文章目录
- 前言
- 开发环境
- SSH源码获取
- SSH源码分析
- 最后
前言
上篇文章中提出了存在一些默认密钥文件会被SSH自动添加的猜测,现在我们通过一些分析来验证这个猜测。
开发环境
- MacOS: 14.3.1
- SSH: OpenSSH_9.4p1
SSH源码获取
该怎么验证这个猜测呢?有个方法简单又可靠:翻源码!先执行ssh -V命令看看当前SSH的版本什么:
OpenSSH_9.4p1, LibreSSL 3.3.6
从版本信息可知,用的是OpenSSH的便携式版本。从GitHub克隆项目到本地(镜像很多,按需选择):
git clone https://github.com/openssh/openssh-portable.git
SSH源码分析
将已知的默认名称id_rsa作为关键词搜索项目,可以找到pathnames.h文件:
/*
* The directory in user's home directory in which the files reside. The
* directory should be world-readable (though not all files are).
*/
#define _PATH_SSH_USER_DIR ".ssh"
...
/*
* Name of the default file containing client-side authentication key. This
* file should only be readable by the user him/herself.
*/
#define _PATH_SSH_CLIENT_ID_DSA _PATH_SSH_USER_DIR "/id_dsa"
#define _PATH_SSH_CLIENT_ID_ECDSA _PATH_SSH_USER_DIR "/id_ecdsa"
#define _PATH_SSH_CLIENT_ID_RSA _PATH_SSH_USER_DIR "/id_rsa"
#define _PATH_SSH_CLIENT_ID_ED25519 _PATH_SSH_USER_DIR "/id_ed25519"
#define _PATH_SSH_CLIENT_ID_XMSS _PATH_SSH_USER_DIR "/id_xmss"
#define _PATH_SSH_CLIENT_ID_ECDSA_SK _PATH_SSH_USER_DIR "/id_ecdsa_sk"
#define _PATH_SSH_CLIENT_ID_ED25519_SK _PATH_SSH_USER_DIR "/id_ed25519_sk"
/*
* Configuration file in user's home directory. This file need not be
* readable by anyone but the user him/herself, but does not contain anything
* particularly secret. If the user's home directory resides on an NFS
* volume where root is mapped to nobody, this may need to be world-readable.
*/
#define _PATH_SSH_USER_CONFFILE _PATH_SSH_USER_DIR "/config"
结合源码注释和后续分析可知,_PATH_SSH_USER_DIR即默认目录(由后续fill_default_options函数中该常量的使用可知默认路径指的是~/.ssh),_PATH_SSH_CLIENT_ID_xxx即默认名称(拼接了默认目录),_PATH_SSH_USER_CONFFILE即默认配置文件。
关于id_xmss,上一片文章中没有写上是因为ssh-keygen -t创建时并不支持xmss参数(可以通过man ssh-keygen命令查看)。个人猜测是由于XMSS算法比较新还未广泛普及验证,所以OpenSSH还没有正式支持。
继续将_PATH_SSH_CLIENT_ID_RSA作为关键词继续在项目中搜索,可以在搜索结果中找到readconf.c文件,打开找到相关源码:
void
add_identity_file(Options *options, const char *dir, const char *filename,
int userprovided)
{
char *path;
int i;
// SSH_MAX_IDENTITY_FILES = 100 (定义于ssh.h文件),密钥文件个数不能超过100
if (options->num_identity_files >= SSH_MAX_IDENTITY_FILES)
fatal("Too many identity files specified (max %d)",
SSH_MAX_IDENTITY_FILES);
// 添加用户提供的密钥文件时,文件名就是绝对路径(由后续分析可知,config配置文件中的IdentityFile值会作为filename传入,而dir是NULL)
if (dir == NULL) /* no dir, filename is absolute */
path = xstrdup(filename);
else if (xasprintf(&path, "%s%s", dir, filename) >= PATH_MAX)
fatal("Identity file path %s too long", path);
// 避免重复添加密钥文件,通过比较密钥文件来源和路径是否一致判断是否重复
/* Avoid registering duplicates */
for (i = 0; i < options->num_identity_files; i++) {
if (options->identity_file_userprovided[i] == userprovided &&
strcmp(options->identity_files[i], path) == 0) {
debug2_f("ignoring duplicate key %s", path);
free(path);
return;
}
}
// 保存密钥文件路径
// 补充一点,当前函数并没有检查密钥文件路径是否有效,只有在使用时出现问题才会报错
options->identity_file_userprovided[options->num_identity_files] =
userprovided;
options->identity_files[options->num_identity_files++] = path;
}
...
/*
* Called after processing other sources of option data, this fills those
* options for which no value has been specified with their default values.
*/
int
fill_default_options(Options * options)
{
...
if (options->num_identity_files == 0) {
add_identity_file(options, "~/", _PATH_SSH_CLIENT_ID_RSA, 0);
#ifdef OPENSSL_HAS_ECC
add_identity_file(options, "~/", _PATH_SSH_CLIENT_ID_ECDSA, 0);
add_identity_file(options, "~/",
_PATH_SSH_CLIENT_ID_ECDSA_SK, 0);
#endif
add_identity_file(options, "~/",
_PATH_SSH_CLIENT_ID_ED25519, 0);
add_identity_file(options, "~/",
_PATH_SSH_CLIENT_ID_ED25519_SK, 0);
add_identity_file(options, "~/", _PATH_SSH_CLIENT_ID_XMSS, 0);
#ifdef WITH_DSA
add_identity_file(options, "~/", _PATH_SSH_CLIENT_ID_DSA, 0);
#endif
}
...
}
顾名思义,fill_default_options函数用于填充默认值,当满足条件num_identity_files == 0时添加默认密钥文件,同时也通过userprovided = 0标记该密钥不是用户提供的(来源系统默认)。
在add_identity_file函数最后保存密钥文件时,对num_identity_files进行了递增操作(++)。如果SSH在fill_default_options函数调用前先添加config配置文件中指定的密钥文件,这时应该会调用add_identity_file函数进而导致num_identity_files == 0条件不满足,不再自动添加默认密钥文件。真的会这样吗?
将fill_default_options作为关键词在项目中搜索,可以在ssh.c文件找到相关源码:
/*
* Read per-user configuration file. Ignore the system wide config
* file if the user specifies a config file on the command line.
*/
static void
process_config_files(const char *host_name, struct passwd *pw, int final_pass,
int *want_final_pass)
{
char buf[PATH_MAX];
int r;
if (config != NULL) {
if (strcasecmp(config, "none") != 0 &&
!read_config_file(config, pw, host, host_name, &options,
SSHCONF_USERCONF | (final_pass ? SSHCONF_FINAL : 0),
want_final_pass))
fatal("Can't open user config file %.100s: "
"%.100s", config, strerror(errno));
} else {
// _PATH_SSH_USER_CONFFILE即.ssh/config,定义于pathnames.h文件
r = snprintf(buf, sizeof buf, "%s/%s", pw->pw_dir,
_PATH_SSH_USER_CONFFILE);
if (r > 0 && (size_t)r < sizeof(buf))
(void)read_config_file(buf, pw, host, host_name,
&options, SSHCONF_CHECKPERM | SSHCONF_USERCONF |
(final_pass ? SSHCONF_FINAL : 0), want_final_pass);
/* Read systemwide configuration file after user config. */
(void)read_config_file(_PATH_HOST_CONFIG_FILE, pw,
host, host_name, &options,
final_pass ? SSHCONF_FINAL : 0, want_final_pass);
}
}
...
/*
* Main program for the ssh client.
*/
int
main(int ac, char **av)
{
...
/* Parse the configuration files */
process_config_files(options.host_arg, pw, 0, &want_final_pass);
if (want_final_pass)
debug("configuration requests final Match pass");
...
/* Fill configuration defaults. */
if (fill_default_options(&options) != 0)
cleanup_exit(255);
...
}
fill_default_options函数的调用位置位于SSH的入口函数(main),这无疑验证了前面关于SSH会自动添加默认密钥的猜测。 同时,在fill_default_options函数调用前会先解析配置文件。不过,还不确定配置文件是否会导致不再自动添加默认密钥文件。
继续往下分析,加载及解析配置文件的相关函数在readconf.c文件,函数的大致调用顺序:read_config_file -> read_config_file_depth -> process_config_line_depth。其中的逻辑阅读不难,本质是逐行解析,着重看看process_config_line_depth函数:
static struct {
const char *name;
OpCodes opcode;
} keywords[] = {
...
{ "identityfile", oIdentityFile },
...
{ "host", oHost },
...
};
/*
* Returns the number of the token pointed to by cp or oBadOption.
*/
static OpCodes
parse_token(const char *cp, const char *filename, int linenum,
const char *ignored_unknown)
{
int i;
// keywords数组存储着关键字(例如identityfile)和操作码(例如oIdentityFile)的映射关系
// 通过遍历数组匹配关键字并返回对应操作码
for (i = 0; keywords[i].name; i++)
if (strcmp(cp, keywords[i].name) == 0)
return keywords[i].opcode;
if (ignored_unknown != NULL &&
match_pattern_list(cp, ignored_unknown, 1) == 1)
return oIgnoredUnknownOption;
error("%s: line %d: Bad configuration option: %s",
filename, linenum, cp);
return oBadOption;
}
...
static int
process_config_line_depth(Options *options, struct passwd *pw, const char *host,
const char *original_host, char *line, const char *filename,
int linenum, int *activep, int flags, int *want_final_pass, int depth)
{
...
// 将关键字转为小写,这是因为在keywords数组中关键字全是小写的
// 由此可见config文件中的关键字并不区分大小写,在这之前我还以为config文件中的关键字必须要用大驼峰命名(建议还是继续使用大驼峰命名,可读性高)
/* Match lowercase keyword */
lowercase(keyword);
...
// 将关键字转为操作码
opcode = parse_token(keyword, filename, linenum,
options->ignored_unknown);
...
switch (opcode) {
...
case oIdentityFile:
arg = argv_next(&ac, &av);
if (!arg || *arg == '\0') {
error("%.200s line %d: Missing argument.",
filename, linenum);
goto out;
}
if (*activep) {
intptr = &options->num_identity_files;
if (*intptr >= SSH_MAX_IDENTITY_FILES) {
error("%.200s line %d: Too many identity files "
"specified (max %d).", filename, linenum,
SSH_MAX_IDENTITY_FILES);
goto out;
}
add_identity_file(options, NULL,
arg, flags & SSHCONF_USERCONF);
}
break;
...
case oHost:
if (cmdline) {
error("Host directive not supported as a command-line "
"option");
goto out;
}
*activep = 0;
arg2 = NULL;
while ((arg = argv_next(&ac, &av)) != NULL) {
if (*arg == '\0') {
error("%s line %d: keyword %s empty argument",
filename, linenum, keyword);
goto out;
}
if ((flags & SSHCONF_NEVERMATCH) != 0) {
argv_consume(&ac);
break;
}
negated = *arg == '!';
if (negated)
arg++;
if (match_pattern(host, arg)) {
if (negated) {
debug("%.200s line %d: Skipping Host "
"block because of negated match "
"for %.100s", filename, linenum,
arg);
*activep = 0;
argv_consume(&ac);
break;
}
if (!*activep)
arg2 = arg; /* logged below */
*activep = 1;
}
}
if (*activep)
debug("%.200s line %d: Applying options for %.100s",
filename, linenum, arg2);
break;
...
}
从处理oIdentityFile操作码的逻辑可知,当*activep等于1时,将会调用add_identity_file函数添加配置文件中指定的密钥文件,进而导致num_identity_files == 0条件不满足,后续不会再自动添加默认密钥文件。
所以,如果config配置文件中指定了的密钥文件,确实会导致不再自动添加默认密钥文件。
这里还有一个疑问,*activep什么时候会等于1?请看处理oHost操作码的逻辑,只有当Host匹配上时*activep才会等于1。举个简单的例子🌰:
你使用SSH连接Host为github.com的服务器,然后你在config文件的配置如下:
Host github.com
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.github
解析配置文件时,Host就匹配上了。你用ssh -G github.com命令(ssh -G命令用于打印SSH客户端的配置信息)就会看到输出中和IdentityFile相关的只有你配置的:
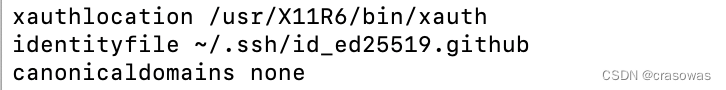
此时默认密钥文件并没有自动添加(具体原因前面已分析)。如果你用ssh -G github.cn命令,由于需要连接的Host为github.cn,与配置文件中的不匹配,你会在输出中看到一堆自动添加的默认密钥文件:
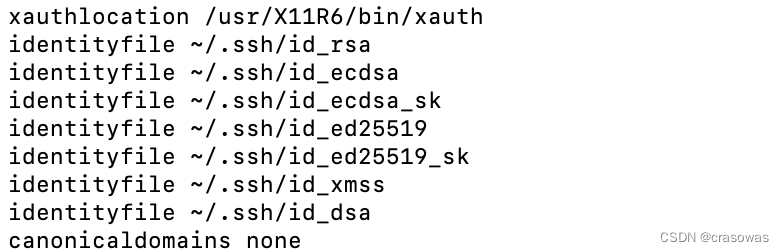
综上,确实存在一些默认密钥文件会被SSH自动添加。不过,当SSH连接的Host在config文件有配置IdentityFile时,将不会自动添加这些默认密钥文件。
最后
如果这篇文章对你有所帮助,点赞👍收藏🌟支持一下吧,谢谢~
本篇文章由@crasowas发布于CSDN。