样的顺序,这样就能检查了,我在Leetcode上提交之后通过了95%的测试,但是不能通过一个全部都是1的,超出时间限制
class Solution:
def combinationSum2(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
path = []
candidates.sort()
def backtracking(candidates, res, path, sum_, start_index):
if sum_ > target:
return
if sum_ == target and path not in res:
res.append(path[:])
return
for i in range(start_index, len(candidates)):
if sum_ + candidates[i] > target:
continue
sum_ = sum_ + candidates[i]
path.append(candidates[i])
pre = candidates[i]
backtracking(candidates, res, path, sum_, i + 1)
sum_ = sum_ - candidates[i]
path.pop()
backtracking(candidates, res, path, 0, 0)
return res讲解后:
其实卡哥的解法我一开始也想到了,排序之后其实避免重复组合的方法就是看新的开始遍历的startindex上的数字是否和之前上一轮遍历的一样,也就是在for 循环的层中,我们不能让path从已经用过了的数字重新开始但是在树的深度也就是找path的层面是可以的,我一开始写的时候只用了一个pre来记录之前的数字所以我没办法区分这两种情况,卡哥的使用一个used数组的方法很好的解决了这个问题,当我们的i-1的used中是1的时候我们就知道如果当前的i也是1的话,是没关系的,因为他们在同一个path里面,但是如果i-1的used是0的话,证明i-1开头的path已经结束了,现在是一个新的path在i开始,并且i和上一轮的path开头一样,那么就证明这个i开头的path会带我们找到一个重复的数组,所以continue跳过
class Solution:
def combinationSum2(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
path = []
used = [0] * len(candidates)
candidates.sort()
def backtracking(candidates, res, path, sum_, start_index, used):
if sum_ > target:
return
if sum_ == target:
res.append(path[:])
return
print(path)
for i in range(start_index, len(candidates)):
if (i > 0 and used[i - 1] == 0 and candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]):
continue
if sum_ + candidates[i] > target:
break
sum_ = sum_ + candidates[i]
path.append(candidates[i])
used[i] = 1
backtracking(candidates, res, path, sum_, i + 1, used)
sum_ = sum_ - candidates[i]
path.pop()
used[i] = 0
backtracking(candidates, res, path, 0, 0, used)
return res并且这里还有一个很好用的剪枝就是因为我们这个解法中candidate数组已经排过序了,所以当我们发现sum_已经被加的大于target之后,可以直接break结束掉来结束后面所有的递归,因为是有序的,只会越来越大
看完了文字版讲解之后发现去重的思路甚至可以更简单,就像我们所说的,去重其实就是要确定当前的i是在横向的for循环中的和i-1相等,其实这就是说i > startindex, 因为我们在纵向的找path的时候,每一次进行递归其实就是把startindex传入i+1,所以纵向的情况下,i每一次就是从startindex开始的,是和startindex相等的,所以这里可以得到一个更精简的版本
class Solution:
def combinationSum2(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
path = []
candidates.sort()
def backtracking(candidates, res, path, sum_, start_index):
if sum_ > target:
return
if sum_ == target:
res.append(path[:])
return
for i in range(start_index, len(candidates)):
if i > start_index and candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]:
continue
if sum_ + candidates[i] > target:
break
sum_ = sum_ + candidates[i]
path.append(candidates[i])
backtracking(candidates, res, path, sum_, i + 1)
sum_ = sum_ - candidates[i]
path.pop()
backtracking(candidates, res, path, 0, 0)
return resLeetcode 131. 分割回文串
讲解前:
这道题让我很懵,没有思路
讲解后:
这道题要做好其实需要掌握好两点,第一点就是理解分割问题和组合问题其实是同样的思路,利用我们的回溯模版通过递归和for循环能够找到任意一个string的所有子串的切割可能就如下图所示
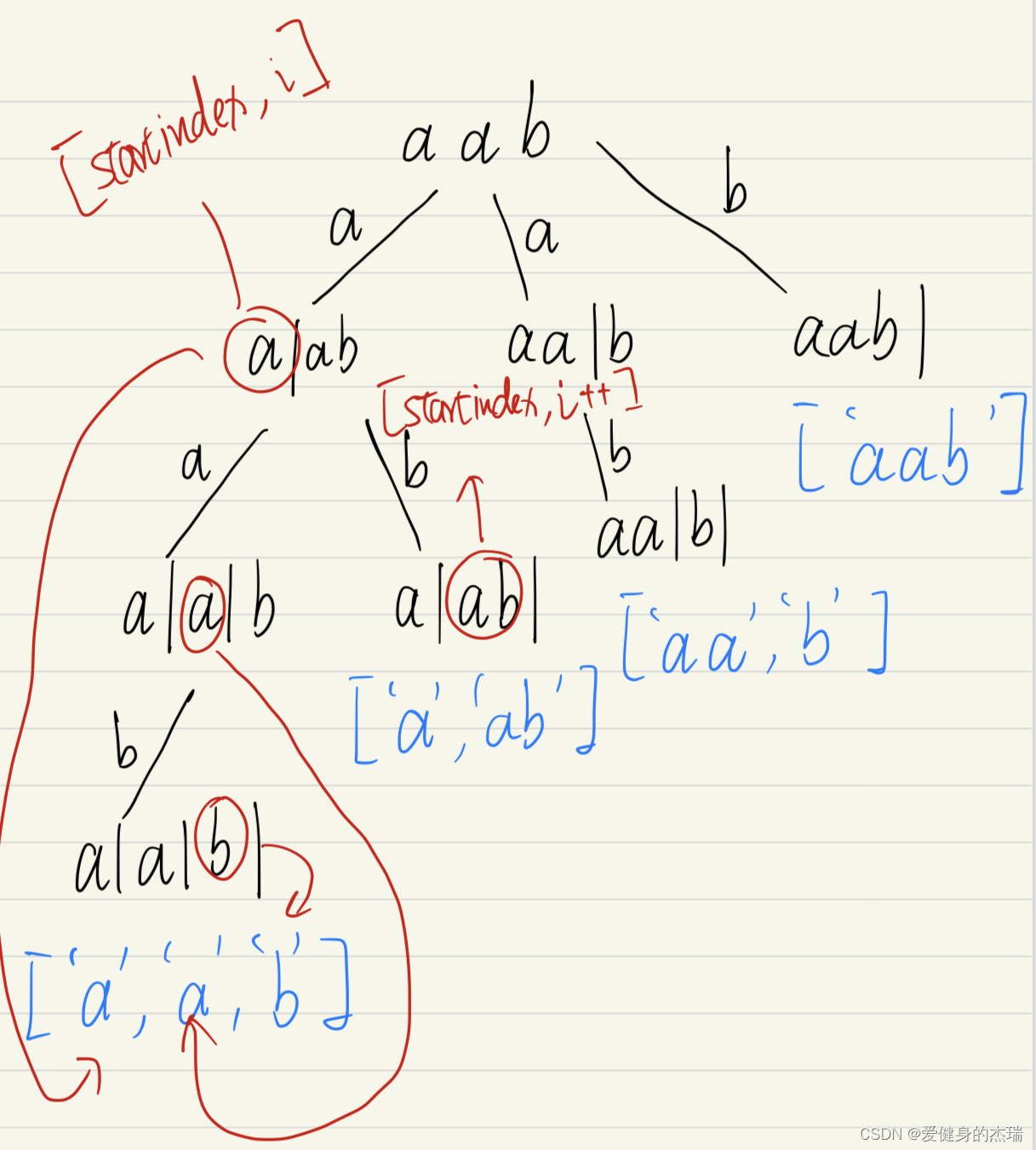
在图中我们就像在组合问题中选取数字一样选取切割点,然后for循环中我们每一个分支的起点就是当前剩余的位置的开头,然后我们纵向遍历寻找结果的时候,就是不断选取可能的新切割点然后进行切割,知道我们的切割点切到了string的最后一个字符的时候,也就是到了叶子节点的时候,我们这时候通过所有的切割点切好的string就是一个分割好的字符串,切割点之间都是我们的子串
然后呢就是第二个思路,如何来取到我们的子串然后加入到path数组中去呢?其实看图就可以发现,我们就拿第一个分支来说,最后的结果是['a', 'a', 'b'], 也就是说这三个子串分别在三次递归中被加入到了我们的path中,然后在这三次递归中,因为他们是纵向递归寻找的叶子节点,所以他们在每一次递归中,startindex都被更新成了i+1,所以其实每一次选取的时候,startindex和i都是指向的同一个下标,所以我们的子串其实应该取的值就是[startindex, i] 然后是左闭右闭,因为你如果看向横向,也就是图中的['a', 'ab'], ab的值其实就是在for loop中,我们同一横向的属于同一个for循环意味着startindex没有变,然后这是i已经更新到了b的下标,所以我们能通过[startindex, i] 取到'ab'这个子串然后加入到path中去
class Solution:
def partition(self, s: str) -> List[List[str]]:
# initialize variables
res = []
path = []
# define backtracking function
def backtracking(s, res, path, start_index):
# base case when we reach leaf call, add path to res
if start_index >= len(s):
res.append(path[:])
return
# recursive case
for i in range(start_index, len(s)):
# check if the current substring is palindrome
substring = s[start_index: i + 1]
if substring == substring[::-1]:
path.append(substring)
# do the recursive call to as i + 1 for next startindex
backtracking(s, res, path, i + 1)
path.pop()
backtracking(s, res, path, 0)
return res 这里用到了python中字符串切片从后遍历的技巧来验证是否为回文串,如果不是我们就不加入到path中去,也不继续进行递归,因为题目要求最后传入的子串都需要是回文串,如果当前path中出现了不是回文串的子串,整个path就可以放弃了,同理for 循环中也可以直接开始下一个了