文章目录
- 1.自动配置FeignAutoConfiguration
- 2.生成 Feign Client
- 2.1 从Feign Client子容器获取组件
- 2.2 Feign Client子容器的创建
- 2.3 构建Feign Client实例
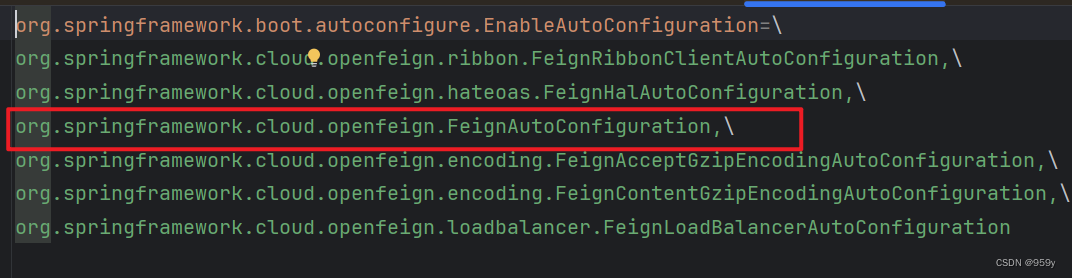
1.自动配置FeignAutoConfiguration
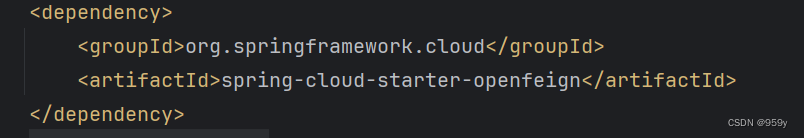
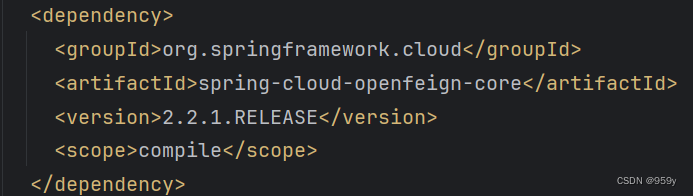
spring-cloud-starter-openfeign 包含了 spring-cloud-openfeign-core
FeignAutoConfiguration:
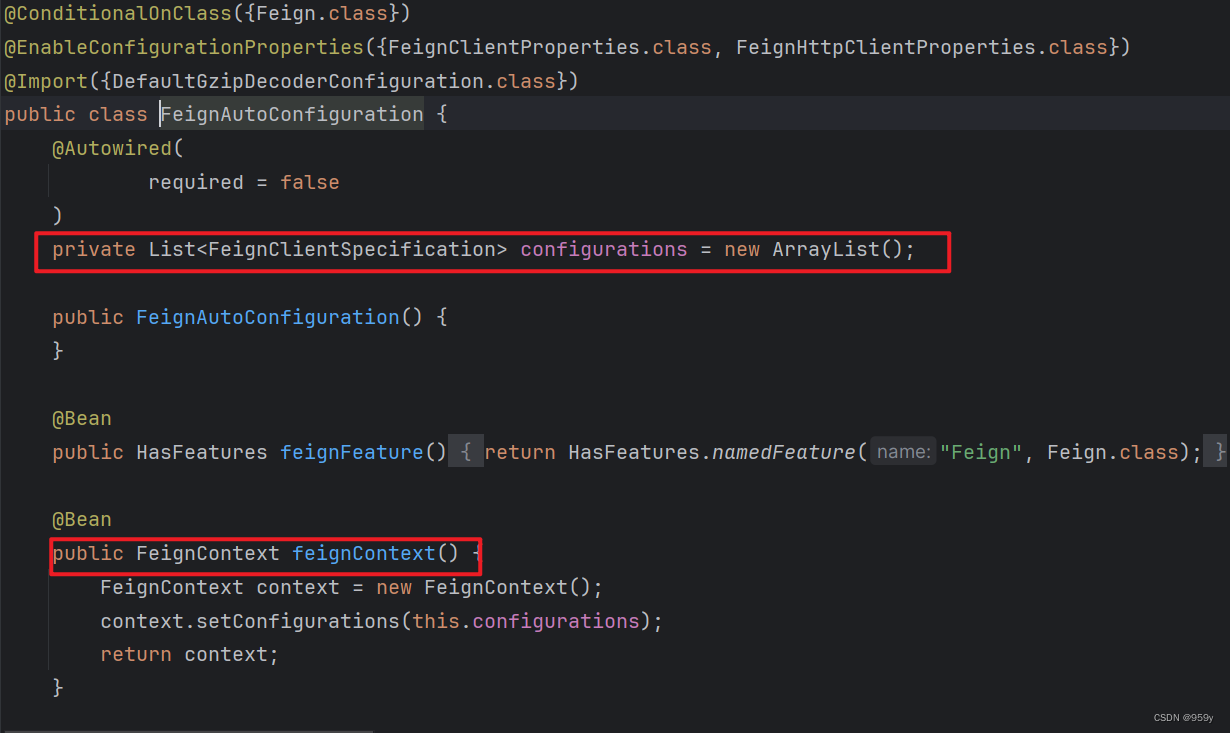
- FeignClientSpecification: FeignClient的配置类。
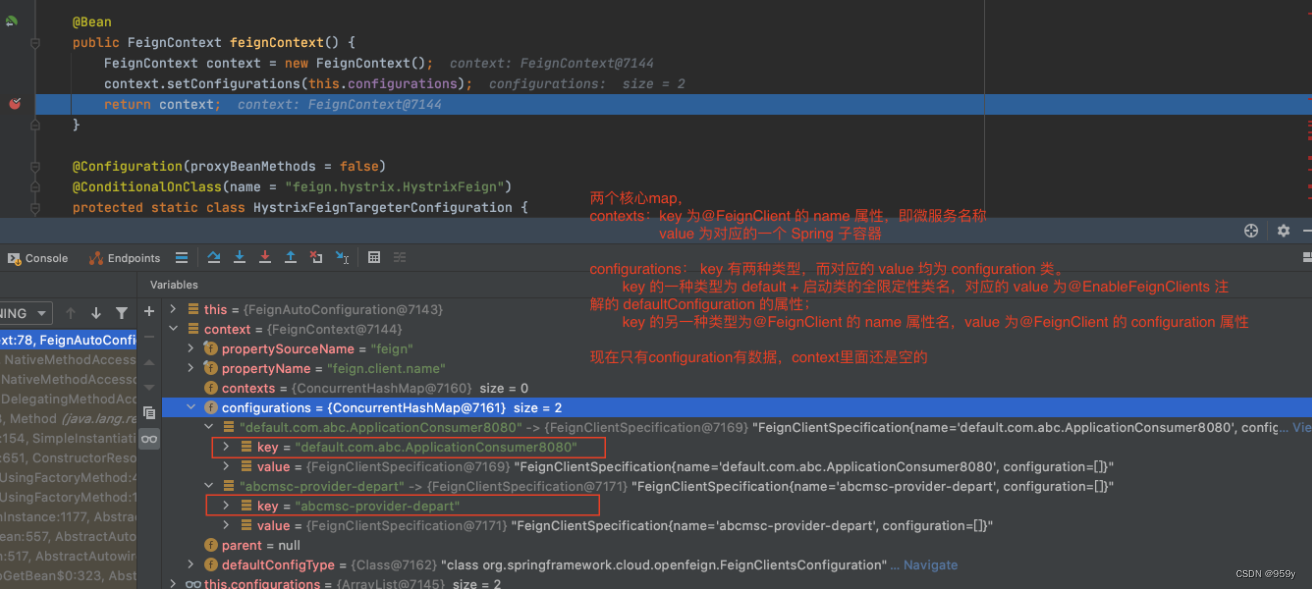
- FeignContext: Spring容器中所有的FeignClient规范类实例都放入了FeignContext。其中存在两个map。
2.生成 Feign Client
FeignClientFactoryBean: 就是Spring的FactoryBean。

2.1 从Feign Client子容器获取组件
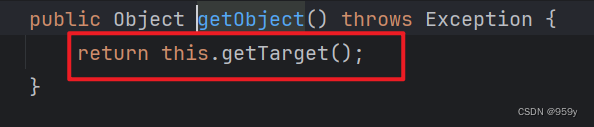
FeignClientFactoryBean.getObject():
//FeignClientFactoryBean.java
public Object getObject() throws Exception {
return getTarget();
}
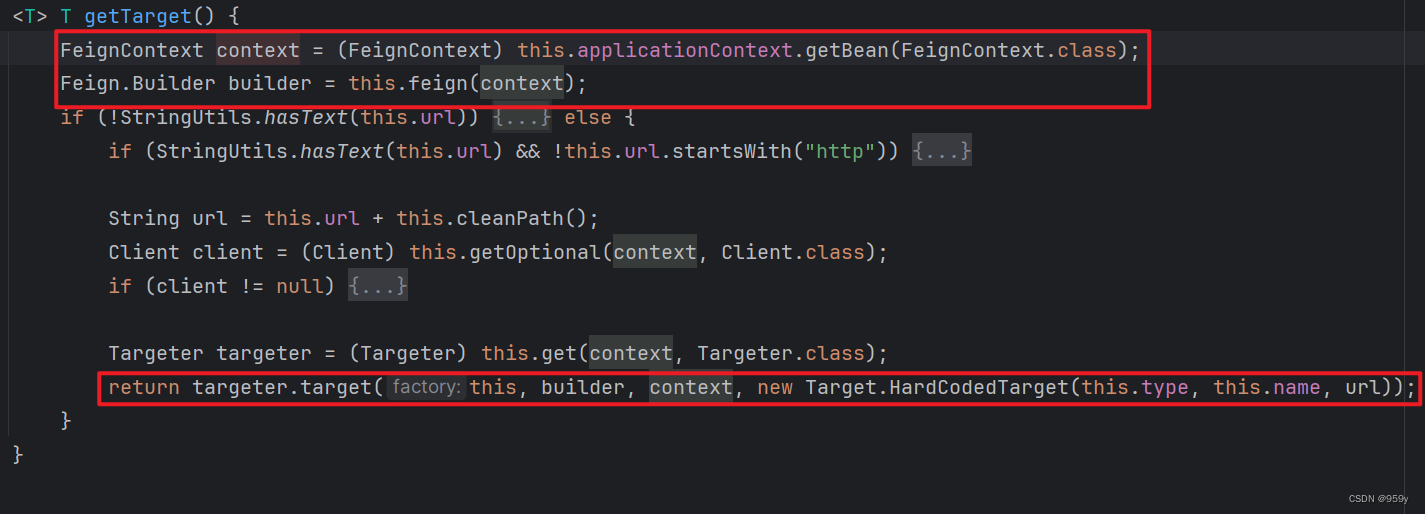
//FeignClientFactoryBean.java
<T> T getTarget() {
//根据spring容器,获取FeignContext,Feign的上下文,也是FeignClient的工厂类
FeignContext context = this.applicationContext.getBean(FeignContext.class);
//根据FeignContext,获取一个Feign的构建器
Feign.Builder builder = feign(context);
...
return (T) targeter.target(this, builder, context,
new HardCodedTarget<>(this.type, this.name, url));
}
- 根据spring容器, 获取FeignContext, 是FeignClient的工厂类。
- 根据FeignContext, 获取Feign的构造器。
feign: 从Feign Client子容器获取组件。
//FeignClientFactoryBean.java
protected Feign.Builder feign(FeignContext context) {
//get方法:从FeignContext中获取对应类型的实例,底层会从当前FeignClient对应的子容器中获取
//这里获取Feign的日志工厂
FeignLoggerFactory loggerFactory = get(context, FeignLoggerFactory.class);
Logger logger = loggerFactory.create(this.type);
// @formatter:off
//这里获取Feign的构建器
//构建器的意义我们不需要关注复杂的构建流程,只需要给构建器传递一些需要的组件即可
//这里主要往构建器放入一些FeignClient依赖的一些组件
Feign.Builder builder = get(context, Feign.Builder.class)
// required values
.logger(logger)
.encoder(get(context, Encoder.class))
.decoder(get(context, Decoder.class))
.contract(get(context, Contract.class));
// @formatter:on
//获取FeignClientProperties进行一些属性的配置
configureFeign(context, builder);
return builder;
}
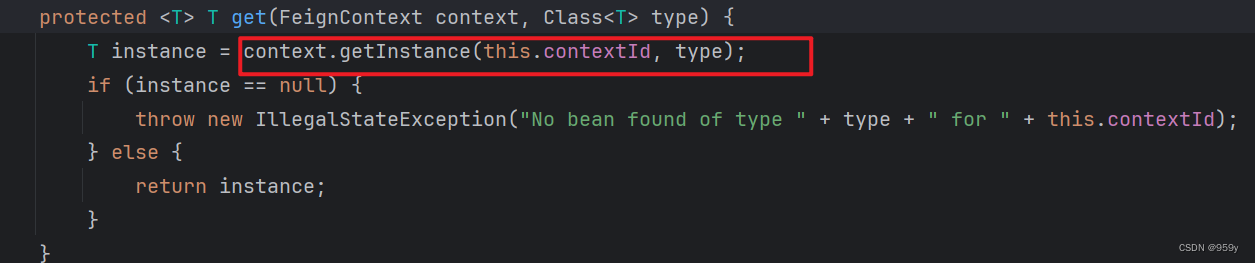
//看其中一个get方法:
//FeignClientFactoryBean.java
protected <T> T get(FeignContext context, Class<T> type) {
//注意,当前类是FeignClientFactoryBean
//所以这个this.contextId实际上是当前FeignClient的服务id、微服务名称
T instance = context.getInstance(this.contextId, type);
if (instance == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"No bean found of type " + type + " for " + this.contextId);
}
return instance;
}
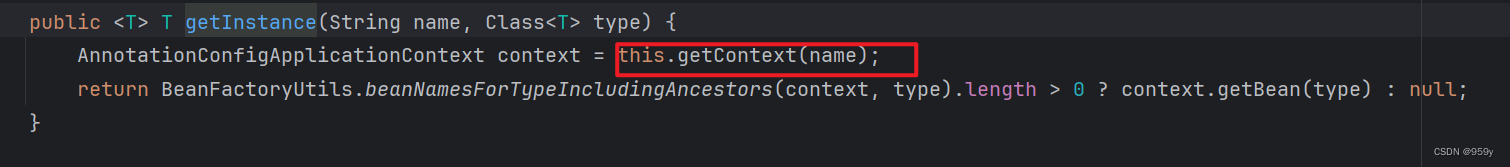
//NamedContextFactory.java,就是FeignContext.java
public <T> T getInstance(String name, Class<T> type) {
//根据name先获取对应的子容器
//name就是微服务名称,FeignClient的名称
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = getContext(name);
//根据类型从当前子容器,和子容器所有的祖先容器中查找bean的名称,判断是否存在
if (BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(context,
type).length > 0) {
//存在就返回对应类型的实例
return context.getBean(type);
}
return null;
}
2.2 Feign Client子容器的创建
获取子容器, 如果获取不到的话则创建子容器。
getContext -> createContext:
//NamedContextFactory.java
//FeignContext.java继承自NamedContextFactory.java
protected AnnotationConfigApplicationContext getContext(String name) {
if (!this.contexts.containsKey(name)) {
synchronized (this.contexts) {//双重检查锁,线程安全问题
if (!this.contexts.containsKey(name)) {
//子容器还不存在则进行创建
this.contexts.put(name, createContext(name));
}
}
}
return this.contexts.get(name);
}
//创建子容器
//NamedContextFactory.java
protected AnnotationConfigApplicationContext createContext(String name) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
//这里configurations存的就是各个feign client的规范类
if (this.configurations.containsKey(name)) {
//获取规范类中的配置类
for (Class<?> configuration : this.configurations.get(name)
.getConfiguration()) {
//将对应服务名称的配置类注册到该容器
context.register(configuration);
}
}
for (Map.Entry<String, C> entry : this.configurations.entrySet()) {
//default开头的是全局的规范类,存的是@EnableFeignClients的defaultConfiguration属性配置的配置类
if (entry.getKey().startsWith("default.")) {
for (Class<?> configuration : entry.getValue().getConfiguration()) {
//将全局的配置类注册到该容器
context.register(configuration);
}
}
}
//注册占位符配置解析器,可以解析bean定义属性值和{@code @Value}注解中的占位符。
//注册默认配置类,defaultConfigType就是FeignClientsConfiguration.class
context.register(PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration.class,
this.defaultConfigType);
//添加具有最高优先级的给定属性源对象。
context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources().addFirst(new MapPropertySource(
this.propertySourceName,
Collections.<String, Object>singletonMap(this.propertyName, name)));
if (this.parent != null) {
// 关键!为当前容器设置父容器
context.setParent(this.parent);
context.setClassLoader(this.parent.getClassLoader());
}
context.setDisplayName(generateDisplayName(name));
//刷新容器
context.refresh();
return context;
}
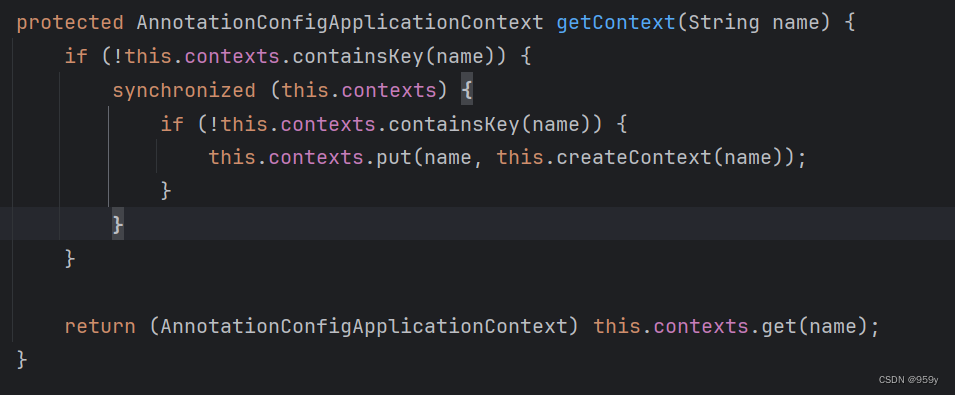
采用DCL锁来控制单例。
2.3 构建Feign Client实例
FeignClientFactoryBean.getObject():
//FeignClientFactoryBean.java
public Object getObject() throws Exception {
return getTarget();
}
//FeignClientFactoryBean.java
<T> T getTarget() {
//根据spring容器,获取FeignContext,Feign的上下文,也是FeignClient的工厂类
FeignContext context = this.applicationContext.getBean(FeignContext.class);
//根据FeignContext,获取一个Feign的构建器
//底层就是从当前feignClient名称对应的子容器中获取一些
// 创建FeignClient所依赖的组件实例
Feign.Builder builder = feign(context);
//判断是否指定url属性,没有指定了就会负载均衡的方式进行远程调用
if (!StringUtils.hasText(this.url)) {
//为服务名补全协议
if (!this.name.startsWith("http")) {
this.url = "http://" + this.name;
}
else {
this.url = this.name;
}
//拼接前缀,就是path属性,cleanPath会先格式化一下
this.url += cleanPath();
//没有指定url,使用具有负载均衡的远程调用客户端 构建feignClient
return (T) loadBalance(builder, context,
new HardCodedTarget<>(this.type, this.name, this.url));
}
//指定了url,则是直连方式
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.url) && !this.url.startsWith("http")) {
//补全协议
this.url = "http://" + this.url;
}
//拼接前缀,就是path属性,cleanPath会先格式化一下
String url = this.url + cleanPath();
//getOptional:也是从context中对应的feignClient名称的子容器中获取Client类型的实例
//这个Client就是发起远程调用的客户端
Client client = getOptional(context, Client.class);
if (client != null) {
//判断client是否是具有负载均衡的功能client,如果是的话取消包装
//确保直连
if (client instanceof LoadBalancerFeignClient) {
// ribbon的负载均衡客户端
// not load balancing because we have a url,
// but ribbon is on the classpath, so unwrap
// 没有负载平衡,因为我们有一个URL,但是ribbon在类路径中,所以请取消包装
client = ((LoadBalancerFeignClient) client).getDelegate();
}
if (client instanceof FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient) {
// openFeign的负载均衡客户端
// not load balancing because we have a url,
// but Spring Cloud LoadBalancer is on the classpath, so unwrap
// 因为我们有一个URL,所以没有负载均衡
// 但是Spring Cloud LoadBalancer在类路径上,因此请取消包装
client = ((FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient) client).getDelegate();
}
builder.client(client);
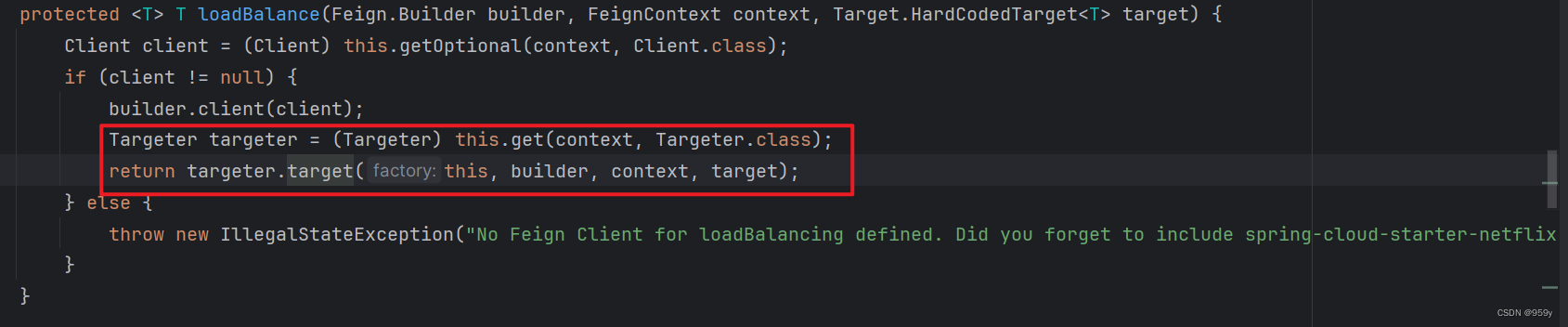
}
//从子容器获取对应类型的实例
Targeter targeter = get(context, Targeter.class);
//直连方式创建
return (T) targeter.target(this, builder, context,
new HardCodedTarget<>(this.type, this.name, url));
}
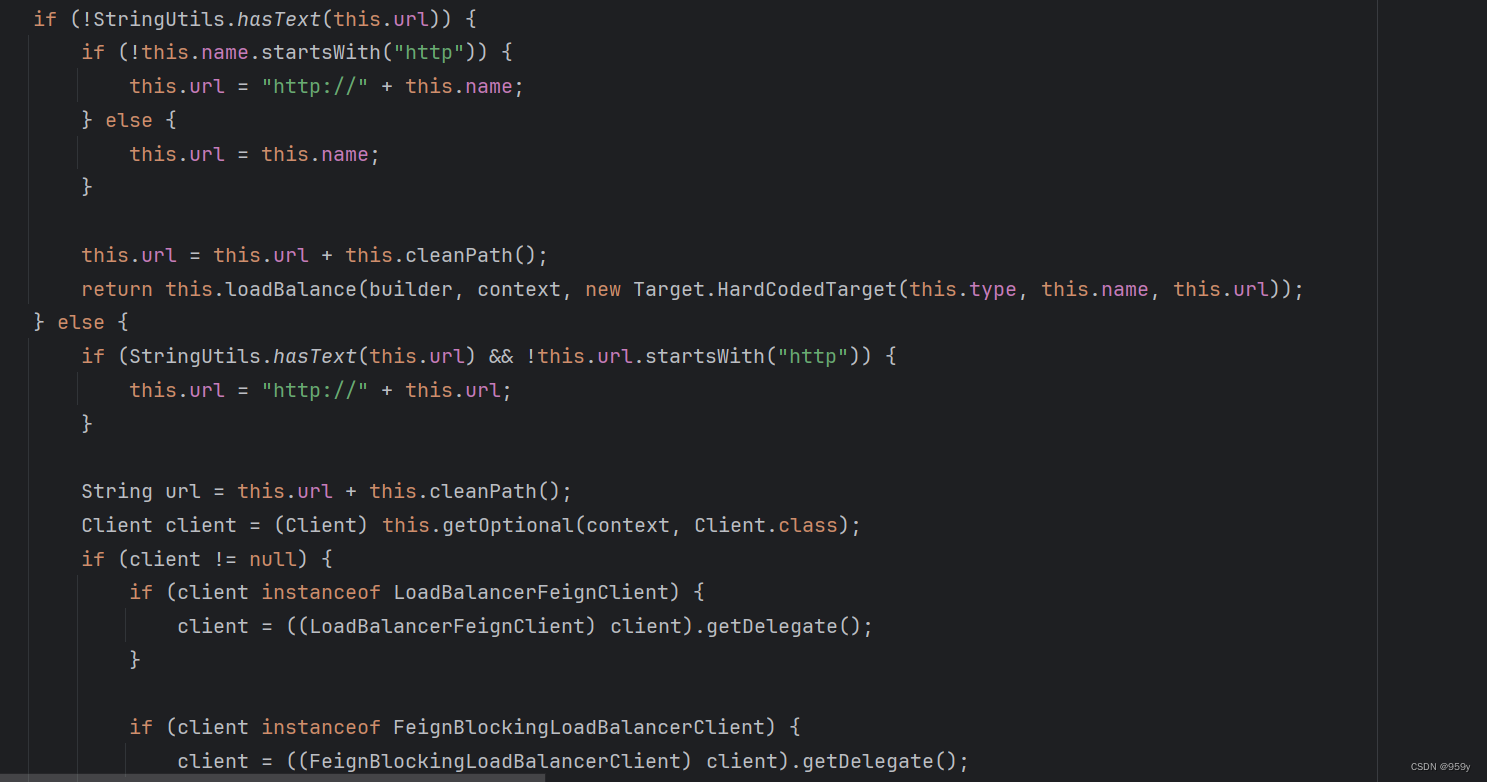
没有指定url,使用具有负载均衡的远程调用客户端 构建feignClient。
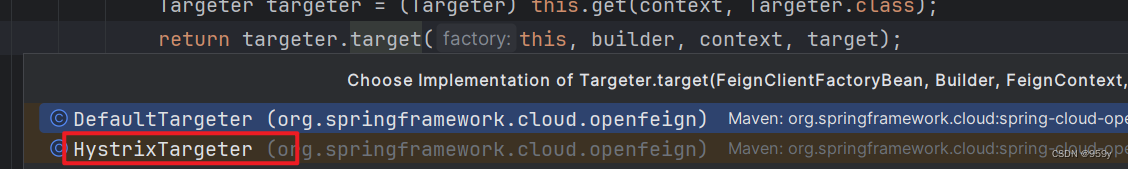
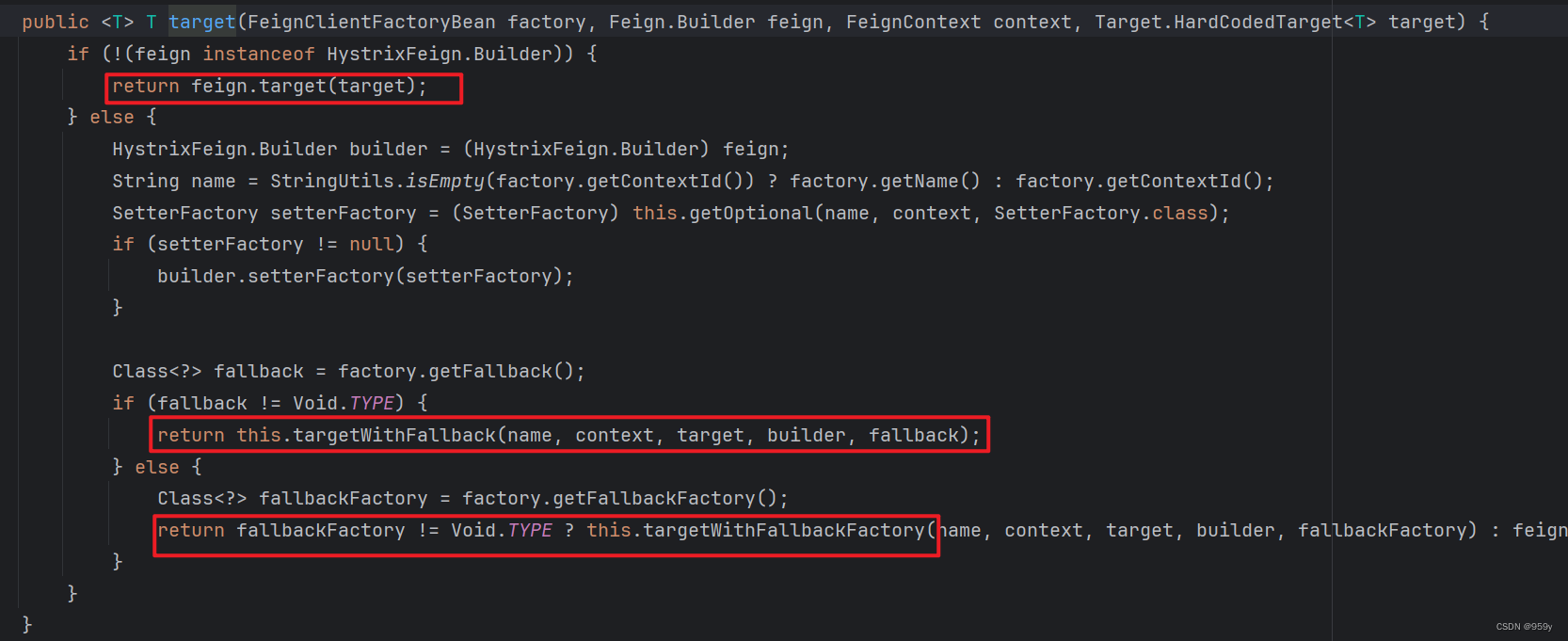
//HystrixTargeter.java
public <T> T target(FeignClientFactoryBean factory, Feign.Builder feign,
FeignContext context, Target.HardCodedTarget<T> target) {
if (!(feign instanceof feign.hystrix.HystrixFeign.Builder)) {
//没有开启熔断功能话就不是熔断的Builder走这
return feign.target(target);
}
//如果开启了熔断,就会处理一些服务降级的配置:
feign.hystrix.HystrixFeign.Builder builder = (feign.hystrix.HystrixFeign.Builder) feign;
String name = StringUtils.isEmpty(factory.getContextId()) ? factory.getName()
: factory.getContextId();
SetterFactory setterFactory = getOptional(name, context, SetterFactory.class);
if (setterFactory != null) {
builder.setterFactory(setterFactory);
}
Class<?> fallback = factory.getFallback();
if (fallback != void.class) {
return targetWithFallback(name, context, target, builder, fallback);
}
Class<?> fallbackFactory = factory.getFallbackFactory();
if (fallbackFactory != void.class) {
return targetWithFallbackFactory(name, context, target, builder,
fallbackFactory);
}
//也是调feign.target
return feign.target(target);
}
- 没有开启熔断功能话就不是熔断的Builder。
- 如果开启了熔断,就会处理一些服务降级的配置。
//Feign.java
public <T> T target(Target<T> target) {
return build().newInstance(target);
}
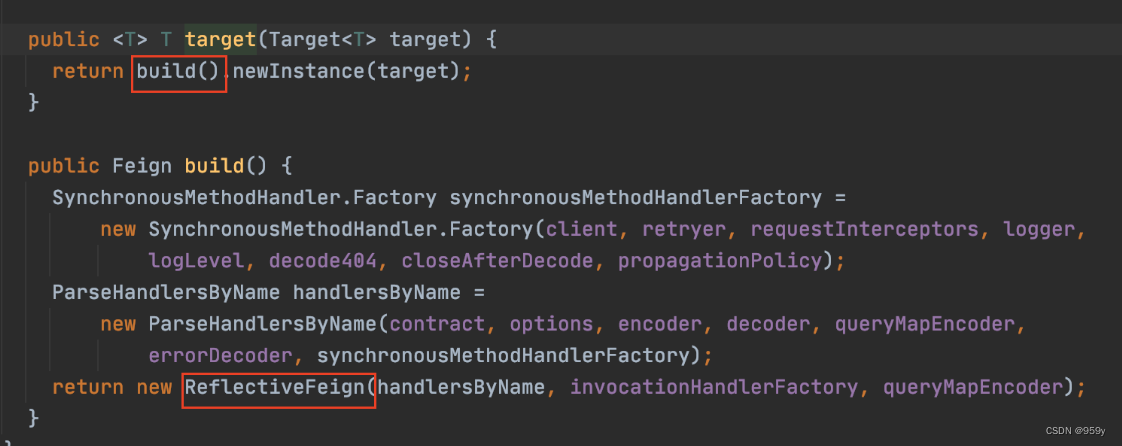
ReflectiveFeign.newInstance():
//ReflectiveFeign.java
public <T> T newInstance(Target<T> target) {
//targetToHandlersByName.apply:生成方法处理器
//返回值nameToHandler:
// key:当前feignClient的方法名
// value:方法处理器
Map<String, MethodHandler> nameToHandler = targetToHandlersByName.apply(target);
//methodToHandler:key是方法对象,value是方法处理器
Map<Method, MethodHandler> methodToHandler = new LinkedHashMap<Method, MethodHandler>();
//默认方法处理器列表
List<DefaultMethodHandler> defaultMethodHandlers = new LinkedList<DefaultMethodHandler>();
//遍历当前feignClient的接口的所有的方法
for (Method method : target.type().getMethods()) {
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
//Object的方法不处理
continue;
} else if (Util.isDefault(method)) {//是否是接口中的默认方法
//默认方法创建一个默认方法处理器
DefaultMethodHandler handler = new DefaultMethodHandler(method);
//添加到默认方法处理器集合
defaultMethodHandlers.add(handler);
//保存方法和处理器映射关系
methodToHandler.put(method, handler);
} else {
//不是默认方法,就是抽象方法
//从nameToHandler获取已经生成好的对应的方法处理器
methodToHandler.put(method, nameToHandler.get(Feign.configKey(target.type(), method)));
}
}
//jdk动态代理,创建InvocationHandler,再创建代理对象
InvocationHandler handler = factory.create(target, methodToHandler);
T proxy = (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.type().getClassLoader(),
new Class<?>[] {target.type()}, handler);
for (DefaultMethodHandler defaultMethodHandler : defaultMethodHandlers) {
defaultMethodHandler.bindTo(proxy);
}
return proxy;
}
通过jdk动态代理, 创建InvocationHandler, 再创建代理对象。







![[优选算法专栏]专题十五:FloodFill算法(二)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/eee5a1c43d0442b9be034f6fbfd8e6ff.png)