萌新的学习笔记,写错了恳请斧正。
目录
链表的定义
链表的分类
方向(单向还是双向)
头节点(哨兵节点)的有无
循环或不循环
8种分类
不带头单向不循环链表的实现
带头单向循环链表的实现
链表与顺序表的差异
链表的定义
链表是一种基于指针的,物理结构不连续而逻辑结构连续的数据结构。大概就是说,把一个一个数据存放在一个一个节点中,每一个节点可能创建在内存的不同区域,但是每个节点都包括了至少一个指向下一个节点的指针。这样,我们就可以通过指针来按顺序找到整个链表的数据。
我们一般创建一个结构体类型作为链表的节点,结构体的成员包括若干数据和若干指针,其中数据部分称为链表的数据域,指针部分称为链表的指针域。(有些指针属于数据,要具体分析其功能)
链表的分类
方向(单向还是双向)
链表可以是单向的也可以是双向的。
单向代表链表每个节点的指针域指向其下一个节点,可以顺着指针一路向后寻找而不能反过来向前寻找;而双向链表的节点一般有两个指针,一个指向后一个节点,另一个指向前一个节点。
头节点(哨兵节点)的有无
头结点本身不存储任何实际的数据元素,而是作为链表的第一个节点存在,其主要作用是指向链表的第一个实际存储数据的节点。使用头结点的好处在于可以使链表的插入和删除操作更加统一和简洁,因为即使是在链表的开头进行操作,也不需要对链表进行特殊处理,从而避免了一些边界条件的检查。
在不带头结点的链表中,插入新的第一个元素或删除现有的第一个元素时,需要特别处理链表的头指针,这可能会使代码变得复杂且容易出错。而在带有头结点的链表中,无论插入或删除操作发生在链表的哪个位置,操作流程都是统一的,因为头结点为链表提供了一个统一的入口。
循环或不循环
如果链表的最后一个节点再次指向整个链表的第一个节点(哨兵节点或数据节点),那么这个链表就是循环的。循环的结构可以为实现很多比较复杂的数据处理功能带来便利。
8种分类
所以从上面3个角度考虑,链表一共可以分为8种(排列组合),但是最常用的有两种:不带头单向不循环链表(简称单链表)、带头双向循环链表。
这两种链表中,单链表结构最简单,但是一般不会直接使用,而是作为一些更复杂的数据结构的子结果,也频繁出现在试题中。
而带头双向循环链表则是实际作为链表使用最频繁的,在实现诸多功能上都存在明显优势。
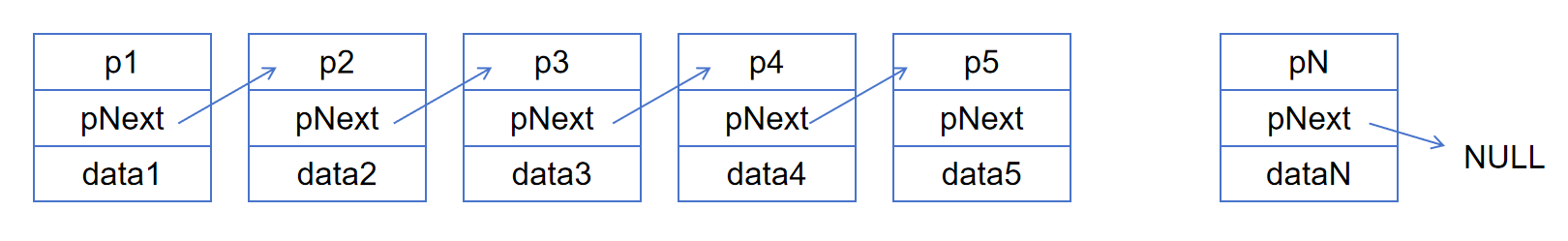
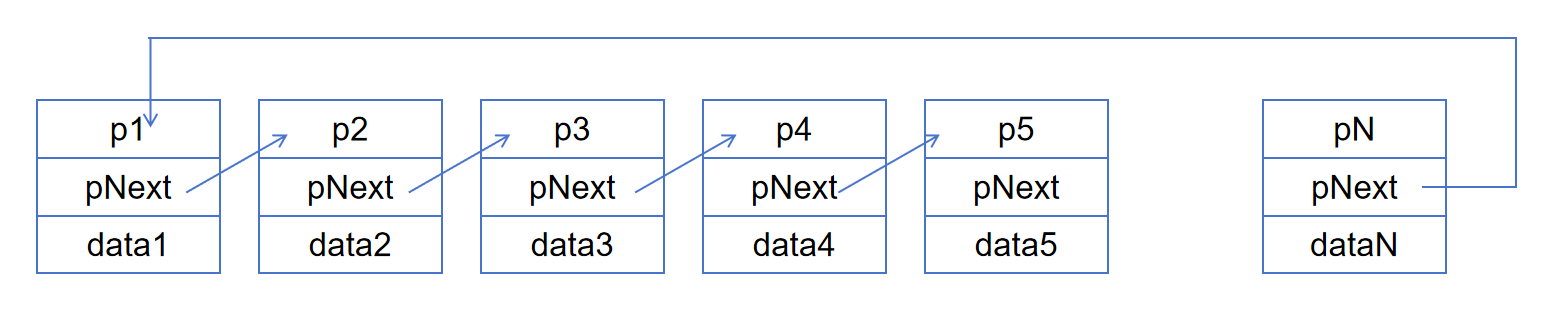
下面是8种链表的示意图:
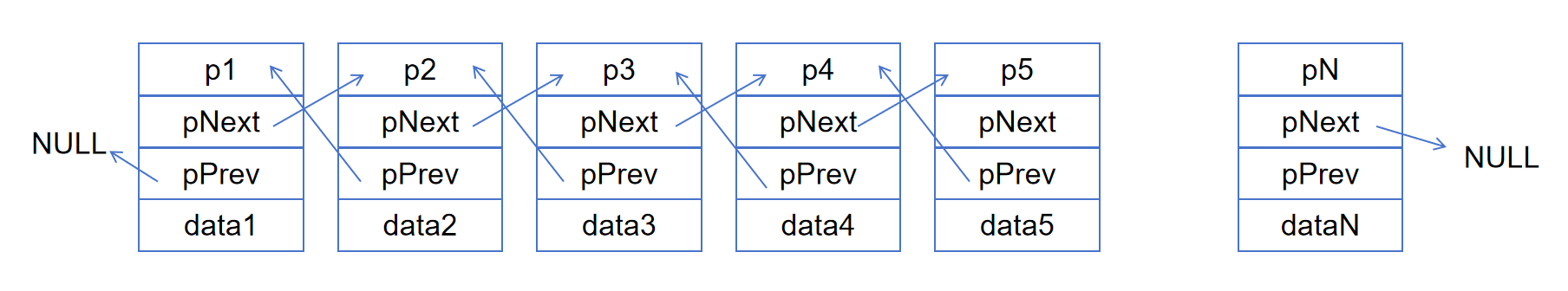
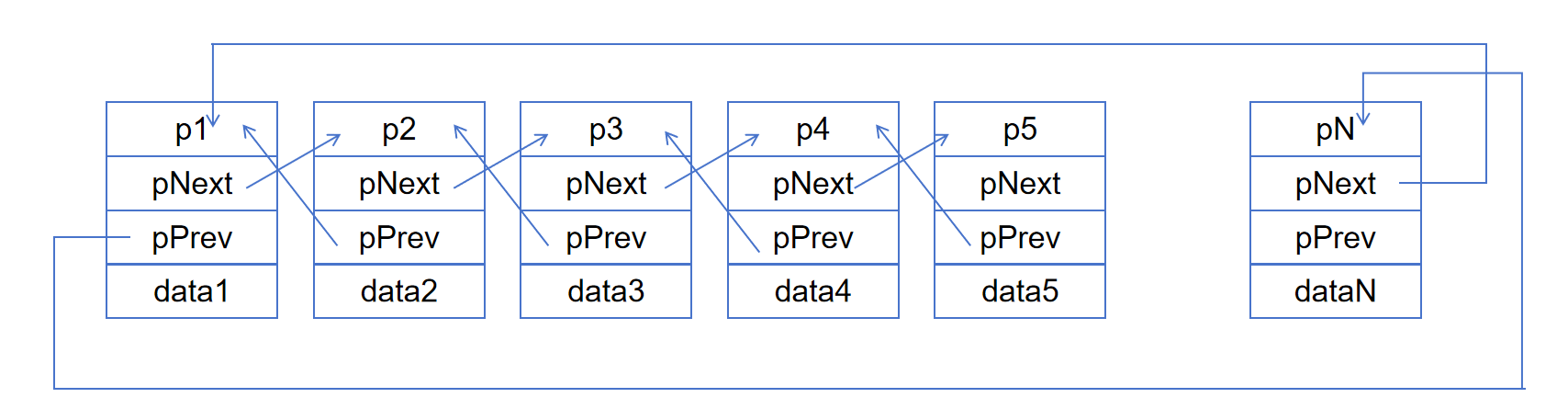
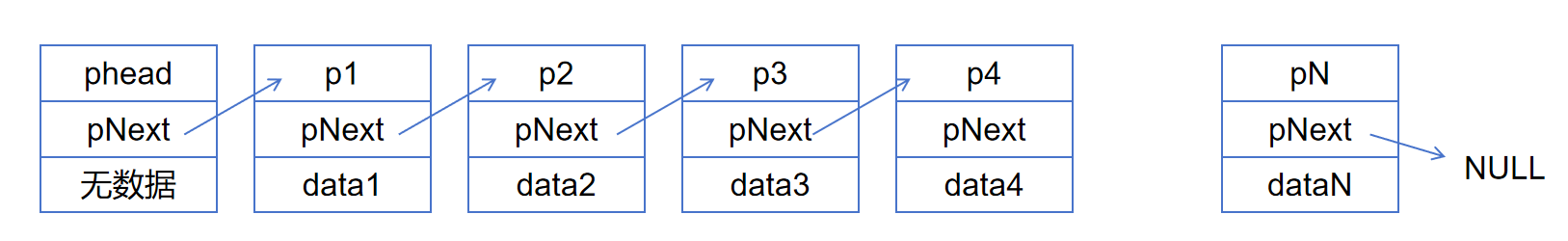
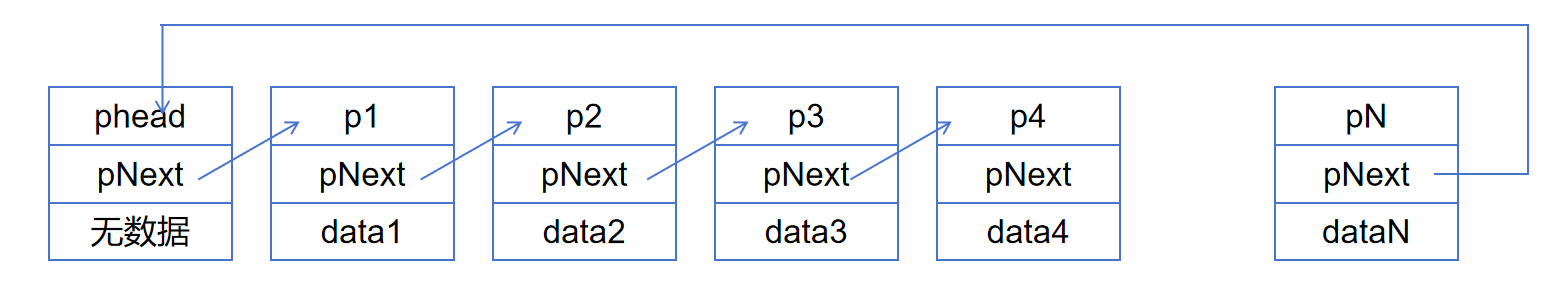
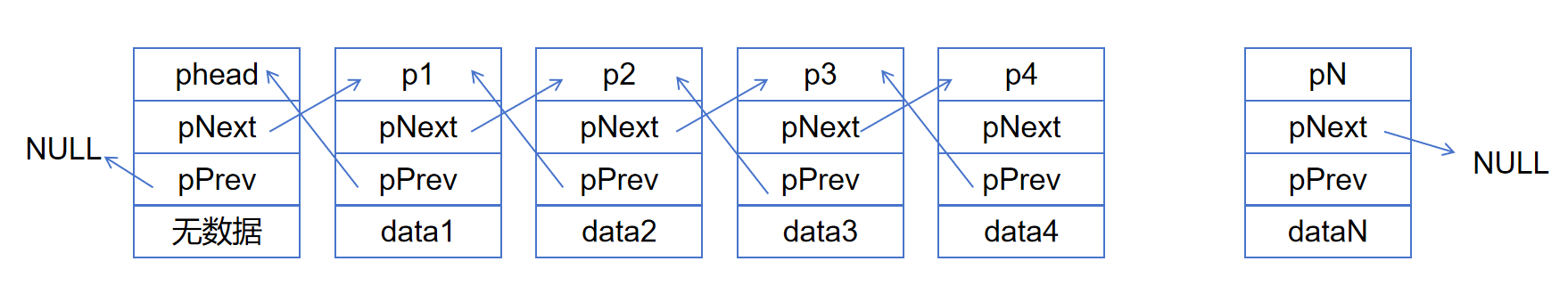
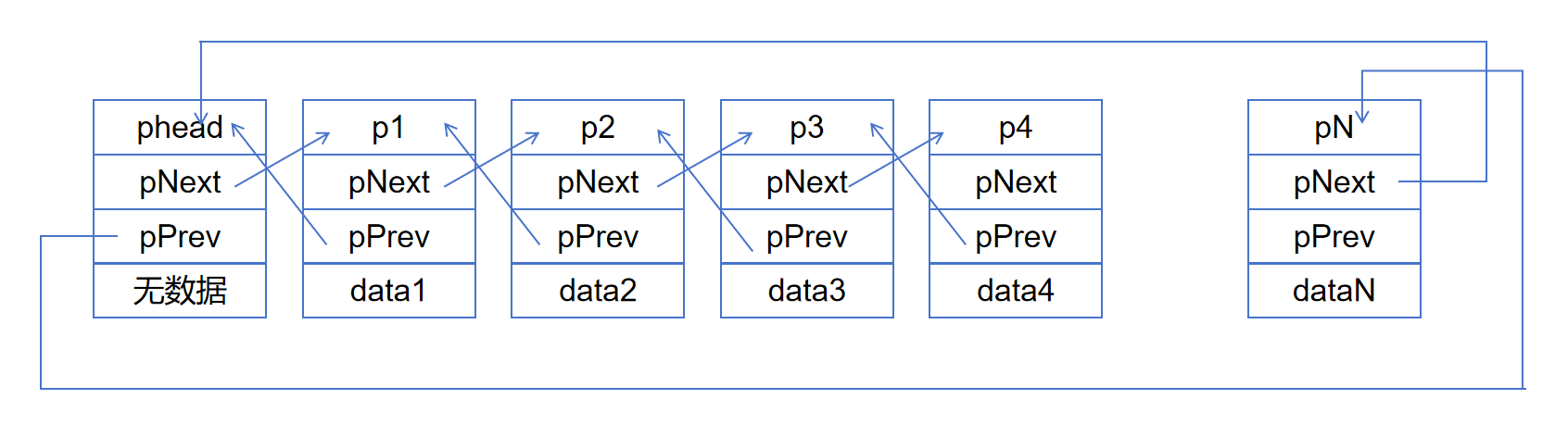
不带头单向不循环链表的实现
头文件SList.h
//不带头单向不循环链表(single linked list)
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
//单链表节点的值类型
typedef int SLDataType;
//单链表节点
typedef struct SListNode
{
SLDataType data;
struct SListNode* next;
} SListNode;
//单链表的初始化
#define SListInit(pList) SListNode* pList = NULL
//单链表的销毁
void SListDestory(SListNode** ppList);
//单链表的头插
void SListPushFront(SListNode** ppList, SLDataType x);
//单链表的尾插
void SListPushBack(SListNode** ppList, SLDataType x);
//单链表指定位置后插入
void SListInsertAfter(SListNode* pos, SLDataType x);
//单链表指定位置前插入
void SListInsertBefore(SListNode** ppList, SListNode* pos, SLDataType x);
//单链表的头删
void SListPopFront(SListNode** ppList);
//单链表的尾删
void SListPopBack(SListNode** ppList);
//单链表删除指定位置的节点
void SListErase(SListNode** ppList, SListNode* pos);
//单链表指定位置后删除
void SListEraseAfter(SListNode* pos);
//单链表指定位置前删除
void SListEraseBefore(SListNode** ppList, SListNode* pos);
//单链表删除所有指定值的节点
void SListRemove(SListNode** ppList, SLDataType x);
//单链表查找
SListNode* SListFind(SListNode* pList, SLDataType x);
//单链表中间节点
SListNode* SListFindMidNode(SListNode* pList);
//单链表的长度
int SListSize(SListNode* pList);
//单链表的判空
int SListEmpty(SListNode* pList);
//单链表打印
void SListPrint(SListNode* pList);
//单链表逆序
void SListReverse(SListNode** ppList);
//单链表冒泡排序
void SListBubbleSort(SListNode** pList);
//合并两个有序链表
SListNode* SListMerge(SListNode* pList1, SListNode* pList2);源文件SList.c
#include "SList.h"
//单链表的销毁
void SListDestory(SListNode** ppList)
{
//断言
assert(ppList);
SListNode* cur = *ppList;
while (cur)
{
SListNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
*ppList = NULL;
}
//新节点申请
SListNode* SListBuyNode(SLDataType x)
{
SListNode* newNode = (SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));
if (newNode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
newNode->data = x;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
//单链表的头插
void SListPushFront(SListNode** ppList, SLDataType x)
{
//断言
assert(ppList);
SListNode* newNode = SListBuyNode(x);
newNode->next = *ppList;
*ppList = newNode;
}
//单链表的尾插
void SListPushBack(SListNode** ppList, SLDataType x)
{
//断言
assert(ppList);
SListNode* newNode = SListBuyNode(x);
if (*ppList == NULL)
{
*ppList = newNode;
}
else
{
SListNode* cur = *ppList;
while (cur->next)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = newNode;
}
}
//单链表指定位置后插入
void SListInsertAfter(SListNode* pos, SLDataType x)
{
//断言
assert(pos);
SListNode* newNode = SListBuyNode(x);
newNode->next = pos->next;
pos->next = newNode;
}
//单链表指定位置前插入
void SListInsertBefore(SListNode** ppList, SListNode* pos, SLDataType x)
{
//断言
assert(ppList&&pos);
if (*ppList == NULL || *ppList == pos) //空链表或者pos为头节点
{
SListPushFront(ppList, x);
}
else
{
SListNode* cur = *ppList;
while (cur->next != pos)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
SListNode* newNode = SListBuyNode(x);
newNode->next = cur->next;
cur->next = newNode;
}
}
//单链表的头删
void SListPopFront(SListNode** ppList)
{
//断言
assert(ppList);
if (*ppList == NULL)
{
return;
}
else
{
SListNode* next = (*ppList)->next;
free(*ppList);
*ppList = next;
}
}
//单链表的尾删
void SListPopBack(SListNode** ppList)
{
//断言
assert(ppList);
if (*ppList == NULL)
{
return;
}
else if ((*ppList)->next == NULL)
{
free(*ppList);
*ppList = NULL;
}
else
{
SListNode* cur = *ppList;
while (cur->next->next)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
free(cur->next);
cur->next = NULL;
}
}
//单链表删除指定位置的节点
void SListErase(SListNode** ppList, SListNode* pos)
{
//断言
assert(ppList&&pos);
if (*ppList == NULL)
{
return;
}
else if (*ppList == pos)
{
SListPopFront(ppList);
}
else
{
SListNode* cur = *ppList;
while (cur->next != pos)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = pos->next;
free(pos);
}
}
//单链表指定位置后删除
void SListEraseAfter(SListNode* pos)
{
//断言
assert(pos);
if (pos->next == NULL)
{
return;
}
else
{
SListNode* next = pos->next->next;
free(pos->next);
pos->next = next;
}
}
//单链表指定位置前删除
void SListEraseBefore(SListNode** ppList, SListNode* pos)
{
//断言
assert(ppList&&pos);
if (*ppList == NULL || *ppList == pos) //空链表或者pos为头节点
{
return;
}
else if ((*ppList)->next == pos) //pos为第二个节点
{
SListPopFront(ppList);
}
else
{
SListNode* cur = *ppList;
while (cur->next->next != pos)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
free(cur->next);
cur->next = pos;
}
}
//单链表删除所有指定值的节点
void SListRemove(SListNode** ppList, SLDataType x)
{
//断言
assert(ppList);
if (*ppList == NULL)
{
return;
}
else
{
SListNode* cur = *ppList;
while (cur->next)
{
if (cur->next->data == x)
{
SListNode* next = cur->next->next;
free(cur->next);
cur->next = next;
}
else
{
cur = cur->next;
}
}
if ((*ppList)->data == x)
{
SListPopFront(ppList);
}
}
}
//单链表查找
SListNode* SListFind(SListNode* pList, SLDataType x)
{
//断言
assert(pList);
SListNode* cur = pList;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
//单链表中间节点
SListNode* SListFindMidNode(SListNode* pList)
{
//断言
assert(pList);
SListNode* fast = pList;
SListNode* slow = pList;
while (fast && fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
//单链表的长度
int SListSize(SListNode* pList)
{
//断言
assert(pList);
int count = 0;
SListNode* cur = pList;
while (cur)
{
count++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return count;
}
//单链表的判空
int SListEmpty(SListNode* pList)
{
return pList == NULL ? 1 : 0;
}
//单链表打印
void SListPrint(SListNode* pList)
{
//断言
assert(pList);
SListNode* cur = pList;
while (cur)
{
printf("%d->", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
//单链表逆序
void SListReverse(SListNode** ppList)
{
//断言
assert(ppList);
if (*ppList == NULL || (*ppList)->next == NULL)
{
return;
}
else
{
SListNode* cur = *ppList;
SListNode* next = cur->next;
SListNode* nextNext = next->next;
while (next)
{
next->next = cur;
cur = next;
next = nextNext;
if (nextNext)
{
nextNext = nextNext->next;
}
}
(*ppList)->next = NULL;
*ppList = cur;
}
}
//单链表冒泡排序
void SListBubbleSort(SListNode** pList)
{
//断言
assert(pList);
if (*pList == NULL || (*pList)->next == NULL)
{
return;
}
else
{
SListNode* tail = NULL; //尾节点
while (tail != *pList) //只有一个节点时,tail==*pList
{
SListNode* cur = *pList; //当前节点
SListNode* next = cur->next; //下一个节点
SListNode* prev = NULL; //当前节点的前一个节点
while (next != tail) //只有两个节点时,next==tail
{
if (cur->data > next->data) //交换
{
if (cur == *pList) //头节点交换
{
cur->next = next->next;
next->next = cur;
*pList = next;
prev = next;
next = cur->next;
}
else
{
cur->next = next->next;
next->next = cur;
prev->next = next;
prev = next;
next = cur->next;
}
}
else //不交换
{
prev = cur;
cur = next;
next = next->next;
}
}
tail = cur;
}
}
}
//单链表合并
SListNode* SListMerge(SListNode* pList1, SListNode* pList2)
{
if (!pList1)
{
return pList2;
}
if (!pList2)
{
return pList1;
}
SListNode* newList = NULL;
SListNode* cur1 = pList1;
SListNode* cur2 = pList2;
SListNode* cur = NULL;
while (cur1 && cur2)
{
if (cur1->data < cur2->data)
{
if (!newList)
{
newList = cur = cur1;
}
else
{
cur->next = cur1;
cur = cur->next;
}
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
else
{
if (!newList)
{
newList = cur = cur2;
}
else
{
cur->next = cur2;
cur = cur->next;
}
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
}
if (cur1)
{
cur->next = cur1;
}
else
{
cur->next = cur2;
}
return newList;
}带头单向循环链表的实现
头文件List.h
//带头双向不循环链表(List)
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
//定义数据类型
typedef int LTDataType;
//定义链表节点
typedef struct ListNode
{
LTDataType data;
struct ListNode* next;
struct ListNode* prev;
} ListNode;
//申请节点
ListNode* BuyListNode(LTDataType x);
//初始化链表
ListNode* ListInit(void);
//销毁链表
void ListDestory(ListNode** pphead);
//打印
void ListPrint(ListNode* phead);
//尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x);
//头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x);
//尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead);
//头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead);
//查找
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x);
//在pos位置之后插入x
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x);
//删除pos位置的节点
void ListErase(ListNode* pos);
源文件List.c
#include "List.h"
//申请节点
ListNode* BuyListNode(LTDataType x)
{
ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = newnode->prev = NULL;
return newnode;
}
//初始化链表
ListNode* ListInit(void)
{
ListNode* phead = BuyListNode((LTDataType)0);
phead->next = phead->prev = phead;
return phead;
}
//销毁链表
void ListDestory(ListNode** pphead)
{
//断言
assert(pphead);
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
return;
}
ListNode* phead = *pphead;
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
ListNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
free(phead);
*pphead = NULL;
}
//打印
void ListPrint(ListNode* phead)
{
//断言
assert(phead);
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
printf("head->");
while (cur != phead)
{
printf("%d->", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("tail\n");
}
//尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode * phead, LTDataType x)
{
//断言
assert(phead);
ListNode* tail = phead->prev;
ListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
newnode->next = phead;
newnode->prev = tail;
tail->next = newnode;
phead->prev = newnode;
}
//头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
//断言
ListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
newnode->next = phead->next;
newnode->prev = phead;
phead->next->prev = newnode;
phead->next = newnode;
}
//尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead)
{
//断言
assert(phead);
ListNode* tail = phead->prev;
ListNode* prev = tail->prev;
prev->next = phead;
phead->prev = prev;
free(tail);
}
//头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead)
{
//断言
assert(phead);
ListNode* first = phead->next;
ListNode* second = first->next;
phead->next = second;
second->prev = phead;
free(first);
}
//查找
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
//断言
assert(phead);
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
//在pos位置之后插入x
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x)
{
//断言
assert(pos);
ListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
newnode->next = pos->next;
newnode->prev = pos;
pos->next->prev = newnode;
pos->next = newnode;
}
//删除pos位置的节点
void ListErase(ListNode* pos)
{
//断言
assert(pos);
ListNode* prev = pos->prev;
ListNode* next = pos->next;
prev->next = next;
next->prev = prev;
free(pos);
}链表与顺序表的差异
| 区别 | 链表 | 顺序表 |
|---|---|---|
| 物理结构 | 不连续 | 连续 |
| 随机访问(通过下标任意的访问节点) | 不支持,O(N) | 支持,O(1) |
| 任意位置插入删除 | 只需要修改指针的方向即可 | 可能需要大量挪移数据,效率低下 |
| 容量 | 没有容量的概念 | 需要管理容量,扩容 |
| 应用场景 | 频繁发生任意位置插入时 | 需要高效频繁访问各节点元素时 |
| 缓存命中(意味着CPU访问内存的效率) | 低 | 高 |